Enzymes
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What is the word for enzymes speeding up reactions?
They are catalysts
Because enzymes are found in living organisms, what are they called?
Biological catalysts
What does intracellular enzyme mean?
Because they are found inside cells
How does catalase work?
It binds the toxic molecule hydrogen peroxide and speeds up its breakdown to the harmless molecules water and oxygen
What is amylase? What is its job?
Produced in the pancreas and released into small intestine.
It’s Job is to catalyse the breakdown of starch molecules into the disaccharide maltose. Which is then broken down by other enzymes into glucose which is absorbed into the bloodstream
What is an extracellular enzyme?
An enzyme that is found outside cells – e.g. amylase
What do enzymes call a sub substrate attached to the active site?
Scientist call this an enzyme-substrate complex
How is the enzyme complementary to the substrate?
The tertiary structure of the active site is complementary to the structure of the substrate
What happens once the substrate binds to the enzyme?
The amino acids on the surface of the active site conform temporary bonds of the substrate molecule – the enzyme then catalyse the reaction to form the enzyme product complex
What happens after a enzyme product complex is formed?
Products are released from the active site
Molecules must have a certain amount of energy before they react – what is this certain amount of energy called?
Activation energy
How do enzymes increase the rate of reaction?
They provide a pathway for the reaction with a lower activation energy barrier – in the presence of an enzyme activation energy barrier is lower than it would be without the enzyme– Means more substrate molecules now have enough energy to cross the activation energy barrier and react
What did scientists think when they first began to look at enzymes?
They thought tertiary structure of active site is fixed and does not change shape – substrate molecule slots perfectly into the site
What did they call this hypothesis?
Lock and key hypothesis
What is the induced fit model – correct model?
Siri, the tertiary structure of active site changes as the substrate molecule approaches. As substrate starts to form bonds with the amino acids in the active site tertiary structure of the enzyme adjust so the active site itself tightly around the substrate.
What does the change in the tertiary structure of the enzyme ensure?
