EBD RESEARCH DESIGN II
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
what is a systematic review (what does it aim to do)
systematic review: aims to identify, select and synthesise all research published on a particular question or topic
systematic reviews adhere to… based on…
ideally they provide… about…
systematic reviews adhere to a strict scientific design based on pre-specified and reproducible methods
ideally they provide reliable estimates about the effects of interventions (prevention/ treatments)
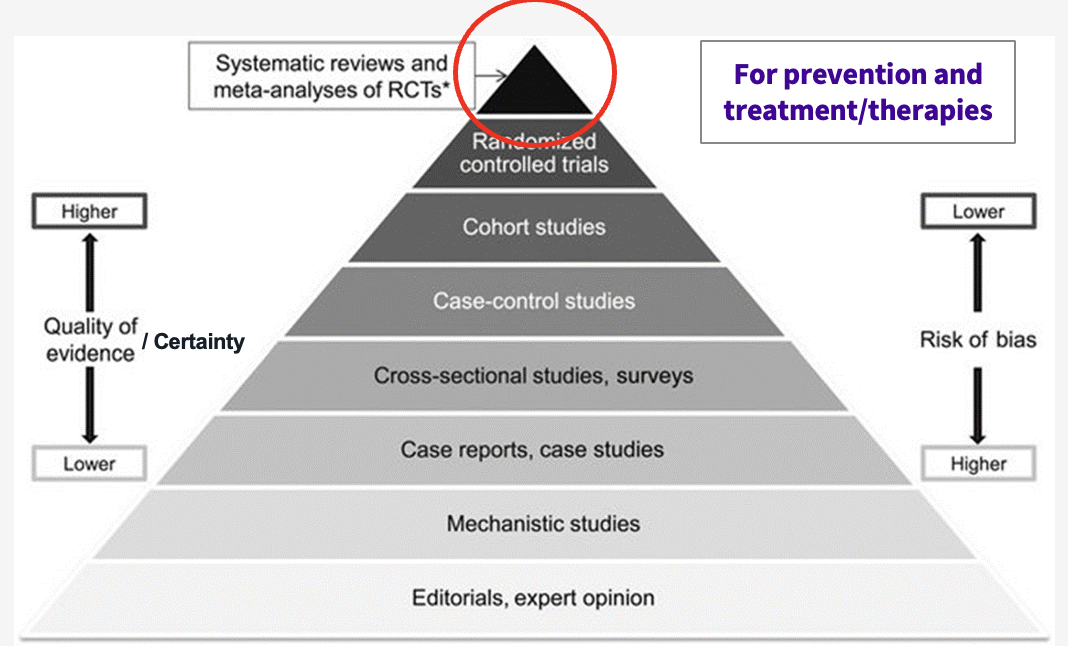
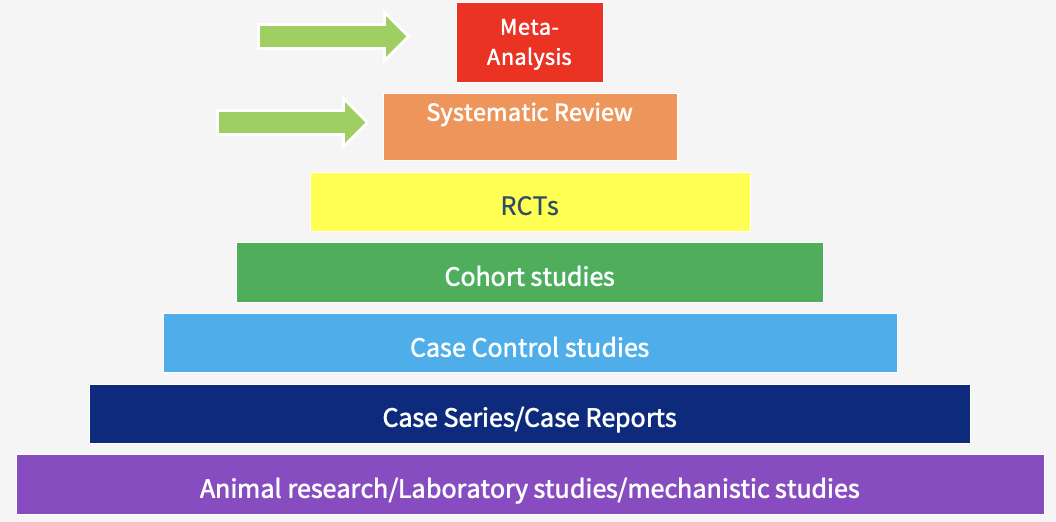
not all systematic reviews include a ____-________
not all systematic reviews include a meta-analysis
not all systematic reviews only include __________ ___________ ______
not all systematic reviews only include randomised control trials (unavailable/ inappropriate)
why are systematic reviews useful
find results of research (fairly) quickly - long procedure
