Biology Chapter 33, Animal Nutrition (Exam 2)
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bio III, Ch. 33
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is an Omnivore?
A Species That Consumes Both Meat and Plants
What is a Carnivore?
A Species That Consumes Only Meat
What is a Herbivore?
A Species That Consumes Only Plants
What are the Three Nutritional Needs an Adequate Diet Must Satisfy?
Chemical Energy for Cellular Processes, Organic Building Blocks for Biosynthesis, and Essential Nutrient
What are Essential Nutrients?
Required Substances That Cannot Be Assembled From Simple Organic Molecules
What are Vitamins?
Organic Molecules
What are Minerals?
Inorganic Molecules
What is Ingestion?
The Act of Eating Food
What is Digestion?
The Process of Breaking Down Food into Molecules Small Enough to Absorb
What is Absorption?
Cells Taking Up Small Molecules
What is Elimination?
Passage of Undigested Material Out of Digestive System
Where Does the Esophagus Lead to?
The Stomach
Where Does the Trachea Lead to?
The Lungs
How is Food Kept From Entering the Trachea When We Swallow?
The Epiglottis, Which Covers the Trachea When We Swallow
What is Peristalsis?
The Act of Food Being Pushed Through the Esophagus into the Stomach
What are the Two Functions of the Stomach?
To Store Food and Secrete Gastric Juice
What Enzyme is Produced in the Stomach?
Pepsin
How Does the Stomach Lining Prevent Itself From Digesting Itself?
By a Thick Mucus Layer That is Secreted by the Cells in the Stomach Walls
What is Bile?
Aids in Digestion and Absorption of Fats
Where is Bile Produced?
In the Liver
Where is Bile Stored?
In the Gallbladder
What are the Two Digestive Functions of the Small Intenstine?
Absorption of Nutrients and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Macromolecules
What is the Function of Villi and Microvilli of the Small Intestine?
They Greatly Increase the Surface Area
What is the Function of the Cecum in Grazing Animals?
To Perform Further Microbial Fermentation of Undigested Fiber That Was Not Broken Down
What is Suspension Feeding?
Filter Food From Surrounding Medium
What is Fluid Feeding?
Ingestion of Nutrient Rich Fluids From a Host
What is Substrate Feeding?
Living in or on Their Food Source
What is Bulk Feeding?
Eating a Relatively Large Piece of Food
What is Mechanical Digestion?
Breaking Food into Small Pieces and Increases Surface Area
What is Chemical Digestion?
Splits Food into Small Molecules That Can Pass Through Membranes
What is Enzymatic Hydrolysis?
Breaking Down of Molecules Using Water Catalyzed by Enzymes
What is Intracellular Digestion?
Food Particles are Engulfed by Endocytosis
What is Extracellular Digestion?
Breakdown of Food Particles Outside of Cells
What is the Gastrovascular Cavity?
Animals With Simple Body Plans That Have a Single Opening in Their Digestive Compartment
What is the Alimentary Canal?
Animals With Complex Body Plans That Have Two Openings in Their Digestive Compartments
Where Does the Alimentary Canal Start and End?
Starts at the Mouth, Ends at the Anus
Where is the Appendix Located?
At the End of the Large Intestine
What is the Function of the Appendix?
Thought to Help With Gut Health
What is the Major Function of the Colon?
To Complete H2O Recovery
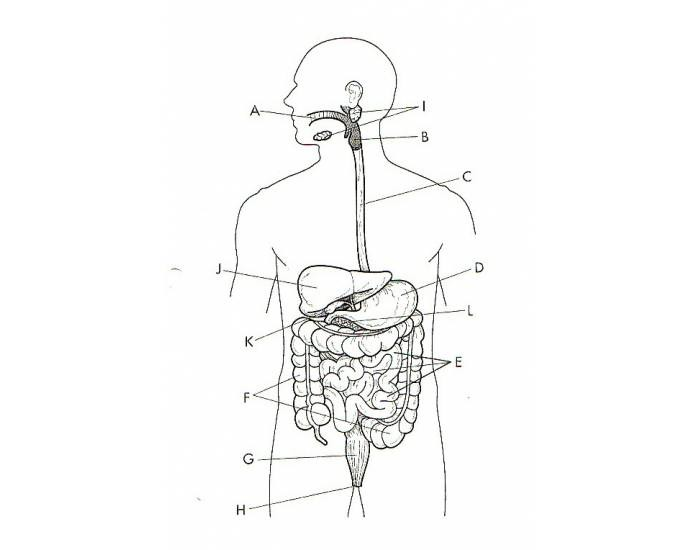
What is A?
