Unit 8: World War 2
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Fascism
Extreme nationalism and patriotism; military is supreme; punishments are severe; specific groups are blamed for society's problems

Adolf Hitler
Fuhrer, or dictator, of Germany. First elected as chancellor, Hitler later became a dictator with absolute power.

Nazis
The political party of Hitler known for their extreme fascism and racism

Axis Powers
Germany, Italy, and Japan.

Appeasement
The practice of giving in to aggression in order to prevent a war.

Allied Powers
France, England, and Russia. The U.S. joined in December 1941.

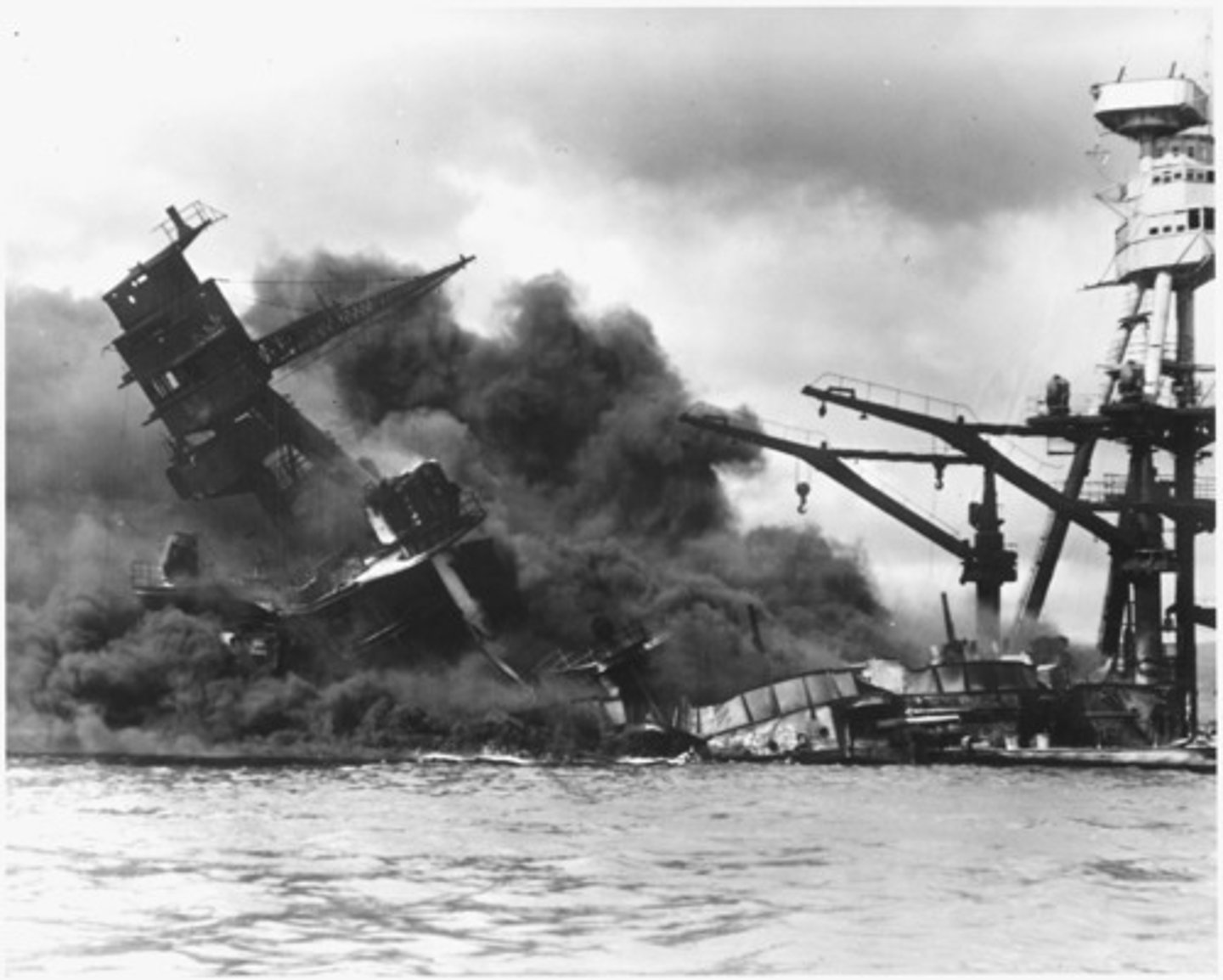
Pearl Harbor
Surprise military attack by Japan against the United States. Occurred at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on December 7th, 1941.