assess validity, applicability and implications of results
guides reviewers to report work explicitly and concisely
advantages of systematic reviews
structured
rigorous
well-defined
each stage is peer reviewed
kept up to date
hence a key tool in EBD
which organisations undertake high quality reviews
Cochrane
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD)
York University
others e.g. Campbell (Canada)
how are systematic reviews undertaken
independently - not as stringent as organisational ones
Cochrane

Cochrane background
founded in memory of Archie Cochrane (British epidemiologist)
Cochrane centre opened in Oct 1992
52 specialist groups
Oral Health Group started June 1994
currently based at Manchester University
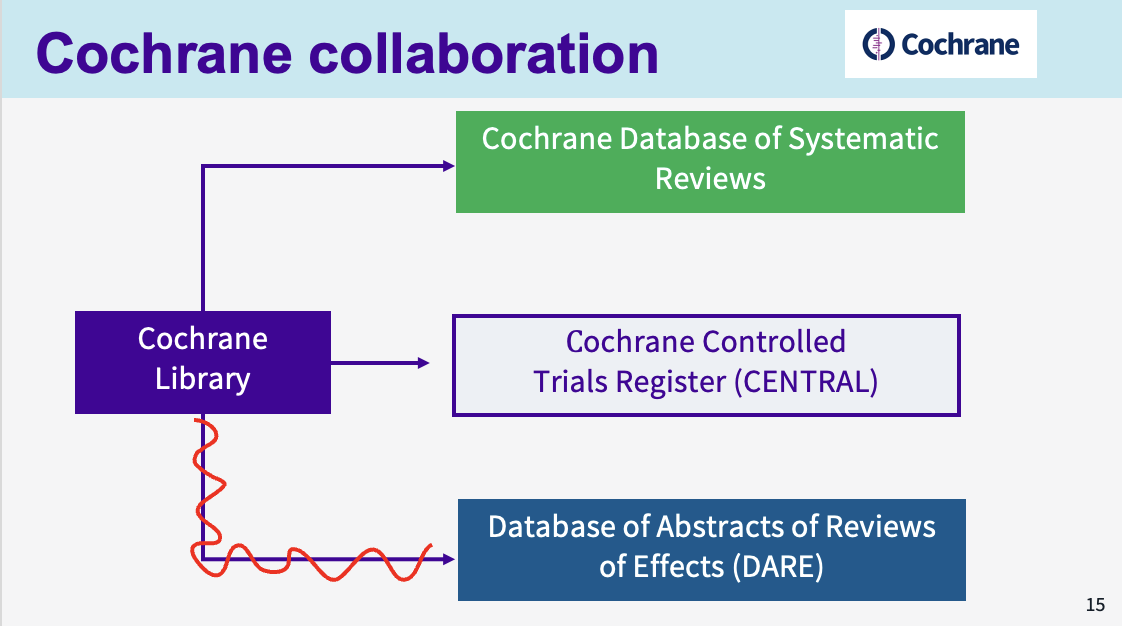
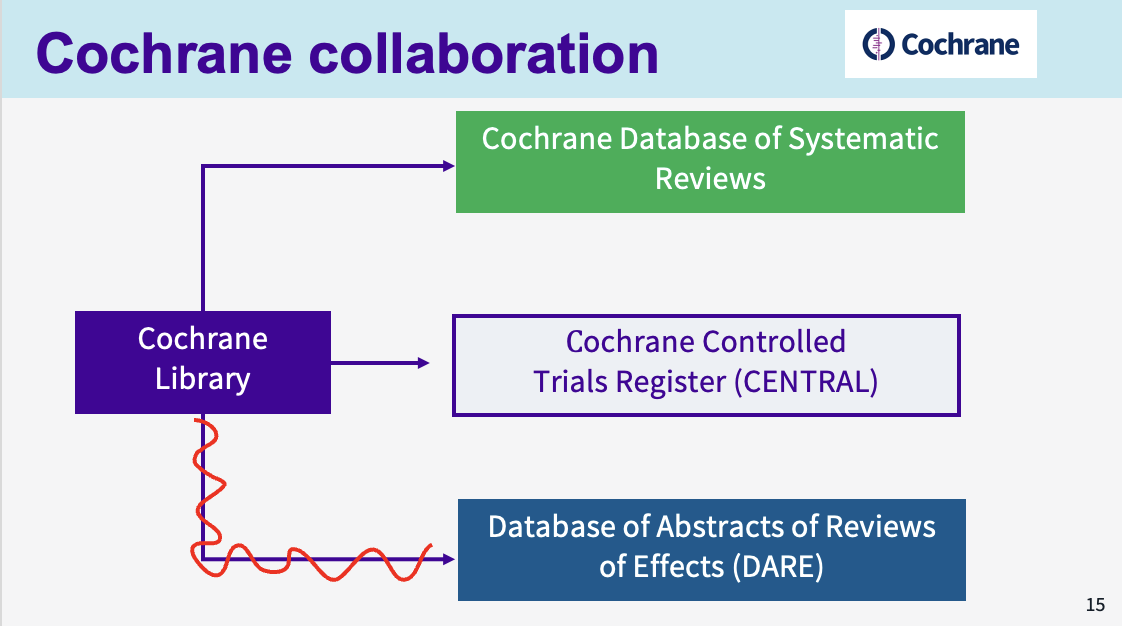
what is the aim of the Cochrane Oral Health Group