The active site fits perfectly into the substrate – bonds that substrate forms with active site help to catalyse reaction
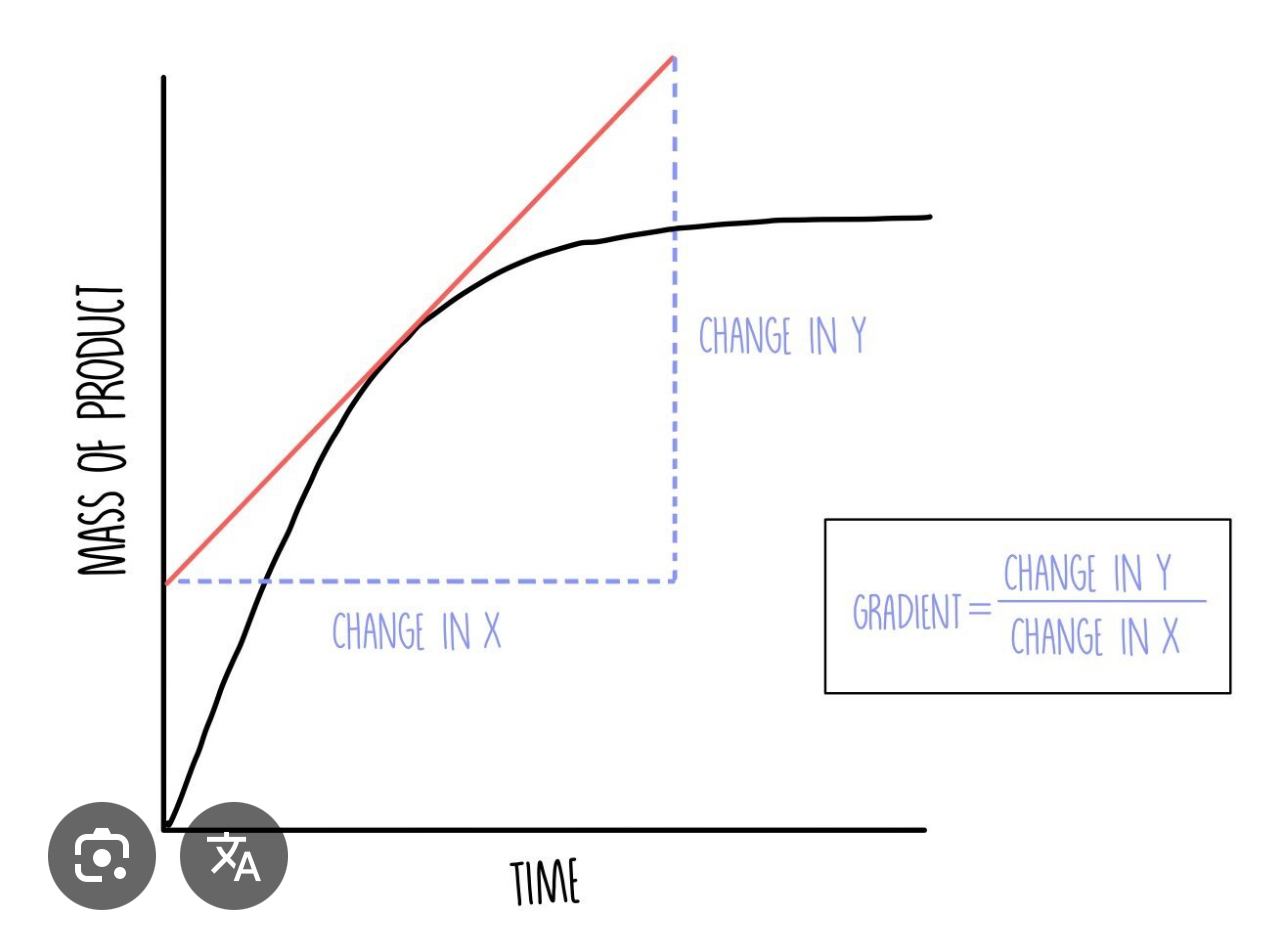
Amount of product formed at different times graph
Line is steep up start – large amount of product is produced in a short amount of time – rapid rate of reaction
Line becomes less steep – less amount of product being formed– Rate of reaction is decreased – reaction slowing down
Line is horizontal at the end – no more product being formed – reaction is stopped
Graph measuring amount of substrate remaining
Rapid initial rate
Reaction slowing down
Reaction stopping
How do you measure the rate of reaction at any point on the graph?
During the tangent to the curve
What does frequency mean?
Number of collisions per second
What does the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction depend upon?
It depends on the frequency of successful collisions between the substrate molecules and the active site.
How to describe shape of this graph?
at the start large amount of substrate molecules which means there is a high frequency of successful collisions between the substrate and the active site – rapid initial rate reaction
As a reaction takes place some substrate is converted to product – amount of substrate molecules force so chances of substrate molecules collide with active site decreases which makes the reaction slow down
Eventually, all of the substrate molecules have been converted to product. There are no more substrate molecules left to collide with the active side and the reaction stops.
Effective temperature on the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction graph shape
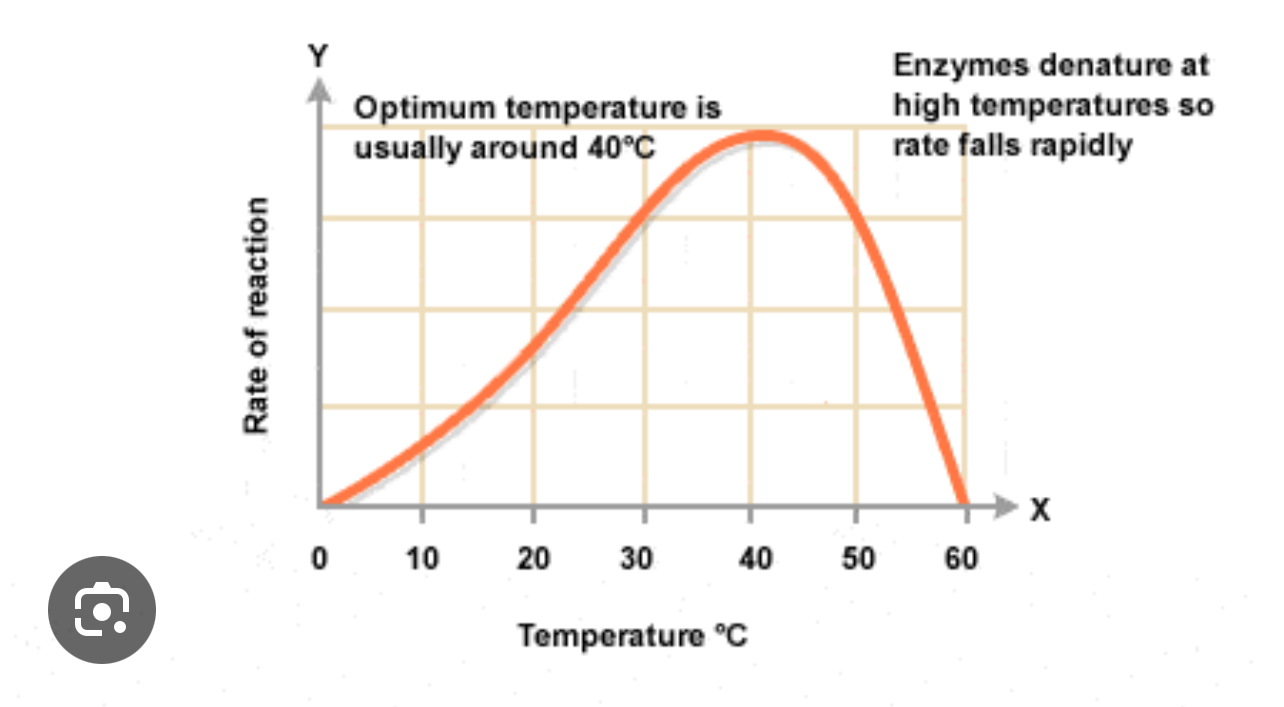
Why does the rate increase as we increase the temperature?
Because we are increasing in the kinetic energy of the enzyme and the substrate – they move more rapidly so the chance that the substrate will collide with the active site increases – increases the frequency of collisions between the substrate and the active site causes the rate of reaction to increase
What is the optimum temperature?
When the reaction rate is at its maximum – optimum frequency of collisions between the substrate and the active site
What is the optimum temperature for human enzymes?
~40°
Why does the rate of reaction decrease after the optimum temperature?
At higher temperatures enzyme molecules are vibrating more rapidly – vibrations causes bonds within enzymes such as hydrogen bonds to break – tertiary structure changes. As the active site changes, it becomes no longer complementary to the substrate.
