Chapter 6 - PCR Bio-Rad
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
PCR
polymerase chain reaction
What is PCR?
in vitro (outside of cell), targeted for a specific sequence, done to amplify DNA quantity
What do you need for PCR?
Template DNA, Forward and reverse primers, heat stable DNA polymerase, dNTPs, Buffer, MgCl2
Master Mix
dNTPs + Buffer + MgCl2
Why do you need aerosol tips for PCR?
PCR is very sensitive to contamination
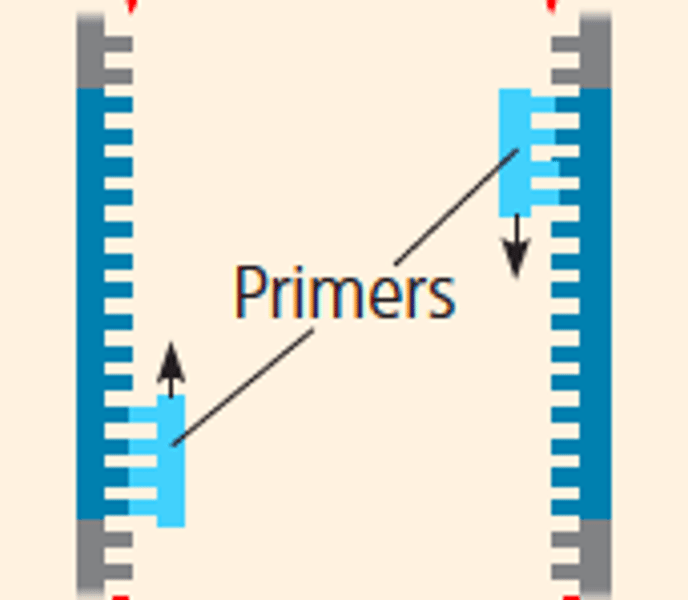
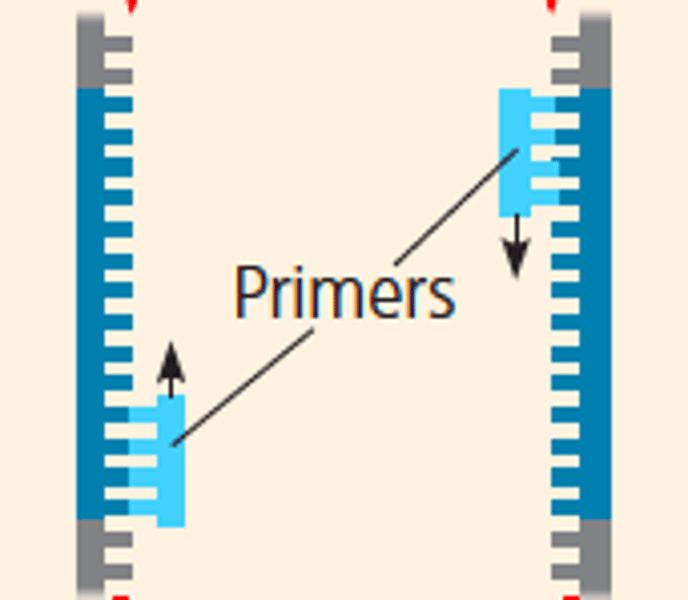
Primers
short pieces of DNA that mark the beginning and end of the target DNA
melting temperature (Tm)
This is a factor that effects the PCR reaction. Ideally, primers in the pair must be within a few degrees of each other.