the COHG aims to produce systematic reviews which primarily include all randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of oral health
what does ‘oral health’ include
prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of oral, dental and craniofacial diseases and disorders
there are currently how many completed systematic reviews related to dentistry and oral health
219 completed systematic reviews related to dentistry and oral health
there are currently how many protocols related to dentistry and oral health
41 protocols related to dentistry and oral health
Cochrane systematic review order of sections

what does the ‘Text of review’ section include (12)

what does PRISMA stand for
Preferred Reporting in Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis
what is PRISMA
a method of ‘Search strategy for identification of studies’ (included in ‘Text of review’)
very strict
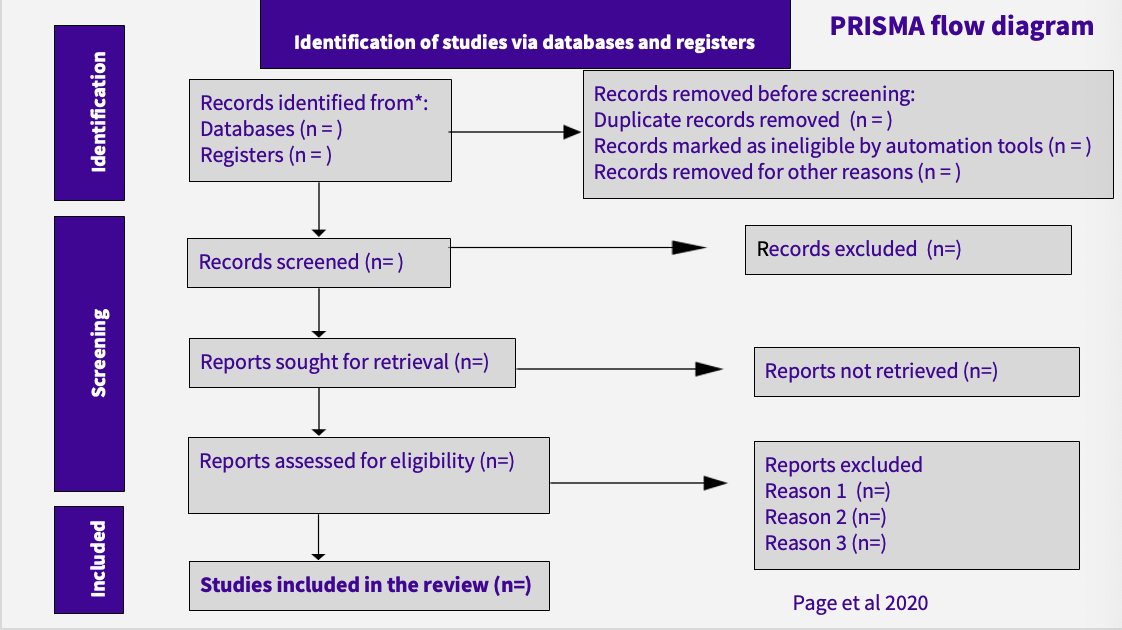
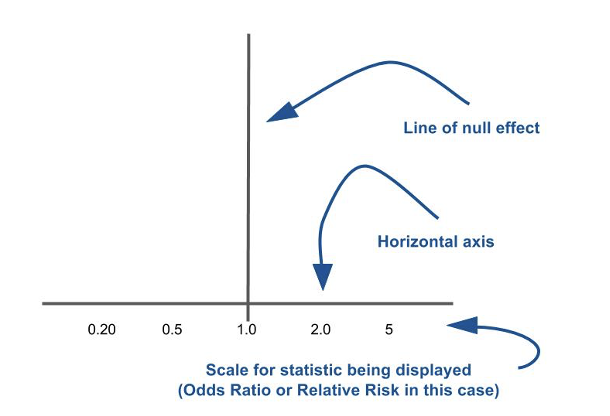
