Clinical Chemistry Final Review
1/208
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
209 Terms
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides
a. Guidelines for writing procedure manuals
b. Safe environments for patients
c. Specimen collection guidelines
d. Criteria for disposal of chemical waste
b. Safe environments for patients
Universal Precautions states that blood and body fluids should be considered a biohazard
a. At all times
b. When it comes from a hepatitis patient
c. If the color is green or yellow
d. Never
a. At all times
Hand-to-mouth contact is a hazard in the laboratory. Of the following situations, the one that is not hand-to-mouth contact is
a. Chewing on a pencil eraser
b. Pipetting without a suction device
c. Not wearing a face shield
d. Wiping your face with a laboratory coat sleeve
c. Not wearing a face shield
Class A fire extinguishers may be used to put out a fire where the burning substance is
a. A window shade
b. Paint thinner
c. A computer terminal
d. An oscillating fan
a. A window shade
Special collection requirements for specimens may be found in the
a. Collection tray
b. Fire and safety manual
c. OSHA regulations
d. Specimens collection manual
d. Specimen collection manual
Of the following tests, the one performed in Special Chemistry is
a. Electrolytes
b. Drug screen
c. Glucose
d. Protein
b. Drug screen
A test profile is
a. Single test which diagnoses a clinical condition
b. Special chemistry test which requires special instrumentation
c. Group of tests arranged by the organ which is being analyzed
d. Set of criteria for performing a specific test
c. Group of tests arranged by the organ which is being analyzed
Of the following substances, which would not be covered under the concept of Universal Precautions?
a. Chemicals
b. Serum samples
c. Urine
d. Spinal fluid
a. Chemicals
Removal of gloves should take place when
a. The gloves are soiled
b. Leaving the laboratory
c. Shaking hands with the sales representative
d. All of the above
d. All of the above
Biohazardous spills are cleaned by
a. Wiping with a paper towel
b. Diluting with soap and water
c. Decontaminating with sodium hypochlorite (NaCLO)
d. Calling the housekeeping department
c. Decontaminating with sodium hypochlorite (NaCLO)
A pipet that has an etched ring near the mouth end should be
a. Rinsed after delivery of the liquid
b. Be allowed to freely drain
c. Blown out
d. Used for critical measurements
c. Blown out
A flat-bottom flask with sloping sides and a neck that resembles a bottle is a
a. Griffin beaker
b. Erlenmeyer flask
c. Florence flask
d. Graduated cylinder
b. Erlenmeyer flask
A pipet marked with a TD should be
a. Rinsed after delivery of the liquid
b. Allowed to freely drain
c. Blown out
d. used for critical measurements
b. Allowed to freely drain
To make critical dilutions and measurements, one should use a
a. Beaker
b. Volumetric flask
c. Florence flask
d. Graduated cylinder
b. Volumetric flask
A standard curve for glucose is prepared using 3 standards of varying concentrations. Some unknown patient samples are analyzed. The concentration of the patient samples may be determined by
a. Choosing a value which is close to one of the standards
b. Evaluating one additional standard with these patient
c. Reading the patient values from the standard curve
d. Averaging the patient sample results with those from the standards
c. Reading the patient values from the standard curve
When using a volumetric pipet, a drop remains. The technician should
a. Blow out the remaining drop
b. Touch the tip to the side of the tube
c. Rinse the pipet
d. Do nothing
b. Touch the tip to the side of the tube
When making a dilution in a volumetric flask, the technician adds water until it is above the fill line. The technician should
a. Remove the excess water with a pipet
b. add more water to bring the level to the top of the flask
c. Mix the flask and then remove a small amount of water
d. Begin preparing the solution again
d. Begin preparing the solution again
The system that includes standards of quality for all stages of the analytical process is called
a. Quality insurance
b. Controls
c. Quality assurance
d. Standardization
c. Quality assurance
*Double check answer*
The part of quality assurance system that involves the analyses done in the laboratory is
a. The pre-analytical stage
b. The analytical stage
c. The post-analytical phase
d. External quality control
b. The analytical stage