DNA polymerase
builds DNA by adding nucleotides (original one from Thermus Aquaticus)
DNA in PCR
doubles each cycle, exponential
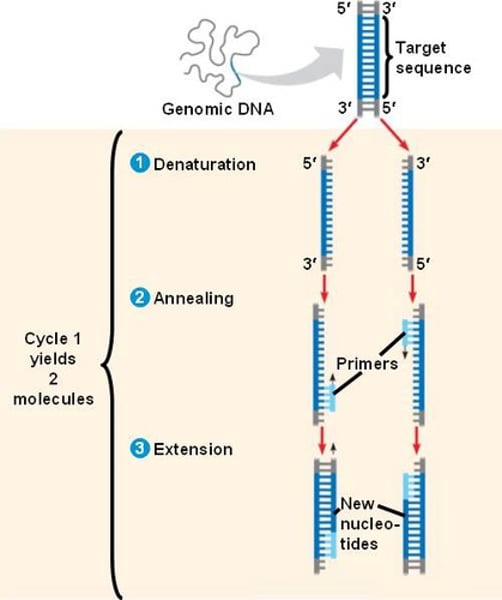
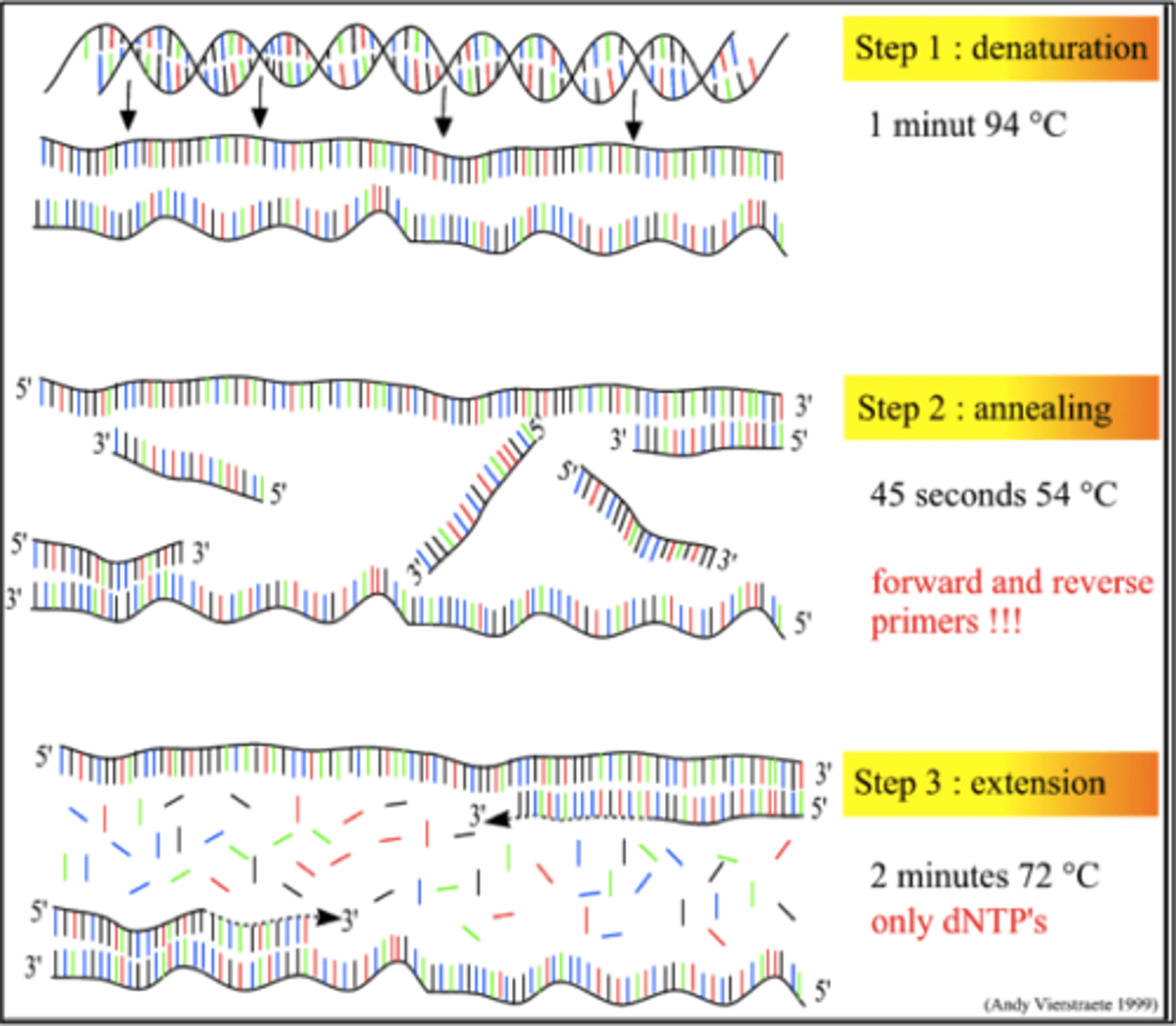
PCR steps
denaturation, annealing, extension
Denature DNA
(~94 C) breaks hydrogen bonds holding double stranded DNA together to produce single stranded DNA
annealing
(40-60 C) cools down to allow primers to hydrogen bond to the DNA sequence
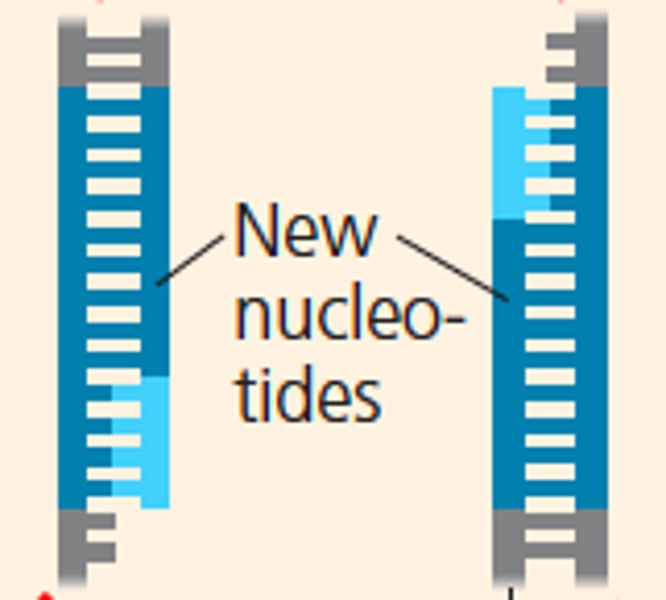
Extension of DNA
