IME 319 Quiz 3
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
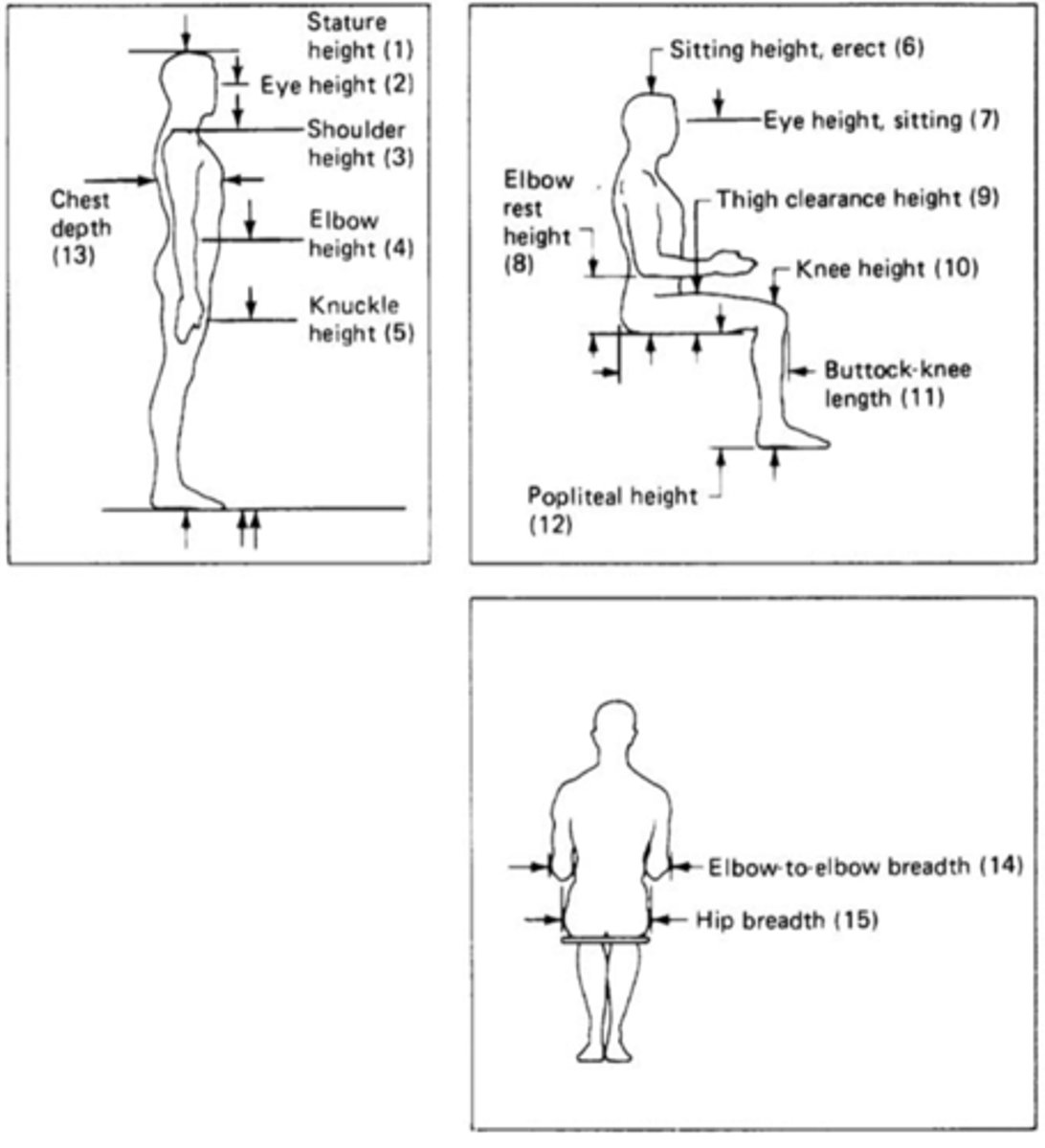
Anthropometry
Measures the physical characteristics of the human body
What is Anthropometry concerned with?
1) Heights
2) Weights
3) Inertial Properties
4) Volumes
5) Centers of Gravity
What are the 2 types of measurement for Anthropometry?
1) Static
2) Dynamic (functional)
What does a dynamic measurement look like?
