microanatomy, joints, diseases, and development
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
hyaline cartilage
embryonic skeleton, ribs, synovial joints, trachea, nose
elastic cartilage
ear lobes, epiglottis
fibrocartilage
knee, vertebrae, pubis
endochondral ossification
cartilage is replaced by bone
compact bone
dense and strong
spongy bone
porous and weaker- found in epiphyses
osteon
building blocks of compact bones
dynamic
bone material is _______ it is constantly recycled (7-10 years)
osteoblasts
cells that deposit new bone material (bone builders)
-take calcium from the blood and put into bone
osteoclasts
cells that are responsible for bone resorption
-breaking down bone and putting into bloodstream
blasts and clasts in adults
balance between blasts and clasts
blasts and clasts in juvenile
MORE OSTEOBLASTS than osteoclasts
blasts and clasts in elderly
MORE OSTEOCLASTS than osteoblasts (less dense)
wolff's law
weight bearing exercise stimulates osteoblasts (bones build back stronger/thicker)
sunlight's effect on bones
vitamin D helps absorption of calcium= strong bones
estrogen
what hormone leads to more osteoblast activity?
osteoblasts
bone building cells
growth plate
where the primary growth meets the secondary growth
periosteum
covers the diaphysis part of the bones
calcium
primary mineral found in bones
small intestines
takes calcium into the body through a proper diet and absorbs into the bloodstream
osteogenesis OR deposit
process of bone formation (by osteoblasts)
resorption
process of bone removal (by osteoclasts)
osteoporosis
loss in bone mass, bone tissue breaks down with age
fractures
after menopause, women are at a higher risk for developing what?
Vitamin D
Needed for proper calcium absorption
weight bearing exercises
have been shown to resist osteoporosis because they place stress on the bones that forces them to absorb more bone
estrogen
hormone released by the ovaries that plays important role in bone remodeling
osteoclasts
a lack of estrogen allows _____ to remove more bone than normal
spine, hip, wrist
regions of bone most affected by bone loss in osteoporosis
thyroid gland
gland that deals with elevated blood Ca2+
calcitonin
hormone released by thyroid gland that brings down calcium levels
parathyroid gland
gland that monitors decrease in blood Ca2+
PTH (parathyroid hormone)
hormone released by parathyroid that brings up calcium
not enough PTH, low blood calcium, brittle bones
parathyroid gland stops functioning
density would decrease because of the reduced stress on bones from lack of gravity
what would happen to bone density on the moon?
mitosis
process of cellular division that allows new cells to form and push the bone out longer
slide 7
A- mostly cartilage
B- beginnings of mitosis
C- grown/matured cartilage
D- ossified bone
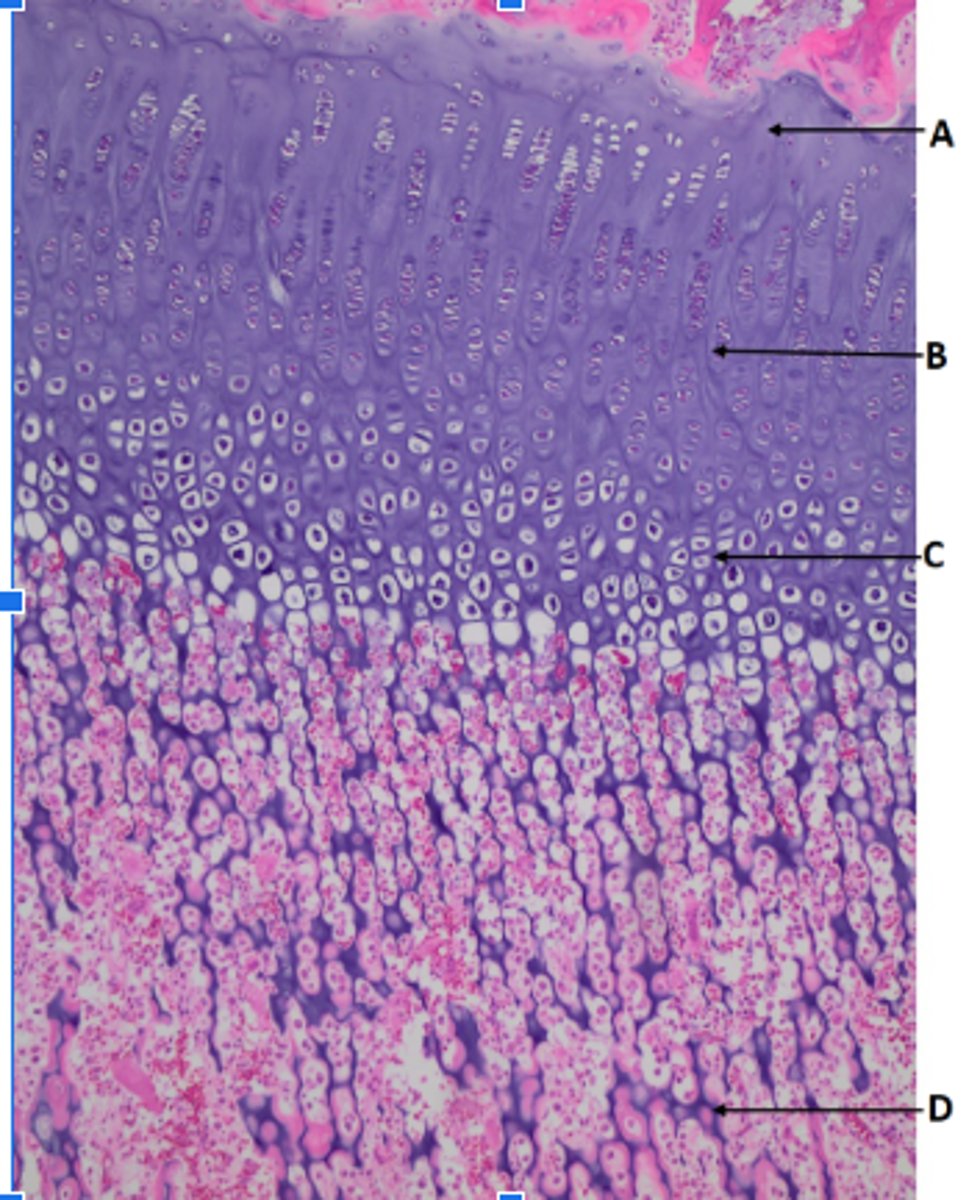
differentiation
when a stem cell takes on a specific job