(~72 C) warm temperature to optimize the rate that the DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the DNA strand, template strand reads 5' -> 3' while new strand reads 3' -> 5'
extracting DNA from food for PCR
grind up and heat food sample to 95 C to release DNA, use InstaGene Matrix to remove metal ions that the DNA needs to function (protects DNA from degrading and is more efficient and faster)
Multiplex PCR
multiple primers for multiple targets
Real Time PCR
newly made DNA is tagged with a fluorescent dye; the levels of fluorescence can be measured after every PCR cycle
PCR sequencing
small amount of dNTPs are ddNTPs, missing one more oxygen to prevent the chain from growing further
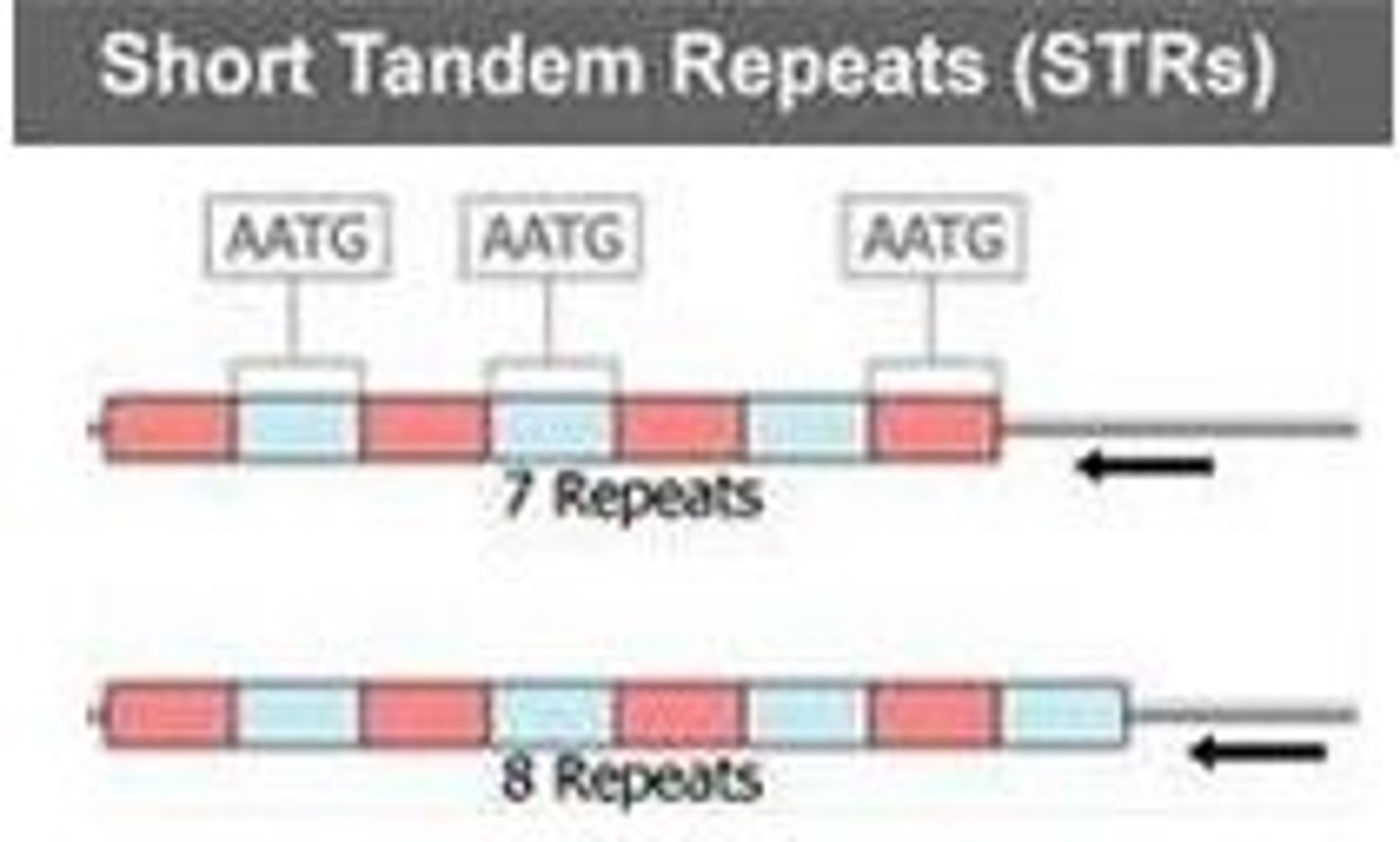
STRs
Portions of the DNA that are extremely variable between people, analyzing STRs will greatly reduce the chance of two people matching
Alu insertion
A sequence of DNA repeated at different locations on different chromosomes that are only in primates, repetitions caused by