Module 9: Acute Spinal Cord Injury & TBI
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
What is the primary function of the spinal cord?
To provide two-way communication between the brain and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
What are the two types of matter in the spinal cord?
Gray matter (neuron cell bodies) and white matter (myelinated axons).
What do the posterior/dorsal branches of spinal nerves carry?
Sensory perception information to the spinal cord (afferent pathway).
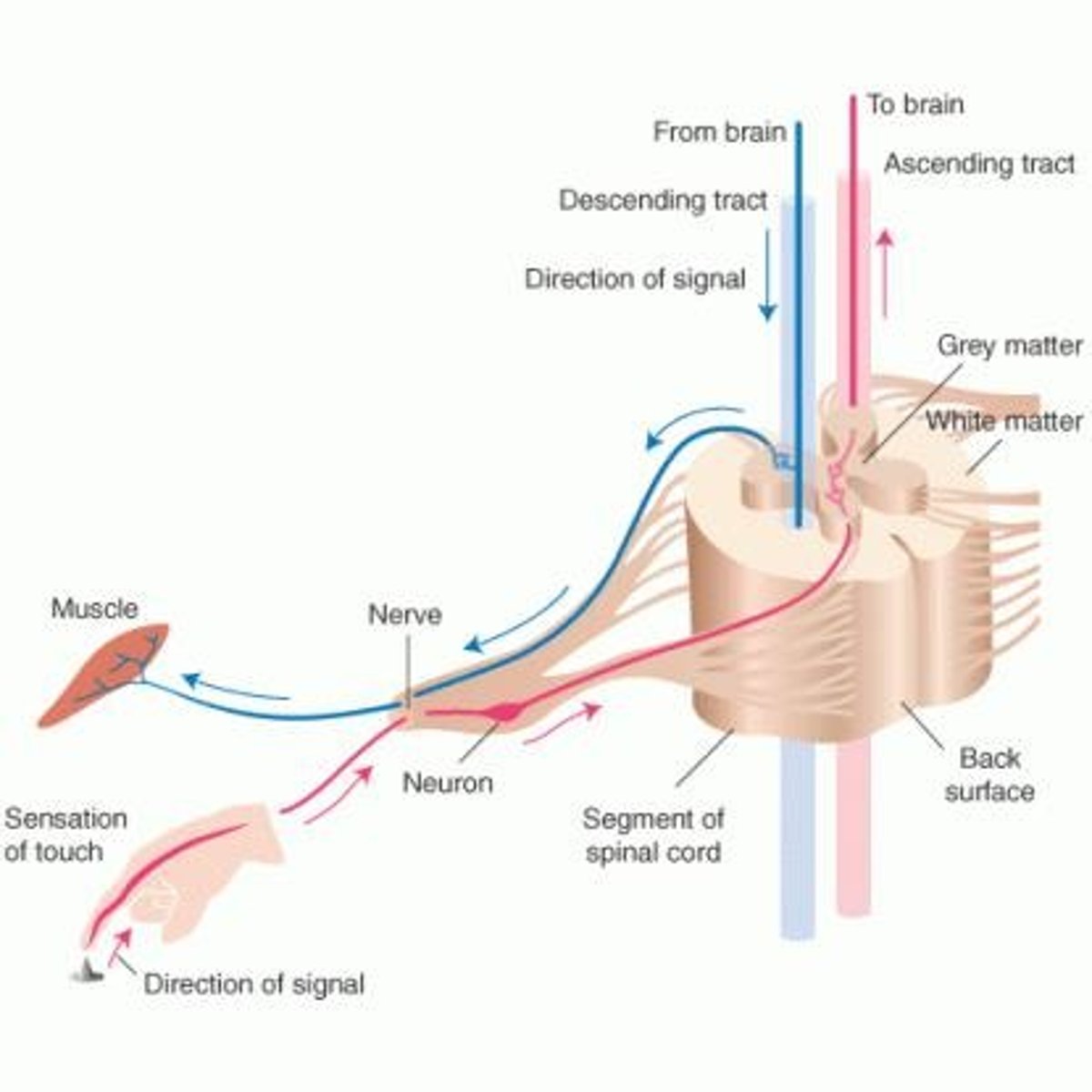
What do the anterior/ventral branches of spinal nerves transmit?
Motor impulses to peripheral target cells (efferent pathway).
How many pairs of spinal nerves exit the spinal cord?
31 pairs.
What is the average age of someone who sustains a spinal cord injury (SCI) in Canada?
55 years.
What are the two causes of spinal cord injuries?
Trauma (MVC, falls, violence, sports) and non-traumatic causes (degenerative disease, tumors, infections).
What is the difference between primary and secondary spinal cord injury?
Primary injury is the initial mechanical damage
Secondary injury worsens damage through inflammatory processes.
