Lower Leg and Ankle/Foot Pain
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
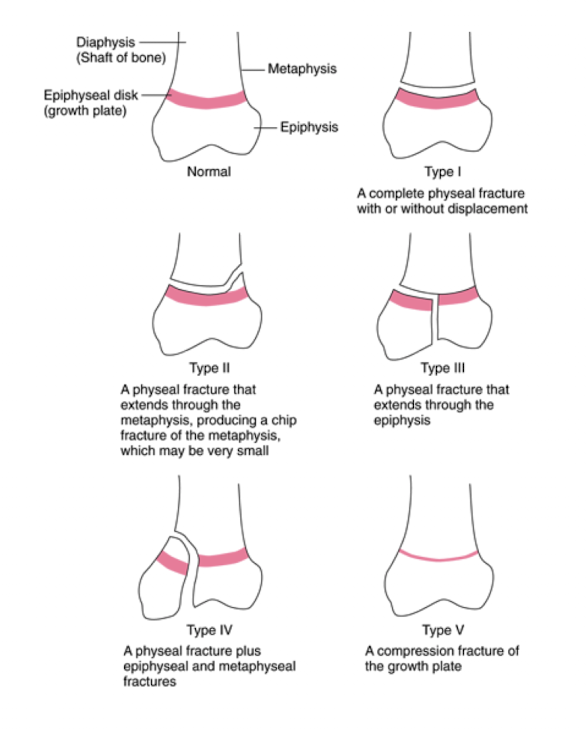
What are the 5 types of a Salter-Harris fracture classification?
Type I: fx through the physis (growth plate)
Type II: fracture partway through the physis extending up into metaphysis
Type III: fx partway through the physis extending down into the epiphysis
Type IV: fx thorugh the metaphysis, physis, and epiphysis can lead to angulation deformities when healing
Type V: crush injury to the physis
What is the healing time table for a fracture repair?
Soft callus: 2 weeks
Hard callus: 4-6 weeks
Lamellar bone: 6-12 weeks
What are the methods of correcting a fracture?
Closed reduction
Preferred method no hospital stay
Non surgical, manual reaglinment
Open reduction
Correction of bone alignment through a surgical incision
Allows earlier mobilization of pt and the joints involved, decreased risk of contractures
Arthroplasty
Traction
Skin traction (short term)
Skeletal traction (longer periods)
What are complications to watch for after a fracture?
Swelling, especially with casting
Fat embolism, especially when pelvic fx and long bones
Fixation devices (break or displacement)
Skin issues
Infections
Delayed union, malunion, non-union, etc.
Nerve or vascular compromise
Which has earlier mobility: post-operative or non-operative?
Post-operative.
Non-operative takes longer to mobilize due to callus formation
What are the symptoms of someone with tibialis posterior dysfunction?
Impaired mobility and function
Medial ankle pain with loss of strength in posterior tibialis
Flat foot deformity, loss of medial arch height, swelling at medial ankle with forefoot valgus (too many toes sign)
Where is the pain located in a pt with tibialis posterior dysfunction?
Behind medial malleolus
What type of treatment is used for stage I and II tibialis posterior tendinopathy?
Conservative treatment:
Focus on strengthening the posterior tibialis
Unload tendon with taping and/or orthotics
Balance and stretching/manual therapy for improving ankle DF
What are interventions used for tibial posterior tendinopathy?
Talocreual mobilization for posterior glide, distraction prn
Gastro-soleus stretching/mobility exercise for DF
Foot intrinsic strengthening
Closed chain for control of pronation (anti-pronation exercise)
Hip strengthening
Progress walking and functional exercises (squats, step downs)
Limited mobility of the hip causes shin splints.
Limited hip IR
What are the 4 grades of pain for medial tibial stress syndrome?
Grade I: pain after activity
Grade II: pain before and after activity and not affecting performance
Grade III: pain before, during, and after activity, affecting performance
Grade IV: pain so severe performance is impossible
What treatments can be done to help with medial tibial stress syndrome?
Education (activity mod., footwear, modalities)
Manual therapy to improve DF
Exercise
Calf stretching
Strength for foot intrinsic muscles
Eccentric strengthening for ant tib
Hip strengthening
Gait retraining: cadence
What are the symptoms of chronic exertional compartment syndrome (5 P’s)
5 P’s
Pain: ache, sharp dull
Pallor
Paresthesia
Pulselessness
Paralysis
Tightness form to touch
No symptoms at rest
S/S of tibial stress fractures?
Focal, sharp palpable pain
Progression of weight-bearing pain to pain at rest/night
Location: ant tibia vs post tibia
Tuning fork (Sp 19-83%) vs US (63-66%)
What is turf toe?
