(39-40) Peroxisome and mitochondria
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Organelle
membrane bound unit within a cell with a specific function
Peroxisomes look like — however they are involved in — instead of —
lysosomes; oxidation/detoxification; digestion
series of enzymes found in peroxisomes. What activities are all of these enzymes involved in?
peroxidases, d-amino oxidases, and catalases; oxidative activities (production and destruction of hydrogen peroxide [H2O2])
t/f you may tell the difference between peroxisomes and lysosomes using a light microscopy
false
Similarities in lysosomes and peroxisomes
shape and size
Differences in lysosomes and peroxisomes
fewer peroxisomes than lysosomes in cell, lysosomes are made in the golgi and peroxisome membrane components are made in the ER while other components come from the cytosol
Where are peroxisomes made?
the membrane components comes from the ER and many other proteins are moved from the cytosol/cytoplasm
What is considered the most important enzyme in the peroxisome? This protein consists of — percent of proteins in a peroxisomes
catalase; 40
Catalase
tetrameric proteins (4 different protein subunits) with a heme group to help oxidize various compounds. Monomeric units are synthesized in the cytoplasm and come together inside the peroxisome. Primarily involved in destroying hydrogen peroxide.
t/f catalase monomers have a leader sequence on their mRNA (explain answer)
false, they are made in the cytoplasm, not the rough ER
How is catalase formed in peroxisomes?
monomeric units of catalase are moved from the cytoplasm into the peroxisome. They then form a tetramer and bind with a heme ring to form functional catalase within the peroxisome.
Toxic compounds are typically highly (reduced or oxidized)
reduced
t/f hydrogen peroxide is not toxic to our cells, which makes it ok to clean wounds with.
false, it kills all cells (both bacteria and our cells)
Show the reaction equations of how peroxisomes typically breakdown toxic compounds.
RH2 represents a reduced toxic compound, DAO= D-amino oxidase
The first reaction step that peroxisomes use to breakdown toxins is a — reaction while the second step is a — reaction
oxidative; peroxidative
Glutathione peroxidase
enzyme found in the cytoplasm responsible for destroying any hydrogen peroxide that may escape a peroxisome
When is the only time you will normally see hydrogen peroxide in a cell?
apoptosis
Mitochondria is a Greek term meaning what? What was its old name?
thread and granule; bioclast
How are mitochondria unique from other organelles?
It has its own DNA
t/f mitochondria make all of their own proteins
false, they make some but not all
Some proteins in the mitochondria are under nuclear control. What does this mean?
they are synthesized in the cytoplasm from mRNA that comes from the nucleus. These proteins have a leader sequence which makes them transport to the mitochondria.
Where do the lipids of the mitochondria come from?
the ER
Why are mitochondria referred to as dynamic?
they are constantly moving
Cytoplasmic streaming
the way in which cytoplasm moves in a cell. Mitochondria often use this to go where they are needed
Mitochondria may accumulate anywhere in the cell where there is —
a need for energy
Although the — and — of a mitochondria may vary, the — stays roughly uniform
length and shape; width
Average mitochondria width
0.5 microns (500 nm)
Range of lengths of mitochondria
5-7 microns (5,000-7,00 nm)
What do mitochondria do as the cell is about to divide?