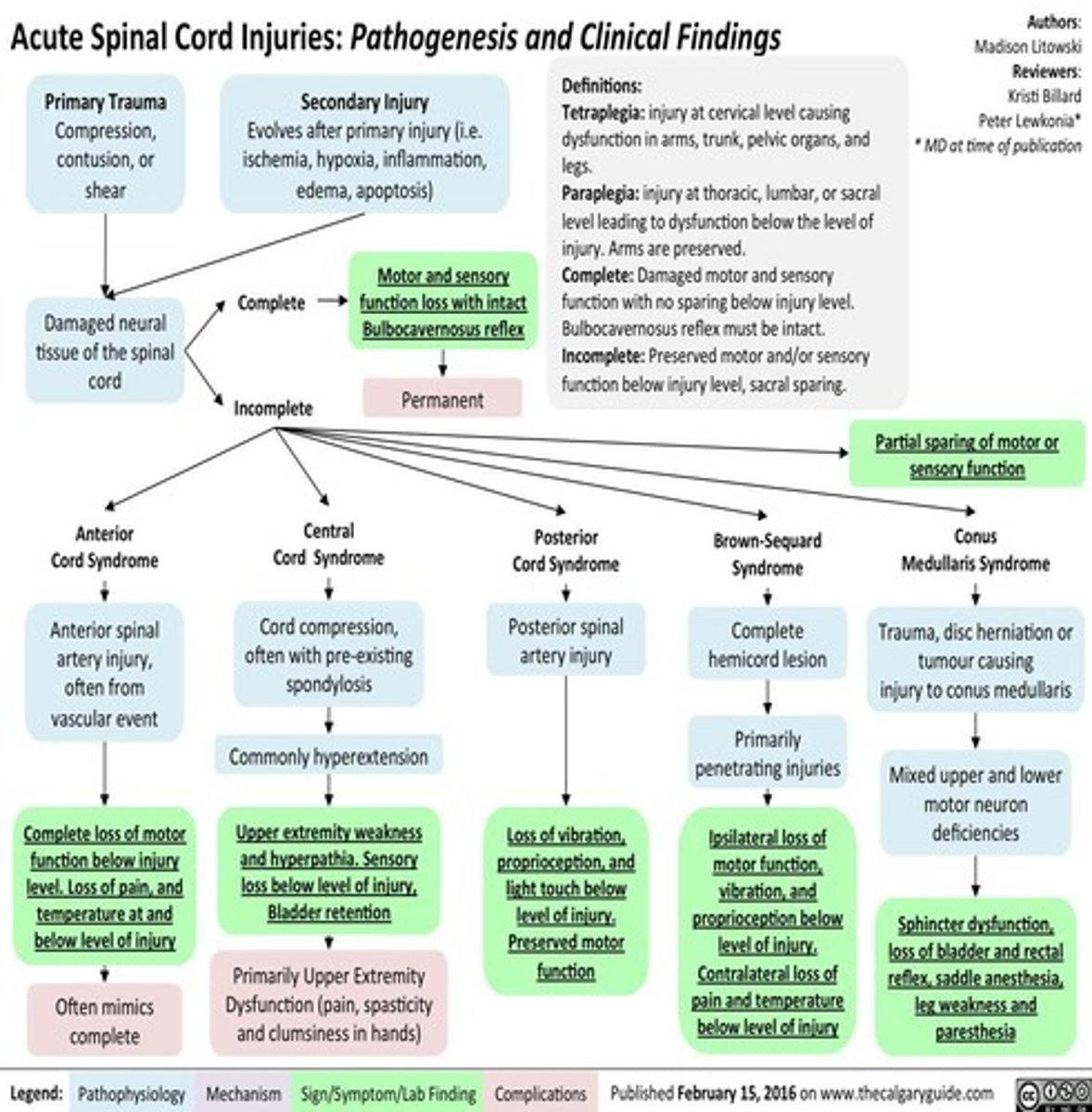
What are the 5 mechanisms of injury (MOI) for spinal cord injuries?
Hyperflexion – Sudden forward bending of the neck (e.g., head-on collision). Causes tearing of ligaments, vertebral dislocation, and cord compression.
Hyperextension – Sudden backward movement of the head (e.g., rear-end collision). Can compress spinal structures and damage the spinal cord.
Axial Loading– Force applied straight down on the spine (e.g., diving into shallow water, falling and landing on feet/buttocks). Can cause vertebral burst fractures.
Rotational Injury – Twisting forces that cause vertebrae to rotate or dislocate, leading to cord damage.
Penetrating Injuries – Direct injury to the spinal cord from objects like bullets or knives; damage depends on the path of penetration.
What defines a complete spinal cord injury?
Complete loss of all voluntary motor and sensory function below the level of injury.
