Health Assessment -- (Exam III) Head, Neck, Eyes, Ears, Nose, Throat & Regional Lymphatics
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
face -- symmetric
the nasolabial folds and palpebral fissures (the opening between the eyelids) are ideal places to check facial features for symmetry
cranial nerve 5
- trigeminal nerve; responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing
- LARGEST of the cranial nerves
- trigeminal neuralgia: intermittent sharp shooting facial pain lasting several minutes over the divisions of the trigeminal nerve
cranial nerve 7
facial nerve; for facial expression
face -- salivary glands
- parotid glands are just below and in front each ear
- parotid gland connects to a tube called Stensen's duct that carries saliva to the mouth, releasing it near upper molar teeth
- sialolithiasis-calcified stones (calculi)
migraine headache
throbbing SEVERE pain on one side of the head, along with ringing in the ears prior to the headache
headache history -- meningitis
headache that moves into the neck causing neck pain with head flexion
headache history -- migraine
- a typical migraine headache has prodromal symptoms that may include visual disturbances, vertigo, tinnitus, and/or numbness or tingling of the fingers and toes
- throbbing, severe pain on one side of the head along with ringing in the ears prior to the headache
physical exam -- objective data (temporal artery)
temporal artery:
- a major artery, located between the eye and the top of the ear pulse
- hard, thick, and tender with inflammation (temporal arteritis may lead to blindness)
- strength of the pulsation of the temporal artery may be decreased in older adults
physical exam -- objective data (temporomandibular joint)
TMJ; place your index finger over the front of each ear as you ask the patient to open mouth and palpate for swelling, tenderness, crepitation, pain, and range of movement
facial abnormalities
- viral infections such as mumps or flu can cause swelling of the parotid gland
- asymmetry of face anterior to the earlobes occurs with parotid gland enlargement
- BELL'S PALSY
parkinson's disease
MASK like facial appearance, along with a shuffling gait, rigid muscles, and diminished reflexes
neck
nuchal rigidity, headache, & elevated temperature (red flag; associated with meningitis or encephalitis)
the neck -- regional lymph nodes
- preauricular
- postauricular
- tonsillar
- occipital
- submandibular
- submental
- superficial cervical
- posterior cervical
- deep cervical
- supraclavicular
regional lymphatics
- axillary lymph nodes (usually not palpable)
- nodes enlarge with local infection of the breast
abnormal lymph nodes
- HIV: enlarged, firm, non-tender, mobile (occipital nodes often involved)
- cancer: hard > 3cm, unilateral, non-tender, fixed matted
- virchow's node: hard, non-tender, left supraclavicular node highly suggestive of thoracic or abdominal cancer
thyroid gland
in about one-third of the population, a third lobe extends upward from the isthmus or one of the two lobes
palpation of trachea
to palpate trachea, the nurse would first place a finger in the sternal notch, then feel each side of the notch and palpate the tracheal rings
thyroid
- a soft, blowing, swishing sound auscultated over the thyroid lobes is often heard in hyperthyroidism because of increased blood flow through the thyroid arteries
- if thyroid can be palpated, the right lobe is often 25% larger than the left lobe normally
thyroiditis
enlarged, tender thyroid gland
malignancy of thyroid
a rapid enlargement of a single nodule suggests a malignancy
hyperthyroidism
diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland
thyroid -- older adult
increase in nodularity in the thyroid without any abnormality
thyroid -- auscultation
- after inspection and palpation auscultating the thyroid, the patient should HOLD their breath to obscure any tracheal breath sounds during auscultation
- during the exam, the neck should be slightly EXTENDED without being turned to any side
- the patient swallows water during inspection and palpation of the thyroid gland but NOT during auscultation
thyroid nodule
- thyroid gland symmetrical with small lobes, gland rises freely with swallowing
- right lobe may be up to 25% larger than left and tissue firm and pliable
hypothyroidism/myxedema
hypothyroidism manifestations include edema around the eyes, dry, coarse, and sparse hair, a puffy, dull face, cold intolerance, muscle cramps and constipation
hyperthyroidism
- lab data indicates that the patient's T4 and T3 hormone levels are elevated (too much of the hormone thyroxine is secreted)
- stimulate the rate of cellular metabolism, sudden weight loss, a rapid or irregular heartbeat (tachycardia), sweating, nervousness, or irritability
enlarged thyroid gland
the nurse should auscultate thyroid for the presence of a bruit
oral history (meds)
misuse of OTC nasal meds irritate mucosa & cause rebound (common)
oral history (lips)
cheilosis of lips forms scaling painful fissures at the corner of the lips
nose bleed patient instructions
- "sit up, lean forward and pinch your nose"