At what point does the enzyme denature?
When the substrate can no longer fit into the active site
When an enzyme denatures due to high temperatures, can it re-nature?
No
Why can it not be re-natured?
Because the test structure has changed so much that it cannot be reversed
What is temperature coefficient?
(Q10) = Rate of reaction at temperature X+10°C/ Rate of reaction at temperature X
what does the pH of a solution depend on?
The concentration of hydrogen ions
What does a high concentration of hydrogen ions mean?
Low pH - Acidic
What does a low concentration of hydrogen
High pH - Alkaline
What happens if the pH changes away from the optimum pH?
Rate of reaction decreases
How was the rate of reaction decreased?
Hydrogen ions can bond with the R groups of amino acids in the protein – Include amino acids in the active site which form temporary bonds with the substrate – prevents R groups from bonding with the substrate – Reducing rate of reaction
How can changing the pH brake Bonds which are essential for the enzymes tertiary structure?
Hydrogen ions bond with R groups on amino acids in the rest of the enzyme molecule – can break bonds holding to restructure together.
What is the rate of an enzyme catalysed reaction directly proportional to?
The rate of an enzyme catalysed reaction is directly proportional to the substrate concentration – if we double the substrate concentration then the rate of reaction also doubles.
What is Vmax?
Where the rate stops increasing any further – the enzyme is working at its fastest rate
What does saturated mean?
At any given time every active site will be colliding with a substrate molecule. If we add more substrate then there will be no free active sites for the extra substrate molecules to collide with – any increase in substrate concentration will not increase the rate of reaction any further.
What happens when a competitive inhibitor binds to the active site of an enzyme?
The competitive inhibitor has a similar but not identical structure to the substrate so when it binds to the active site, no reaction takes place - After a short time, molecule leaves active site
How does the effect of this molecule reduce the rate of reaction?
By occupying the active site, the molecule prevents the actual substrate from colliding with the active site – frequency of collisions between substrate and active site is reduced
How can we reduce the effect of a competitive inhibitor?