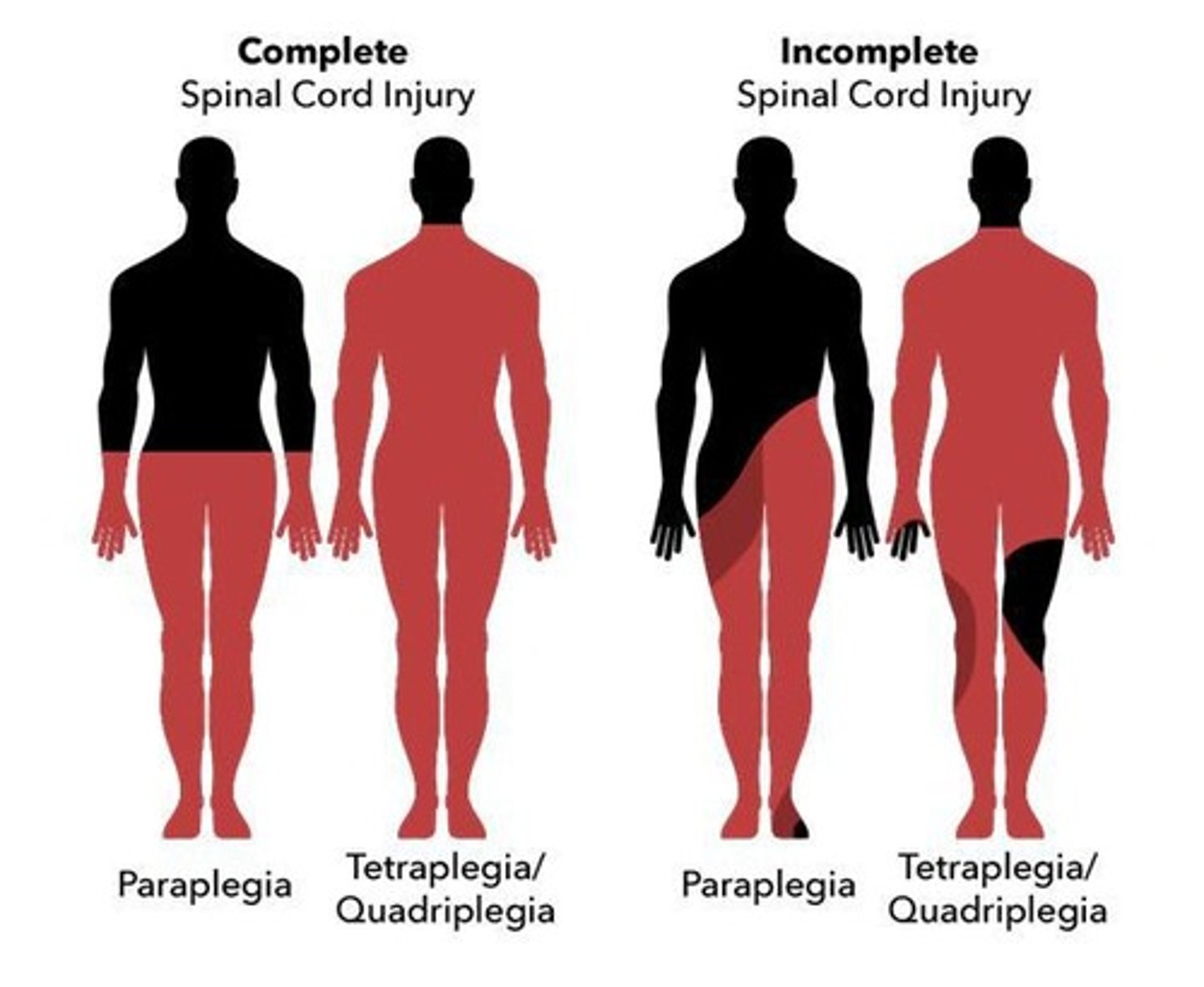
What defines an incomplete spinal cord injury?
Some function or movement remains below the level of injury.
What is tetraplegia?
Complete or partial loss of sensation and/or movement in all four extremities and torso.
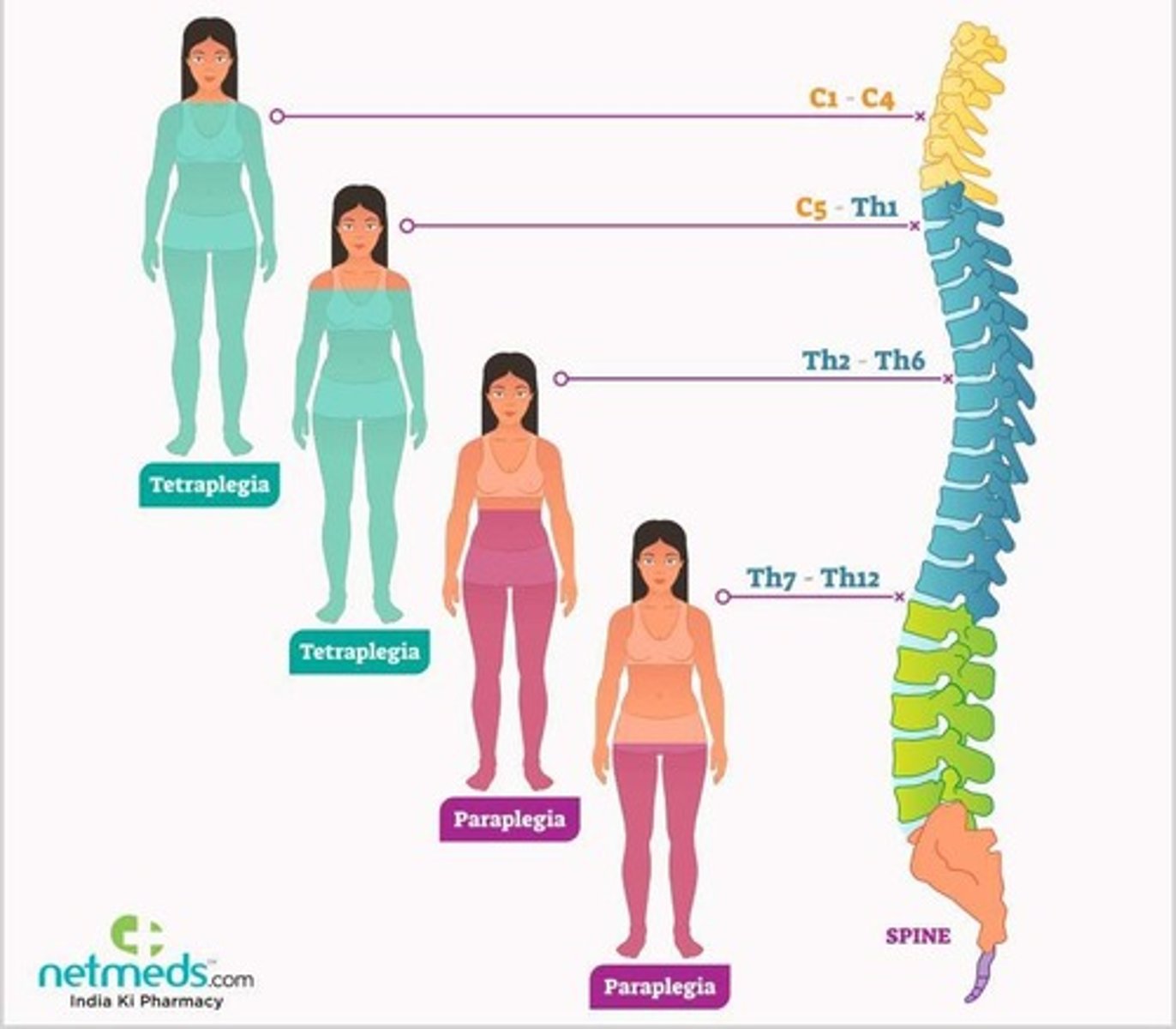
What is paraplegia?