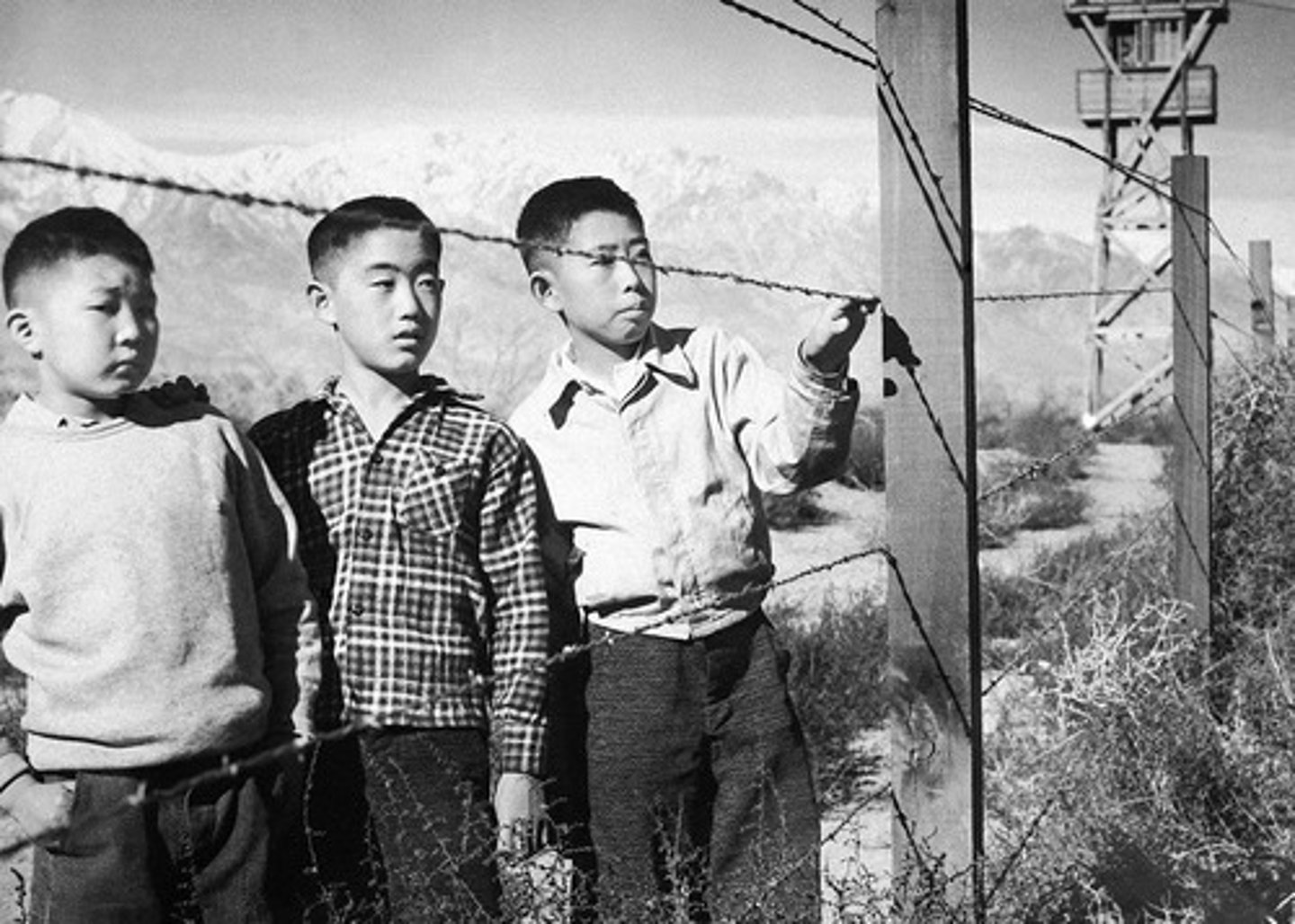
Internment Camps
camp that was like a prison. The U.S. forced Japanese-Americans to live in internment camps during the war.

