Lecture 16: Angiosperms
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
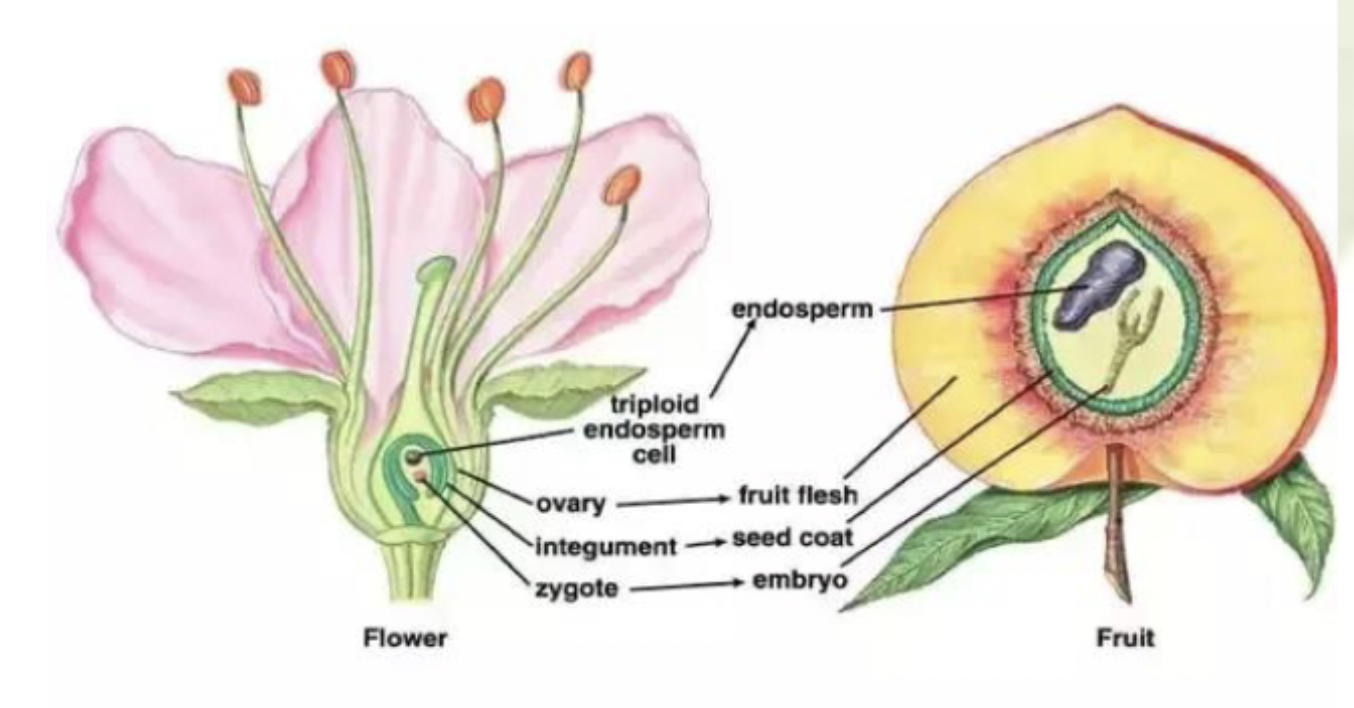
Flower
structure of modified leaves—>some are sporophylls
basis of modern taxonomy
grouping together species with similar floral characteristics
Fruit
seed bearing structure, ovary tissues encircle the ovule
angio=case
sperm=seed
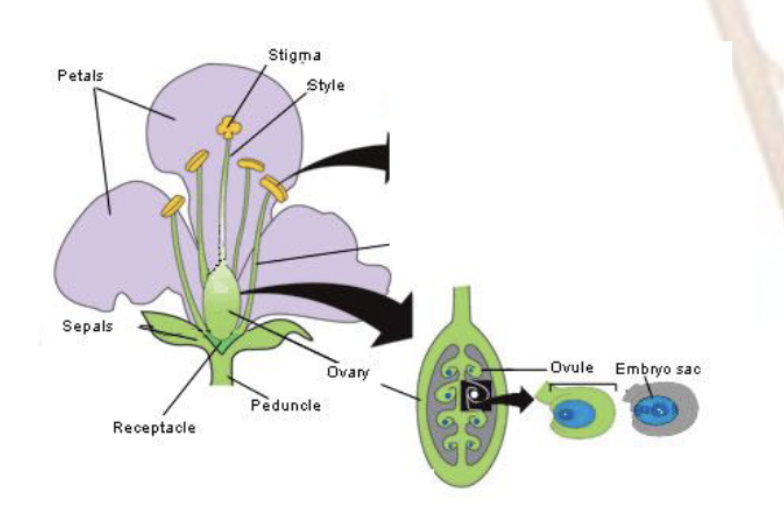
Ovary
tissues that encircle the ovule
Albian-Aptian gap
Dominant plant Gymnosperms-Angiosperms (over 35 MY)
soil condition changed to favor angiosperm species
gymnosperms are limited to more extreme environments where angiosperms can’t thrive
angiosperms have short growing seasons so won’t do well in cold areas
Angiosperm Dicots
aka eudicots (largest group)
Characteristics:
2 cotyledons (upon germination)
netted venation in leaves
Unique organization of stem, root, leaf tissues
taproot mainly
flower petals in multiples 4-5
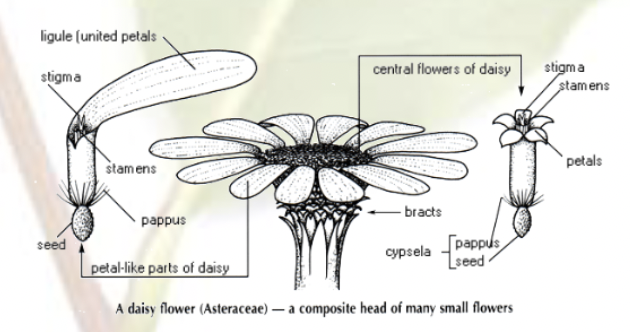
Dicots: Asteraceae
Sunflower family
largest plant family
Flower shape:
radially symmetrical
petals are modified smaller flowers with ovules
Dicots: Fabaceae
legume family- 3rd largest
Fruit shape:
bean “pod” (called legume)
any plant with legume=Fabaceae family