Complete or partial loss of sensation and/or movement in the legs and often the torso.
What is the purpose of the ASIA scale in spinal cord injury assessment?
A standardized tool used to classify the severity of a spinal cord injury (A-E/Complete-Normal)
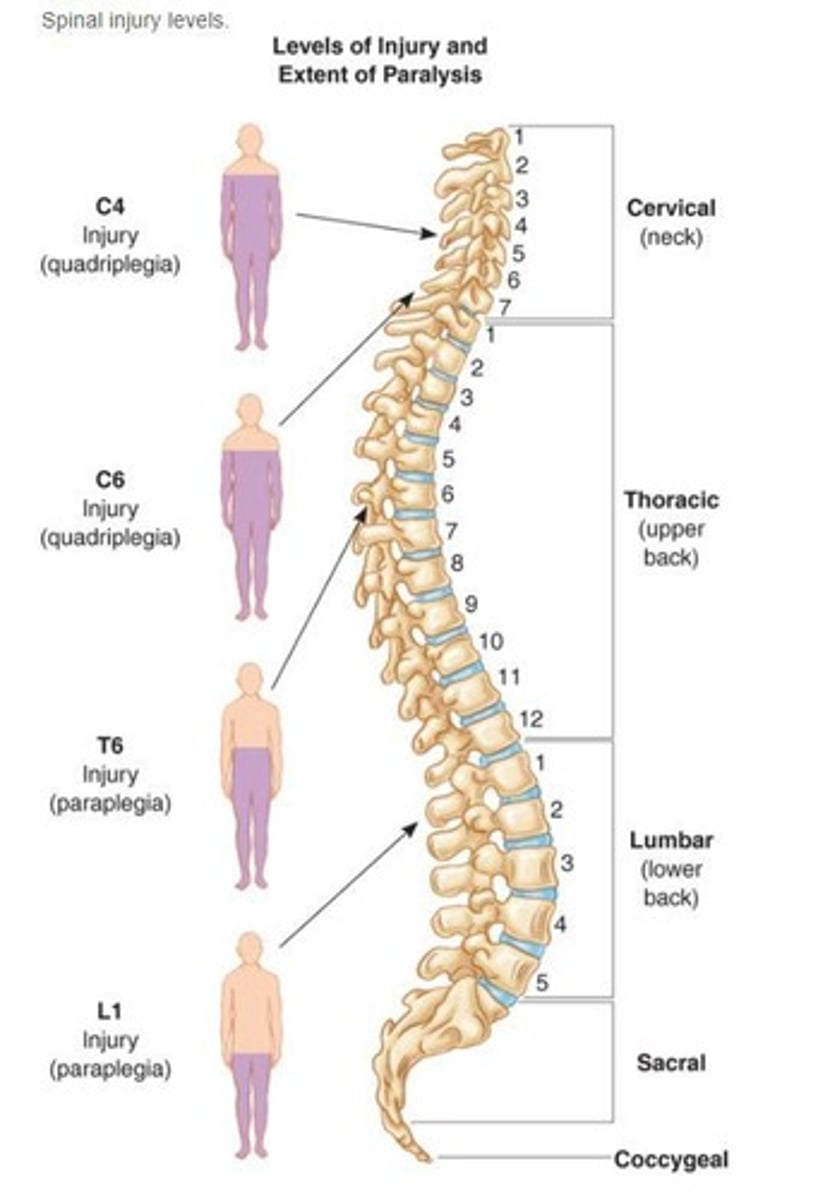
What is a dermatome?