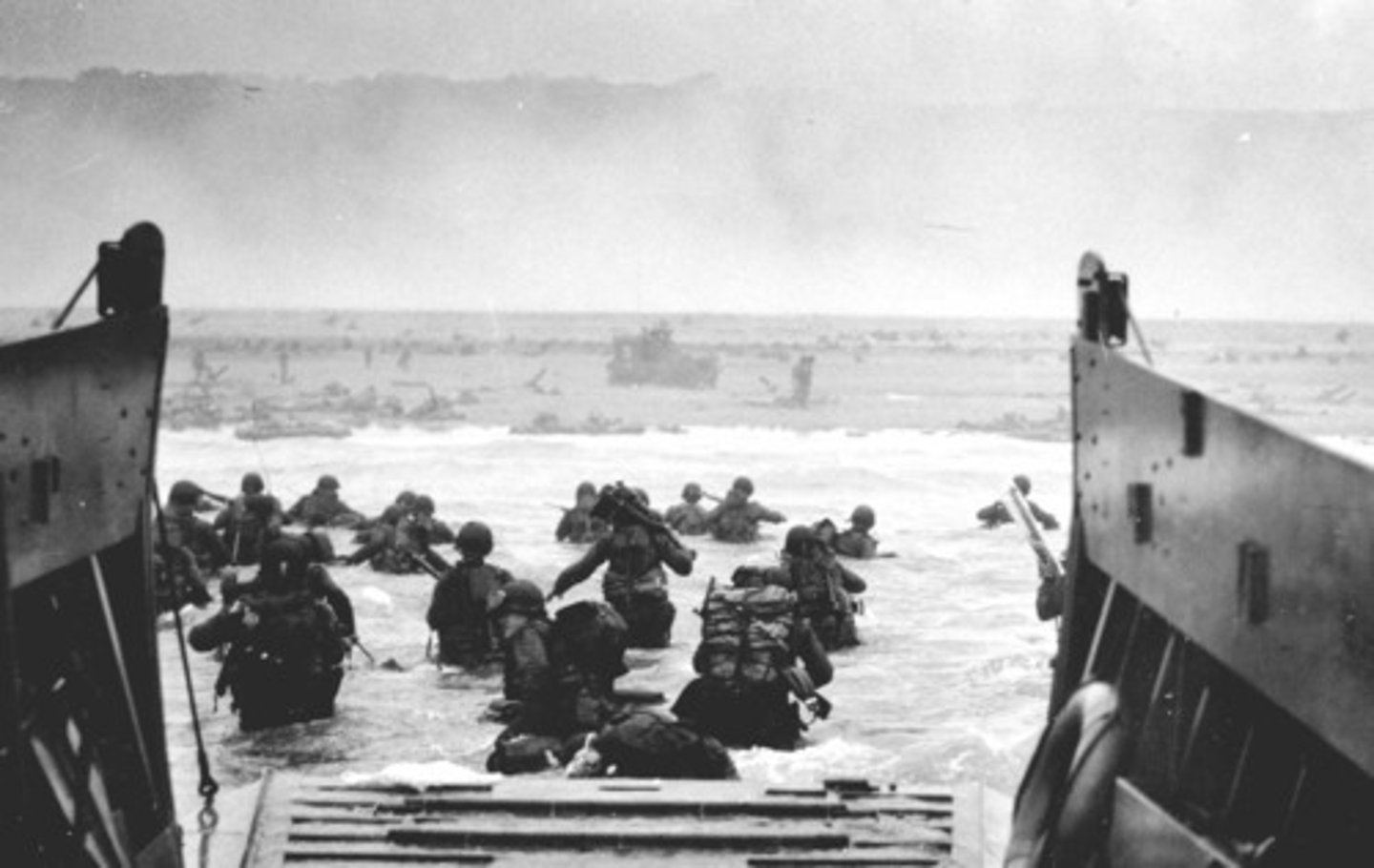
D-Day
The US and Allies invaded Normandy, France. With this invasion, the Allies began to take back France which had been captured by Germany.

