chem Topic 6 kinetics
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:16 AM on 8/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
1
New cards
What are the two things for a successful collision?
1. Particles colliding must have kinetic energies equal to or grater than the reaction’s activation energy.
2. The particle must collide with the correct geometry/orientation
2
New cards
What is the activation energy and what does it represent?
The activation energy is defined as the m**inimum value of kinetic energy** which particles must have to react.
\
It represents an **“energy barrier”** for the reaction.
\
It represents an **“energy barrier”** for the reaction.
3
New cards
What are the factors affecting rates of reaction
* Temperature (only one that does it in 2 ways)
* Catalyst
* Conentration
* Surface area (particle size)
* Pressure (reactions involving gases)
* Catalyst
* Conentration
* Surface area (particle size)
* Pressure (reactions involving gases)
4
New cards
How do catalysts work and why do they increase rate of reaction.
They provide an alternate reaction pathway that has a lower activation energy.
* Catalysts increase the number and proportion of particles that have sufficient energy to meet or exceed activation energy.
* ∴ increase freuency and proportion of successful collisions
* ∴ increase ROR
* Catalysts increase the number and proportion of particles that have sufficient energy to meet or exceed activation energy.
* ∴ increase freuency and proportion of successful collisions
* ∴ increase ROR
5
New cards
How does increasing temperature affect rate of reaction?
* Increasing the temperature increases the proportion of reactant particles with sufficient energy to meet or exceed the reactions activation energy. As well as increases the average random kinetic energy of particles.
* ∴ increase freuency and proportion of successful collisions
* ∴ increase ROR
* ∴ increase freuency and proportion of successful collisions
* ∴ increase ROR
6
New cards
How does increasing concentration affect rate of reaction?
As concentration increases there are more particles available to react in a given volume.
∴ increase freuency of successful collisions
∴ increase ROR
7
New cards
How does decreasing particle size affect rate of reaction?
* decreasing particle size increases total surface area
* ∴ increase in number of particles available to react
* ∴increase in number and frequency of successful collisions
* ∴ increase ROR
* ∴ increase in number of particles available to react
* ∴increase in number and frequency of successful collisions
* ∴ increase ROR
8
New cards
How does increasing pressure increase the rate of reaction in a reaction involving gases?
* as pressure increases the gas is compressed and so the concentration increases.
* As concentration increases there are more particles available to react.
* ∴ increase freuency of successful collisions
* ∴ increase ROR
* As concentration increases there are more particles available to react.
* ∴ increase freuency of successful collisions
* ∴ increase ROR
9
New cards
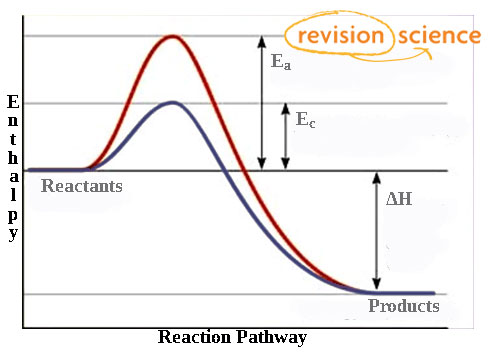
Catalysts and enthalpy level diagrams
* equal redutoin in the activation energy of both forward and backwards reactions
* hump is lowered
* hump is lowered
10
New cards
rate of reaction
is expressed by change in concentration of a particular reactant/product per unit time
\
this can be indirectly observed through changes in mass, volume and color.
\
this can be indirectly observed through changes in mass, volume and color.
11
New cards
Why does rate of reaction plateua or decrease over time
less frequency/chance of collisions as reaction proceeds