An area of skin where sensory nerves derive from a single spinal nerve root.
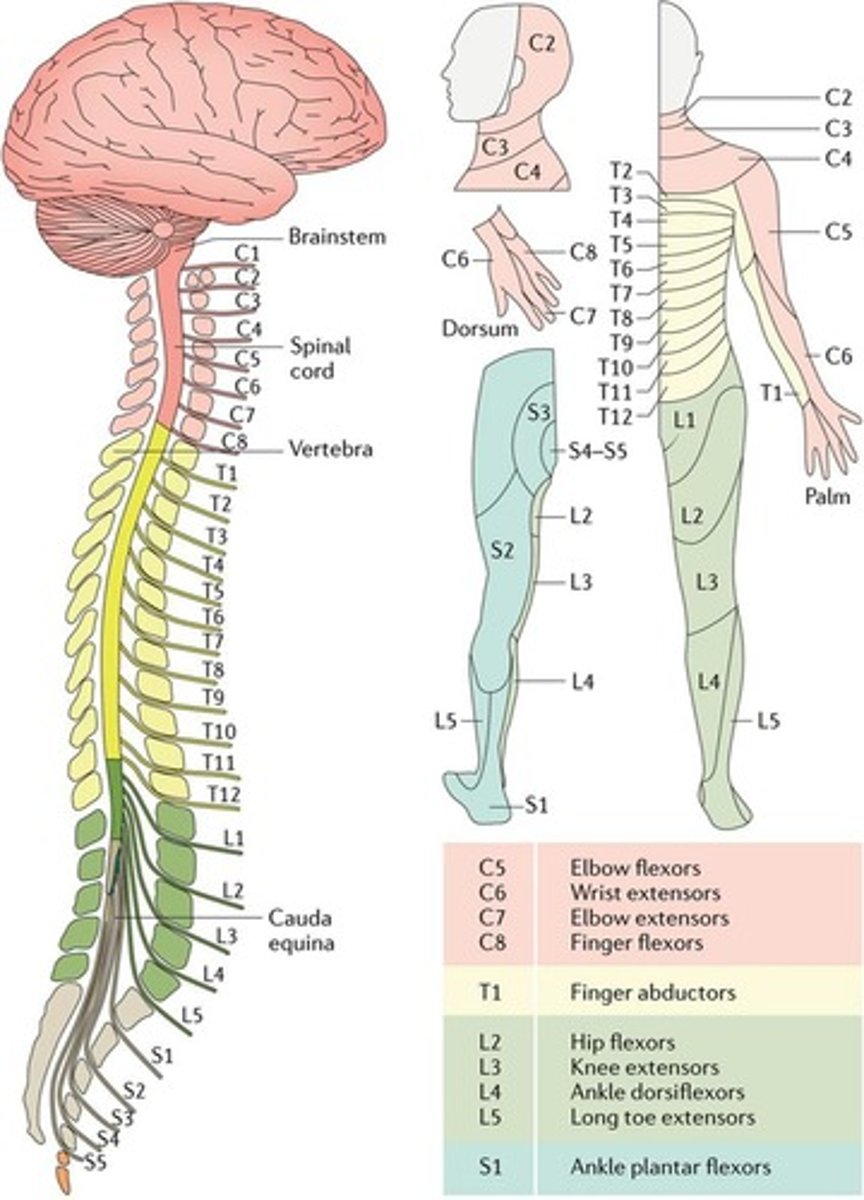
What is a myotome?
A set of muscles innervated by a spinal nerve.
What are the initial priorities in the first 24 hours after a spinal cord injury?
Stabilize the patient, manage damage to the spinal cord, and prevent secondary injuries.