Quality control that involves control specimens coming to a laboratory from an outside source and being evaluated by an outside agency is called
a. External quality control
b. Internal quality control
c. Pre-analytical phase
d. Post-analytical phase
a. External quality control
Reference ranges are usually established on a population of
a. Healthy people
b. Unhealthy people
c. A mixture of healthy, and unhealthy people
d. Geriatric people
a. Healthy people
On a Levy-Jennings chart. the center line is given a designation of the
a. Coefficient of variation
b. Mean
c. Standard deviation
d. Variance
b. Mean
Acceptable range is commonly defined as the
a. Mean plus or minus 2%
b. Mean plus 1 standard deviation
c. Mean plus the variance squared
d. Mean plus or minus 2 standard deviations
d. Mean plus or minus 2 standard deviations
Which of the following is included in the post-analytical phase
a. Commercial controls
b. Reporting results
c. Manual test methods
d. Specimen collection
b. Reporting results
The mean value is also known as the
a. Average
b. Coefficient of variation
c. Standard deviation
d. Variance
a. Average
The spectrophotometer makes its measurements based on the principle of light
a. Transmittance
b. Scatter
c. Color
d. Wavelength
A. Transmittance
The spectrophotometer's light path is determined by the size of the
a. Bulb
b. Photodetector
c. Cuvette
d. Monochromator
c. Cuvette
When light passes through a solution in a cuvette, the measurement that is actually registered on the photodetector is light which was
a. Absorbed by the solution
b. Transmitted through the solution
c. All the light from the tungsten lamp
d. Reflected from the monochromator
b. Transmitted through the solution
Cuvette matching is vital to accurate measurements because mismatches cuvettes
a. Can lead to errors in colorimetry
b. Will be difficult to use
c. Will not fit into the sample well properly
d. Will not have etched markings on them
a. Can lead to errors in colorimetry
Many chemical reactions require that an instrument maintain a specified incubation temperature. How frequently should the accuracy if the thermometer used to monitor the incubation temperature be verified?
a. Daily
b. Monthly
c. Weekly
d. Biannually
d. Biannually
Checking instrument calibration, temperature accuracy, and electronic parameters are part of
a. Preventative maintenance
b. Quality control
c. Function verification
d. Precision verification
a. Preventative maintenance
For which of the following laboratory instruments should preventive maintenance procedures be performed and recorded?
a. Analytical balances
b. Centrifuge
c. Chemistry analyzers
d. All of the above
d. All of the above
What term applies to the sum of all the values in a set of numbers divided by the number of values in that set?
a. Median
b. Mode
c. Arithmetic mean
d. Geometric mean
c. Arithmetic mean
What assistance does an external quality assurance program provide for a laboratory?
a. Means to correlate tests performed by different departments within the same laboratory
b. Delta checks was previous tests on the same patient
c. Evaluation of its performance by comparison with other laboratories using the same method
d. Limits for reference intervals
c. Evaluation of its performance by comparison with other laboratories using the same method
What percentage of values will fall between +/- 2s in a Gaussian (normal) distribution?
a. 34.13%
b. 68.26%
c. 95.45%
d. 99.74%
c. 95.45%
which of the following is material of known composition available in a highly purified form?
a. Standard
b. Control
c. Technical reagent
d. Test analyte
a. Standard
In spectrophotometric analysis, what is the purpose of the reagent blank?
a. Correct for interfering chromogens
b. Correct for lipemia
c. Correct for protein
d. Correct for color contribution
d. Correct for color contribution of the reagents
Which of the following formulas is an expression of the Beer-Lambert law that is routinely applied to spectrophotometric analysis?
a. Au/As × Cs = Cu
b. Cu × Cs/As = Au
c. As × Cs/Cu = Au
d. A = 2 - log %T
a. Au/As × Cs = Cu
In spectrophotometry, which of the following is a mathematical expression of the relationship between absorbance and transmittance?
a. A = abc
b. a = 2 - log %T
c. a= log %T
d. Au/Cu = As/Cs
b. a = 2 - log %T
What term describes the extent of agreement between repeated analysis
a. Random error
b. Precision
c. Accuracy
d. Reliability
b. Precision
What is the following formula used to calculate?