they align themself with the spindle apparatus so that the mitochondria are divided approximately evenly between the two new cells
Amount of mitochondria found in a normal cell (ie liver cell)
1000- 1600
Egg cells may have upwards of — mitochondria within them
300,000
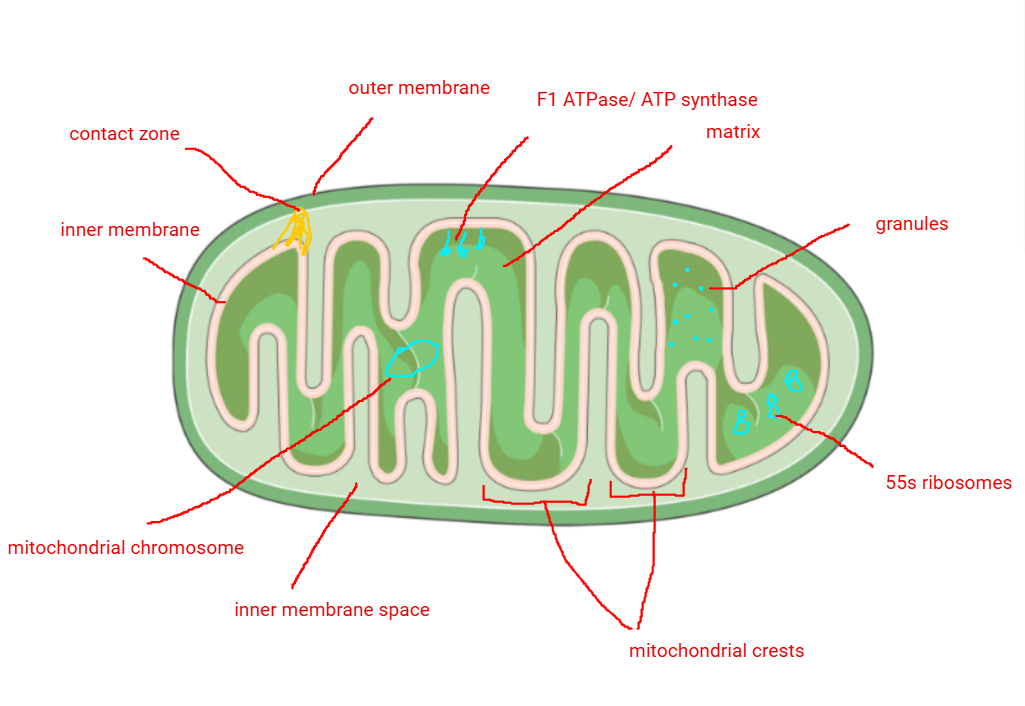
Mitochondrial crests/cristae
folds in the inner membrane of the mitochondria which increases its surface area
At its closest, the inner membrane and outer membrane of the mitochondria are — nm apart
6-8
Contact zones
locations in which the inner membrane of the mitochondria fuses with the outer membrane. Represents a region where the molecules may be moved into the mitochondrial with ease ( they only need to pass through one membrane)
Porin
29,000 dalton channel protein on the outer membrane of the mitochondria. Found only on mitochondria and gram negative bacteria. Supports the hypothesis that mitochondria’s origins are that of a bacteria which eventually became the mitochondria
The mitochondrial outer membrane is about —% lipid while the inner membrane is about —% lipid. What does this difference mean?
40;20; the outer membrane allows for much easier movement of solutes while the inner membrane acts much more like a barrier which requires a transport or channel protein to move in
What makes mitochondrial DNA unique??
mitochondrial DNA comprises of a singular circular chromosome with a high G-C content
Why is mitochondrial DNA “heavier”?
it has a higher G-C content
If there is more than one mitochondrial chromosomes this indicates what?
that the chromosomes has been replicated in preparation for formation of new mitochondria
Granules
associated with the mitochondrial matrix, either calcium or phospholipid granules. Storage form for calcium or phospholipids.
What type of ribosome is found within mitochondria? What are its subunits?
55s ribosomes with 35s and 25s subunits
F1 ATPase
lines the matrix side of the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Responsible for producing ATP from the flow of protons from the inner membrane space into the matrix.
F1 ATPase is Spaced at about — nm apart and they look like a — in shape
10; cone
In order for ATP to be made, — precursors are required which most move through specific — proteins
ADP; channel
— moves out of the mitochondria through specific —
ATP; channels
Beta oxidation
the process by which fatty acids are broken down into acetates which are then used to produce NADH and GTP. This process occurs within both the mitochondria and peroxisomes.
Similarities in mitochondria and peroxisomes
both are oxidative and both include the process of beta-oxidation
Draw and label a mitochondria