By increasing the concentration of the substrate – Greater chance that the substrate molecule will occupy the active site rather than competitive inhibitor.
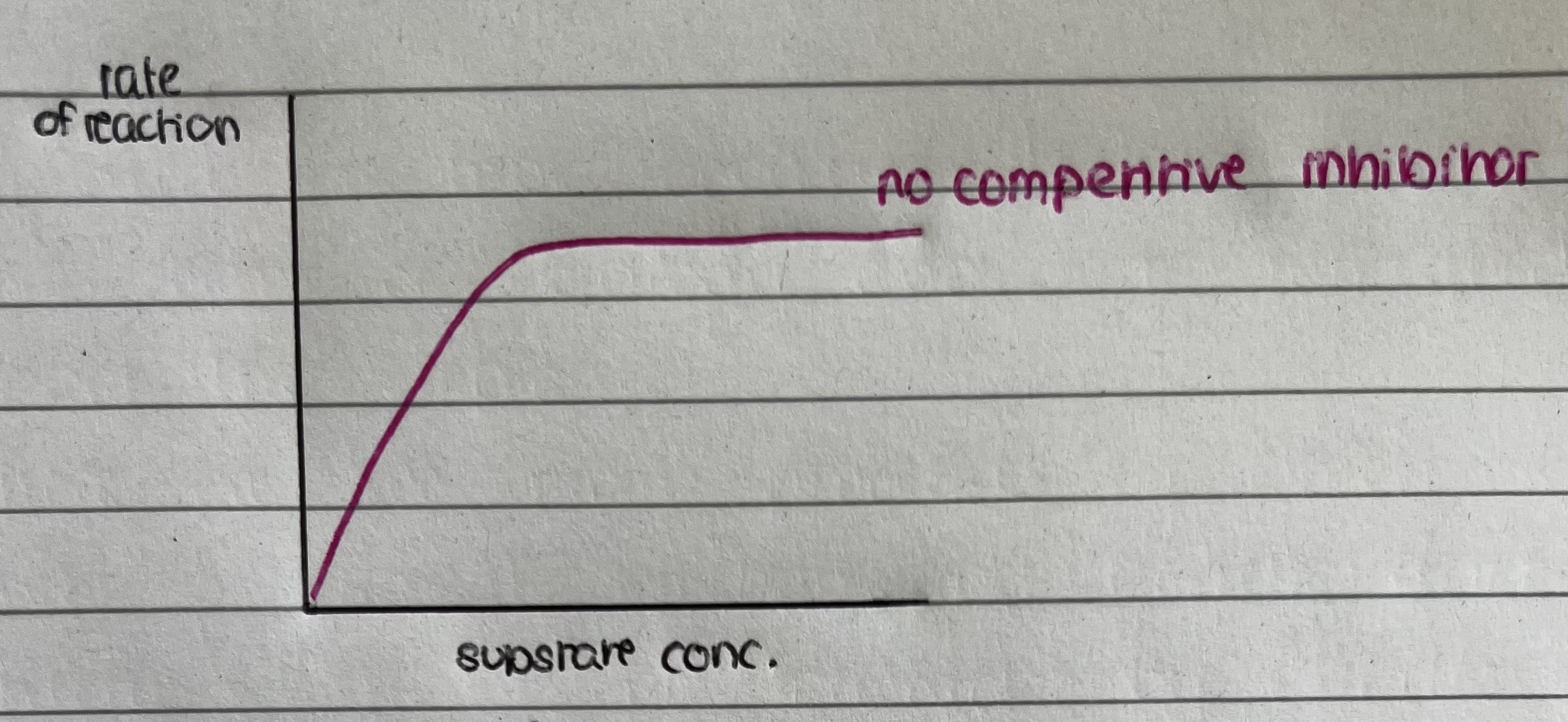
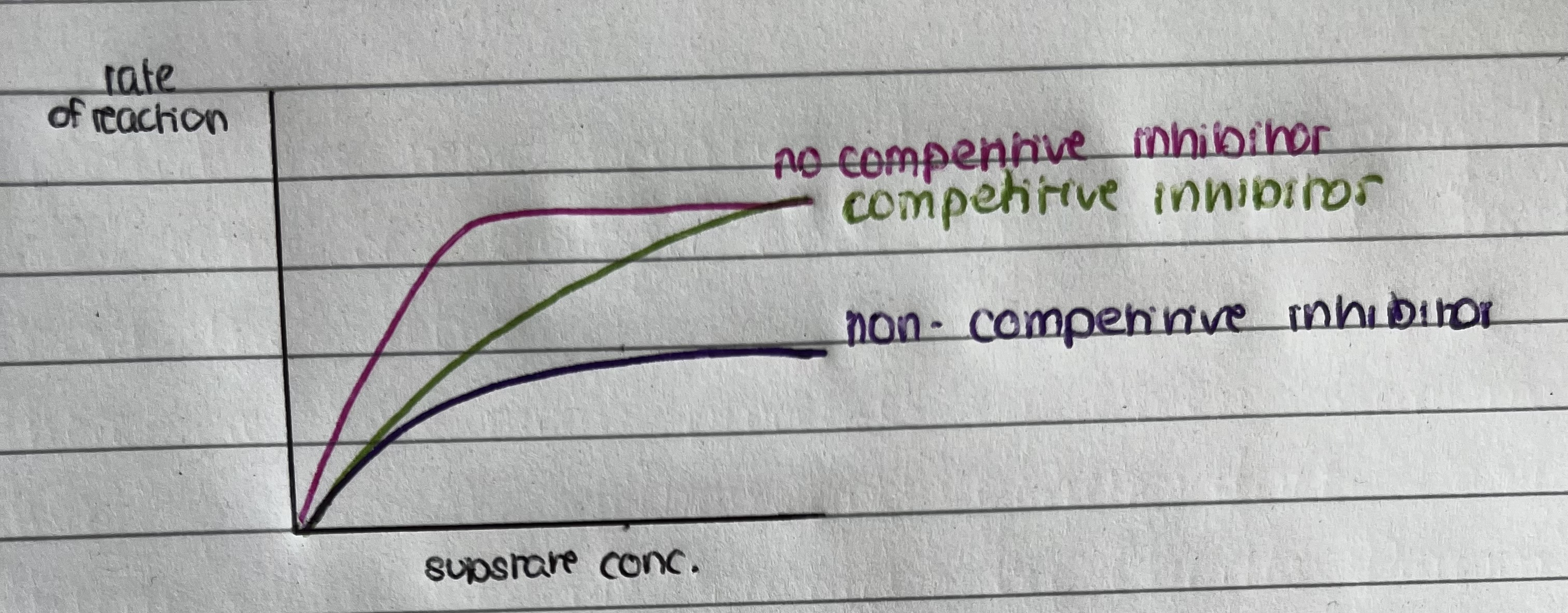
Graph showing enzyme in the absence of a competitive inhibitor
as the substrate concentration increases the rate increases in proportion – at certain substrate concentration rate no longer increases – all active sites are occupied so rate is at its maximum (Vmax)
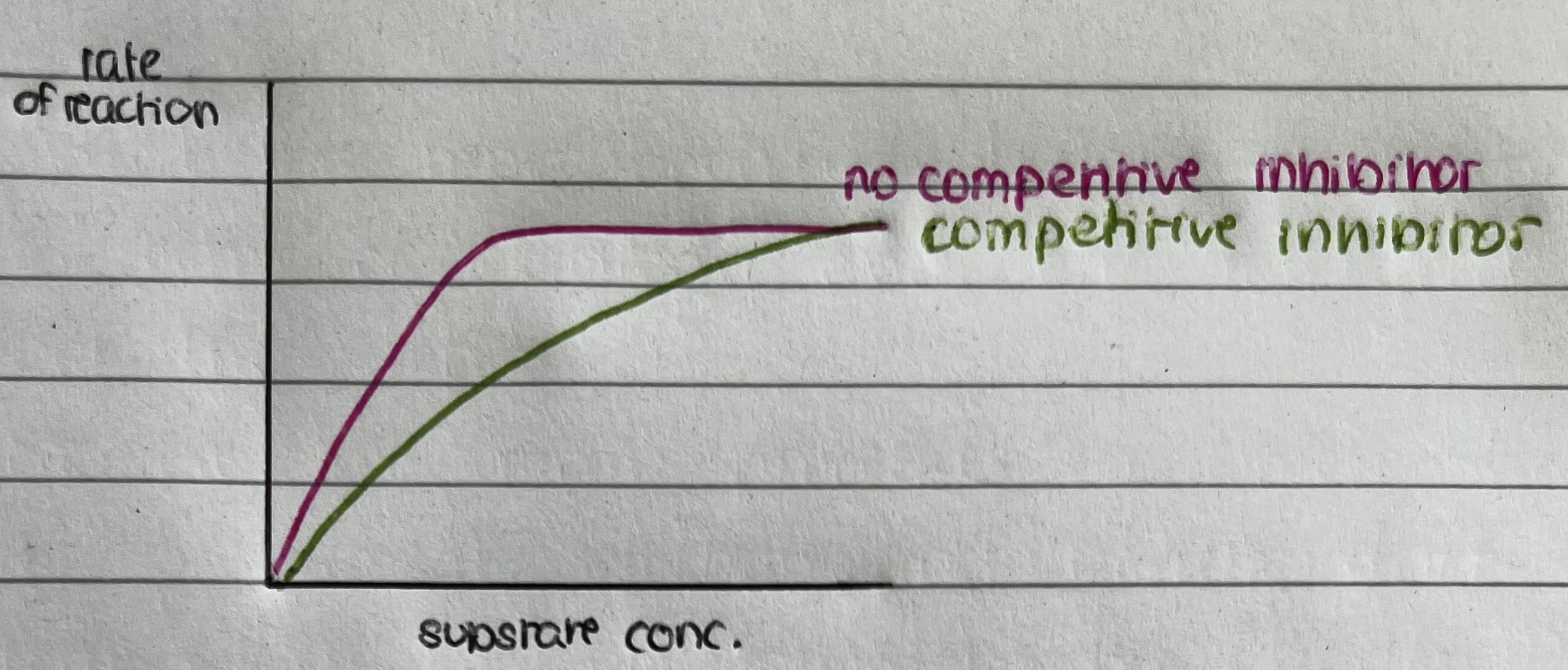
Graph showing effect of competitive inhibitor
Increasing the rate of substrate concentration decreases the effect of the competitive inhibitor
What is an irreversible competitive inhibitor?