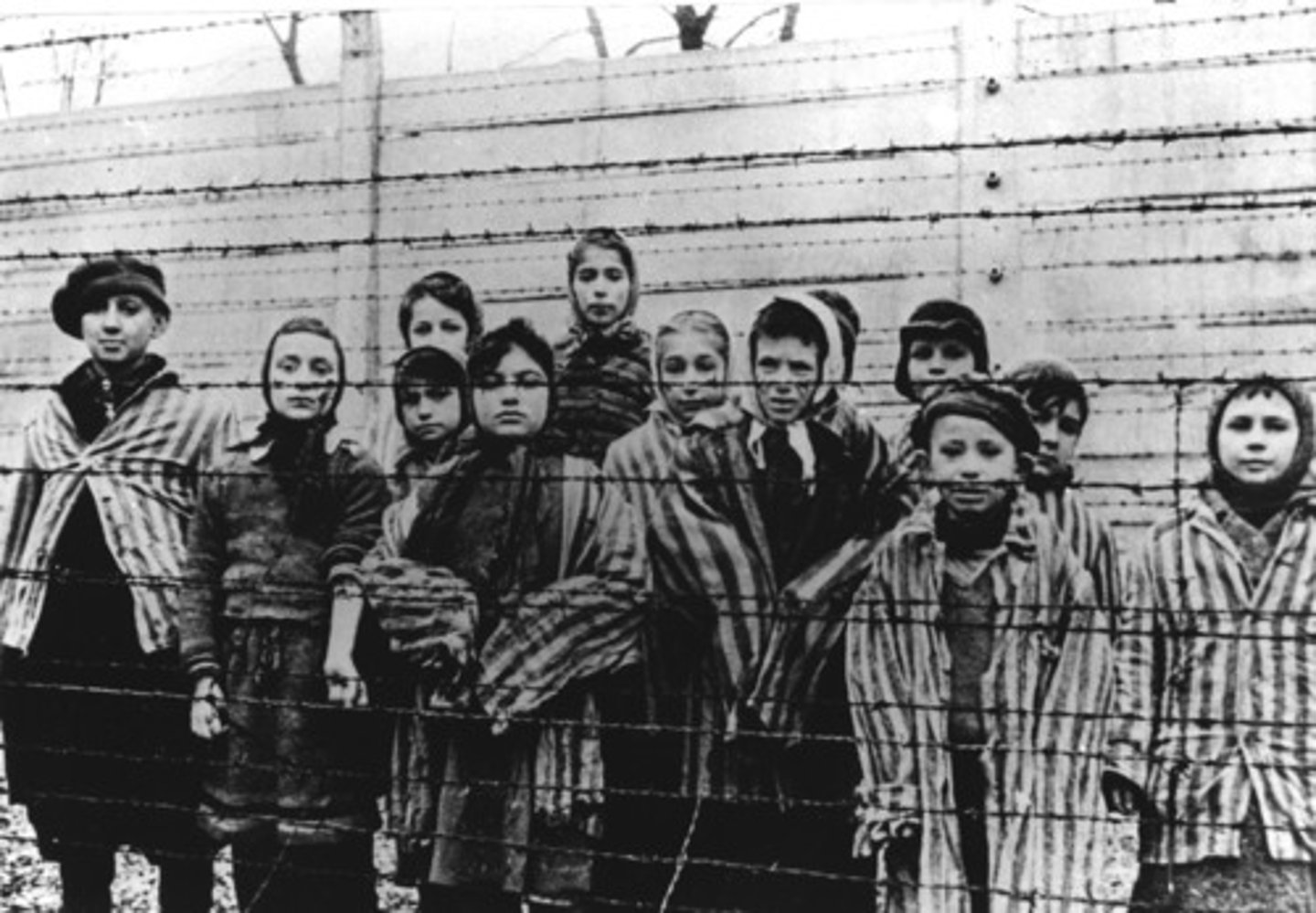
Holocaust
when millions of Jewish men, women, and children died from being in concentration camps.

