Electrical Impulses Lab
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1% of muscle cells?
generate electrical signals that coordinate contractions
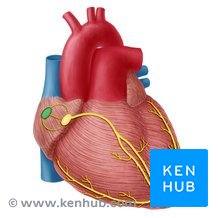
Cardiac conduction system
a system of specialized muscle tissues that conducts electrical impulses that stimulate the heart to beat
Pacemaker
A group of cells located in the right atrium that sends out signals that make the heart muscle contract and that regulates heart rate.
Internodal fibers impulses
Transmits electrical impulses from the SA node to the AV node. modified cardiac muscle cells.
SA node impulses
Specialized cluster of cells that generate electrical impulses. Primary pacemaker of the heart
AV node impulses
slows the electrical impulse from the atria to allow them to fully contract and fill the ventricles with blood before the ventricles themselves contract. It acts as an electrical "gatekeeper" and an intrinsic pacemaker
AV Bundle (His Bundle) impulses
Receives electrical impulses from the AV node and transmits them to the Right and Left bundles
Right and Left bundle branches impulses
Split from the bundle of His and carry electrical impulses to the right and left ventricles
Purkinje fibers impulses
Receives impulses from the right and left bundles, thus rapidly distributing electrical impulses to the ventricular myocardium, ensuring a coordinated and synchronized contraction of the ventricles for efficient blood pumping
Cardiac muscle long refractory period
allows time for the heart to relax and fill with blood after each contraction, preventing tetany and ensuring a rhythmic and effective pumping action
ECG
a test that records the electrical activity of the heart. It measures the heart rate, rhythm, and electrical signals produced by the heart muscle
Atrial systole
Atria contract, pushing blood into ventricles. Ventricles are relaxed
Ventricular systole
Ventricles contract, ejecting blood to the body. Atria relaxed
P
Atrial depolarization
QRS
Atrial repolarization and ventricular depolarization
T
Ventricular repolarization
Order of electric impulses
SA node, internodal fiber, AV node, AV bundle, Right + Left branches, bundle branches, purkinje fibers, myocardium in the ventricles
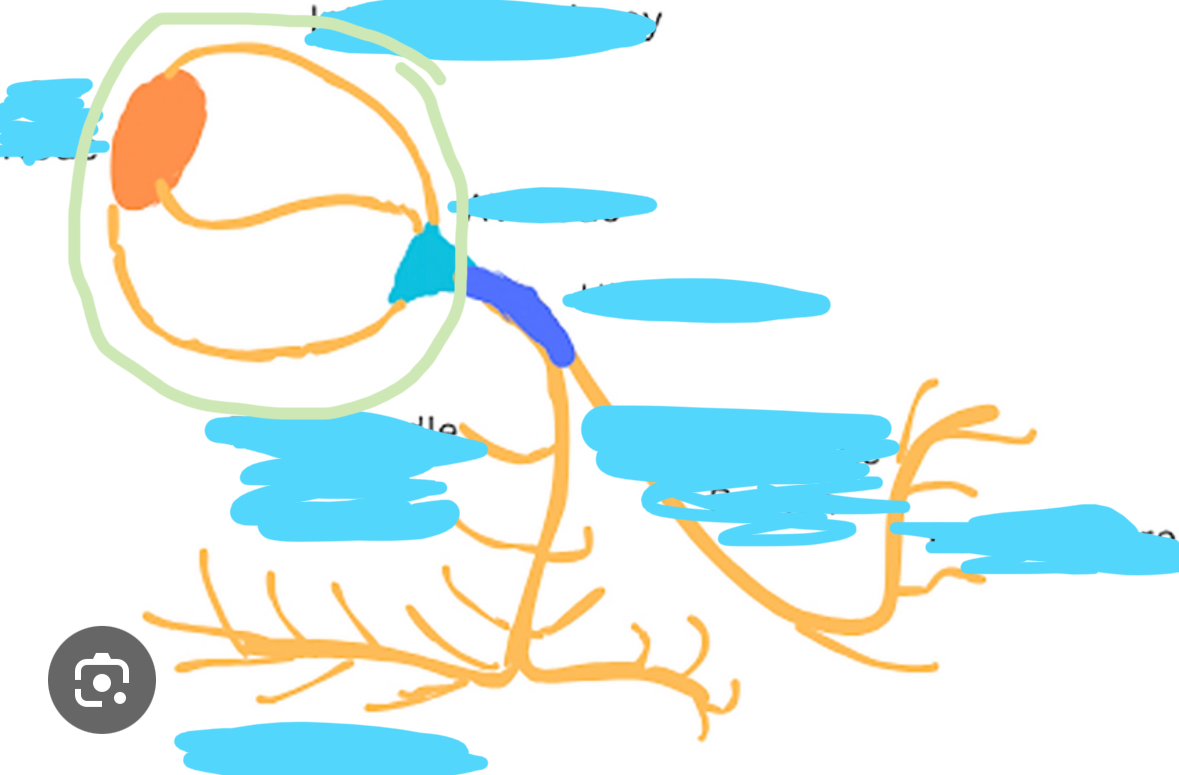
SA node
Internodal pathways
Bundle of his
Right and left bundle branches
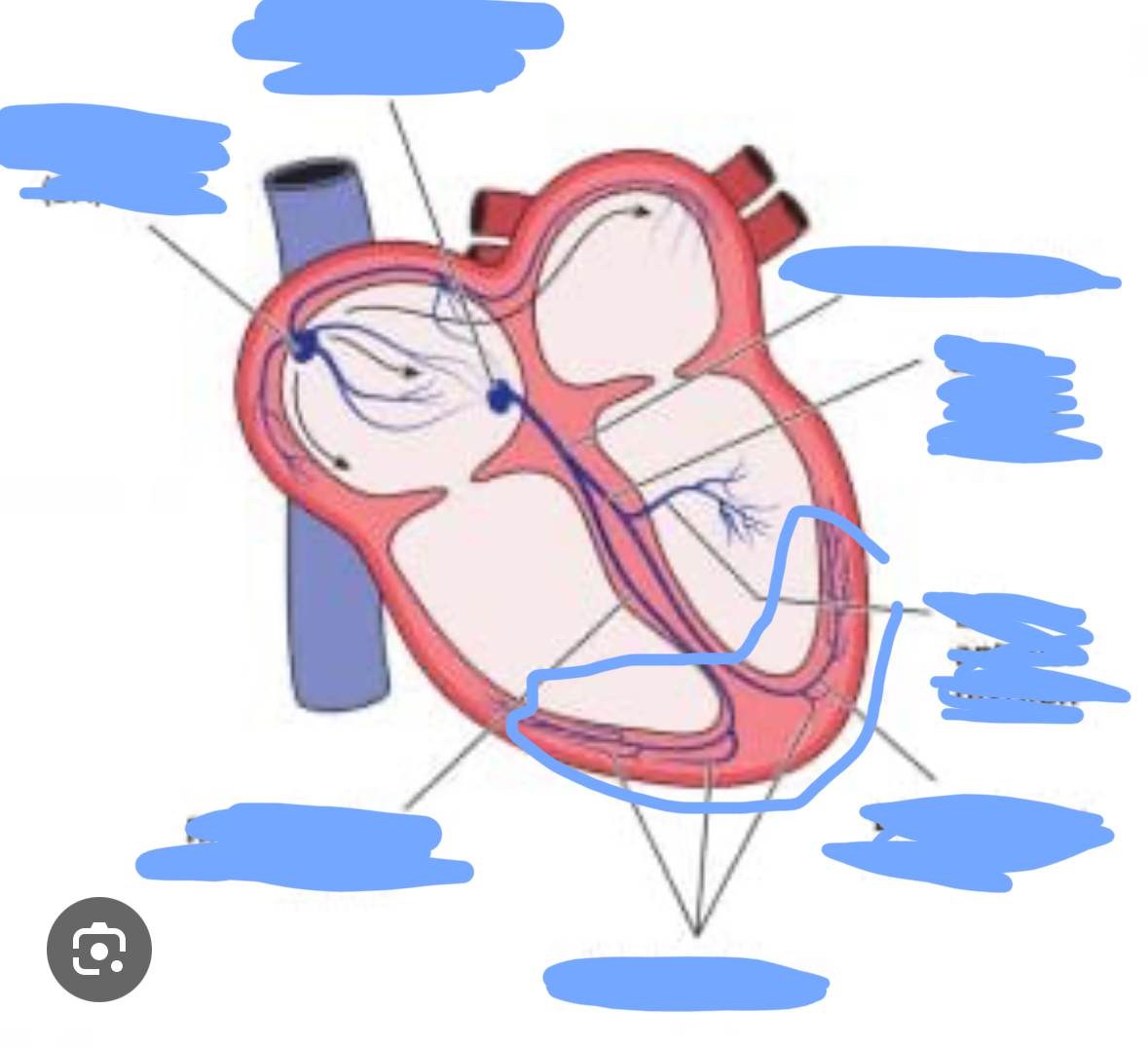
Purkinje fibers
Where is the SA node located?
