Nurse Stats
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Research
systemic inquiry that uses disciplined methods to asnwer questions or solve problems. The goal is to develop, refine, and expand knowledge.
developing new knowledge
Nursing research
a systematic inquiry designed to develop trsutworty evidence about issues of importance of the nursing porfession, including nursing pracitce, education, administartion, and informatics
what is EBP (evidence based practice)
approach to clinical decision making withing healthcare orginization, that integrates best available scientific evidence with best available experiential evidence
uses bodies of evidence, clinicians expertise, and pt’s family’s preferences adn values to make best decision about patient/client care list
seven steps of EBP
cultivate
spirit of inquiry
ask
a clinical question
search
for best evidence
appraise
critically appraise the evidecne
integrate
integrate evidence with clinical expertise patient preferences adn values
evaluate
evaluate outcomes of practicing decisions changes based on evidence
disseminate
share EBP results so others can learn replicate hone
statistics
Defined
science of collection analyzing, presenting, and interpreting data
two majorareas
descriptiver and inferential
descriptive
takes sample date and describes it
facilitates summary interpretation adn presentation of data
represented as tabular ( ex frequency table) graphical, numerical
inferential
takese sample data and makes inferences about hte larger population from which the sample was taken
tests a hypothesis or assess whether your data is generalizable to the broader population
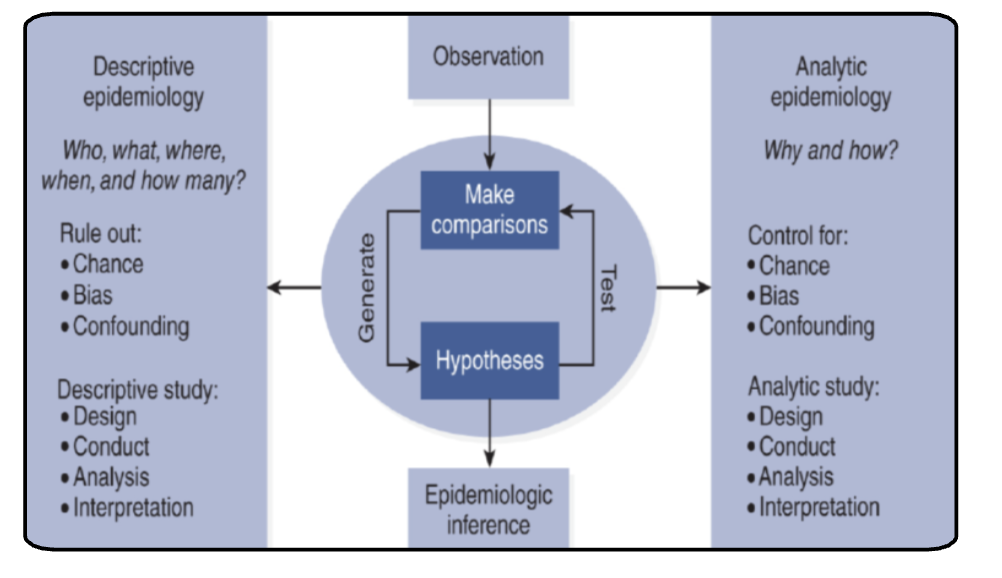
descriptive vs analyitical epidemiology
Descriptive
examines disease distrubtuiong by age, gender location and time in a population to identify patterns and generate hypothesis about possible causes
analytic
examines disease causes (determinants) asking why and how by testing hypotneses and making associations between exposures and outcomes using groups for comparison
descriptive vs inferential statistics
descriptive
summarize and present date form a sample
calculating averages, medians, ranges, adn frequencies
inferential
make predicitons, inferences and conclusiosn about a alrger population bases on sample data, involving hypothesis testing, regression, and correlation to understand relationships
independent variable explanatory
one you can change or control in a study, to see how it affects the dependent variable
dependent variable
variable being tested adn measures in an experiments it is called dependent becuase its values depends on changes in independent variable
nominal
Definition: Categorical data where the categories have no natural order.
Example: Gender (male, female), blood type (A, B, AB, O).
ordinal
Definition: Categorical data where the categories have a meaningful order, but the differences between them are not necessarily equal.
Example: Pain level (mild, moderate, severe), education level (high school < bachelor’s < master’s).
continous
Definition: Numeric data that can take any value within a range, including decimals. There is a meaningful zero, and differences/ratios are interpretable.
Example: Age in years, weight in kilograms, blood pressure in mmHg.
discrete
Definition: Numeric data that can take only specific, separate values (usually counts). There are no intermediate values between points.
Example: Number of siblings, number of cars, number of hospital visits.
quantitaitve variables
continuous:
take numerical value over an interval, age, weight discrete
discrete
takes a limited number of values: petals in a flower, amount of siblings
qualitative variables
nominal:
qualitative an unordered e.g. colour of a flower
ordinal:
data can be ranked e.g. likert sclaes
individuals
study objects, people, animals, things
variables
characteristics of an individual