Atomic Bomb
Powerful, nuclear weapon

Rationing
Limiting the amount of something that a person can buy

Ration card
Cards used to distribute rations

Propaganda
Messages used to create support for the war

War bond
People invested money with the government in order to help pay for the war effort. The gov't had to pay back the money, plus interest, after the war.

militant nationalism
a form of nineteenth-century nationalism that focused on cultural and racial differences and advocated an aggressive, heroic approach to international relations

totalitarian rule
a form of government in which the political authority exercises absolute and centralized control over all aspects of life, the individual is subordinated to the state, and opposing political and cultural expression is suppressed

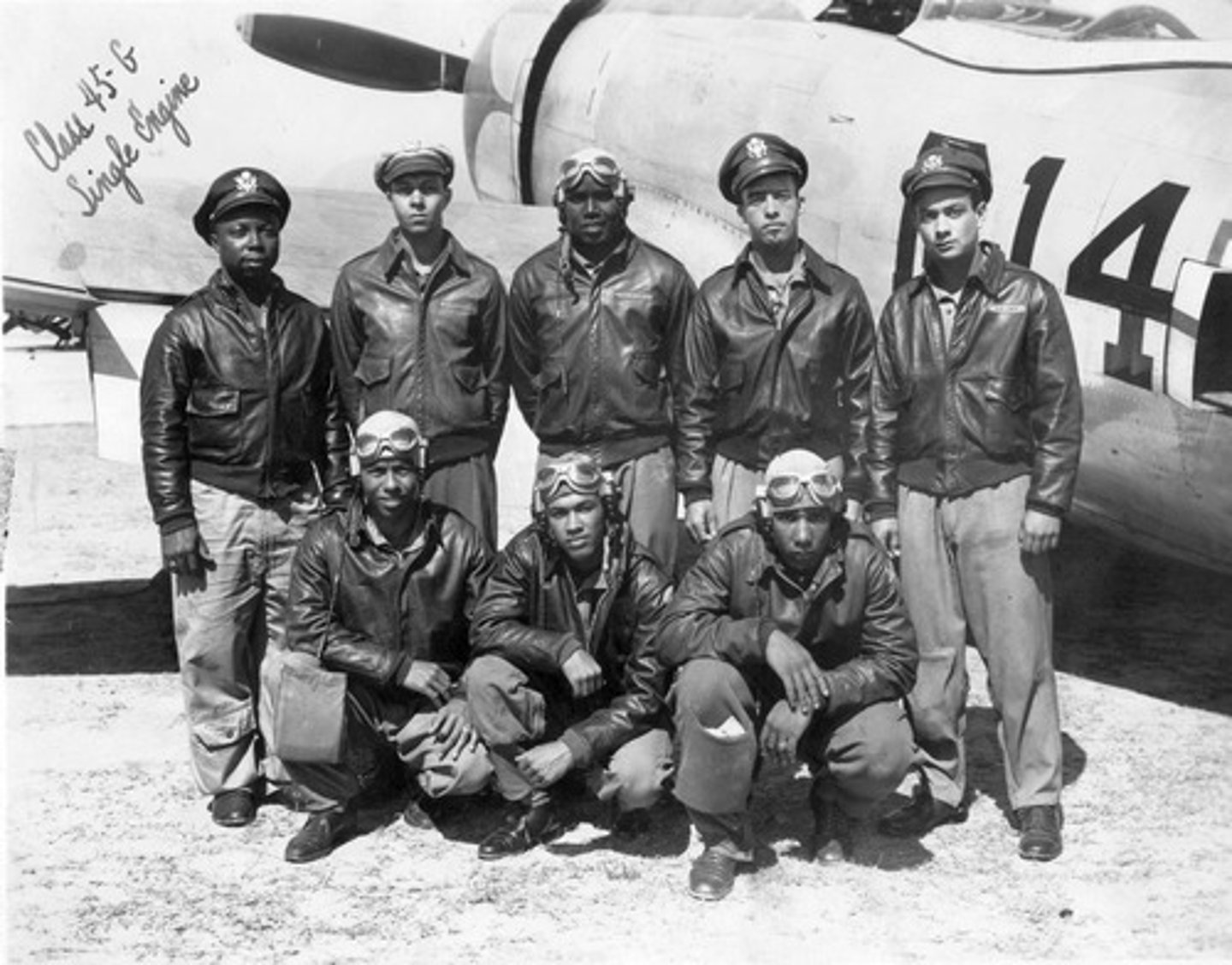
Tuskegee Airmen
332 Fighter Group famous for shooting down over 200 enemy planes. African American pilots who trained at the Tuskegee flying school.

