Unit 7 - Pathology of Biliary Tree & Dilated Ducts ~ Elie
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Is a Choledochal Cyst acquired or congenital?
Congenital
A choledochal cyst is the result of?
Pancreatic juices refluxing into bile duct
How are choledochal cysts formed?
By weakening & “outpouching”
What is the sonographic appearance of a Choledochal Cyst?
•True cysts in RUQ
•Enlarged CBD, CHD
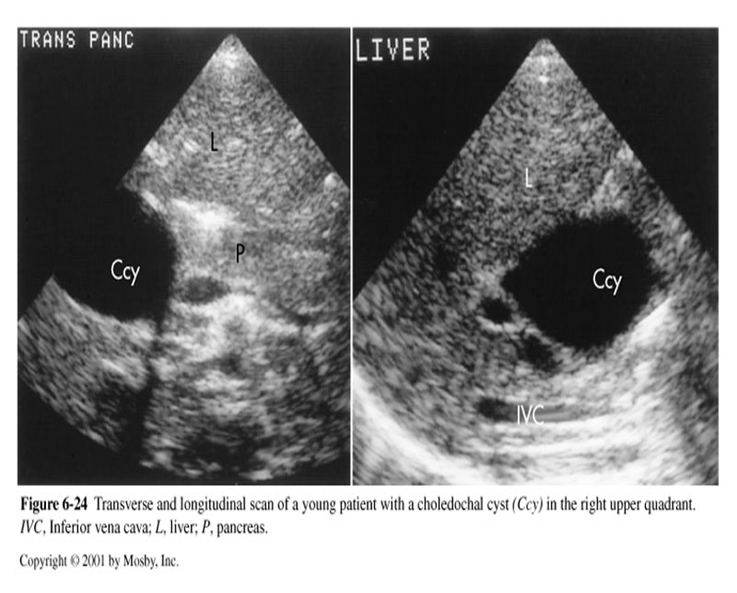
What is this sonographic image showing?
Choledochal Cysts
What is Caroli’s Disease
A rare congenital abnormality
Is Caroli’s Disease acquired or inherited?
Inherited
In Caroli’s disease, it is characterized by congenital segmental saccular cystic dilation of _________ ____ _____
Intrahepatic bile ducts
Caroli’s Disease is most prevalent in:
young adult or pediatric population
Caroli’s disease is associated with:
•renal disease (medullary sponge) or congenital hepatic fibrosis
What is the symptoms associated with Caroli’s Disease?
Recurrent cramp-like upper abdominal pain
What is recurrent cramp-like upper abdominal pain secondary too?
Biliary stasis, ductal stones, cholangitis, & hepatic fibrosis
What are the two types of Caroli’s Disease?
•Simple classic form
•Associated with periportal hepatic fibrosis (more common)
Caroli’s Disease US findings: what is seen in the area of the ductal system as converges toward porta hepatis?
Multiple cystic structure
Caroli’s Disease US findings: what type of scattered cysts communicate with bile ducts?
Localized or diffusely
Caroli’s Disease US findings: ducts may show _______ appearance as they extend into periphery of liver
Beaded appearance
Caroli’s Disease US findings: What may be present?
Ectasia of extrahepatic & CBD
Caroli’s Disease US findings: What may reside in the dilated ducts?
Sludge or calculi
What is the differential diagnosis for Caroli’s Disease?
Polycystic liver disease
Dilated Ducts US findings in non-jaundiced patients:
Minimal dilation
With gallstones or tumor
Intermittent stone obstruction
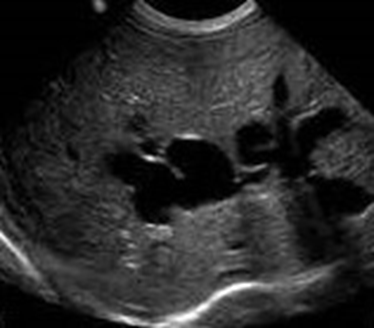
What disease is this sonographic image showing?
Caroli’s Disease
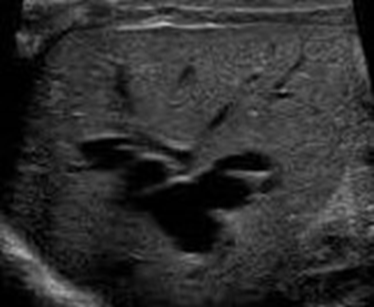
In this ultrasound image what is being displayed?
