Unit 5: Heredity
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Quick Note
The notes on Meiosis can be found in the unit 4 study set.
Mendelian Genetics Overview
Ex.
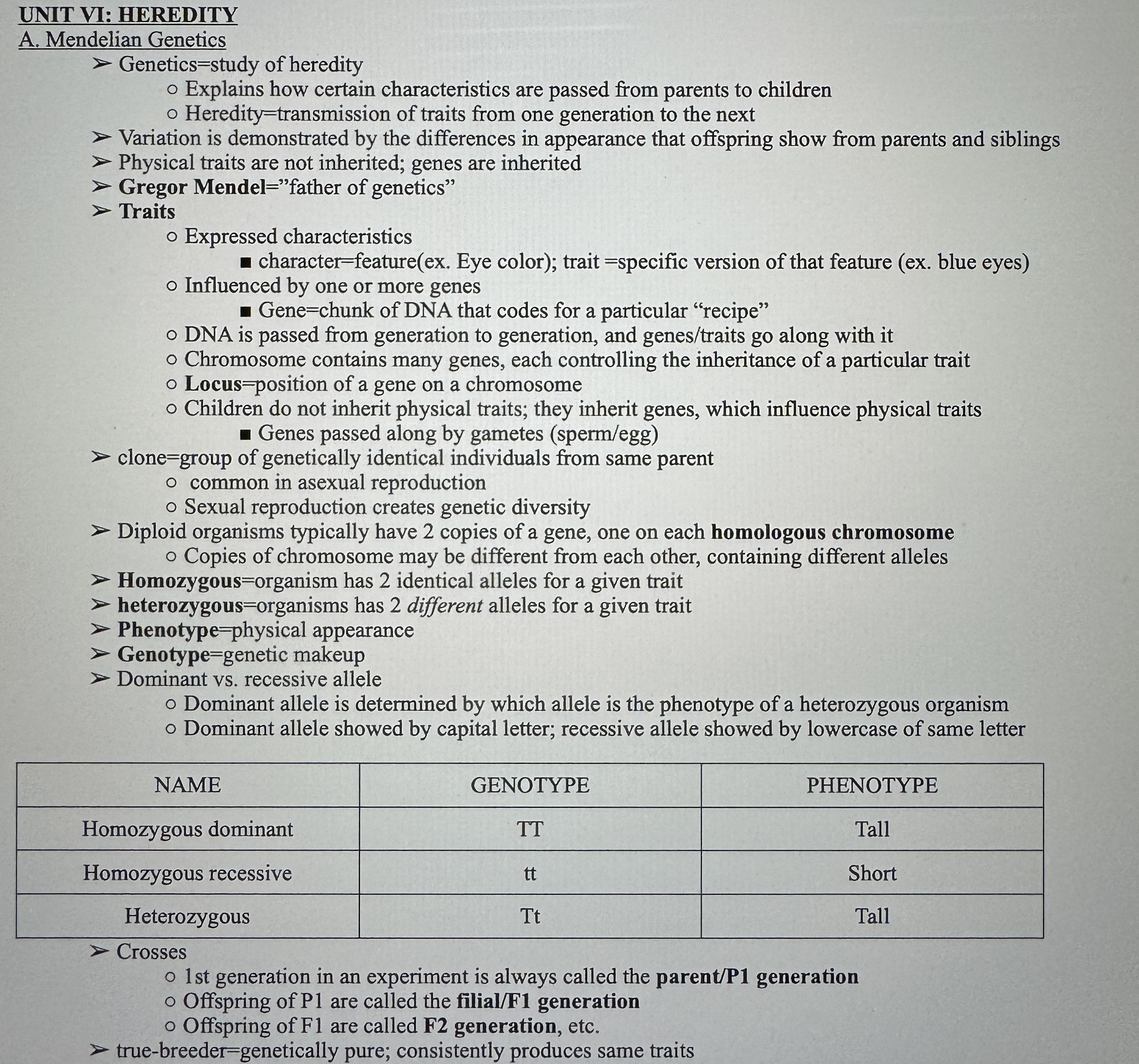
Mendel’s Three Laws
Ex.

Other Heredity Notes
Ex.

Alterations of Chromosomes # or Structure
Ex.

Sex-Linked and Other Patterns of Inheritance
Ex.

