FINAL
1/349
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
350 Terms
What is the principle of Piezoelectricity?
“Some materials, when deformed by an applied pressure, produce a voltage”
What happens when a voltage is applied to a Piezoelectric element? What does this depend on?
Thickness of element increases or decreases
Depends on polarity of voltage
What would happen if a synthetic Piezoelectric element was created and reheated to the Curie point?
Destroys all Piezoelectric properties
What is the fo (operating freq) of a crystal determined by?
Crystal
Propogation speed
Thickness
Operating Frequency (fo) Formula
fo = cPZT / 2 * cth
How are thickness and operating frequency related?
Indirectly
Thin elements = high freq
Thick elements = low freq
What is the sound beam a combination of?
All sound arising from different point-like sources (wavelets) on transducer crystal face
What occurs due to the superposition of all sound waves in the beam?
Natural focusing (narrowing)
How is the shape of the sound beam determined?
Crystals
Axial Plane
Along direction of sound travel
Parallel
Lateral Plane
Perpendicular to direction of sound travel
Elevational Plane
Thickness of sound beam
What produces the width of a sound beam? How is the width determined?
Transducer
The distance from the transducers face
Is intensity uniform throughout a beam? Why?
No
Area varies (intensity = power/area)
How are beam diameter and resolution related?
Inversely
Small beam = good resolution
Large beam = bad resolution
Near Zone
AKA Fresnel zone, near field
Region extending from transducer to minimum beam width
Focal Point
Smallest beam
Maximum intensity
When does a beam have the best resolution?
At the focal point
Focal Zone
Where beam is focused on each side of focal point
Maximum
Sensitivity
Intensity
When does a beam have the best lateral resolution?
At the focal zone
How are diameter and intensity related in the focal zone?
Inversely
Diameter decreases = intensity increases
Diameter increases = intensity decreases
Near Zone Length (NZL)
Distance from transducer face to where the beam has the smallest diameter
Additional focusing can be added
How are diameter and NZL related?
Directly
Increase diameter = increase NZL
Decrease diameter = decrease NZL
How are frequency and NZL related?
Directly
Increase diameter = increase NZL
Decrease diameter = decrease NZL
Far Field Divergence (FFD)
When the beam diameter increases after natural focus
How are diameter and far field divergence related?
Indirectly
Increased diameter = Low divergence
Decreased diameter = High divergence
How are frequency and far field divergence related?
Indirectly
Increased frequency = Low divergence
Decreased frequency = High divergence
At a distance of one near zone length the diameter of the beam is…?
½ the crystal diameter
At a distance of 2 near zone lengths the diameter of the beam is…?
The crystal diameter
What two things does focusing contribute to?
Better resolution (narrow beam)
Stronger beam (decreased area)
A-mode (Amplitude Mode)
Displayed on graph
X-axis = depth
Y-axis = strength
B-mode (Brightness Mode)
2D images, B-scans, displayed on a matrix
Displayed dots with brightness
What does brightness on B-mode show?
Strength
Location
M-mode (Motion Mode)
Displayed on a graph
X-axis = time
Y-axis = depth
What imaging mode is used most used today?
B-mode
What imaging mode is used for cardiac and fetal cardiac?
M-mode
Transducer (Probe)
Device that converts one form of energy to another
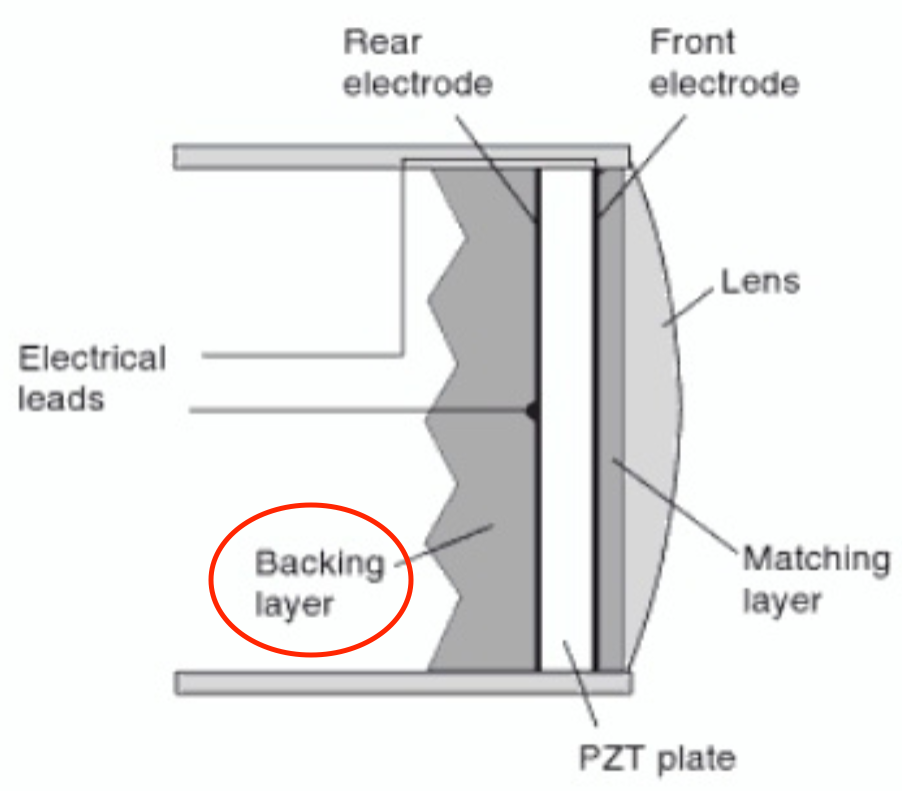
Bandwidth (BW)
Range of frequencies produced by the transducer
How are pulse length and bandwidth diameter related?
