Biology ✿ bioenergetics
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
equation for photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
chemical equation for photosynthesis
CO2 + H2O → O2 + C6 H12 O6
what type of reaction is photosynthesis?
endothermic as energy is transferred from the environment to the chloroplasts
name 3 factors effecting photosynthesis
temperature
light intensity
carbon dioxide concentration,
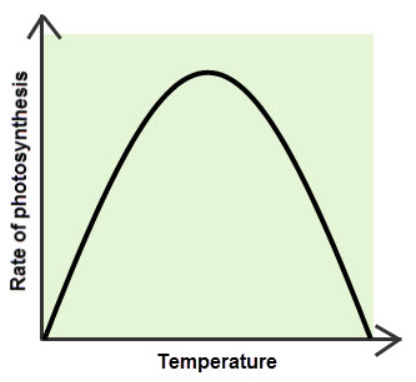
how does temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis?
low temperature → the enzymes work slowly, so the ROP is low
as temperature increases, ROP also increases
40–50°C → enzymes denature at high temperatures
limiting factor
a factor which stops the ROP from increasing
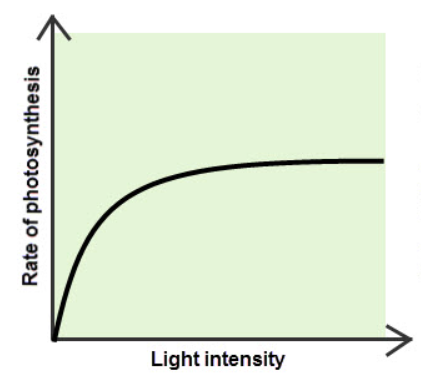
how does light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis?
low light intensity → the ROP is low because light energy is insufficient
as light intensity increases, ROP also increases
if there isn’t enough of one factor, increasing light intensity wont change the rate
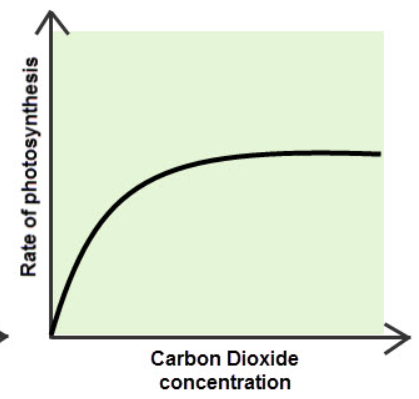
how does carbon dioxide concentration affect the rate of photosynthesis?
low CO₂ levels → the ROP is low as there isnt enough CO₂ to produce glucose
as CO² concentration increases, ROP also increases
if there isn’t enough of one factor, increasing CO₂ levels wont change the rate
how might people in greenhouses maximise the rate of photosynthesis using artificial methods [3]
use artificial light
add carbon dioxide in the air
use heaters
name 4 ways glucose is used
respiration
can be converted into starch, fats and oils for storage
to produce cellulose to strengthen cell wall
to produce amino acids for protein synthesis
cellular respiration
an exothermic reaction which is continuously occurring in living cells
equation for anaerobic respiration
glucose → lactic acid
equation for aerobic respiration
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
fermentation
anaerobic respiration in yeast cells, used for making alcoholic drinks
equation for fermentation
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
how does the human body react when one is exercising and why?
heart rate, breathing rate and breath volume increases to supply the muscles with more oxygenated blood
what is aerobic respiration, where does it occur and what reaction is it?
respiration which releases energy using oxygen
occurs in mitochondria
exothermic (produces heat)
give 2 differences between anaerobic and aerobic
do not refer to use of oxygen
aerobic respiration happens in cells and produces more energy
anaerobic respiration happens in muscles and produces less energy
what is anaerobic respiration and when does it occur ?
respiration without oxygen, it provides less energy as glucose isn’t fully oxidised
occurs during intensive exercises and in cytoplasm
what causes the build up in lactic acid in anaerobic respiration?
the incomplete oxidation of glucose which also creates an oxygen debt
oxygen debt
the amount of extra oxygen the body needs after exercise to react with the lactic acid to remove it from cells
metabolism
the sum of all the reactions in a cell or body
give 4 examples of metabolism reactions
respiration
breakdown of proteins to urea
formation of lipids from glycerol and fatty acids
conversion of glucose into starch, cellulose or glycogen
give am example of an metabolism reaction in plants
use of glucose/ nitrates to make amino acids
why is there less energy produced in anaerobic respiration?
the oxidation of glucose is incomplete
Explain what happens to accumulated lactic acid in the body [3]
It is transported to the liver by the bloodstream
it is converted into glucose which is stored or used during aerobic respiration
this produces the oxygen to repay the oxygen debt
Explain what happens when muscles do not have enough oxygen [4]
anaerobic respiration occurs
less energy is produced, and more lactic acid is produced
build up of lactic acid causes tiredness
Oxygen debt forms