what figure appears in the ‘Results’ section of a systematic review
forest plots
what is a forest plot
forest plot: a graphical representation of the findings of multiple studies that investigated the same scientific question and measured the same outcome
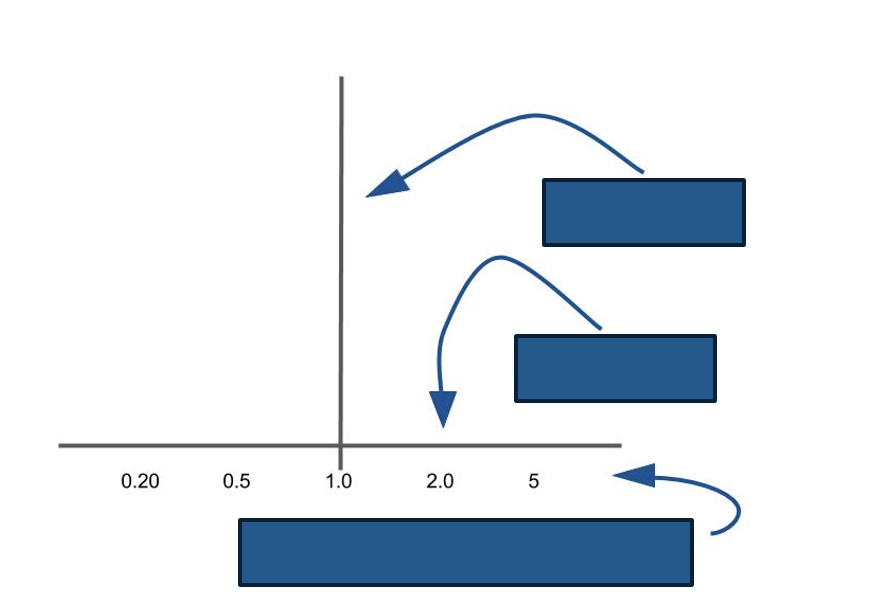
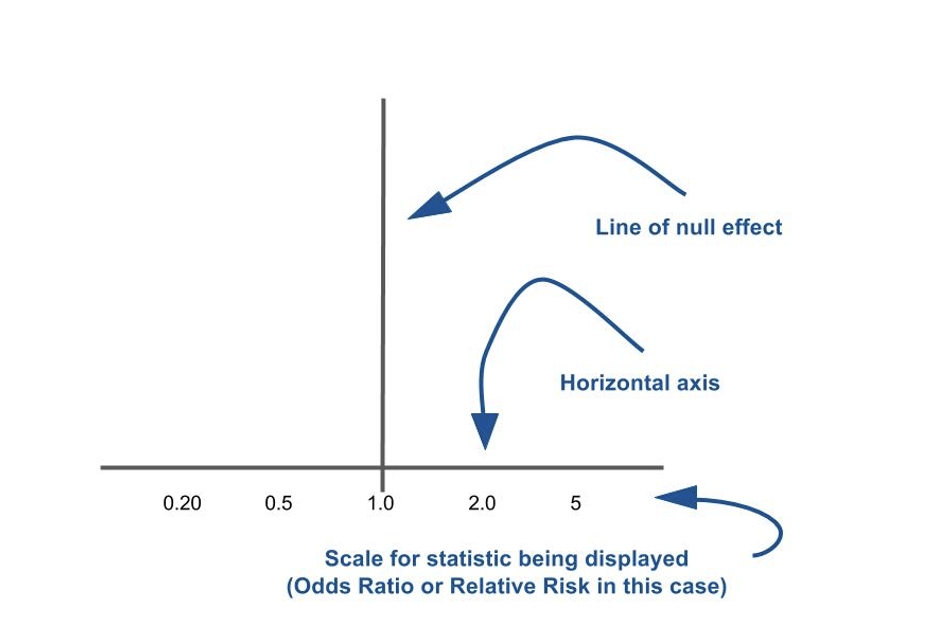
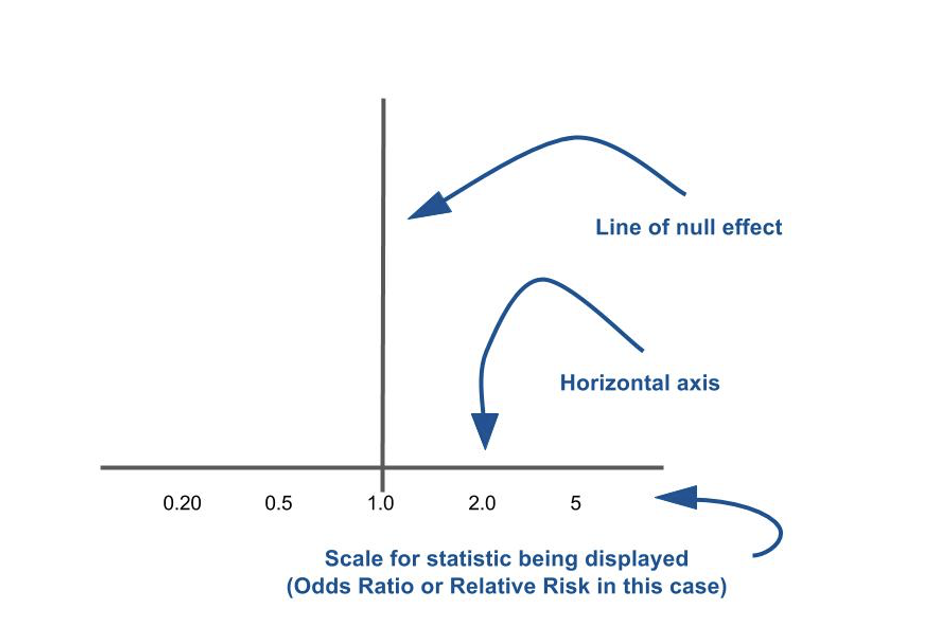
what is the significance of the line of null effect
when comparing two things if the result is on/ around this line there is no difference between them
![<p>what do the numbers in [ ] on the right hand side signify </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c1bf2255-c68f-4007-a8a1-46c07ac09941.png)
what do the numbers in [ ] on the right hand side signify
the confidence interval in numerical form
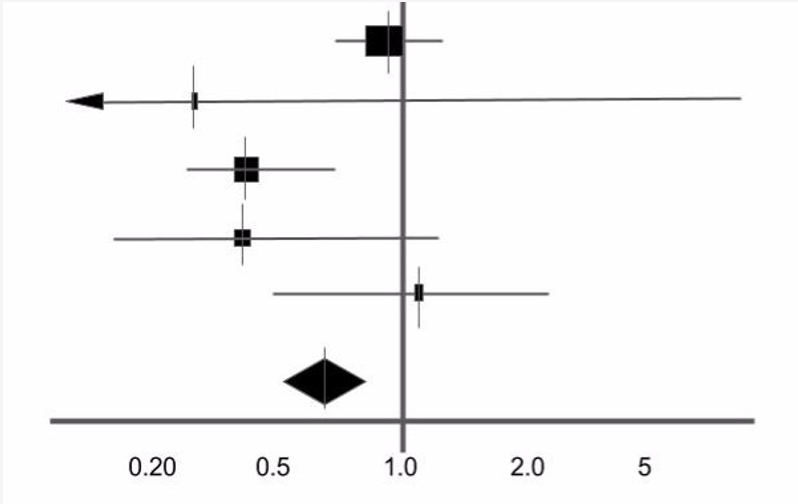
label the point estimate and the horizontal line
point estimate = purple lines
horizontal line = red line
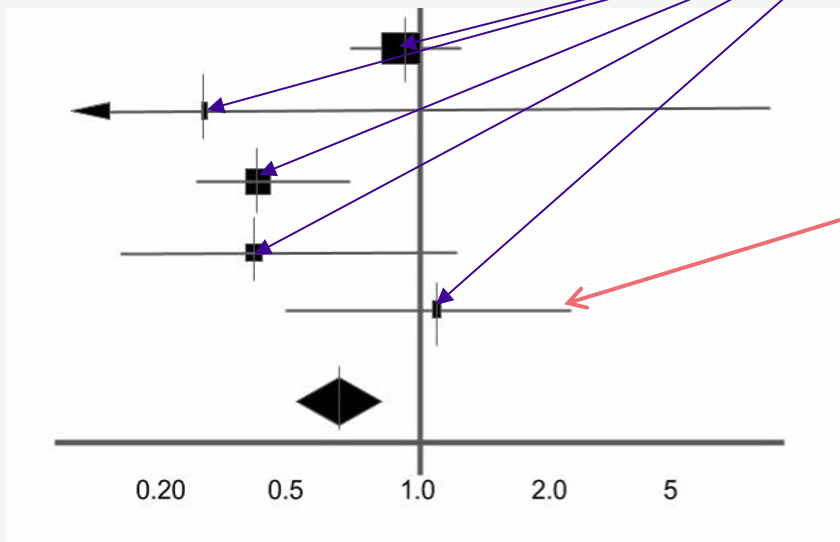