Inversely
Short pulses = broad bandwidth
Long pulses = narrow bandwidth
Damping (Backing) Material
Epoxy resin attached to back of element
What does damping material do?
Absorbs vibrations
Reduces #cycles/pulse
How are pulse duration (PD) and spatial pulse length (SPL) related to resolution?
Low PD and SPL = Improved resolution
High PD and SPL = Reduced resolution
How is bandwidth with damping related to quality factor, efficiency, and sensitivity?
Inversely
Increased bandwidth and damping = Decreased QF, efficiency and sensitivity
Decreased bandwidth and damping = Increased QF, efficiency and sensitivity
How are diagnostic imaging transducers damped? How many cycles per pulse does this produce?
Highly damped
2-3 cycles per pulse
How are pulsed-wave Doppler transducers damped? How many cycles per pulse does this produce?
Less damped
5-30 cycles per pulse
How are continuous wave Doppler transducers damped? Why?
Not damped
Reflects all energy into patient
What does quality factor determine?
Sensitivity
What does quality factor detect?
Weak echoes
Quality Factor (QF) Formula
fo / BW
Matching Layer
Located on the transducer face
Has impedance value between crystal and tissue
What does the matching layer do?
Reduces reflection
How are frequency and penetration related?
Low frequency = Improved penetration
High frequency = Reduced penetration
How are penetration and resolution related?
Improved penetration = Reduced resolution
Reduced penetration = Improved resolution
What is a complete scan of the ultrasound beam called?
Frame
What is required for real-time scanning?
Transducer arrays
What means are used for sweeping, steering, and focusing the beam? What is this accomplished by?
Electronic means involving constructive interference
Accomplished by
Sequencing
Phasing
What is the time delay between pulses determined by?
Depth (time it takes for all echoes to return)
Beam Steering
Sweeping the beam
Accomplished with phasing
What does beam steering produce?
Automatic scanning
How are time and beam steering related?
Directly
Increased delay = Increased steering
Decreased delay = Decreased steering
How do you know what direction a beam is going during beam steering?
Beam goes toward side activated last
Right to left = steered left
Left to right = steered right
How are time and focus related during electronic (transmit) focusing?
Inversely
Increased delay of curvature = Closer focus
Decreased delay of curvature = Deeper focus
Linear Array
Straight line of elements
Rectangular image
Vertical, parallel scan lines
What can be done during linear array to produce a parallelogram?
Can be steered to right or left (in Doppler)
Curved (Convex) Array
Curved line of elements
Produces sector image
Pulses travel in different directions from different origins
Phased (Sector) Array
Compact line of elements
Produced pie shaped image
Pulses travel in different directions from same origin
What occurs during phased array?
Voltage pulses applied to entire group of elements with varying time delays = sweeping of beam
Vector Array
Parallelogram-shaped display
What is a 2D array? What can they do?
Matrix of elements
Ability to steer and focus in two dimensions
Allows for focusing in elevational plane by phasing
Name the three spatial categories of resolution
Axial
Lateral
Elevational
What does spatial resolution give us the ability to see?
Detail on an image
What is spatial resolution related to?
Directly related to # of scan lines
Related to # of pixels in a monitor
What size resolution is always better?
Smaller
Less distance between reflectors to be displayed as separate objects
What is axial resolution?
The minimum reflector separation necessary to resolve reflectors parallel to sound beam
What is axial resolution determined by?
SPL
What does LARD stand for? (Has to do with AR)
Longitudinal, Axial, Range, Depth
To improve AR, SPL must be _____
Reduced
As SPL decreases, AR ____
Decreases
As frequency increases, AR _____
Decreases
Does axial resolution change with depth? Why?
No
AR is constant along beam path
What is lateral resolution?
Minimum reflector separation necessary to resolve reflectors perpendicular to beam
What is lateral resolution determined by?
Beam width
Does lateral resolution vary with depth? Why?
Yes
Because of sound beam shape
What does LATA stand for? (Has to do with LR)
Lateral, Angular, Transverse, Azimuthal
Elevation resolution varies with ____ because of the shape of the sound beam
Depth
What is contrast resolution?
The ability of gray-scale display to distinguish subtle differences in echogenicity, or brightness, of adjacent tissues
What is contrast resolution determined by?
Number of pixels in an image
Number of shades of gray displayed in each pixel
What is contrast resolution controlled by?
System’s memory
Dynamic range settings
What is temporal resolution?
Ability to follow moving structures in temporal detail
What is frame rate?
Number of images displayed per second
Faster FR = _____ temporal resolution
Improved
Frame Rate is dependent on… (5 things)
Line density
Lines per frame
Depth & PRF
Sector Width
Number of foci
What is line density?
# of scan lines per degree of sector
# of scan lines per centimeter
What is lines per frame?
# of lines in each frame
More lines = ____ spatial resolution
Improved
How are line density and lines per frame related to FR?
Inversely
____ sector width improves image quaility
Low
Why does a low sector width improve image quaility?
Less tissue interrogated
Less artifacts
Improved signal to noise ratio
Improves contrast resolution
Depth and PRF are ____ related
Inversely
Depth is ____ related to FR
Inversely