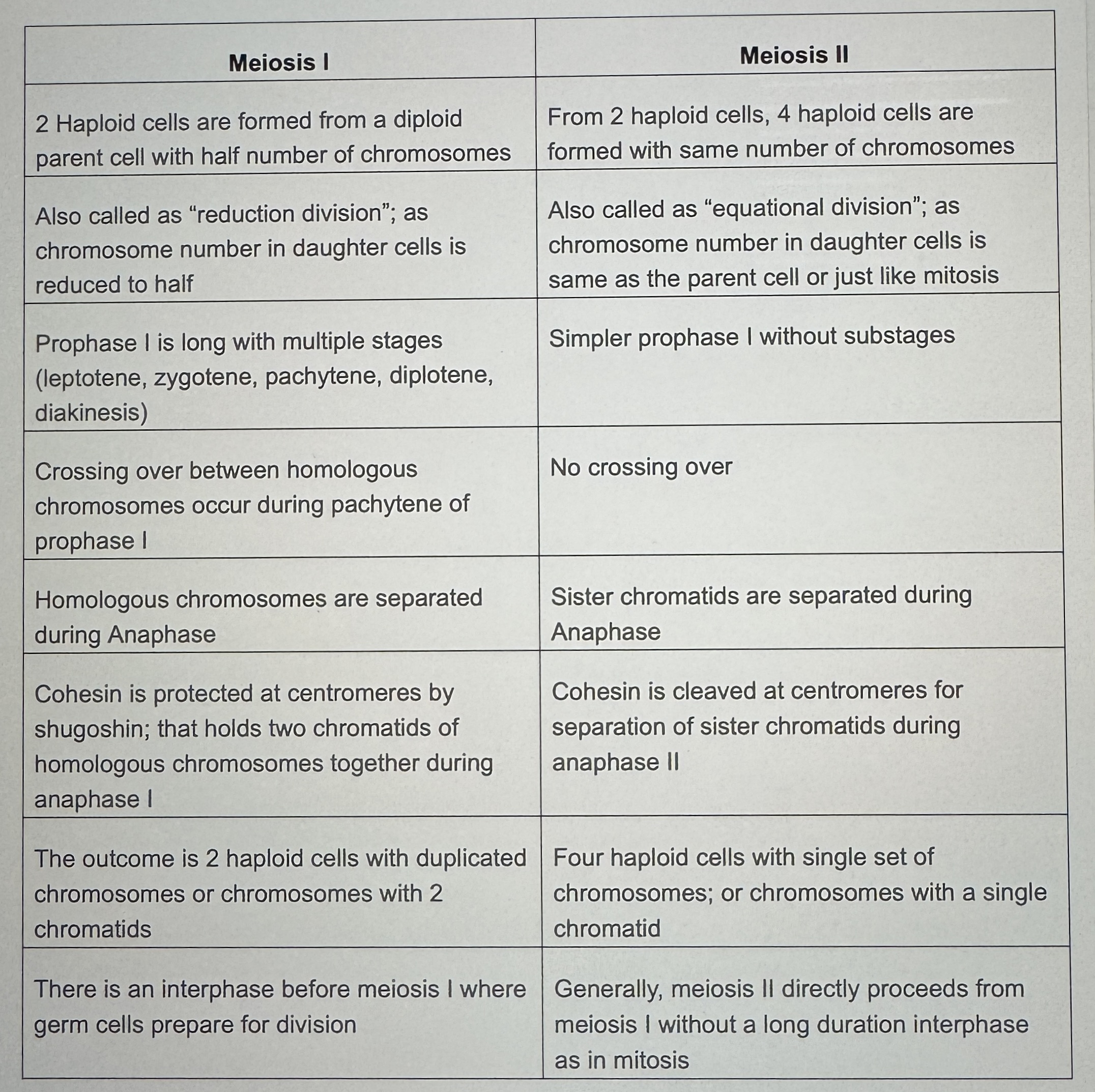
Extra - Differences between Meiosis 1 and 2 (Not everything matters in this chart for AP Bio)
Ex.
Extra - What three things increase genetic variability?
Crossing Over:
During prophase I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material (DNA segments) through a process called crossing over, resulting in new combinations of genes on chromosomes.
Independent Assortment:
During metaphase I, homologous chromosome pairs align randomly at the cell's equator, and these pairs are then separated randomly into different gametes (sperm or egg), leading to a vast number of possible chromosome combinations in each gamete.
Random Fertilization:
Any sperm cell can fertilize any egg cell, further increasing the potential genetic diversity of the offspring, as the combination of gametes is random.