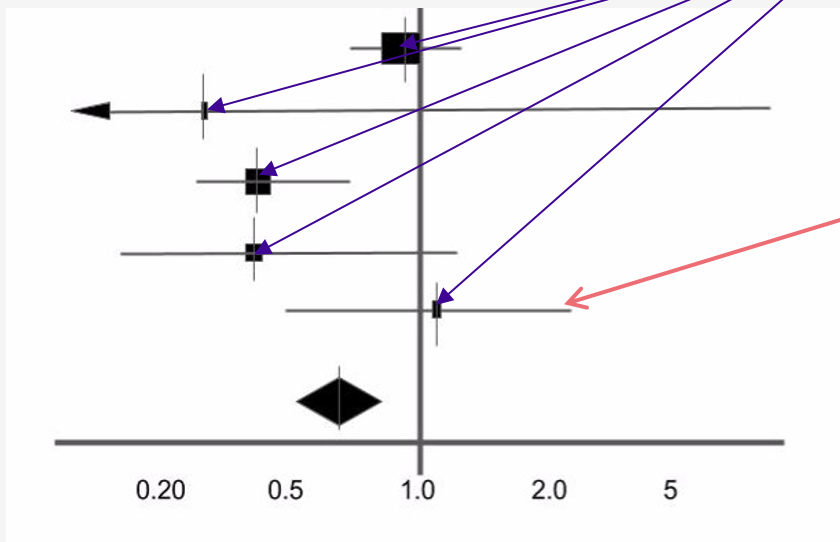
what does the point estimate represent
point estimate
the effect size identified in each study
the size of the box represents the size of the study in terms of participants
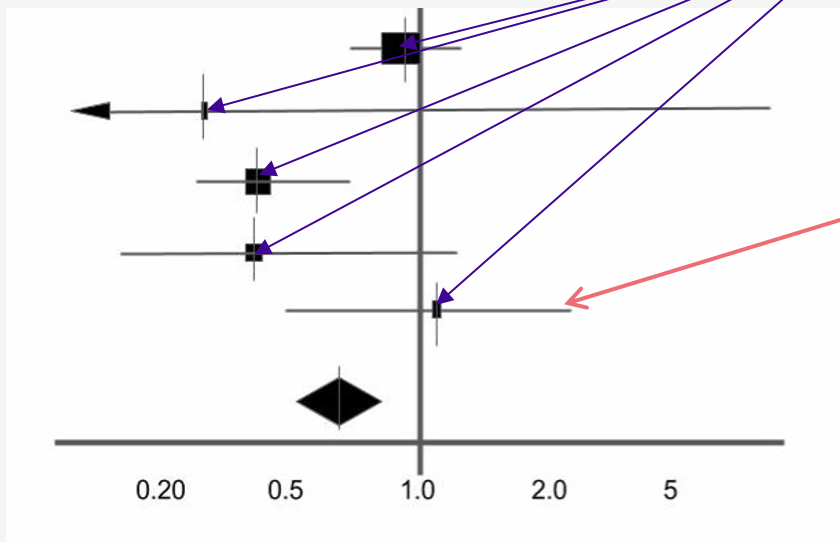
what does the horizontal line represent
horizontal line
95% confidence interval of the study result
i.e. the range of values within which you can be 95% certain the true value lies
the longer this line the less precise the findings are
if a line crosses the line of null effect what does it say about the result
the result is not statistically significant
the ______ the study the _______ the confidence interval and the ______ the point estimate
the bigger the study the smaller the confidence interval and the bigger the point estimate (greater precision of results)
the ______ the study the _______ the confidence interval and the ______ the point estimate