Oral Cavity
What is B?
The Pharynx
What is C?
The Esophagus
What is D?
The Stomach
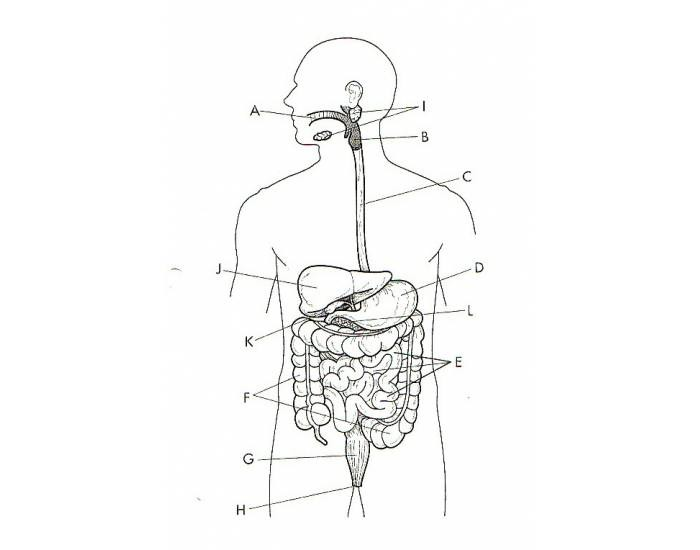
What is E?
The Small Intestine
What is F?
The Large Intestine
What is G?
The Rectum
What is H?
The Anus
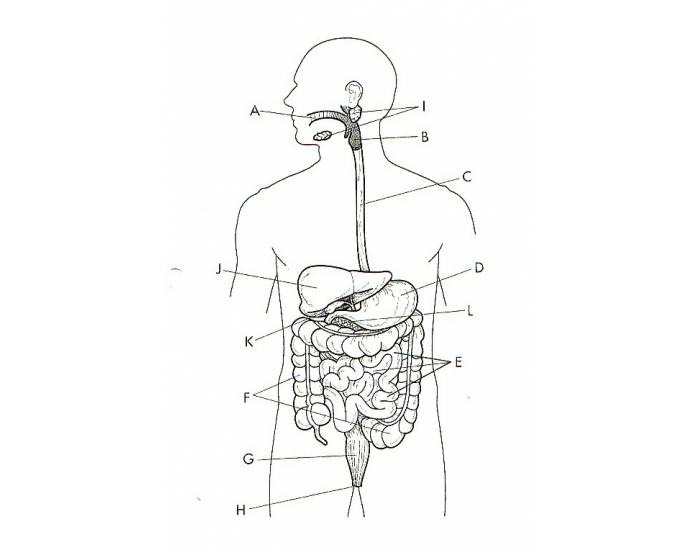
What is I?
The Salivary Glands
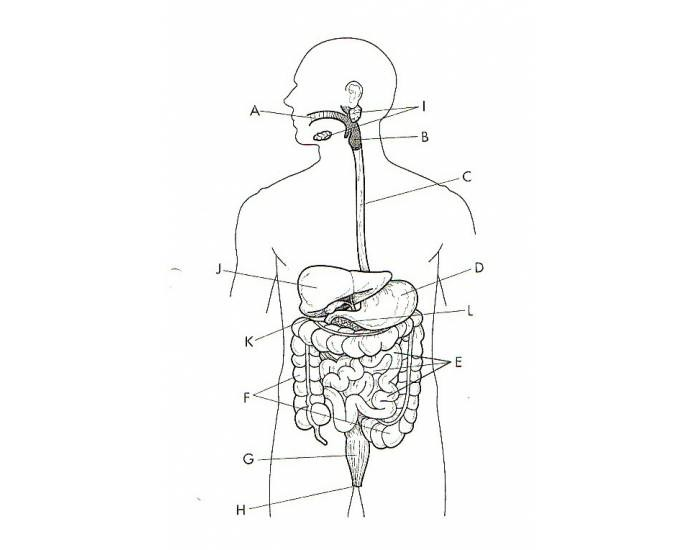
What is J?