a. Coefficient of variation
b. Variance
c. Confidence limits
d. Standard deviation
d. Standard deviation
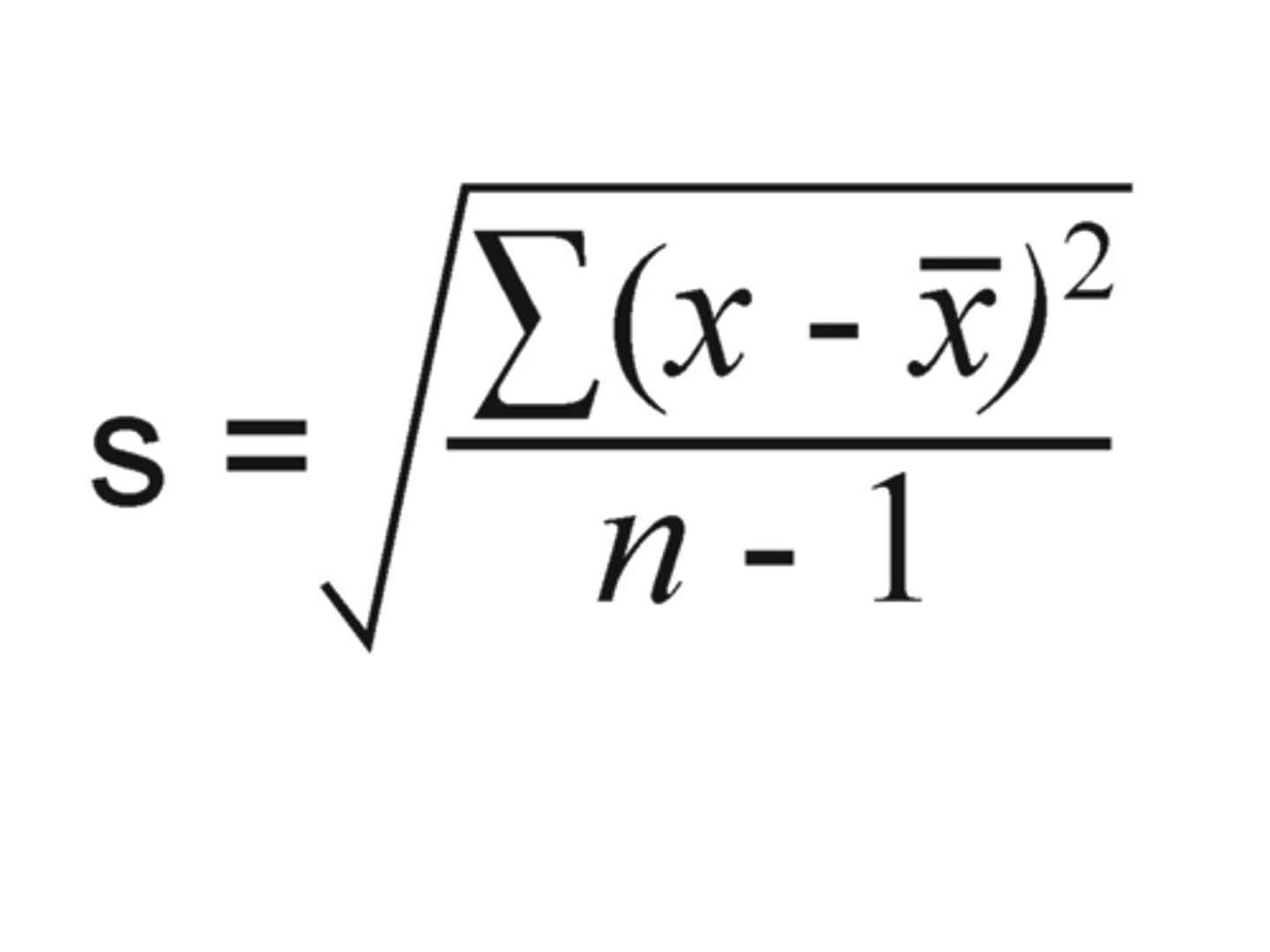
Calculate the coefficient of variation (percent) for a set of data where the mean (x bar) = 89mg/dL and 2 standard deviations (s) = 14 mg/dL
a. 7.8
b. 7.9
c. 15.7
d. 15.8
b. 7.9
CV = (s/(x bar[mean])) x 100
CV = (7/89) x 100
CV = 7.865168539
CV = 7.9
Gaussian distribution
Normal distribution. A population of data that has a tendency to cluster symmetrically.
Shift
An abrupt and sustained change (in one direction) in control values.
Mean
Arithmetic average of a set of data
Trend
A gradual change in the test results obtained from control material that is suggestive of a progressive problem with the testing system or control material; also called drift.
Levy-Jennings plot
A visual tool for evaluating quality control data in the context of previous QC results where data are plotted relative to the mean +/- 2 SD on the vertical (y) axis versus days on the horizontal (x) axis.
Standard Deviation (SD)
Square root of a variance.
CV
Coefficient of variation. A relative standard deviation in which the standard deviation is divided by the mean and multiplied by 100%.
Class A
Ordinary combustible solid materials
Class B
Flammable liquids/gases/petroleum products
Class C
Energized electrical equipment
Class D
Combustible/reactive metals
Match the class of fire with the type of extinguisher:
Class A
Pressurized water, ABC (dry chemical)
Match the class of fire with the type of extinguisher:
Class B
ABC (dry chemical), BC (CO2)
Match the class of fire with the type of extinguisher:
Class C
BC (CO2), Halon, ABC (dry chemical)
Match the class of fire with the type of extinguisher:
Class D
Metal X
The NFPA developed a standard hazard ID system (diamond shaped, color coded). Match the color with the type of hazard.