the smaller the study the larger the confidence interval and the smaller the point estimate (less precision of results)
what is a meta-analysis
meta-analysis: the statistical combination of results from two or more separate studies
what are advantages of meta-analyses
improvement in precision
ability ot answer questions not posed by individual studies
opportunity to settle controversies arising from conflicting claims
what are most methods of meta-analyses
most methods of meta-analyses are variations on a weighted average of the effect estimates from different studies
when was fluoridated toothpaste introduced
1974
which demographic do most studies of benefits of water fluoridation target
children
what do studies on water fluoridation show
water fluoridation is effective in preventing decay in children
^ studies are mainly before 1975 - still relevant today?
update confirms the effect is smaller now (Iheozor-Ejiofor et al. 2024)
there is no credible evidence of adverse effects other than dental fluorosis (Systematic Review of Public Water Fluoridation done by the University of York)
what are other adverse effects of water fluoridation patients may be worried about
bone cancer - osteosarcoma
damage to the brain - affects the pineal gland
causes arthritis problems
increase risk of hip fractures and other bones
lowers IQ
reproductive problems
affects thyroid function
damage to bone
non-IQ neurotoxic effects
when would it be inappropriate to do a meta-analysis
different methods are used in studies
different outcome measures are used
» heterogeneity of methods and outcomes
if it was inappropriate to do a meta-analysis what should be done instead
narrative synthesis - summarise and aggregate findings where possible
highlights weaknesses in evidence
makes recommendations for future research
what is the checklist for systematic reviews
Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP)