Week 9 | Animalia 2 | Nematoda and Arthropoda
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Nematoda apomorphies
Aquatic, moist terrestrial, parasitic
Bilateral, cephalization
Complete gut, pseudocoelomate
Triploblastic; nervous system w/o brain
Hydrostatic skeleton
Dioecious with internal fertilization
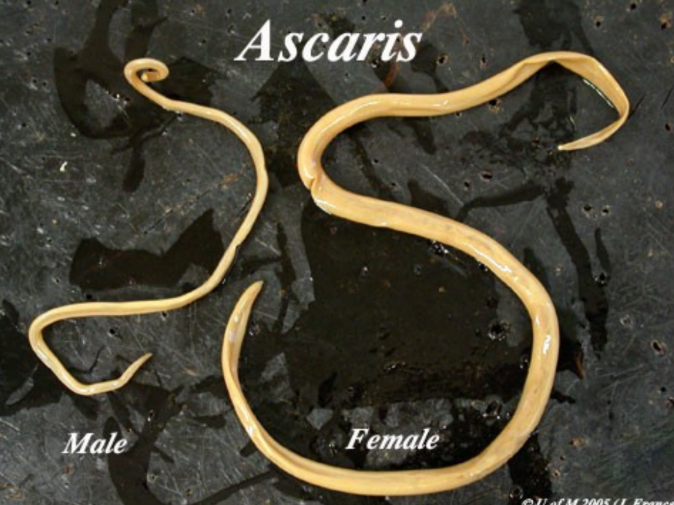

Ascaris characteristics
Slender bodies, tapered at both ends and covered by a cuticle
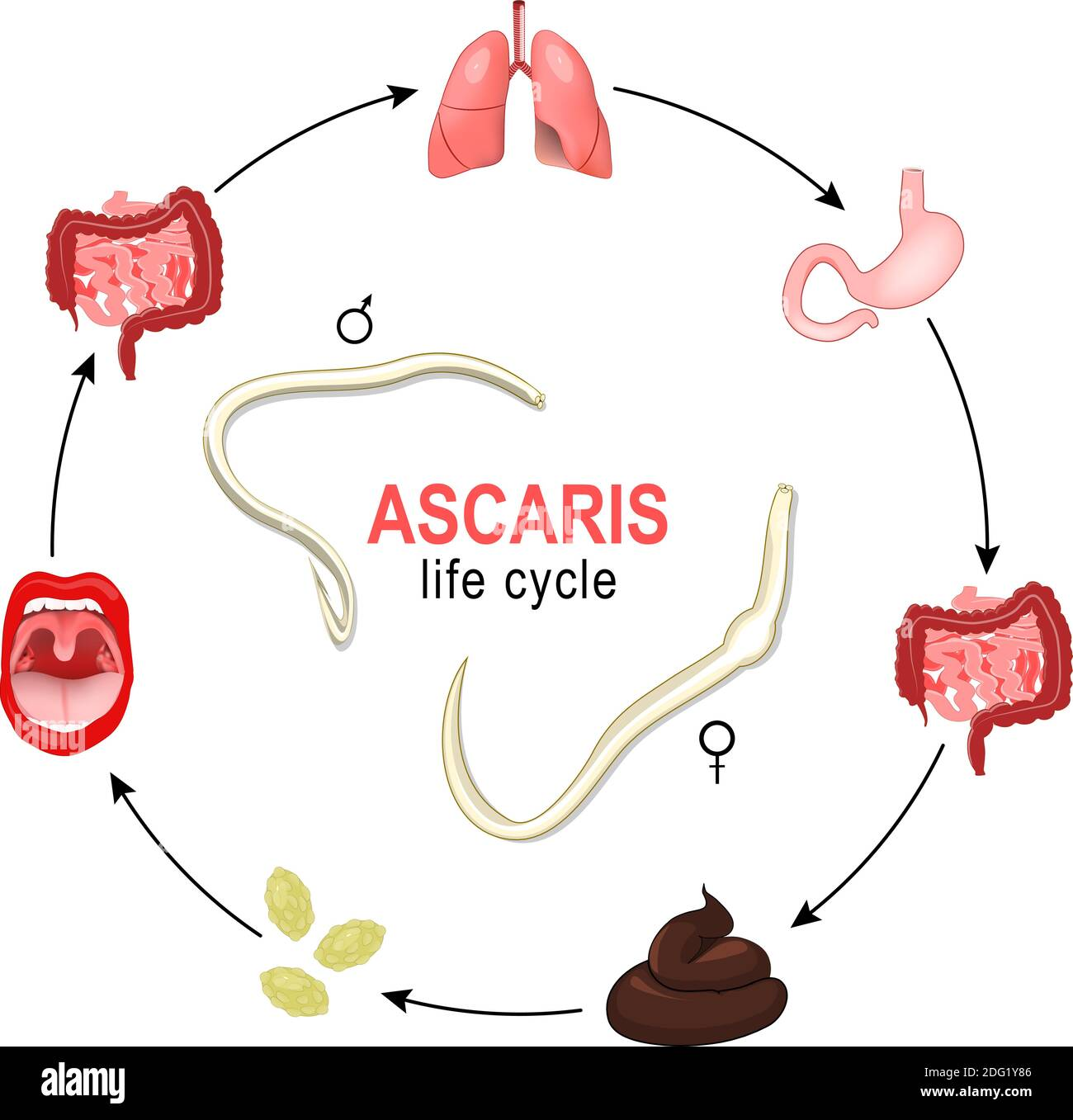
Common parasite of humans, pigs, and other mammals
15-40 cm (6-18 in)
Eggs are eliminated in host feces - are highly resistant
Ingest food/water contaminated with eggs from feces
Eggs pass through stomach and hatch in small intestine. Larvae migrate through blood, exit circulation and enter respiratory tract - out trachea into throat, swallow and reinfect
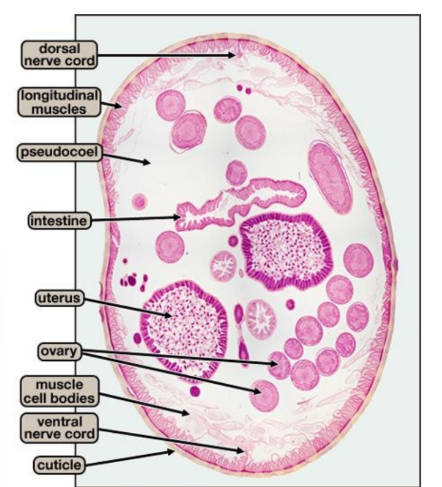
Ascaris female cross-section
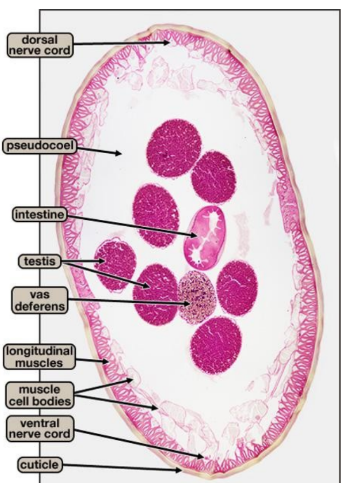
Ascaris male cross-section
Arthropoda apomorphies
Aquatic, terrestrial (land/air), some parasitic
Bilateral, cephalization