In the right atrium
Where is the internodal pathway
In the right atrium, connecting the SA node and AV node
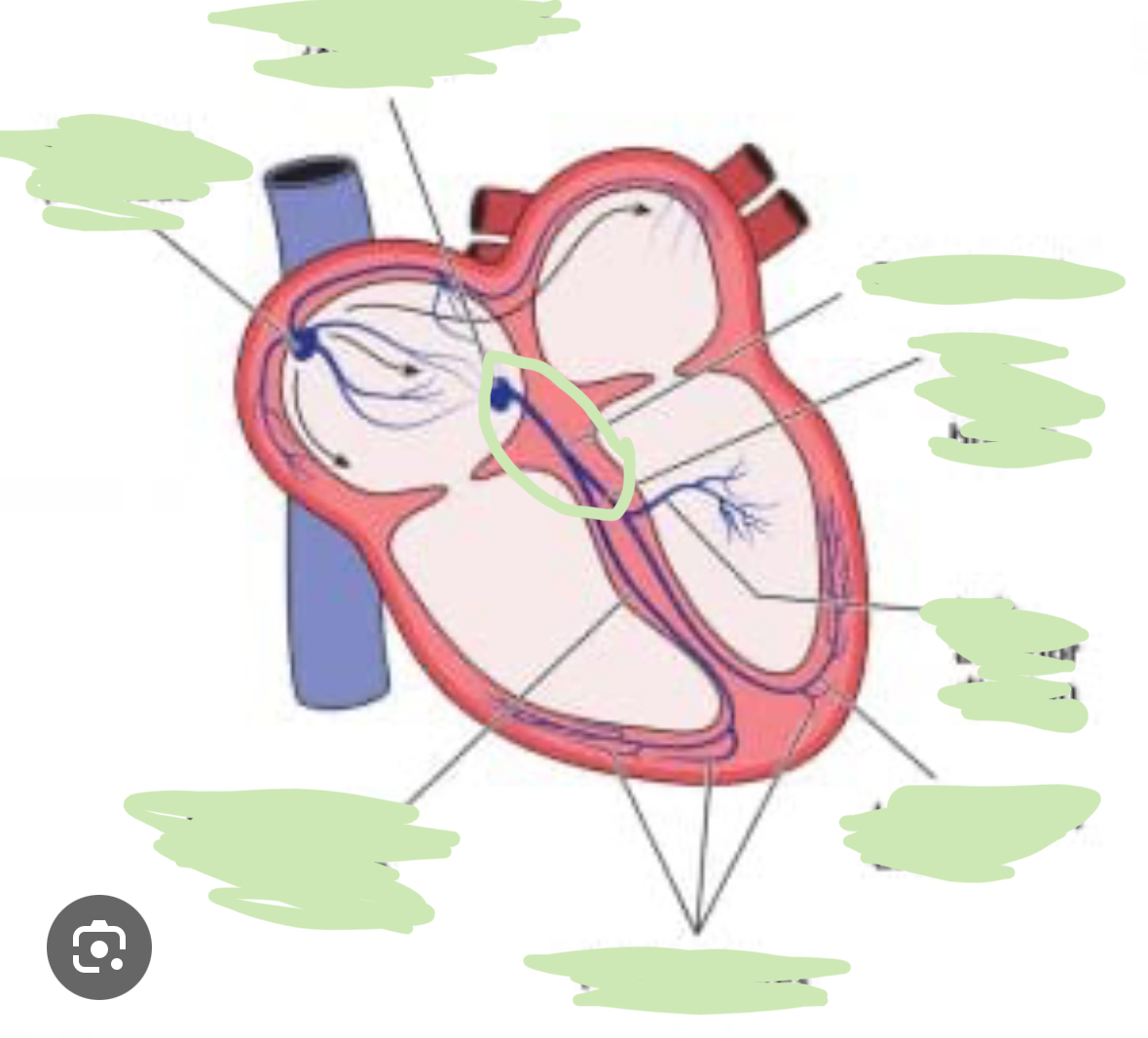
Where is the AV node
Near the bottom of the right atrium and the interatrial septum
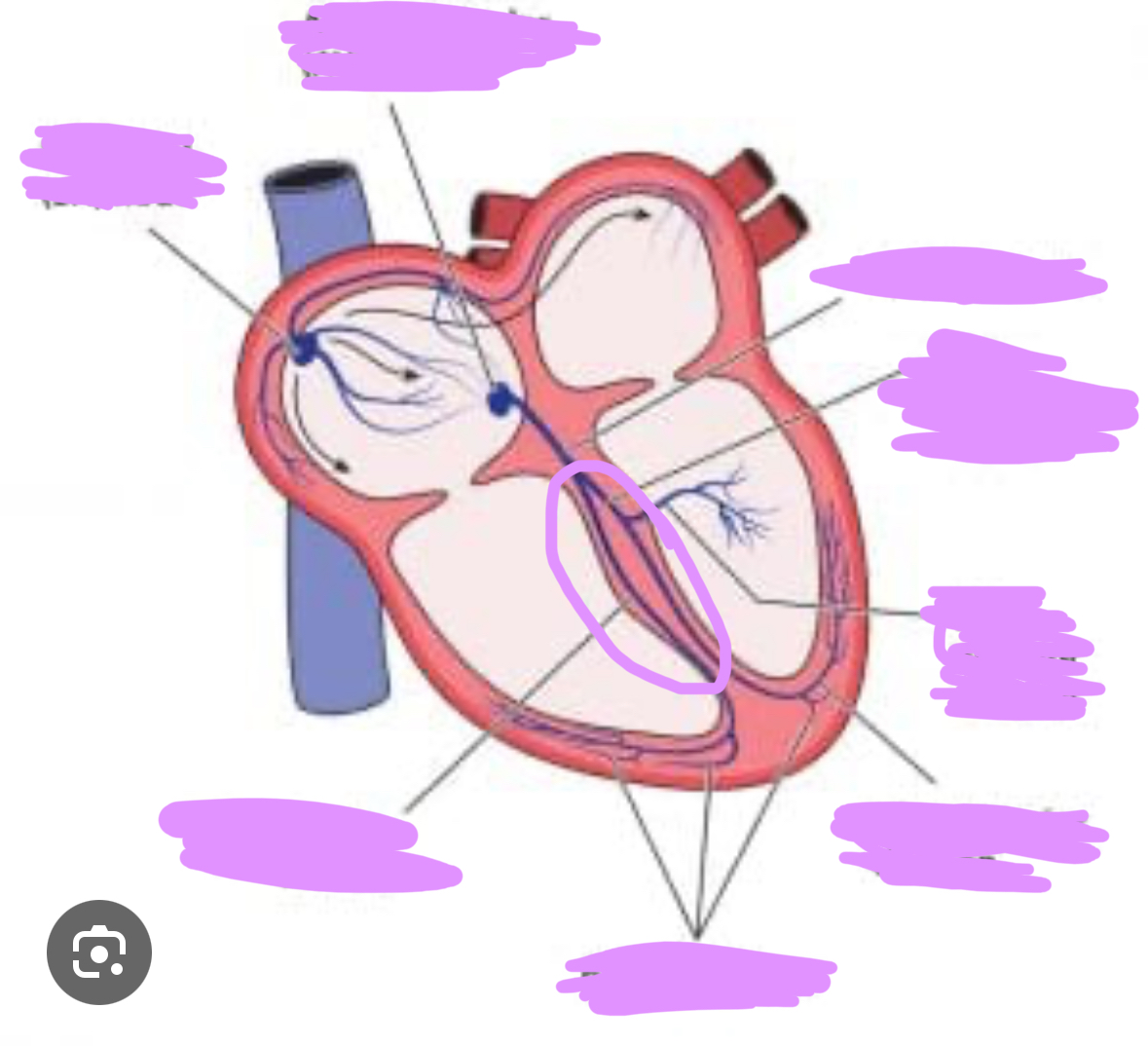
Where is the bundle of his?
Within the top of the interventricular septum
Where are the left and right bundle branches?
In the interventricular septum
Where are the purkinje fibers?
In the ventricle walls
Autorhythmic