Blue quadrant
Health hazard
The NFPA developed a standard hazard ID system (diamond shaped, color coded). Match the color with the type of hazard.
Red quadrant
Flammable hazard
The NFPA developed a standard hazard ID system (diamond shaped, color coded). Match the color with the type of hazard.
Yellow quadrant
Reactivity/stability hazard
The NFPA developed a standard hazard ID system (diamond shaped, color coded). Match the color with the type of hazard.
White quadrant
Other special information
A trend in QC results is most likely caused by
a. Deterioration of the reagent
b. Miscalibration of the instrument
c. Improper dilution of standards
d. Electronic noise
a. Deterioration of the reagent
The term R4s means that:
a. Four consecutive controls are greater than +/- 1 standard deviation from the mean
b. Two consecutive controls in the same run are greater than 4 standard deviation units apart
c. There is a shift above the mean for four consecutive controls
d. Two consecutive controls in the same run are greater than +/- standard deviations from the mean
b. Two consecutive controls in the same run are greater than 4 standard deviation units apart
One of the two controls within a run is above +2 standard deviations and the other control is below -2 standard deviations from the mean. What do these results indicate?
a. Poor precision has led to random error (RE)
b. A systematic error (SE) is present
c. Proportional error is present
d. QC material is contaminated
** Check answer w/ classmates
When referring to quality control (QC) results, what parameter usually determines the acceptable range?
a. The 95% confidence interval for the mean
b. The range that includes 50% of the results
c. The central 68% of results
d. The range encompassed by +/- 2.5 standard deviations
a. The 95% confidence interval for the mean
Which of the following conditions is cause for rejecting and analytical run?
a. Two consecutive controls greater than 2 standard deviations above or below the mean
b. Three consecutive controls greater than 1 standard deviation above the mean
c. Four controls steadily increasing in value but less than +/- 1 standard deviation from the mean
d. One control above +1 standard deviation
a. Two consecutive controls greater than 2 standard deviations above or below the mean
Which of the following quality control (QC) rules would be broken 1 out of 20 times by chance alone?
a. 1 2s
b. 2 2s
c. 1 3s
d. 1 4s
a. 1 2s
Which of the following assays has the poorest precision? (Calculate CV to do this)
a. Analyte: Ca, Mean(mmol/L): 2.5. Standard Deviation: 0.3
b. Analyte: K, Mean(mmol/L) 4.0 Standard Deviation: 0.4
c. Analyte: Na, Mean(mmol/L) 140 Standard Deviation: 4.0
d. Analyte: Cl, Mean(mmol/L) 100 Standard Deviation: 2.5
a. Analyte: Ca, Mean(mmol/L): 2.5. Standard Deviation: 0.3
CV = (s/(x bar[mean])) x 100
(0.3/2.5) x 100 = 12
Which of the following plots is best for detecting all types of QC errors?
a. Levy-Jennings
b. Tonks-Youden
c. Cusum
d. Linear regression
a. Levy-Jennings
A group of physicians consistently complains that they are not receiving STAT patient results quickly enough. The supervisor is likely to refer to which quality assurance variable?
a. Specimen separation and aliquoting
b. Test utilization
c. Analytical methodology
d. Turnaround time
d. Turnaround time
John Smithers (21 years of age) is in to see his physician for a pre-college physical and checkup. john has always been extremely healthy. The following laboratory results were received.
Astandard = 0.679 Acontrol = 0.650
Asmithers = 0.729 Cstandard = 200 mg/dl
Control Range 190-195 mg/dl
Johns cholesterol concentration is approximately:
a. 186 mg/dl
b. 199 md/dl
c. 209 mg/dl
d. 215 mg/dl
d. 215 mg/dl
25℃ is equivalent to how many degrees Fahrenehit?
a. 31.7°
b. 45.9°
c. 77°
d. 102.6°
c. 77°
How would you prepare a 1/5 dilution of a urine sample?
a. 1 part urine + 3 parts diluent
b. 1 part urine + 4 parts diluent
c. 1 part urine + 5 parts diluent
d. 1 part urine + 6 parts diluent
b. 1 part urine + 4 parts diluent
In the calculation of the mean, what does "n" represent?
a. The sum of the values
b. The number of the values in the set
c. The average of the values
d. The middle number of the set
b. The number of values in the set
Which of the following statistics is equivalent to the square root of the variance?