- with a nosebleed, advise the person to sit, lean forward and digitally compress the lower soft part of the nose for 15 to 20 minutes
sinuses
- four pairs (frontal, maxillary, ethmoid, sphenoid)
- examine the sinuses through palpation and percussion
- front or maxillary sinuses are tender to palpation in allergies or acute bacterial rhinosinusitis
- large amount of exudate crepitus upon palpation over the maxillary sinuses
palpating the sinuses
- to palpate frontal sinuses, press both thumbs above eyebrows
- to palpate maxillary sinuses, press thumbs in the area next to both nares
mouth & throat
- gums are pink, moist, and firm, with tight margins to the tooth; no lesions or masses
- color and consistency of tissues along cheeks and gums should be even
- tongue should be pink, moist, a moderate size with papillae (little protuberances) present; no lesions or no red color present
tongue
- the dorsal surface of the tongue is normally roughened from papillae; a thin, white coating may be present; the ventral surface may show veins normally
- SMOOTH, GLOSSY areas are ABNORMAL and may indicate atrophic glossitis
- inspect both sides for CANCER lesions
- palpate any lesions, dryness, ulcers, or nodules for induration
- deep tongue fissures are seen in dehydration
- normal variation in older adults is fissured; topographic, map-like tongue
tongue infections
- the thick, white plaques on the soft palate and tongue suggest yeast infection, requiring treatment with medication
- if white plaque cannot be removed, it is leukoplakia (white/gray patches in the mouth)
- leukoplakia, persistent lesions, ulcers, or nodules may indicate cancer and should be referred
- induration increases the likelihood of cancer
throat
- ask the client to say "aaahhh" and watch for the uvula and soft palate to move bilaterally and symmetrically (testing CN IX and CN X)
- deviation: damage to cranial nerve X, diphtheria, poliomyelitis
- when applying a tongue depressor, depress the tongue slightly off-center to avoid eliciting the gag response
tonsils
- normal tonsils are involuted, granular in appearance, and appear to have deep crypts; pink mucosa with indentations (crypts)
- plugs of white debris can develop in tonsil crypts is normal; bright red & swollen tonsils indicate infection
- white membrane (exudate) covering tonsils can accompany infectious mono, leukemia & diphtheria
tonsil size
1+ -- visible
2+ -- half way between tonsillar pillars & uvula
3+ -- touching the uvula
4+ -- touching one another
the eyes -- subjective data
glaucoma-halos around light
eyes -- objective data
- the sclera is white in color and the palpebral conductive appears pink
- inspect conjunctiva and sclera
- normally, sclera is white in color, and the palpebral conductive appears pink
eyes -- visual acuity
- visual acuity (CN II):
- snellen chart
- 20 feet away from chart (one eye at a time)
- covers one eye with an opaque card
- reads each line of letters until he or she can no longer distinguish them
- normal acuity: 20/20
visual acuity -- near vision
hand-held card (Rosenbaum cards)
- measuring near visual acuity
- about 14 inches away
- lowest possible line
- reads letters with reading glasses
- normal: 14/14
- this means that the person can read what the normal eye can read from a distance of 14 inches
eyes -- visual acuity
- record their visual acuity as a fraction, where the numerator indicates the distance your client is from the chart, and the denominator indicates the distance at which a normal eye can read the line on the chart
- for example, 20/25 vision means that the client can read at 20 feet what the average client can read at 25 feet
eyes -- pupillary response
- pupillary response to light (CN III)
- pupillary size:
- 3 to 5 mm in bright light
- 4 to 8 mm in the dark light
- advances the light from the patient's side to determine the pupillary light reflex
- shine the light from the lateral side of the eye or from beneath to help ensure that the client doesn't accommodate the pupils for near vision
eyes -- pupillary response
- accommodation: focus on distant & near
- document: PERRLA (pupils equal, round, reactive to light, and accommodation)
eyes -- visual fields (confrontation)
- assess peripheral vision with the examiner's vision
- equal height; 2 feet away
- cover one eye; examiner covers opposite eye
- look directly at each other with the uncovered eyes
- next, fully extend left arm at midline and slowly move one finger (or a pencil) upward from below until the client sees finger (or pencil) (inferior)
- test the remaining three visual fields of the client's right eye (i.e. superior, temporal, and nasal)
- repeat the test of the opposite eye
eyes -- extra ocular motion (EOM)
- assess ability of eyes to move through SIX cardinal positions of gaze (CN III, IV, VI)
- head is steady; eyes follow movement of finger through these 6 positions in a clockwise direction
- note conjugate or COORDINATED eye movement
- note NYSTAGMUS
corneal light reflex text (Hirschberg test)
- asymmetric position of the light reflex = deviated alignment of the eyes
- strabismus (or tropia)
what is strabismus?