A competitive inhibitor which binds irreversibly to the active site of an enzyme (they bind permanently to the active site) the effect of these inhibitors cannot be reversed by increase the substrate concentration.
What is a non-competitive inhibitor?
Doesn’t bind to the active site of an enzyme, it binds to the allosteric site
What happens when the non-competitive inhibitor binds to the allosteric site of the enzyme?
The tertiary structure of the enzyme changes – shape of the active site changes. It is no longer complementary to substrate and The substrate molecule cannot bind to the active site to form an enzyme substrate complex
What is the effect on the rate of reaction of this?
Rate of reaction decreases
Can the effect of a non-competitive inhibitor be overcome by increasing the substrate concentration?
No
Effect of non-competitive inhibitor on a graph
Even if we increase the substrate concentration, the non-competitive inhibitor reduces the rate of reaction by the same amount- because the non-competitive inhibitor causes shape of the active site to change.
What is the metabolic pathway?
A series of reactions all catalysed by enzymes, product made by first enzyme uses the substrate for the second enzyme…
Why does the cell use end product inhibition?
E.g. an amino acid made by this pathway will be needed when the cell is synthesising proteins. Under certain conditions protein synthesis can be slowed down now the cell will not require large amounts of the amino acid. If the pathway is allowed to run at its normal rate than the amino acid will build up in the cell – waste valuable resources like energy. Cell needs to reduce the rate of the whole metabolic pathway where it uses end-product inhibition.
What happens during end product inhibition?