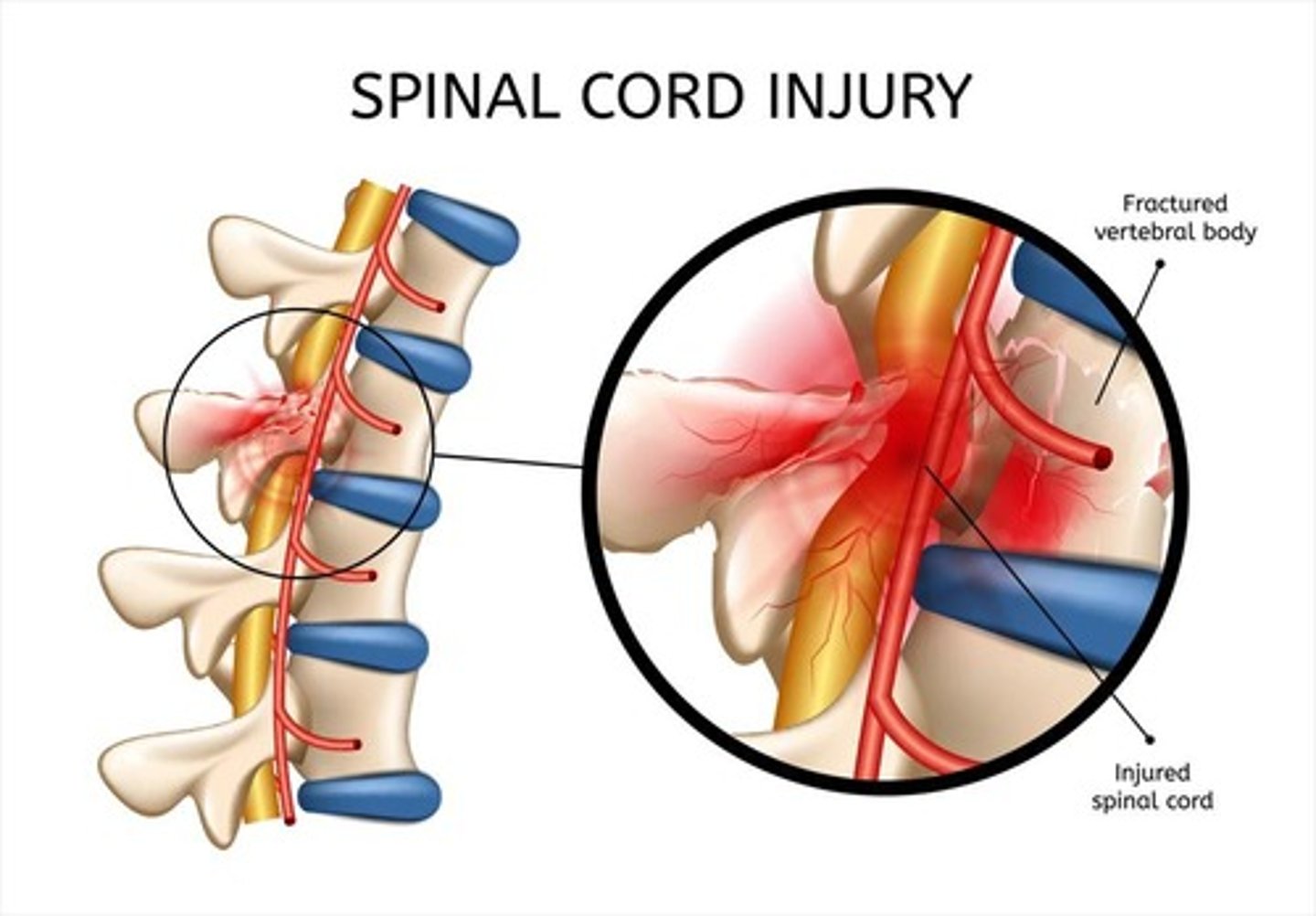
What role do corticosteroids play in spinal cord injury management?
They help control inflammation and minimize further damage.
What is the purpose of logrolling a patient with a spinal cord injury?
To maintain spinal alignment while turning the patient.
What is the cauda equina?
A bundle of spinal nerves and spinal nerve rootlets at the lower end of the spinal cord.
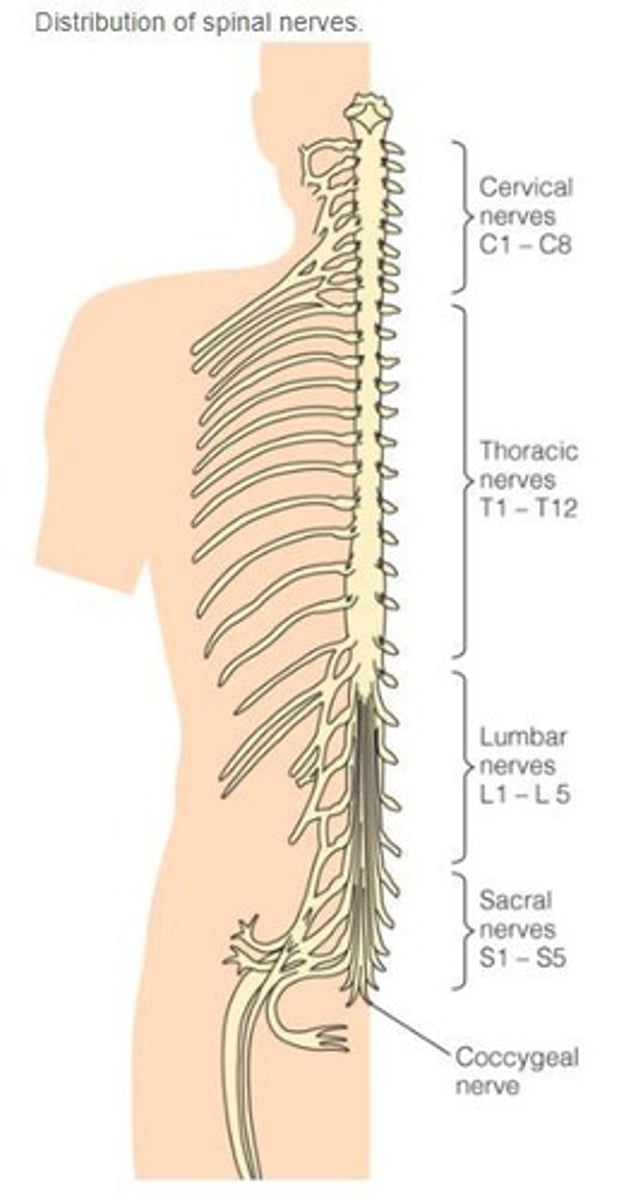
What is the typical anatomical ending point of the spinal cord in adults?