Extra - Laws of Probability
Ex.

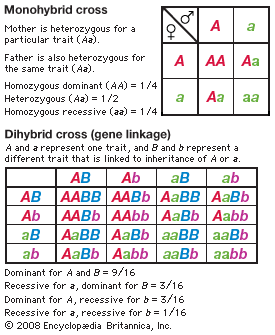
Extra - Monohybrid Cross vs Dihybrid Cross
Ex.
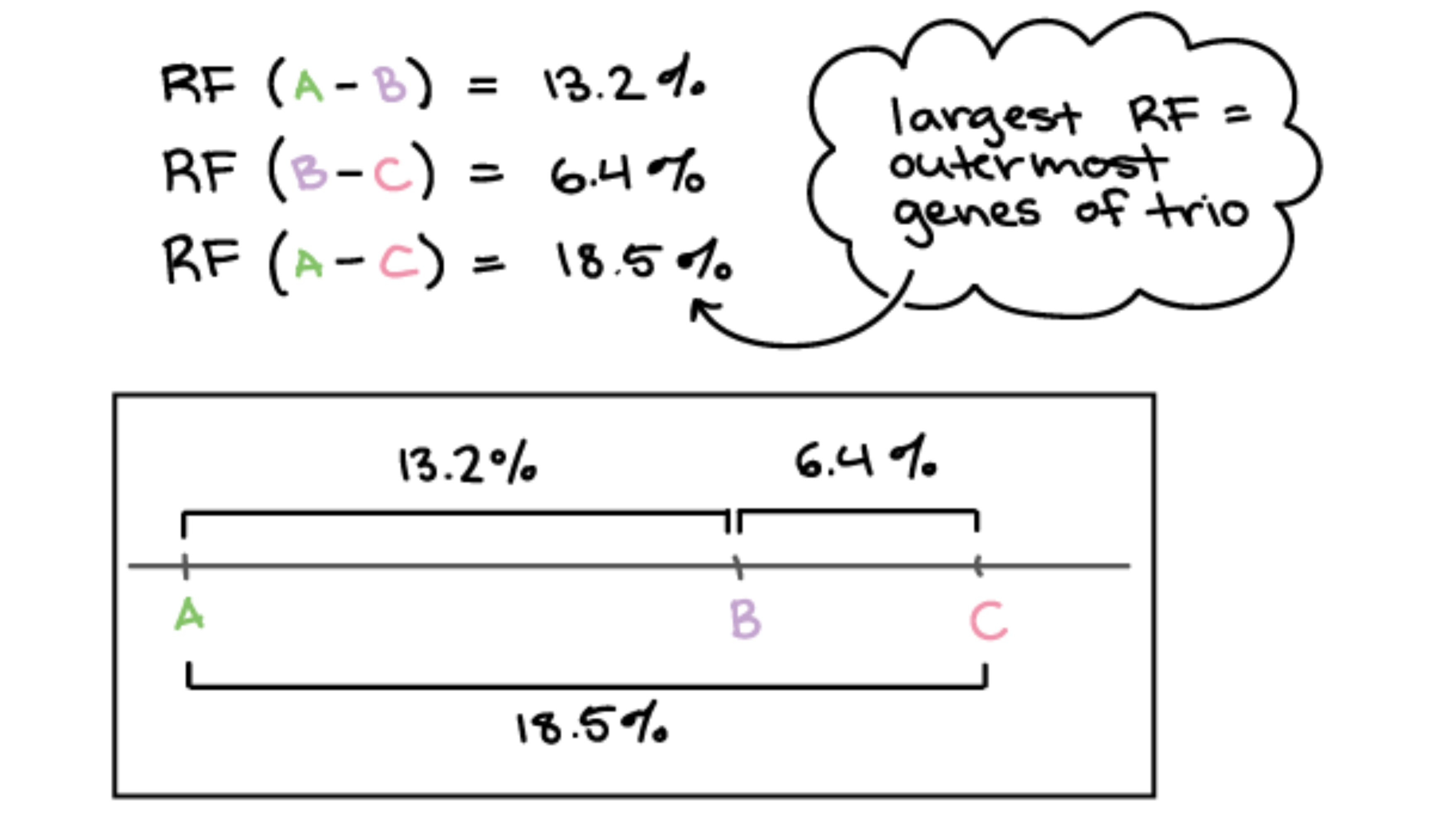
Extra - Gene Mapping
Ex.