Complete gut, coelomate (protostome)
Triploblastic; nervous system w brain, excretory, open circulatory system, respiratory system
Exoskeleton
Dioecious, internal fertilization, metamorphosis, parthenogenic
Arthropoda characteristics
>1M species; largest phylum on Earth
Cuticle has become modified into a hard exoskeleton
Are protostomes with segmented bodies that include one pair of legs per segment
Mouthparts are modified appendages (arm/leg)
Three body regions: head, thorax, abdomen
Coelom filled with hemolymph connected to an open circulatory system
Hemolymph
A fluid equivalent to blood in most invertebrates, occupying the hemocoel
Class Insecta characteristics
More than ¾ of arthropods
Evolution of wings led to exploitation of new environment
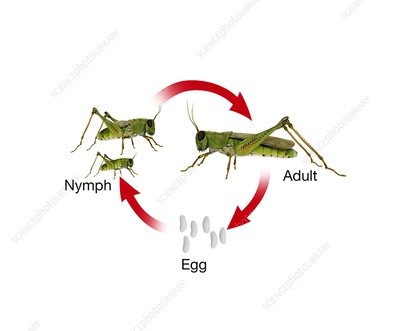
Complete/incomplete metamorphosis
Complete metamorphosis
The type of insect development that includes egg, larva, pupal, and adult stages, which differ greatly in morphology
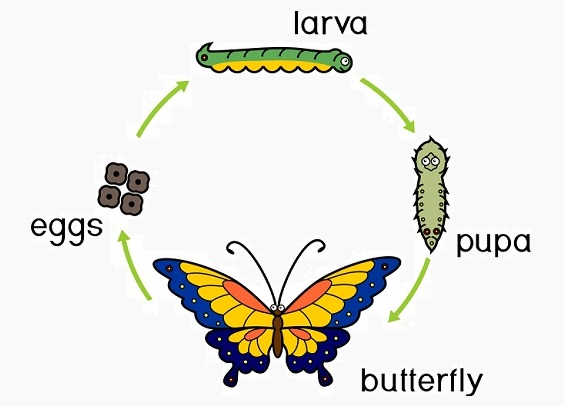
Incomplete metamorphosis
Involves a gradual development where the nymph progressively resembles the adult form