Korematsu v. United States (1944)
Ruled that American citizens of Japanese descent could be interned and deprived of basic constitutional rights due to executive order
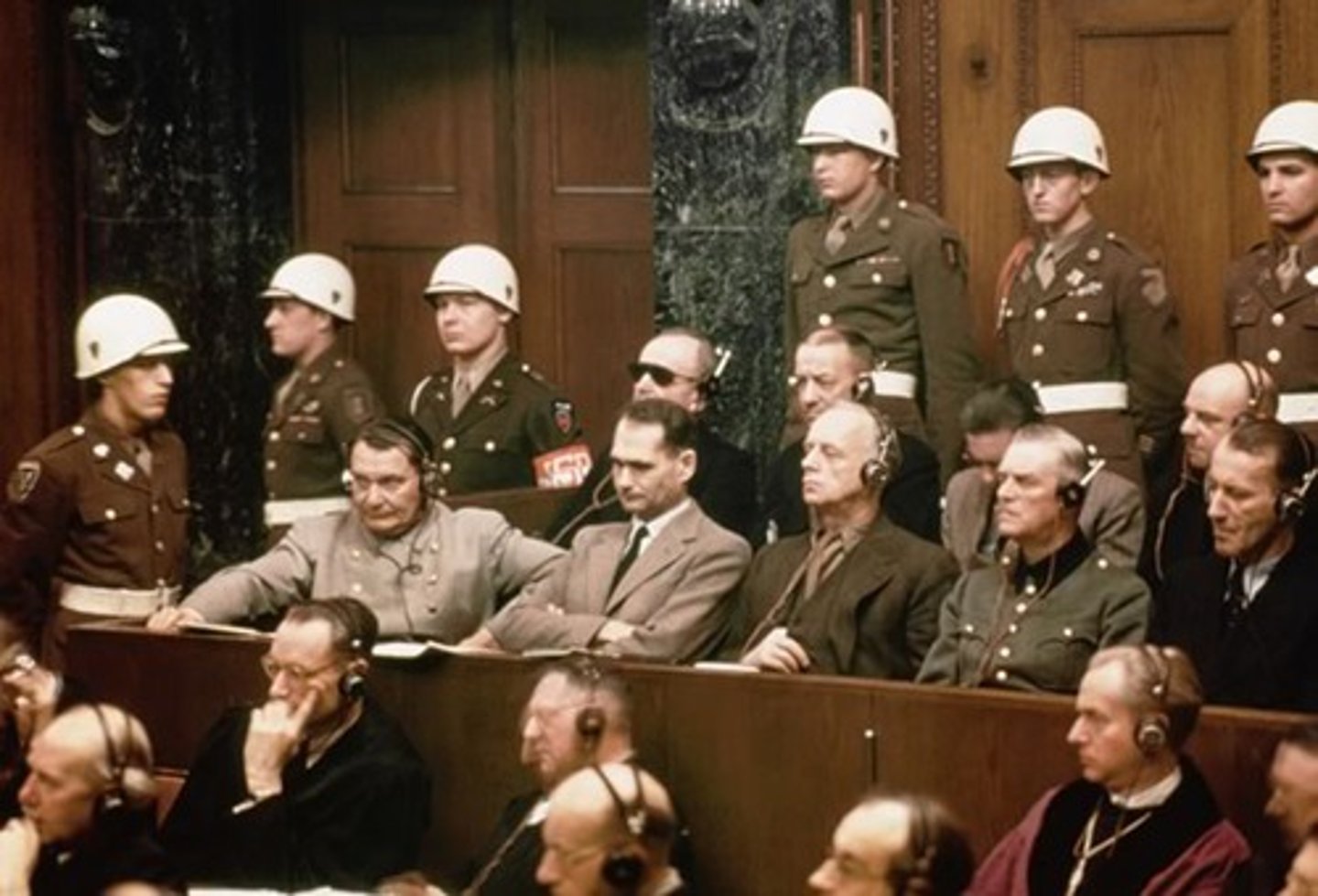
Nuremberg trials
A series of court proceedings held in Nuremberg, Germany, after World War II, in which Nazi leaders were tried for aggression, violations of the rules of war, and crimes against humanity.