Not sitting or standing
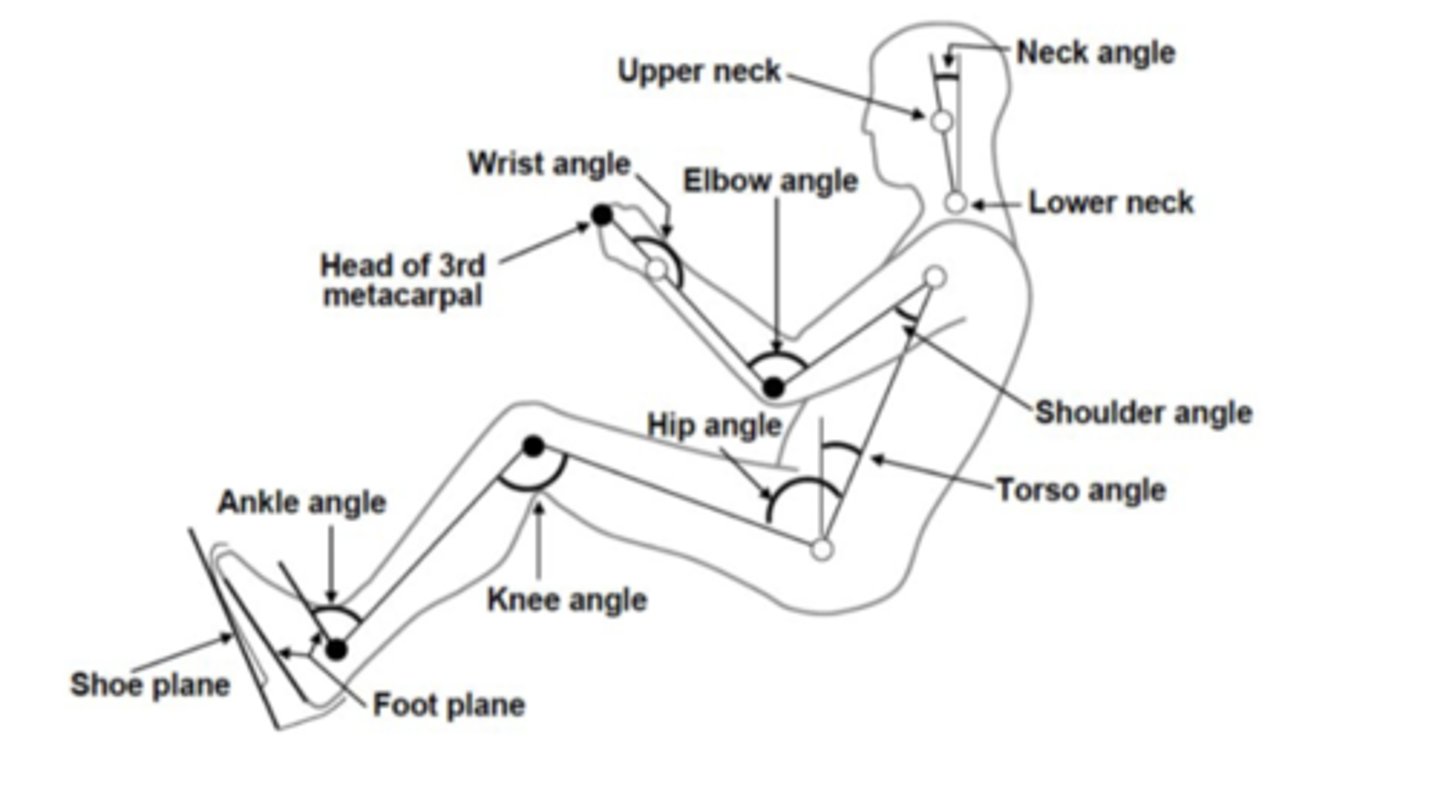
What does a static measurement look like?
Can be sitting or standing
Dynamic (functional) dimensions
- Function of the interactions between body parts
- NOT the result of individual static measurements
Anthropometric Data Facts
- More static than dynamic data
- No direct methods for converting static to dynamic
How is Anthropometric Data used?
- Should be used when appropriate for the specific target population
- Design for adjustability (most desirable)
- ex: designing driver seat, school bus, clothing, etc.
*Workspaces
- Three-dimensional "envelope" within which an individual works
- A function of the work and tasks performed
*What do workplace envelopes represent?
- Functional reach
- Out-of-reach requirements
- Clearance requirements
Out-of reach requirements
- Important to place items out of reach in certain scenarios (ex: museums, unguarded machinery, etc.)