At the L1-L2 vertebrae.
What is the neurological level of injury on an individual with a SCI?
It is the lowest spinal segment where both motor (muscle movement) and sensory (touch/feeling) function are still normal.
What 3 spinal nerves innerve the diaphragm in respiration?
It is innervated by the C3, C4, and C5 spinal nerves
What is orthostatic hypotension?
A drop in blood pressure that occurs when standing up, leading to dizziness or fainting.
What are common complications associated with spinal cord injuries?
Blood pooling, clots, and orthostatic hypotension.
What is Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis?
Preventive measures to avoid venous thromboembolism, often using anticoagulants and antiembolic stockings.
What is neurogenic shock?
A type of distributive shock caused by loss of sympathetic tone, leading to vasodilation and hypotension.
What is spinal shock?
A temporary loss of reflexes and muscle tone below the level of spinal injury, often occurring immediately after injury.
What are the signs and symptoms of neurogenic shock?
Decreased cardiac output, hypotension, bradycardia, and warm dry extremities.
What is autonomic dysreflexia?
A condition that occurs in individuals with spinal cord injuries at T6 or above, characterized by a hyperactive response to stimuli below the injury level.
What triggers autonomic dysreflexia?
Stimuli such as bladder distention, bowel distention, skin irritation, or labor.
What is the treatment for neurogenic shock?
Supportive care including airway management, fluids, vasopressors, and spinal stabilization.
What are common long-term complications of spinal cord injury?
Chronic pain, VTE, contractures, pressure injuries, and impaired bowel and bladder function.
How is bowel and bladder management approached in spinal cord injury patients?
Through retraining, use of catheters, and regular bowel disimpaction.
What is the expected sexual function outcome for men with spinal cord injuries?
75% may experience erectile dysfunction and 95% may have ejaculation problems.
What is the impact of spinal cord injury on women's sexual function?
Women can achieve orgasm but may have decreased lubrication; pregnancy is still possible.
What medications are used for chronic pain management in spinal cord injury patients?
Tricyclic antidepressants, anti-epileptics, steroids, SSRIs, opioids, and NSAIDs.
What is the importance of patient history in spinal cord injury assessment?
Identify the mechanism of injury (MOI) to guide treatment decisions.
What is the expected mobility outcome for a patient with a C6-C7 spinal cord injury?
Limited mobility, primarily affecting upper extremities and trunk control.
What immediate nursing action should be taken for an unconscious MVA victim?
Stabilize the cervical spine and assess the airway.
What clinical manifestations support the diagnosis of neurogenic shock in a T12 SCI patient?
No reflex activity below the waist and hypotension.
What is the role of methylprednisolone in spinal cord injury treatment?
To reduce inflammation and potentially improve neurological outcomes.
What are common nursing actions to manage orthostatic hypotension?
Use of abdominal binders, anti-embolism stockings, and slow repositioning.
What is the expected duration of spinal shock after injury?
Temporary, often lasting less than 72 hours.
What is the physiological response above the SCI during autonomic dysreflexia?
The brain activates the parasympathetic (vagus) nerve, causing bradycardia and vasodilation above the level of injury. This results in flushed, warm skin and sweating above the injury, as the body attempts to counteract severe hypertension
Above injury: vasodilation, flushing, sweating, headache
Below injury: vasoconstriction, cool, pale skin
What are the nursing considerations for managing chronic pain in SCI patients?
Regular assessment and adjustment of pain management strategies, including medication.
What is a Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)?
Damage to the brain from an external mechanical force, not caused by neurodegenerative or congenital conditions.
What are common causes of TBI?
Blunt injuries such as falls, motor vehicle collisions (MVCs), and sports-related incidents; penetrating injuries like firearms and projectiles.
What are the classifications of primary brain injury?
Focal or diffuse
Open or closed
Categorized: mild, moderate, or severe.
What symptoms are associated with mild TBI?
Transient confusion, possible loss of consciousness for up to 30 minutes, and no evidence of brain damage on CT or MRI.
What characterizes moderate TBI?
Loss of consciousness for 30 minutes to 6 hours, possible visible brain injury on CT or MRI, and posttraumatic amnesia lasting up to 24 hours.
What defines severe TBI?
Loss of consciousness for more than 6 hours, high risk for secondary injury, and significant brain damage often visible on CT or MRI.
What is an acceleration injury?
Injury that occurs when a stationary brain is suddenly moved rapidly in one direction, causing damage at the site of impact.
What is a deceleration injury?
Injury that occurs when the brain stops rapidly in the cranial vault, causing damage as the brain continues to move until it hits the skull.
What is a rotational injury?
Injury caused by a force impacting the head in a non-linear fashion, resulting in shearing forces and tearing of axons.
What are the 3 types of skull fractures?
Linear fracture - A simple crack in the bone without displacement; most common and usually low risk unless over a major vessel
Depressed fracture - Bone is pushed inward toward the brain; higher risk of brain injury, bleeding, and infection
Basilar fracture - Fracture at the base of the skull; associated with CSF leaks, raccoon eyes, Battle’s sign, and high infection risk.
What is the classic symptom of an epidural hematoma?