cells that can generate and rhythmically conduct electrical impulses to initiate contractions without external nervous or hormonal stimulation
Chest leads
V1 through V6. Specific electrode placements that provide a horizantal view of the heart’s electrical activity
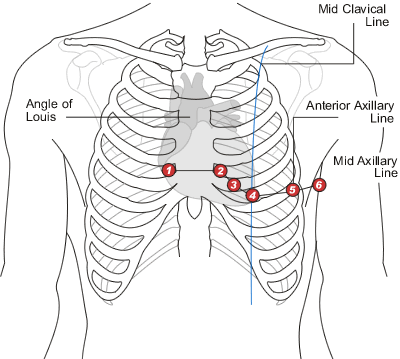
Chest leads
Limb leads
a set of electrodes used in ECG to measure the electrical activity of the heart from different angles in the vertical planes. I, II, III, aVR, aVL, and aVF
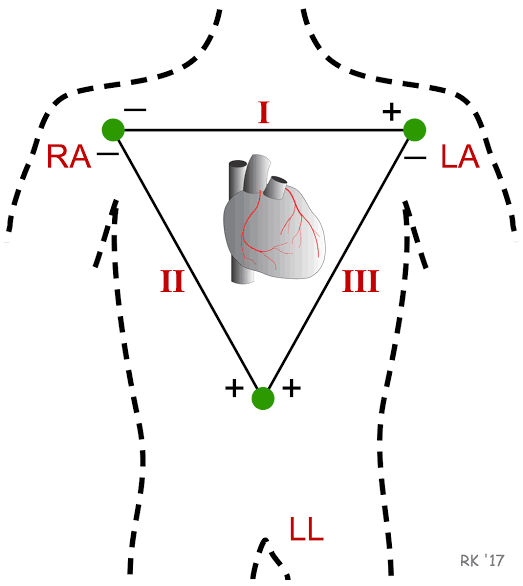
Limb leads