Clearance requirements
Amount of space needed to move comfortably based on the tools used, clothing worn, and tasks performed
Functional reach
Bare minimum amount of space needed to perform a function
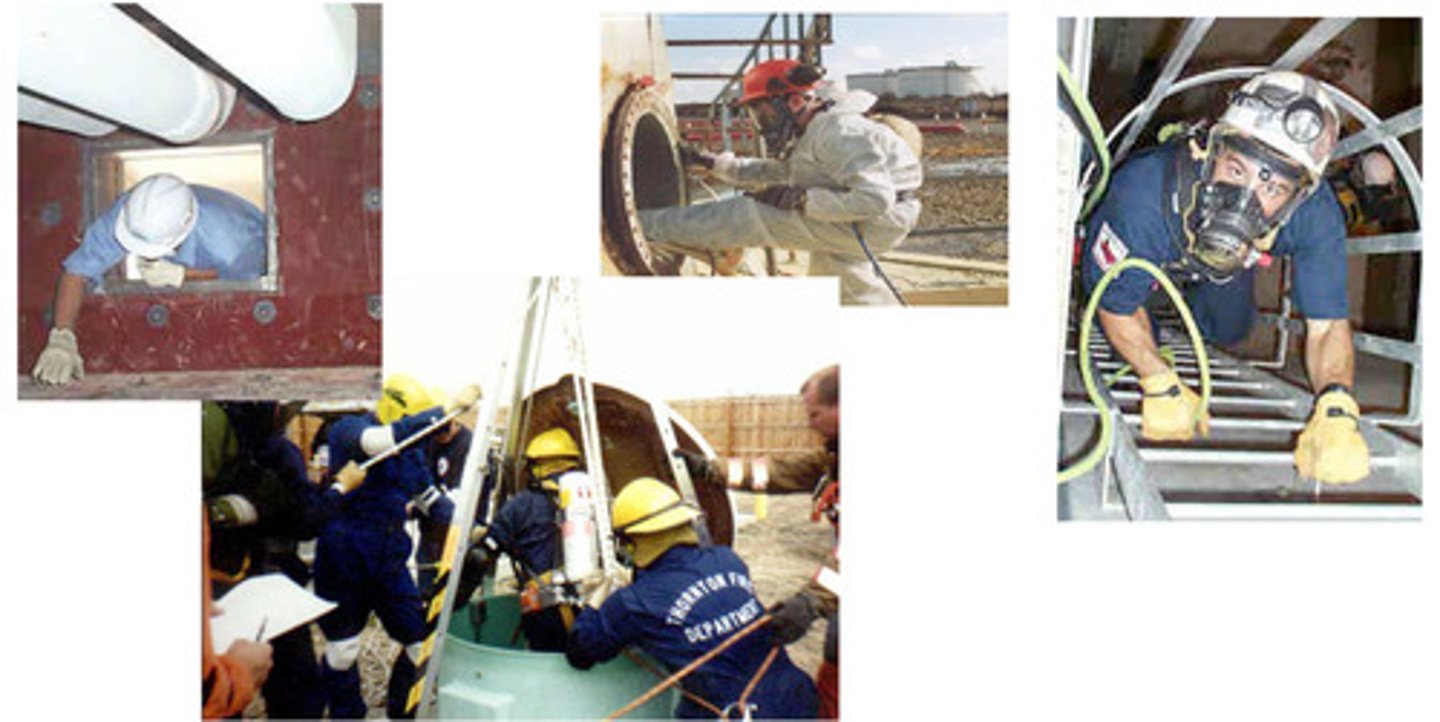
*Clearances for certain workspaces
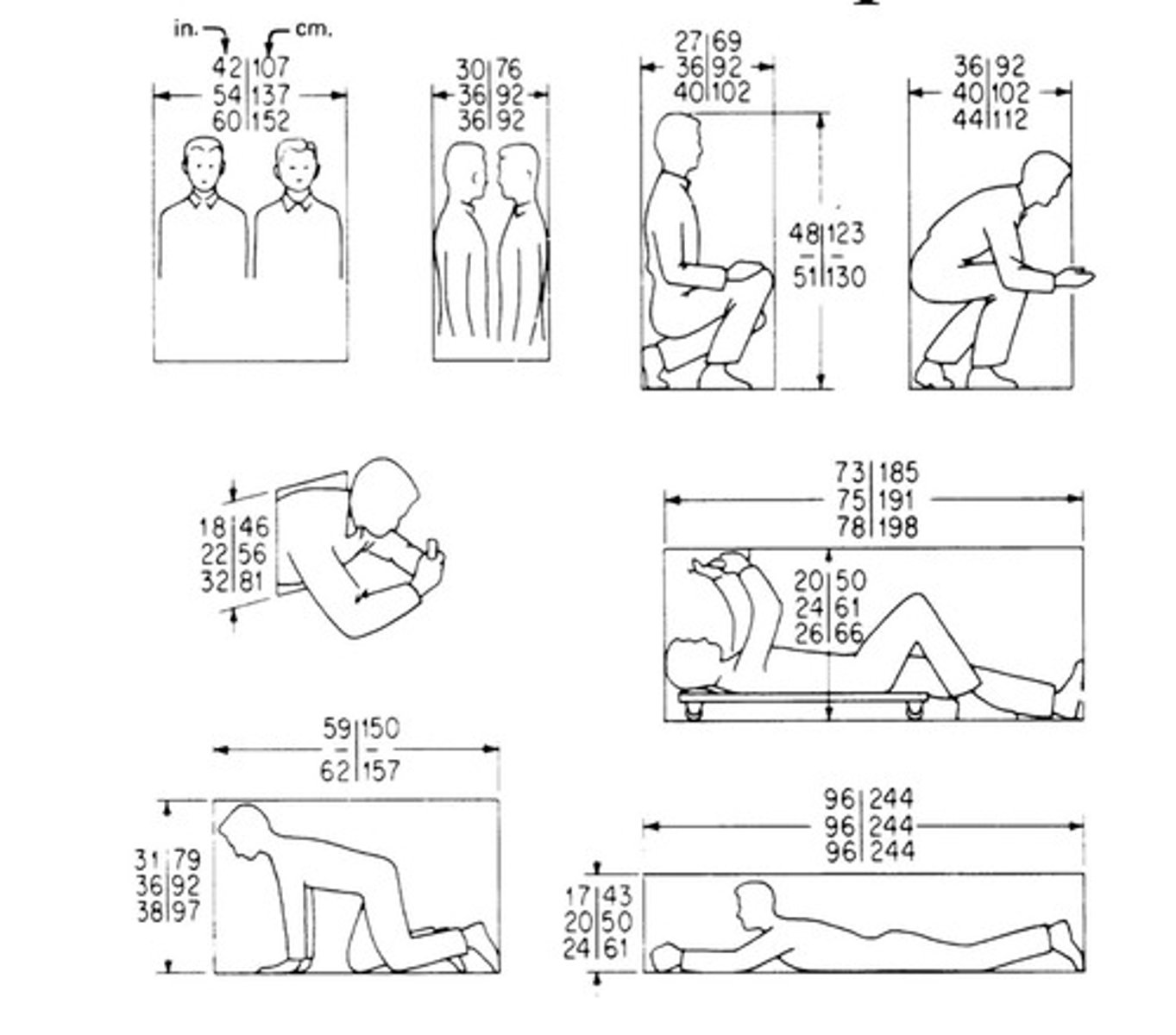
Clearances for confined space entry (CSE)

Standing Work-Surface Height
- Too high or too low of a surface can result in back/neck/shoulder stress
-Proper work-surface height is a function of the task being performed
- Work-surface height should permit relaxed, neutral postures of the upper extremities
The science of seating
- There is no one "best" chair
- Chairs should promote lumbar lordosis (curving inward or forward)
- Lumbar kyphosis (curving outward) results in increased disk pressure
Lumbar lodosis
curving inward or forward
Lumbar kyphosis
curving outward
How is disc pressure elevated?
-Sitting and slumped over
-Postural fixity (remaining static for extended periods)
Principles of Arrangement
1) Importance Principle
2) Frequency-of-use Principle
3) Functional Principle
4) Sequence-of-use Principle
Importance Principle
Important components placed in convenient locations
Frequency-of-use Principle
Frequently used components placed in convenient locations
Functional Principle
Arrangement provides for the grouping of components according to their function
Sequence-of-use principle
Arrangement to capitalize on temporal usage patterns
How do we know in practice which arrangement is best?
- Do testing for frequency of use for each button
- Collect data
Which types of data are relevant to control arrangement?
1) Basic data about humans (anthropometry and biomechanics)
2) Task-Analysis Data (specific system requirements)
3) Environmental data (noise, lighting, etc.)