- defined according to the direction toward which the eye drifts
- part of corneal light reflex test (Hirschberg test)
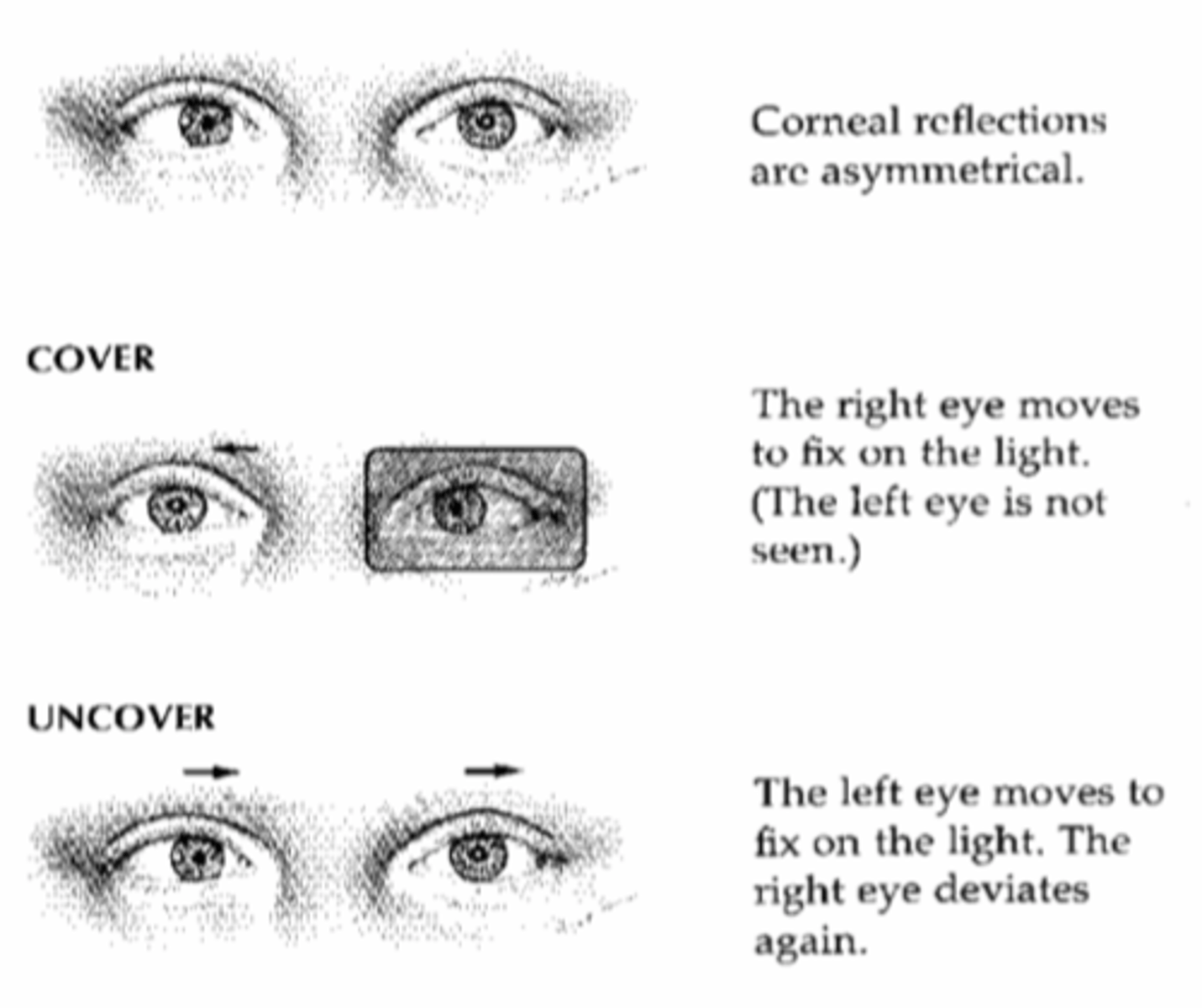
cover-uncover test
- test can be used to screen for strabismus
- patient is instructed to cover one eye, while the nurse observes the uncovered eye for movement as it focuses on an object
- when the left eye is covered, the right eye moves outward to pick up fixation
abnormal finding during testing for strabismus
one eye deviates to the middle due to weakened extraocular muscles
cover test in strabismus
- forms of strabismus: direction of alignment of eyes at rest
- the direction of shift in fixation of the unoccluded eye when the opposite eye is occluded/covered
Hirschberg test (cornea light reflex test)
- use a light source (i.e. penlight)
- from a distance of 2 feet, shine your light source equally into the patient's eyes at midline
- observe the reflection of light off the cornea, which should appear as a pin-point white light near the center of the same pupil spot in each eye
- if there is normal alignment, the reflection will appear in the same position of each pupil
- if there is misalignment of the eyes, the location of the corneal reflex will appear asymmetric and "OFF CENTER" of the pupil of the deviating eye; the relative difference in the position of the reflex will be in the OPPOSITE direction as the eye deviation
objective findings associated with specific eye conditions -- exophthalmos
- apparent eye protrusion
- lids do not reach iris
- measurement of degree of exophthalmos performed using exophthalmometer
objective findings associated with specific eye conditions -- strabismus
- eye will not move in the direction controlled by affected muscle
- abnormal cover-uncover test result
objective findings associated with specific eye conditions -- cataracts
CLOUDY lens, may be obvious without equipment
objective findings associated with specific eye conditions -- glaucoma
- optic nerve damage, clearly seen during dilated eye examination
- characteristic cupid of optic nerve
- visual field test showing loss of peripheral
- an eye that feels FIRM or RESISTANT to palpation could indicate glaucoma/tumor
eyes -- anisocoria
- difference in size of pupils
- BRAIN INJURY
eyes -- ptosis
drooping upper lid
eyes -- mitosis
- constricted pupils (pinpoint pupils)
- NARCOTICS or BRAIN DAMAGE
eyes -- mydriasis
- dilated pupils
- CNS injury, CIRCULATORY COLLAPSE, or deep ANESTHESIA
eyes -- arches senilus
- commonly seen in older eye; cause lipid (fat) DEPOSITS in edge of cornea
- a gray-white arc or circle caused by lipid deposition around the limbus of the older adult is called arcus senilis (there is no effect on vision)
- possibly related to CHOLESTEROL
eyes -- xanthelasma