Tearing of ligament on bottom of great toe
What are the S/S of turf toe?
Decreased weight bearing, toe off
Pain/swelling @ first MTP
Pain w/ passive extension of 1st MTP
What is the treatment of turf toe?
Brace/taping
Exercise to promote motion/strength
Modalities
What is a Jones fracture?
5th metatarsal fracture. Due to overuse
What is a Lis Franc injury?
Tearing of ligament between 1st and 2nd metatarsals and ½ of cuneiforms
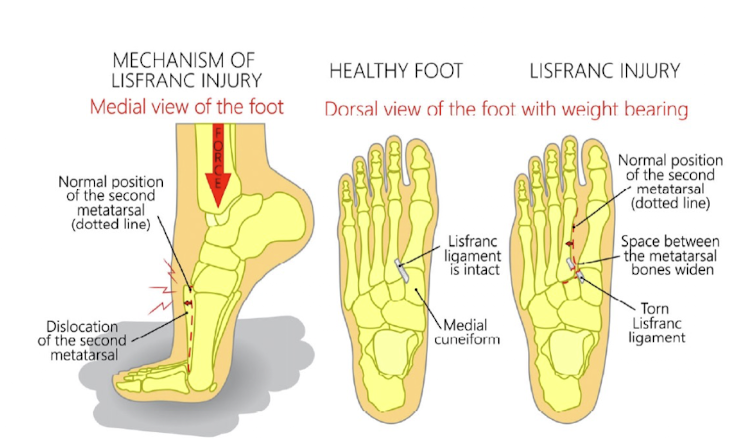
What is the WB status after a Lis Franc surgery?
Arthrodesis: 6 weeks. NWB → 4 weeks in CAM boot
ORIF: 6 weeks. NWB → 6 weeks WBAT in boot → hardware removal and wean from boot as tolerated
Tight rope: 6 weeks. NWB → FWB
What is hallux valgus?
Angle on the 1 MTP (hallux moves laterally relative to metatarsals), >15 degrees = hallux valgus
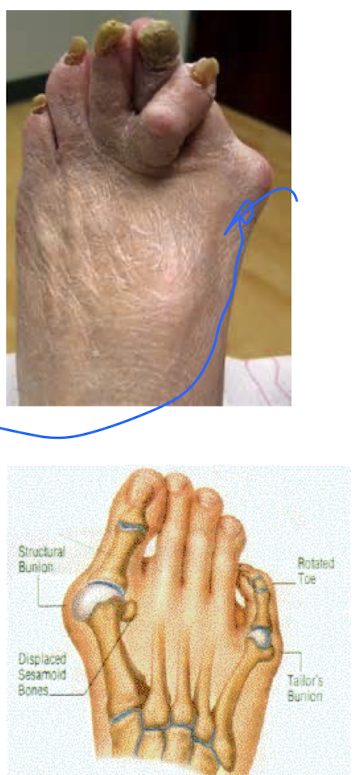
What is the treatment of hallux valgus?
Education (proper footwear, orthotic, rocker bottom shoe)
Manual therapy
First MTP varus mob
Talocrural post glide
Exercise
Stretching first MTP, calf
Balance activity
Often go to surgery depending on angle
What are the symptoms of ankle osteoarthritis?
Stiffness after prolonged inactivity and in early morning
Pain eases after warm up
Pain with WB, walking, and stairs
What will be found upon exam of ankle osteoarthritis?
Joint line and peri-articular tenderness
Limited ankle ROM w/ pain, possible crepitus
Stiffness with passive and accessory motion
Pain and limitation with squatting, STS, and aantalgic gait
Treatment of ankle osteoarthritis?
Education (activity mod, bracing, shoes)
Manual therapy
Joint mobs for talocrural joint, tib-fib glides
Exercise
Stretching and mobility exercise
Strength training
Balance exercises
Functional exercise for gait, STS, step up/down
Modalities
Heat, ESTIM
What is Mortons neuroma?
Irritation and swelling that surrounds the plantar nerve, most often between 3rd/4th digits
What are the S/S of Morton’s Neuroma?
Insidious or post-traumatic onset of sharp, burning pain on the plantar surface near metatarsal heads
Often pt will c/o of pebble in shoe
Pain may radiate into toes and cause numbness
Pain worse with WB activity/walking
Pain relief upon remove of shoe and/or pressure
What would you find upon exam of Morton’s Neuroma?
Point tenderness with palpation
Positive “squeeze test” w possible click
Squeeze metatarsals. Will cause severe pain if positive.
What is the treatment of club foot (talipes equinovarus)?
Serial casting/surgery (go and cut achilles, reform foot and recast the foot into normals position)