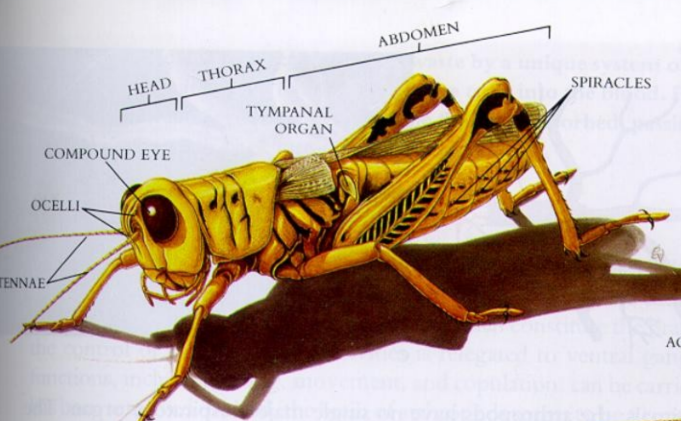
Grasshopper external anatomy
Thorax has 3 segments each with a pair of legs (segments 2 & 3 have wings)
Spiracles
One pair of compound eyes and three ocelli
One pair of antennae
Mouth includes one pair of mandibles
Two pairs of maxillae (2nd pair fused = labium)
Upper lip is the labrum, which covers the mandibles
Class crustacea characteristics
2 pairs of antennae
Carapace
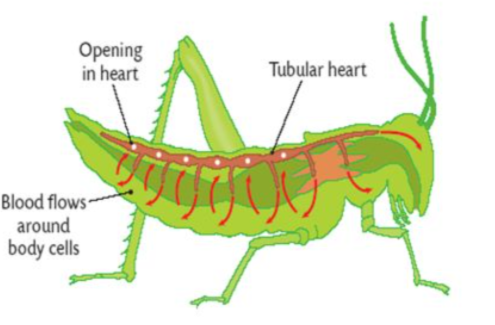
Open circulatory system
Where hemolymph (blood) mixes with interstitial fluid and directly bathes tissues
Spiracles
External openings found in arthropods that allow air or water to enter the respiratory system
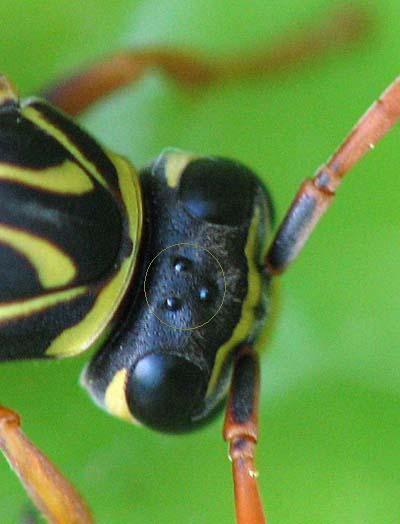

Ocelli
Eyespots on insects
Tapered
To become progressively smaller toward one end
Parthenogenesis
A form of asexual reproduction where offspring develop from unfertilized eggs, meaning a female can produce offspring without the need for a male
Difference between male and female crayfish
The first set of swimmers in the male is larger than the rest