- BENIGN lesions usually on the eyelids, soft, raised yellow plaques occurring on the lids at the inner canthus and are frequently seen in FEMALES
eyes -- corneal abrasion
- one of the most common eye injuries
- pain, erythema (redness), tearing, photophobia
eyes -- conjunctivitis
- clear or purulent discharge; usually viral but can be bacterial
- commonly treated with ANTIBIOTICS
ear -- subjective data
- tinnitus (excessive earwax buildup, high blood pressure, or certain ototoxic medications (such as streptomycin, gentamicin, kanamycin, neomycin, ethacrynic acid, furosemide, indomethacin, or aspirin), loud noises
- vertigo
- environmental noise exposure
- bloody or clear watery drainage (cerebrospinal fluid) can indicate a basal skull FRACTURE after a serious accident or head injury
subjective data -- vertigo
- vertigo: causes dizziness and spinning-inner ear/labyrinthitis/vestibular nerve problem (vestibular neuritis)
tympanic membrane
- pearly gray, shiny, and translucent, with no bulging or retraction; it is slightly concave, smooth, and intact
- a cone-shaped reflection of the otoscope light: 5 o'clock in the right ear and 7 o'clock in the left ear
- dense white patches and scars on the tympanic membrane are sequelae of repeated ear infections in childhood or earlier
cerumen
- ear is lined with glands that SECRETE cerumen
- wet, honey colored cerumen is NOT a sign of infection
ears -- examination
- gross examination of external ear & middle examine with otoscope
- pull auricle of ear UP and BACK (in the adult)
ear -- presbycusis
high frequency hearing loss that occurs with aging
ears -- conductive hearing deficit
cerumen impaction, and otitis media are MOST common cause
inflamed ear labyrinth
- feeds the wrong information to the brain, creating a staggering gait and a strong, spinning, whirling sensation called vertigo
- the spinning sensation (vertigo) that the patient is experiencing is from the labyrinth of the ear or vestibular nerve issue
ears -- weber test
- perform the Weber test if DIMINISHED or lost hearing in one ear
- sensorineural loss will cause the sound to be heard best in NORMAL ear, where you can listen to the sound best in air conduction only; LIMITED perception of the sound due to nerve damage in the bad ear, making the sound seem louder in the unaffected ear
rinne test -- normal
- normal: AC twice as long as the BC
rinne test -- sensorineural hearing loss
the finding be AC > BC
rinner test - conductive hearing loss
BC sound is heard longer than or EQUALLY as long as AC sound (BC ≥ AC)
rinne test
the test is used to determine CAUSE of the hearing loss
rinne test results
normal: sound is heard longer through air than bone (AC > BC)
rinne's test results -- conductive hearing loss
- BC ≥ AC
- sound is heard was long or LONGER through bone than air