Legume
bean “pod”
Dicots:Cucurbitaceae
Cucurbit family
some are important commercial crops!(melon, cucumber, squash)
Fruit characteristics:
three chambers with row of seeds on the interior

Cucurbit
fruit structure: 3 chambers with row of seeds on the interior
Dicots: Rosaceae
rose family
many are commercial crops!
almost all fruit trees!
apples, pears, cherries, etc
Flowers:
- radially symmetrical flowers with MANY petals

Angiosperm Monocots
2nd largest group
Characteristics:
1 cotyledon upon germination
parallel venation in leaves
unique organization of stem, root and leaf tissues
fibrous root system
flower parts in multiples of 3
Monocots: Orchidaceae
Orchid family
Characterized by:
showy bilaterally symmetrical flowers
tiny seeds with no endosperm

Monocots: Poaceae
Grass family
Characteristics:
reduced flowers
mainly wind pollination
flowers don’t need to be showy
long, narrow leaves
Apical shoot meristem at the BASE of the shoot
NOT the tip
because herbivores duh
Magnoliid
only one family: Magnoliaceae
Magnoliid: Magnoliaceae
simplified flowers
examples of early angiosperms
Includes magnolias

Basal angiosperms
aka ANITA (acronym of 5 families)
Representative of earliest forms of angiosperms (debatable)
Water lilies and Hellebores
ANITA
Acronym of 5 basal angiosperms families
Amborellaceae
nympheales
austrobaileyales
Male lifecycle
Similar to gymnosperms
single celled microspore produced
microspore undergoes mitosis
forms pollen (multicellular haploid organism)
Difference: fertilization aspect
pollen lands on stigma of flower
Pollen grain germinates
pollen tube extends down style to micropyle
generative cell releases 2 sperm cells
sperm cells=male gamete
Angiosperm lifecycle-Female
VERY different from gymnosperms
after production of initial megaspore
Differs in
presence/absence of archegonia
structures produced by gametophyte
Ovule contents
Most common type of pollination
what is fertilized by sperm cells
Within the flower:
mother diploid cell—>meiosis
4 daughter cells, 3 die, 4th=megaspore
megaspore → mitosis→ DIRECTLY produces female gametophyte
NO archegonia
further mitosis: single egg produced, +other cells to develop seed
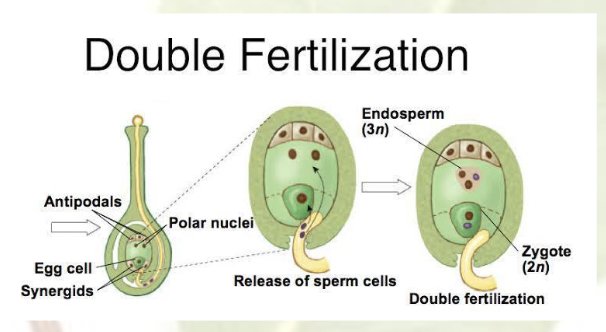
Synergids, antipodals, the central cell with the polar nuclei
Angiosperm Lifecycle
Pollination RIGHT after fertilization
Double fertilization
Each pollen cell releases: 2 sperm cells
One sperm cell
fertilizes egg
becomes zygote
Other sperm cell
fertilizes zygote
becomes endosperm
Stigma
part of male lifecycle
Style