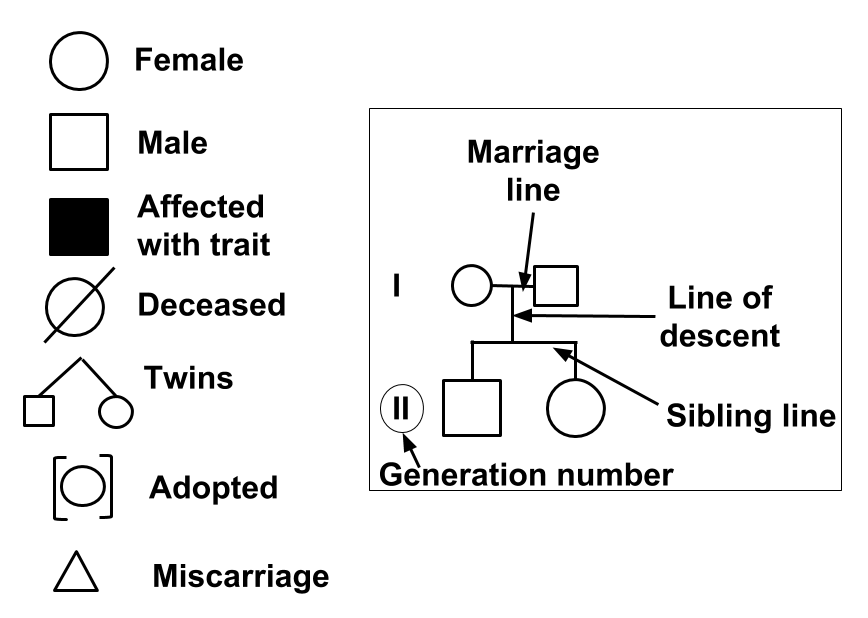
Extra - Pedigree Information
Ex.
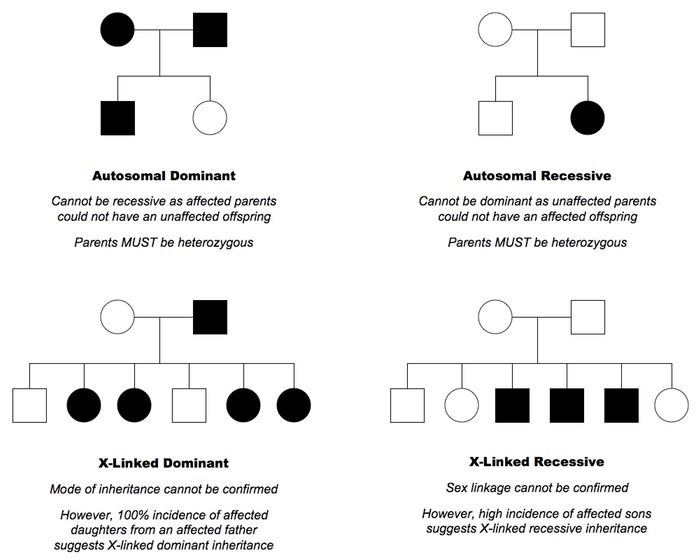
Extra - Types of Pedigrees
Ex.
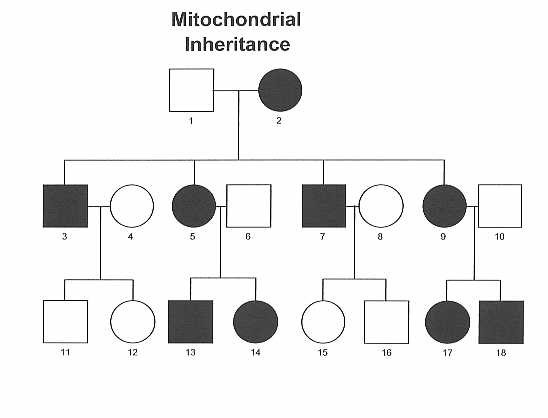
Extra - Non-nuclear inheritance/ Mitochondrial Inheritance
Ex.
Extra - Chi Squares
Ex.
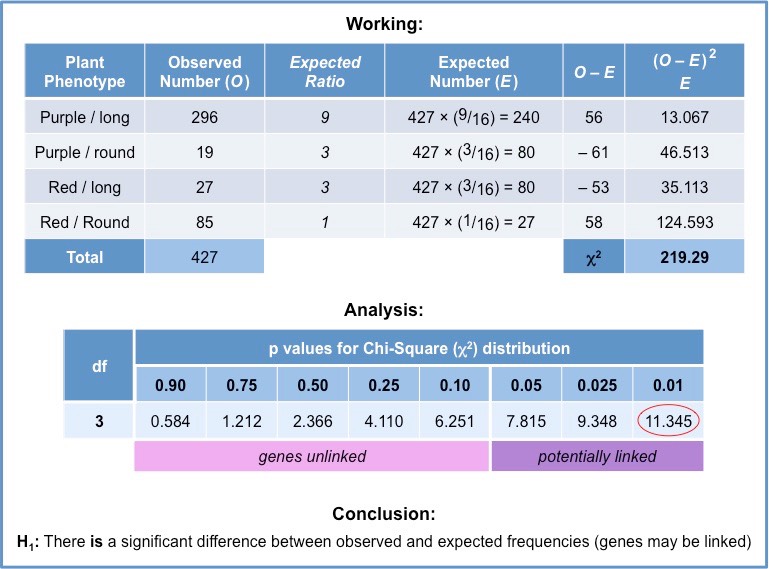
Extra - Chi Squares Null Hypothesis
There is no relationship between expected and observed.
Extra - Phenotype Plasticity
Ex.
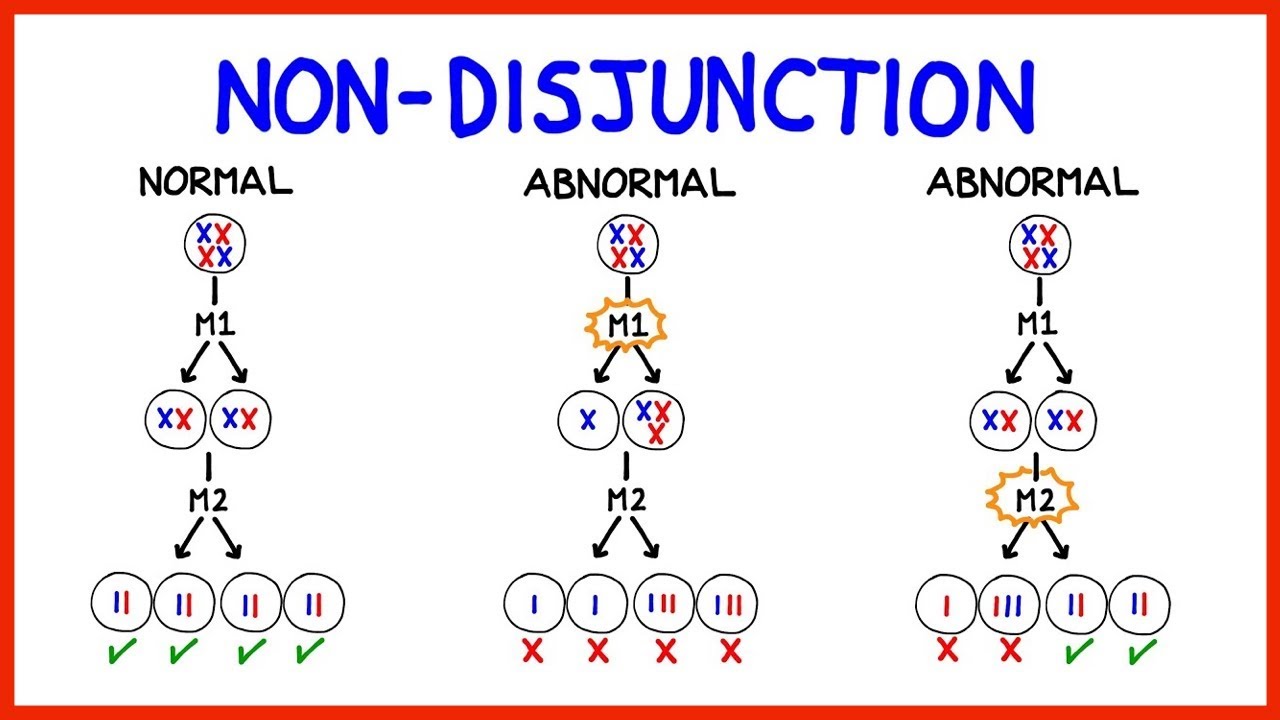
Extra - Nondisjunction Examples
Ex.