Frequency vs. Importance

Manual Materials Handling (MMH)
- "Is the process of routinely moving and handling objects by carrying, holding, lifting, pulling, pushing, and stopping" -CDC
- MMH injuries continue to remain the most common and costly of work-related injuries
Lifting posture
- One may be more beneficial from an energy standpoint and the other from a biomechanical standpoint
Lifting risk factors (SHALLOW T)
Starting Position
Horizontal distance
Load magnitude
Lift frequency
Object coupling
Walking distance
Torso position
Relationship b/w Weight, Frequency and Carrying Distance on Oxygen Consumption
-Directly correlated
-As one increases so does the other
How do you reduce the risk of MMH overexertion? (ELDU MRID)
- Eliminate need for manual handling
- Use lifting aids/devices
- Decrease object weight
- Use two or more people
- Minimize the horizontal distance of the lift
- Reduce lift frequency
- Incorporate rest periods or job rotation
- Design containers with optimal handles
Additional recommendations to reduce the risk of MMH overexertion
- Assess lift
- Do not rotate torso
- Keep back straight
- Bend knees
- Keep head up to align back
- Keep load close to body
- Use support to re-adjust
MMH risk controls
1) Elimination
2) Substitution
3) Engineering Controls
4) Administrative Controls
5) PPE
Elimination (MMH rc)
Reorganize layout of workplace to eliminate carrying, lifting, or moving loads
Substitution (MMH rc)
Decrease the weight of the load by splitting it into smaller loads
Engineering Controls
Use different work practices, lifting equipment or mechanical aids to reduce risk of injury