The Liver
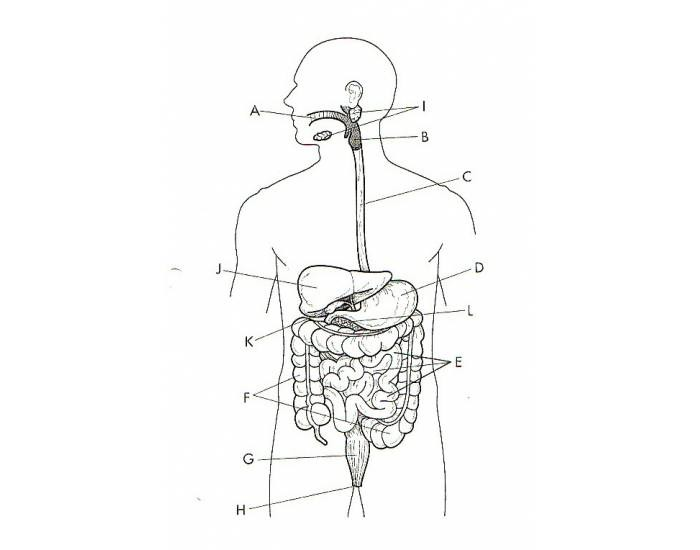
What is K?
The Gallbladder
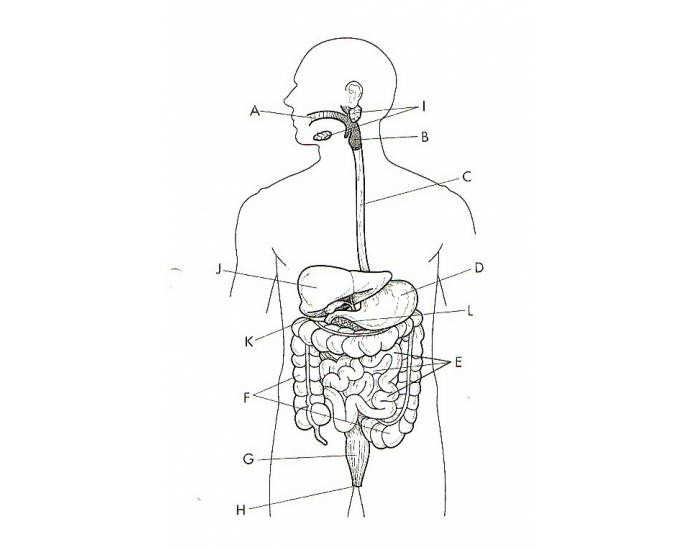
What is L?
The Pancreas
What is the First Step of Digestion?
Takes Place in the Oral Cavity, Where Salivary Glands Secrete Saliva That Breaks Down the Food, Which is Then Received by the Pharynx and Pushed Through the Esophagus into the Stomach
What Happens in the Stomach During Digestion?
Food is Stored and Gastric Juice is Secreted —> Converts Food to Chyme
What Happens in the Small Intestine During Digestion?
Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Macromolecules
What is the Duodenum?
First 20 In. of Small Intestines; Chyme Mixes With Digestive Juices
What is the Pancreas?
Secretes Bicarbonate to Neutralize Acidity of Chyme and Produces Trypsin and Chymotrypsin
What Happens in the Small Intestine During Absorption?
Nutrients are Absorbed Across the Lining of Small Intestine
What Happens in the Large Intestine During Processing?
The Colon Leads to the Rectum, Where Feces is Stored Until Elimination Through the Anus
What is the Enteric Nervous System?
Stimulates Release of Digestive Juices and Regulates Peristalsis