a. Coefficient of variation
b. Standard deviation
c. Sensitivity
d. Specificity
b. Standard deviation
Use the data to answer question
Cholesterol results for 10 patients
180,200,150,170,150,165,205,150,168,145
Using the data, what is the mean of the cholesterol results?
a. 150
b. 168
c. 187
d. 189
b. 168
Use the data to answer question
Cholesterol results for 10 patients
180,200,150,170,150,165,205,150,168,145
Using the data. what is the mode of the cholesterol?
a. 150
b. 165
c. 168
d. 187
a. 150
Use the data to answer question
Cholesterol results for 10 patients
180,200,150,170,150,165,205,150,168,145
Using the data, what is the standard deviation of the cholesterol results?
a. 13.8
b. 15.1
c. 21.2
d. 26.1
c. 21.2
Which of the following is correct when rounding 2.25 to one decimal place?
a. 2.2
b. 2.3
b. 2.3
What is the sum of the following figures: 0.125 + 3.45 + 32.981
a. 36.556
b. 36.55
c. 36.56
d. 36.6
c. 36.56
The closeness of a test value to the actual value describes which of the following?
a. Accuracy
b. Precision
c. Reproducibility
d. Reliability
a. Accuracy
Which of the Westgard rules is violated in the control data below
GO BACK TO THIS PAT IT NEEDS A PICTURE !!!!!!!-maggie ;) <3
Universal Precautions states that blood and body fluids should be considered a biohazard
a. At all times
b. When it comes from a hepatitis patient
c. If the color is yellow or green
d. Never
a. at all times
Special collection requirements for specimens may be found in the
a. collection tray
b. fire and safety manual
c. OSHA regulations
d. specimen collection manual
d. specimen collection manual
A test profile is
a. single test which diagnoses a clinical condition
b. special chemistry test which requires special instrumentation
c. group of tests arranged by the organ which is being analyzed
d. set of criteria for performing a specific test
c. group of tests arranged by the organ which is being analyzed
Of the following substances, which would not be covered under the concept of Universal Precautions?
a. chemicals
b. serum samples
c. urine
d. spinal fluid
a. chemicals
Removal of gloves should take place when
a. the gloves are soiled
b. leaving the laboratory
c. shaking hands with a sales representative
d. all of the above
d. all of the above
Biohazardous spills are cleaned by
a. wiping with a paper towel
b. diluting with soap and water
c. decontaminating with sodium hypochlorite
d. calling the housekeeping department
c. decontaminating with sodium hypochlorite
To make critical dilutions and measurements, one should use a
a. beaker
b. volumetric flask
c. Florence flask
d. graduated cylinder
b. volumetric flask
A standard curve for glucose is prepared using 3 standards of varying concentrations. Some unknown patient samples are analyzed. The concentration of the patient samples may be determined by
a. choosing a value which is close to one of the standard
b. evaluating one additional standard with these patients
c. reading the patient values from the standard curve
d. averaging the patient sample results with those form the standards
c. reading the patient values from the standard curve
When making a dilution in a volumetric flask, the technician adds water until it is above the fill line. The technician should
a. remove the excess water with a pipet
b. add more water to bring the level to the top of the flask
c. mix the flask and then remove a small amount of water
d. begin preparing the solution again
d. begin preparing the solution again
The system that includes standards of quality for all stages of the analytical process is called
a. quality insurance
b. controls
c. quality assurance
d. standardization
c. quality assurance
the part of the quality assurance system that involves the analyses done in the laboratory is
a. the pre-analytical stage
b. the analytical stage
b. the post-analytical stage
d. external quality control
b. the analytical stage
Quality control involves control specimens coming to a laboratory from an outside source and being evaluated by an outside agency is called
a. external quality control
b. internal quality control
c. pre-analytical phase
d. post-analytical phase
a. external quality control
References ranges are usually established on a population of
a. healthy people
b. unhealthy people
c. a mixture of healthy and unhealthy people
d. geriatric people
a. healthy people
On a levy-Jennings chart, the center line is given a designation of the
a. coefficient of variation
b. mean
c. standard deviation
d. variance
b. mean
Acceptable range is commonly defines as the
a. mean plus or minus 2%
b. mean plus 1 standard deviation
c. mean plus the variance squared
d. mean plus or minus 2 standard deviations
d. mean plus or minus 2 standard deviations
which of the following is included in the post-analytical phase
a. commercial controls
b. reporting results
c. manual test methods
d. specimen collection
b. reporting results
The mean value is also known as the
a. average
b. coefficient of variation
c. standard deviation
d. variance
a. average
The spectrophotometer makes its measurements based on the principle of light
a. Transmittance
b. Scatter
c. Color
d. Wavelength
a. transmittance