Administrative Controls
Change work practices so staff are not overworked and provide training in Safe lifting & handling techniques
PPE
Provide Personal Protective Equipment like gloves and footwear
*Approaches to assessing MMH Capabilities
- Physiological Approach
- Biomechanical Approach
- Psychophysical Approach
*Physiological Approach
Energy consumption and the stresses acting on the cardiovascular system
*Biomechanical Approach
Principles of physics used to determine the mechanical stresses on the body and forces necessary to counteract the stresses
*Psychophysical Approach
Subjective evaluation of perceived stress
Fatigue
- The inability to maintain a power output or force during repeated muscle contraction
- Depends on the type of activity and the type of muscle fibers
Fatigue types
Central Fatigue: Inability to fully activate muscle voluntarily (Like CNS failure)
Peripheral Fatigue: Inability of muscle to produce force (Exhaustion)
What is the most common tool used to analyze fatigue?
VO2max TEST
Functions of skeletal muscle
- over 600 in our body
- Force production for locomotion or breathing
- Force production for postural support
- Heat production during cold stress
Important parts of microstructure of skeletal muscle
Cross bridges between Myosin (thick) filaments and Actin (thin) filaments
?Fast fibers exert more force than slow fibers
- Maximal force per cross-sectional area (higher in fast fibers (IIa and IIx) compared to slow (type I) fibers
?Force production relationship to number of myosin cross-bridges