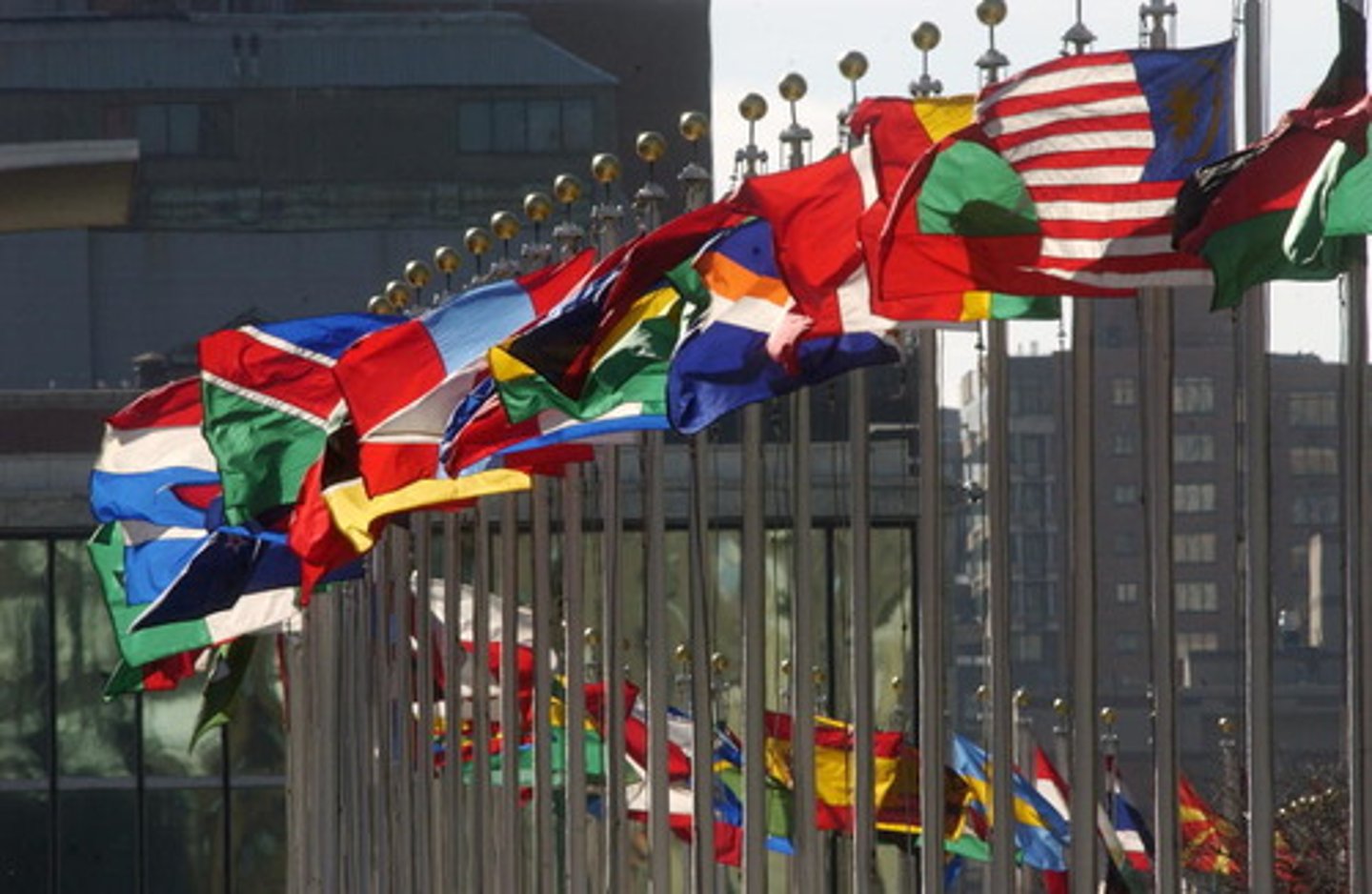
United Nations
An international organization formed after WWII to promote international peace, security, and cooperation.

Neutrality Acts of 1935, 1936, and 1937
Short-sighted acts passed in 1935, 1936, and 1937 in order to prevent American participation in a European War. Among other restrictions, they prevented Americans from selling munitions to foreign belligerents.

Lend-Lease Act
1941 law that authorized the president to aid any nation whose defense he believed was vital to American security

Universal Declaration of Human Rights
A 1948 statement in which the United Nations declared that all human beings have rights to life, liberty, and security.

Elenor Roosevelt
wife to FDR. most active first lady in history. powerfully influenced the politics of the national gov't battling for the impoverished and oppressed.