Caroli’s Disease
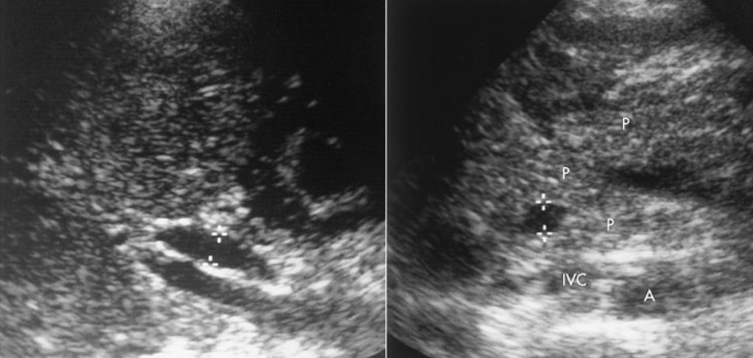
In the image above, what is being shown?
Dilated Ducts
What is the most common cause of a biliary obstruction?
Presence of tumor or thrombus within ductal system
A biliary obstruction can either be _________ or ________:
Extrahepatic or Intrahepatic
What does a biliary obstruction look like on US?
Ductal Dilation
“Too many tubes” or “shotgun”
In an extrahepatic biliary obstruction, what is the sonographer’s job?
To localize level and cause
What are the three primary areas for an extrahepatic biliary obstruction?
Intrapancreatic
Suprapancreatic
Porta Hepatic
What is a subpancreatic obstruction?
An obstruction between pancreas & porta hepatis
What is a Porta Hepatic obstruction?
Obstruction at this level shows intrahepatic ductal dilation & a normal Common duct, Hydrops of GB possible
What is Mirizzi syndrome?
an uncommon extrahepatic obstruction
What is Mirizzi syndrome impacted by?
Stone in the cystic duct or GB neck
What can Mirizzi syndrome cause?
Extrinsic compression of CHD
Painful jaundice is a common symptom of what?
Mirizzi Syndrome
Mirizzi Syndrome US findings:
Intrahepatic ductal dilation
Normal-size common duct
Large stone in neck of GB or cystic duct
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction US findings with minimal dilation: In nonjaundiced patients present with?
Gallstones or pancreatitis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction US findings with minimal dilation: In jaundiced patients, they present with?
Common duct stone or tumor
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction US findings: a diameter greater than ___mm suggests an obstruction by a stone or tumor of the duct, pancreas, or other source
11mm
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction US findings: What are other reasons to why a duct may enlarge?
Age and post cholecystectomy
What are the sonographic characteristics of dilated ducts?
Alteration in anatomic pattern at portal bifurcation
Irregular walls of dilated bile ducts
Stellate confluence of dilated ducts
Acoustic enhancement by dilated ducts
Peripheral duct dilation
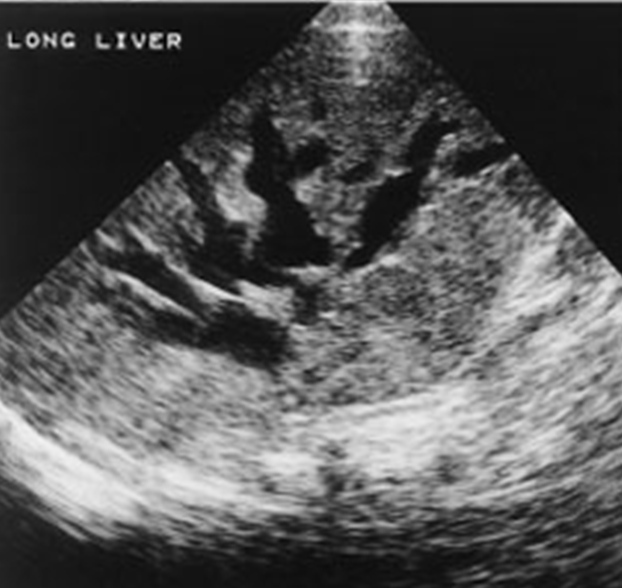
What is being shown in the image above?
A mass in porta hepatis