Fast fibers contain more cross-bridges per cross sectional area
Types of Muscle action
1) Isometric -- muscle exerts force without changing length
2) Dynamic (Isotonic)
a) concentric -- muscle shortens during force production
b) eccentric -- muscle produces force but length increases
Measurement of workload (HBO)
1) Heart Rate -- measured during the task or in recovery
2) Blood Pressure -- systolic or diastolic BP
3) Oxygen Uptake -- VO2 MAX
*VO2 Max
- The gold standard measure of cardiorespiratory endurance
- Depends on work environment and the workload
*VO2 Max vs. VO2 Peak
- VO2 Max is a test for athletes (higher the number the better)
- VO2 Peak is activity related (ALWAYS less than VO2 MAX)
Forces
- Push or pull on an object with mass causes it to change its velocity
- Has magnitude and direction
Moments
Magnitude of a force * perpendicular distance
Biomechanics of Human Motion
Study of forces acting on/within the body and effects of these forces on tissues, fluids, or materials used for diagnosis, treatment, or research purposes
Kinetics
Deals with forces and motion only and reveals how forces affect motion (cause)
Kinematics
Deals with motion only-or how an object moves through space-without reference to any associated force (Result)
Flexion
Movement of a segment of the body causing a decrease in the angle at a joint
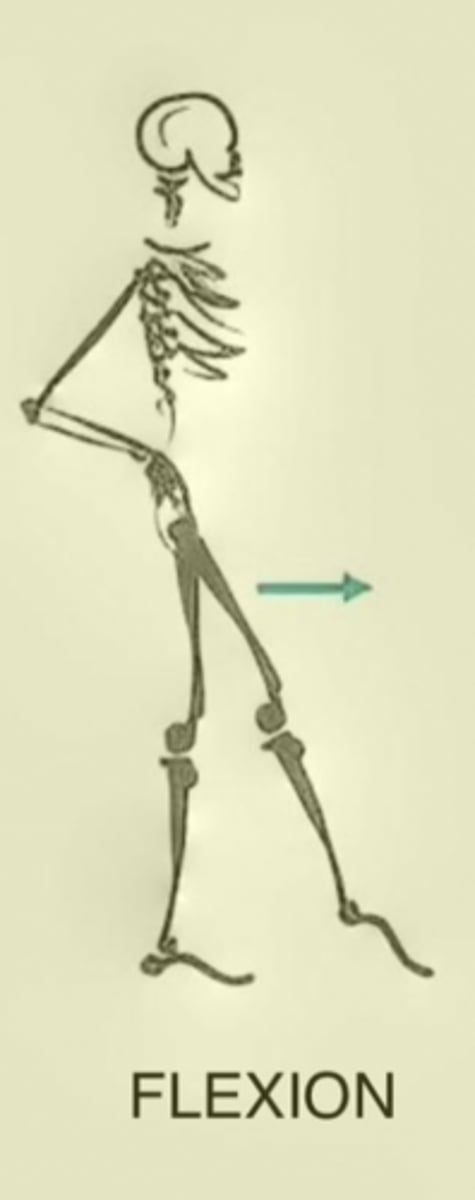
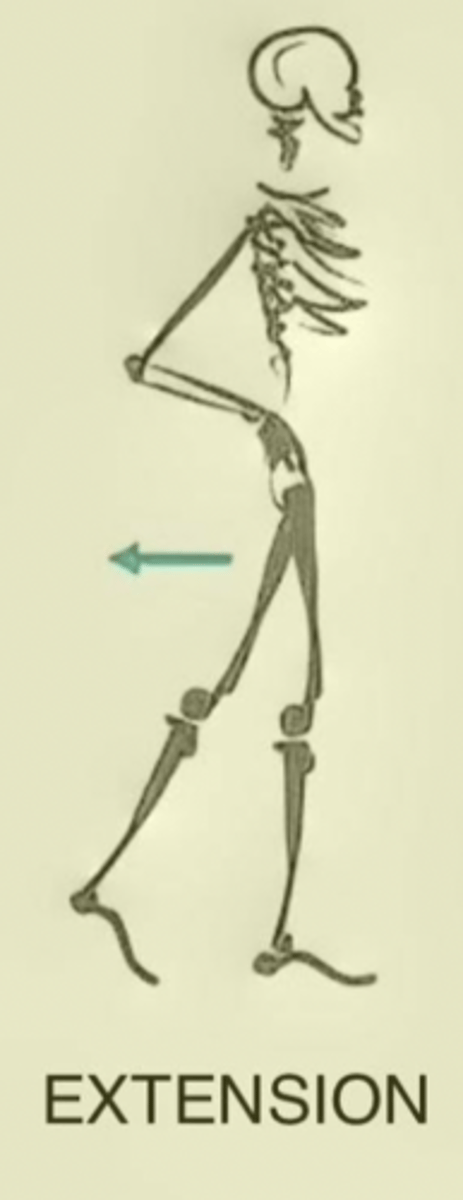
Extension
Movement of a segment of the body causing an increase in the angle at a joint
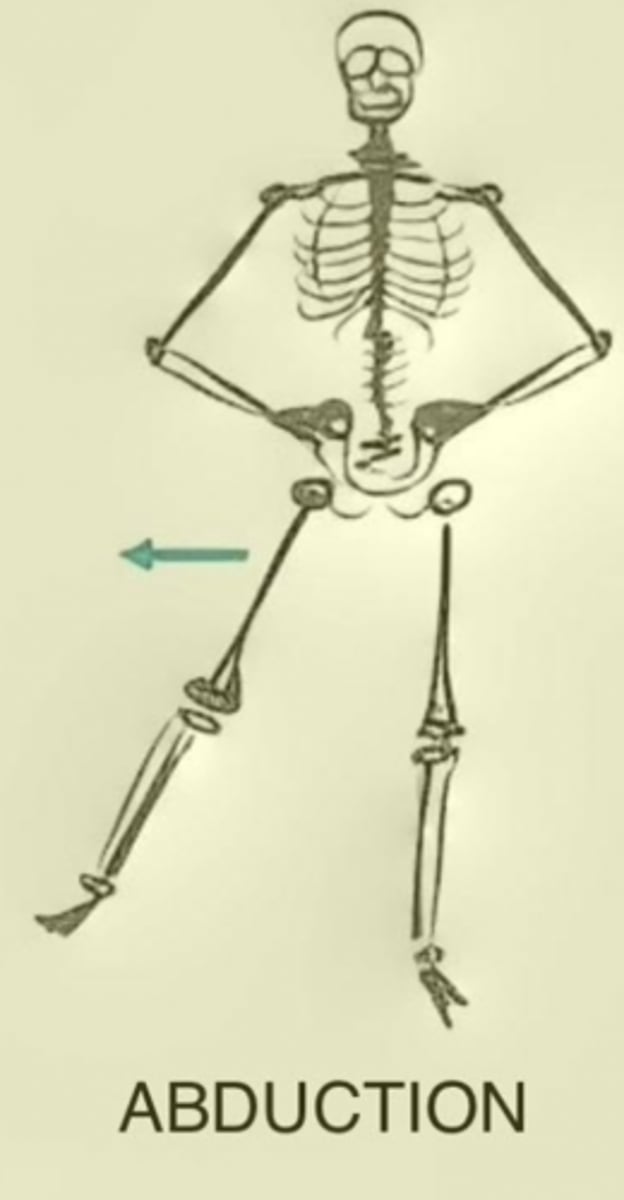
Abduction
Movement of a body segment in a lateral plane away from the body's midline