sequence copying onto mRNA and then reinserting into genome with reverse transcriptase
Amplicons
PCR products
Pharming
using genetically modified animals to make pharmaceutical drugs
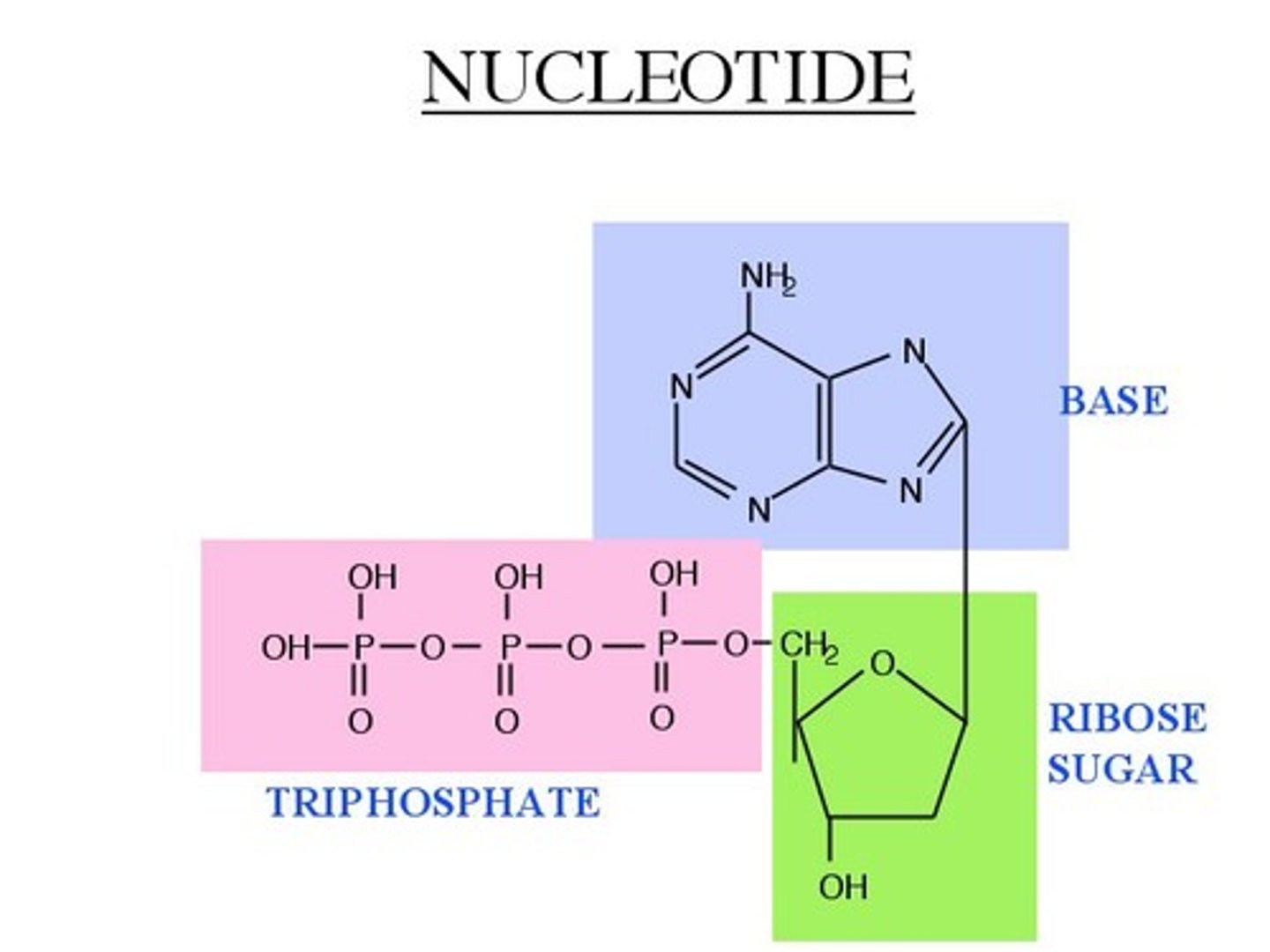
Nucleotides are made up of
sugar, phosphate, base
PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
is used to copy and amplify minute quantities of DNA/
Thermus aquaticus
bacterium that can sustain high temperatures without being denatured
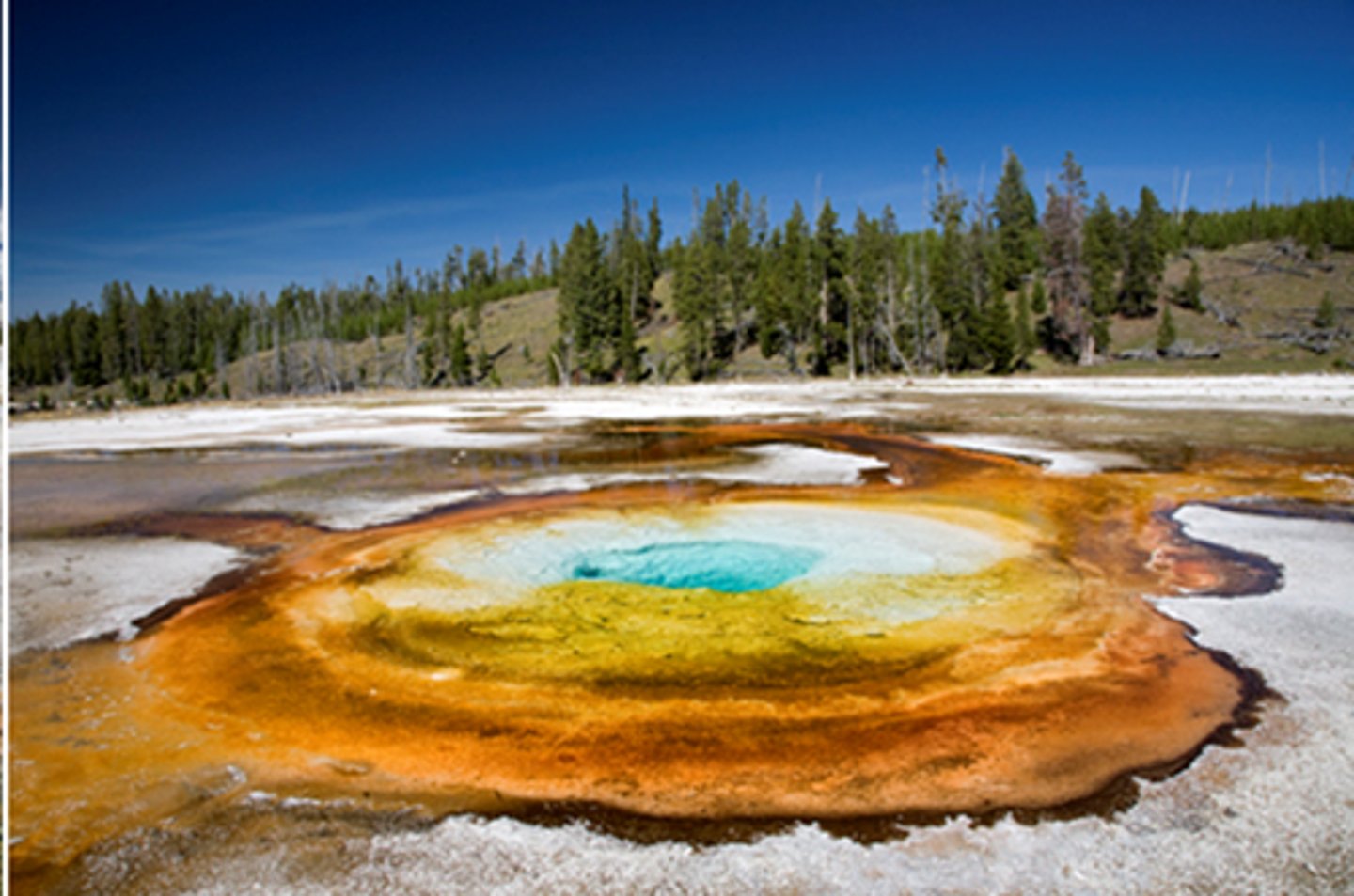