The final products in the pathway inhibits an early stage enzyme. Effect of this is to reduce rate of metabolic pathway. If the amino acid attaches to an inhibits enzyme one because this is so early on in the pathway the rate of the whole pathway is reduced
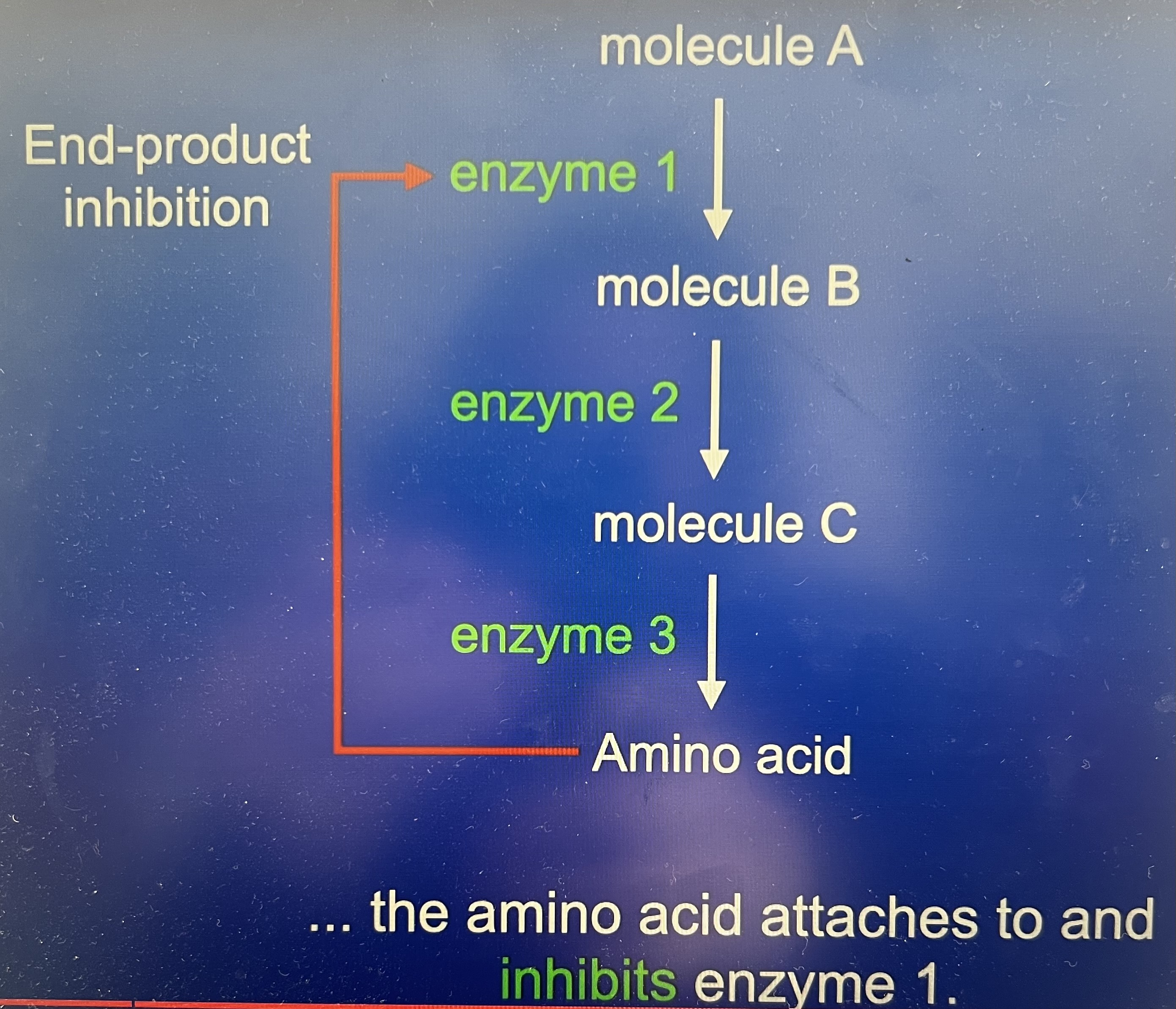
What is end-product inhibition and example of?
Negative feedback – used to keep levels of key molecules within a set range and if the level varies then end products inhibition brings the level back into the range
What is end product inhibition an example of? (Competitive)
It is an example of a non-competitive inhibitor – end product inhibition takes place through the allosteric side of an enzyme
What is a cofactor?
When an enzyme functions in partnership with another chemical (Cofactor)
what is amylase?
Found in the digestive system where catalyses the hydrolysis of starch to the disaccharide maltose.
What are the substrates for amylase?
Starch and water
What has to happen for this reaction to take place? What is the cofactor?
A chloride iron has to attach to the Amylase molecule. Chloride acts as the cofactor.
When a cofactor is a large organic molecule, what do they call it?
Coenzyme
What is a permanent part of the enzymes structure called?
Prosthetic group