Transient loss of consciousness followed by a lucid interval, then rapid deterioration in neurological status.
What is the significance of clear fluid draining from the ears after head trauma?
It may indicate a potential cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak, especially if the fluid tests positive for glucose.
What interventions should be taken for a patient with a suspected skull fracture?
Ensure a patent airway, stabilize the cervical spine, monitor neurological status, and assess for infection.
What is the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score range for mild TBI?
GCS score of 13-15.
What GCS score indicates severe TBI?
GCS score of less than 8.
What are common symptoms of cerebral contusion?
Bruised brain tissue, hemorrhage, and potential midline shift due to swelling.
What is the role of IV fluid monitoring in TBI patients?
To maintain hemodynamic stability and prevent secondary injury.
What is the first action to take for a patient with lightheadedness and low blood pressure after head elevation?
Lower the head of the bed immediately.
What are the common risk factors for TBI in men?
Men are approximately 2 times more likely to be hospitalized and 3 times more likely to die from TBI compared to women.
What is a common cause of epidural hematoma?
Arterial bleeding often caused by a temporal bone fracture that lacerates the middle meningeal artery.
What is the typical management for a small epidural hematoma?
Nonoperative management with frequent neurological assessments and repeat CT scans.
What is the importance of monitoring for infection in open skull fractures?
To prevent complications such as meningitis and other infections due to exposure of brain tissue.
What are focal injuries in the context of TBI?
Localized injuries such as cerebral contusions, intracerebral hematomas, and epidural or subdural hematomas.
What is a subdural hematoma?
An accumulation of blood between the dura and arachnoid layers of the meninges.
What usually causes a subdural hematoma?
Acceleration, deceleration, or combined forces, often from tearing of bridging veins.
What is the typical onset of symptoms for a subdural hematoma?
Symptoms have a slow onset due to slower bleeding.
What is the highest mortality rate associated with subdural hematomas?
They are often unrecognized until severe neurological compromise occurs.
What is the management for a subdural hematoma?
Surgical evacuation of the hematoma and ongoing neurologic assessments.
What are the timeframes for acute and chronic subdural hematomas?
Acute: within 48 hours; Chronic: 2 weeks or longer.
What symptoms might indicate a chronic subdural hematoma?
Worsening headache, cognitive decline, confusion, and motor deficits.
What is an intracerebral hematoma?
An accumulation of blood in the brain tissue caused by tearing of small arteries and veins.
What are common causes of intracerebral hematomas?
Uncontrolled hypertension, ruptured aneurysms, or high-impact trauma.
What are the key symptoms of an intracerebral hematoma?
Headache, rapid decline in level of consciousness, and signs of increased intracranial pressure.
What is a concussion?
The most common type of traumatic brain injury, often resulting from blunt force or acceleration/deceleration.
What are the typical symptoms of a concussion?
Confusion, headache, dizziness, nausea, and poor concentration.
What is post-concussive syndrome?
A common secondary injury from mild TBI that manifests days to months after the trauma.
What are the symptoms of post-concussive syndrome?
Dizziness, persistent headache, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
What is diffuse axonal injury (DAI)?
Widespread microscopic damage to axons, resulting in hemorrhagic lesions and cerebral edema.
What are the cues for diffuse axonal injury?
Unconsciousness, increased intracranial pressure, and abnormal posturing.
What is subarachnoid hemorrhage?
An accumulation of blood between the arachnoid layer and the pia in the subarachnoid space.
What are the symptoms of subarachnoid hemorrhage?
Acute neurological deficits, nuchal rigidity, and sudden severe headache.
What is the best diagnostic test for cranio-cerebral trauma?
CT scan.
What should be maintained for patients with TBI?
SpO2 - >95%
SBP - >100mmHg
CPP - >60mmHg
What are some collaborative interventions for TBI management?
Early intubation, suctioning, IV fluids, and monitoring for pulmonary edema.
What medications are used in TBI management?
Mannitol – Osmotic diuretic that reduces cerebral edema and lowers ICP.
Hypertonic saline – Pulls fluid out of brain tissue, reduces swelling, and supports BP.
Sedatives – Decrease agitation and metabolic demand, helping prevent ICP spikes.
Anticonvulsants – Prevent seizures, which can increase ICP and worsen injury
What are the signs of increased intracranial pressure?
Headache, vomiting, altered consciousness, and abnormal motor responses.
What might indicate the need for ICP monitoring?
Severe TBI or high risk for worsening condition.
What is the role of positioning in TBI management?
Facilitates drainage of CSF and maintains cerebral blood flow.
What is a critical nursing action for patients with head injuries?
Conduct focused neuro exams including assessments of pupils and vital signs.
What should be done prior to drug-assisted intubation or analgesia/sedation?
Perform a baseline assessment.
What is the recommended head elevation for patients with increased intracranial pressure (ICP)?
Elevate the head of the bed to 30 degrees.
What does an intracranial pressure of 12mmHg indicate?
A normal balance between brain tissue, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid.
What is the expected response to hyperventilating a patient with a TBI?
Cerebral blood vessels constrict.
What are common complications associated with traumatic brain injury?
Diabetes insipidus
SIADH
Cerebral salt wasting
Seizures
Brain herniation
Brain death