Taq polymerase
A heat-stable form of DNA polymerase extracted from bacteria that live in hot environments, such as hot springs, that is used during PCR technique
In Vivo
process that takes place in a living organism
PCR tube
small tube that holds .2mL

Nested PCR
2nd set of primers used just inside of first set
chelating
process of using agents to "clean" DNA sample and remove other cellular proteins
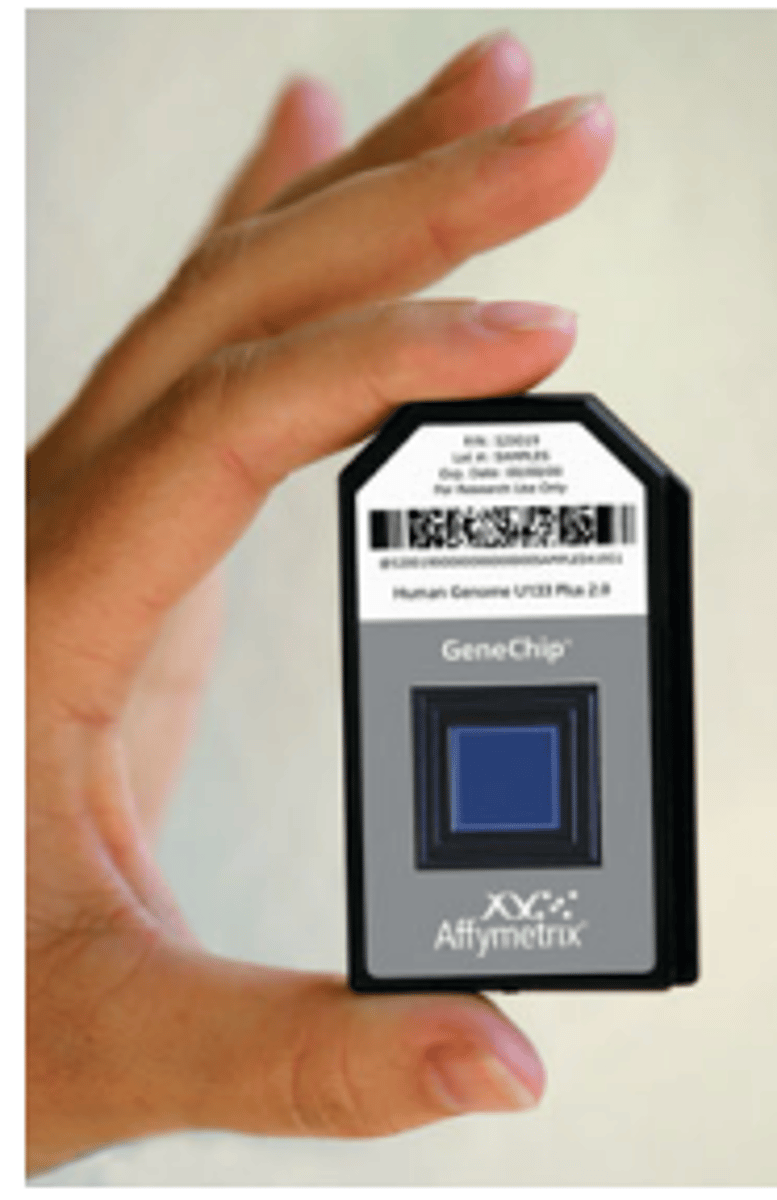
Microarrays (gene chips)
used to study expression of numerous genes