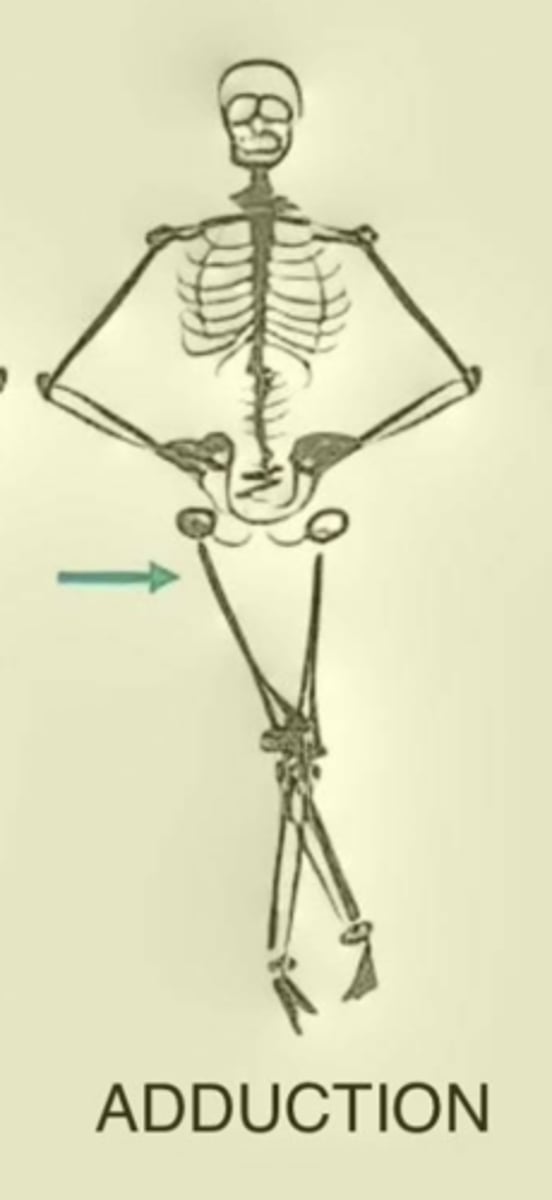
Adduction
Movement of a body segment in a lateral plane toward the body's midline
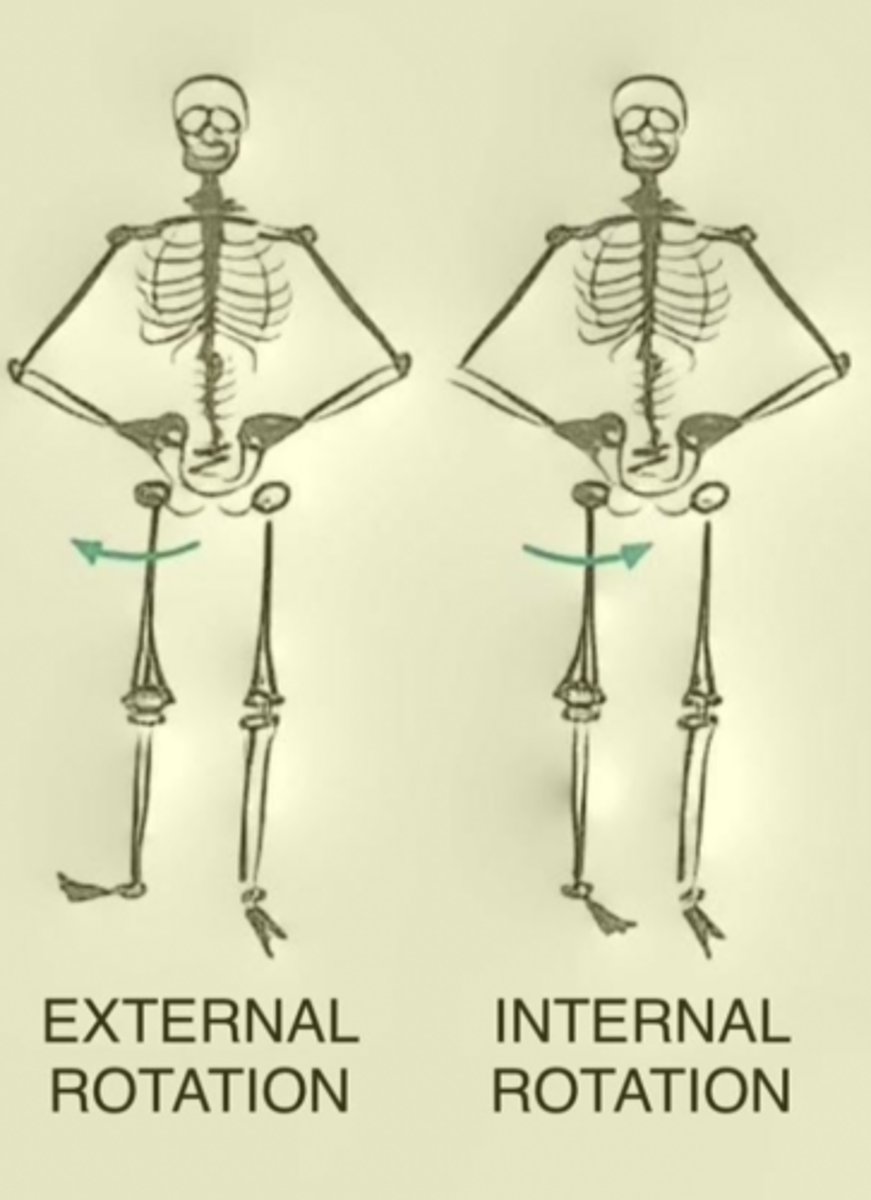
Rotation
Movement of a body segment around its own longitudinal axis
Circumduction
- A circular or cone-like movement of a body segment.
- Combination of all motions.
How can movement be restricted?
- Injury (Can be caused by inflexibility)
- Excess bulk (adipose tissue)
What can too much flexibility lead to?
Stability problems (joint hypermobility)
Psychophysics
Subjective evaluation of perceived stress
- Tools: Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE), Rating of Perceived Dyspnea (RPD), and NASA TLX

Lean six sigma
1) Sort
2) Straighten
3) Shine
4) Standardize
5) Sustain
6) Safety
What does lean focus on?
Eliminating the sources of waste and aiming for a continuous process flow
What does six sigma focus on?
Reducing the process of variability
7 wastes of processes
1) Transport
2) Inventory
3) Motion
4) Waiting
5) Overproduction
6) Over processing
7) Defects
List all 6S
SORT
STRAIGHTEN
SHINE
STANDARDIZE
SUSTAIN
SAFETY
List 7 wastes (TIMWOOD)
TRANSPORT
INVENTORY
MOTION
WAITING
OVERPRODUCTION
OVER PROCESSING
DEFECTS
List types of muscle actions
Isometric
Isotonic: Concentric, Eccentric
List types of Muscle Fibers
Type 1: Slow Fiber
Type IIa: Fast Fiber
Type IIx: Fast Fiber
Describe Isometric action
Muscle exerts force without changing length
Describe Concentric action
Muscle shortens during force production
Describe Eccentric action
Muscle produces force but length increases