- why? air conduction through the external/middle ear is impaired; vibrations through bone bypass the impairment to reach the cochlea
rinne's test results -- sensorineural hearing loss
- AC > BC
- sound is heard longer through air than bone although both are decreased
- why? the inner ear/cochlear nerve is less able to transmit impulses regardless of how the vibrations reach the cochlea
weber test results
- normal: hearing will produce EQUAL sound in both ears
- conductive loss: will cause the sound to be heard best in the abnormal ear/poor ear that CANNOT hear sound through air conduction
- sensorineural loss (related to cochlear issues): cause the sound to be heard best in the normal ear
weber test results -- sensorineural hearing loss
may be caused by PRESBYCUSIS; it is a gradual nerve degeneration that occurs with aging and by ototoxic drugs, which affect the HAIR CELLS in the cochlea
- the nurse should ASK the patient about the MEDS they have been taking
ear infections -- purulent drainage
- purulent drainage associated with pain and a popping sensation is a characteristic of OTITIS MEDIA WITH PERFORATION OF THE TYMPANIC MEMBRANE associated with bloody, clear, or resembles pus
ear infections -- otitis externa
- the patient experiences pain when the pinna and tragus are moved
- ENLARGED superficial cervical nodes
- associated with submersion in water such as in swimming: "swimmer's ear"
age-related changes -- thyroid gland
- older adult's thyroid may feel more nodular or irregular because of fibrotic changes that occur with aging; the thyroid may also be felt lower in the neck because of age-related structural changes
age-related changes -- vision
- decreased visual acuity, visual fields; light/dark adaptation
- presbyopia (loss of near focusing ability)
- increased sensitivity to glare
- increased incidence for glaucoma
- distorted depth perception
- less able to differentiate blues, greens, violets
- increased eye dryness and irritation
- increasing age, especially over 75; risk factor for cataracts
- vision floaters are normal over 40 years of age
OTOSCLEROSIS
- progressive conductive hearing loss in young adults between 20 and 40 years old
- a gradual bone formation causes the stapes footplate to become fixed in the oval window, impeding the transmission of sound and causing progressive deafness
age-related change -- hearing
- DECREASED hearing acuity (especially to hear consonants)
- loss of hearing from high frequency
- presbycusis
- a high-tone frequency hearing loss is apparent for those affected with presbycusis
age-related changes (general)
- in the aging adult, the tongue looks smoother because of PAPILLARY ATROPHY
- teeth are slightly YELLOWED and appear longer because of the recession of gingival margins