Lecture Exam 1 Anatomy
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
225 Terms
What are the basic component of all tissues?
Cells and Extracellular Matrix
Extracellular Matrix
Non-cellular material
Four Basic Tissue Types
Epithelial
Connective
Muscular
Nervous
Major Functions of Epithelial Tissue
Covers body surfaces
Lines hollow organs, body cavities, and ducts
Forms glands
Major Function of Connective Tissue
Protects, supports, and binds organs
Stores energy as fat
Provides immunity
Examples of Connective Tissues
Cartilage
Tendons
Ligaments
Blood
Fat
Major Function of Muscular Tissue
Generates the physical force needed to make structures move
Generates body heat
Major Function of Nervous Tissue
Detects changes in body and responds by generating nerve impulses (control)
General Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue
Cells arranged in continuous sheets- single or multiple layers
Cells are closely packed and held tightly together
Little to no cellular matrix due to a lack of room
Found at boundaries between two different environments
Always have a free surface
General Types of Epithelium
Covering and Lining Epithelium
Glandular Epithelium
General Functions of Epithelium
Protection of underlying tissues
Secretion
Release products onto free surface
Excretion of wastes
Selective barrier
Sensory Reception
Special Features of Epithelia
High cellularity (lots of cells)
Specialized contacts (gap junctions, tight junctions, desmosomes)
Polarity (apical surface and basal surface)
Support by connective tissue
Avascular
Nervous Innervation
Regeneration
Avascular
No direct blood supply
Nervous Innervation
Nerves go into the epithelium
Apical Surface
Faces body surface, body cavity, lumen, duct
Basal Surface
Adheres to/anchored down to basement membrane
Classification of Epithelia
Arrangement of cells into layers
Shapes of cells
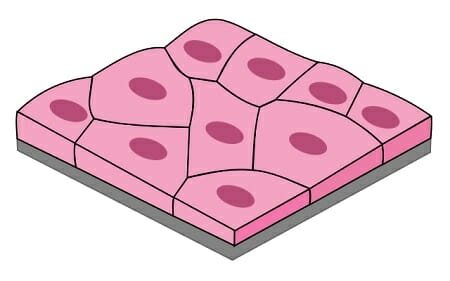
Name the arrangement
Simple
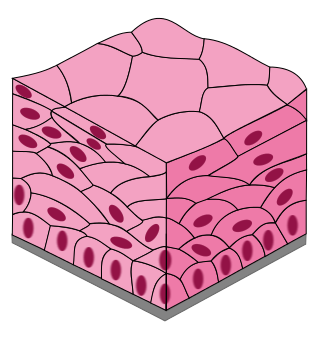
Name the arrangement
Stratified
If there are multiple shapes in different layers, how do you name it?
The shape of the apical layer
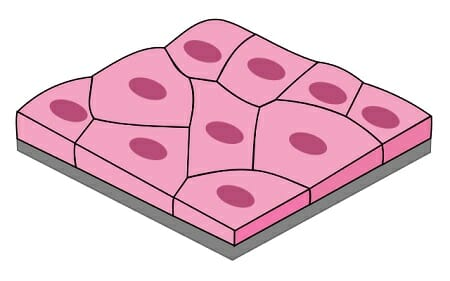
name the shape
Squamous
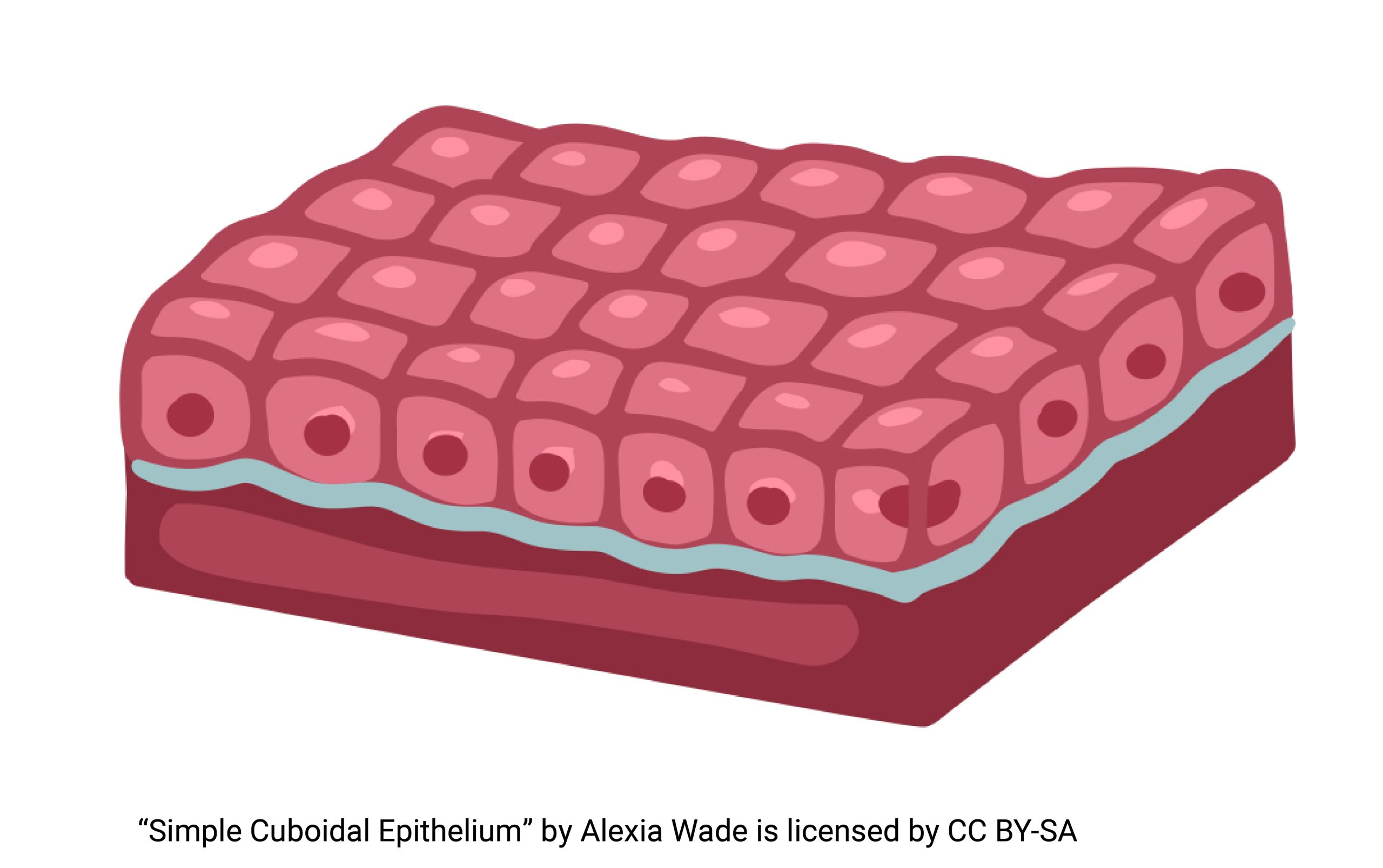
Name the shape
Cuboidal

Name the arrangement
Columnar
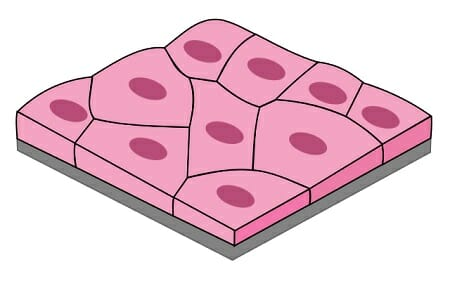
Simple Squamous Epithelial
Function of squamous cell epithelium
Allows easy passage of materials where protection is not important
Produces lubricating fluid in serosae
Location of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Kidney glomeruli
Air sacs of lungs
Lining of heart
Blood vessels
Lining of ventral body cavity (serosae)
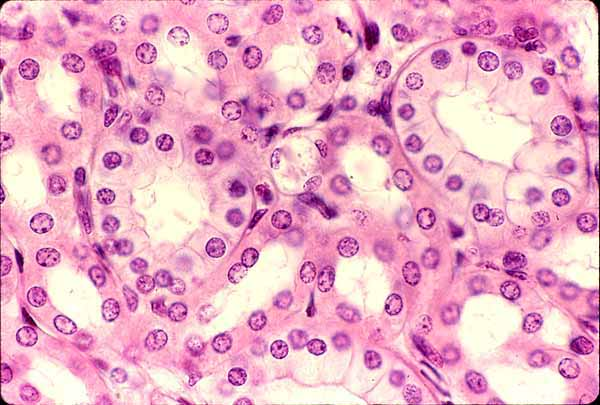
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epthelium
Single layer of cubelike cells with large, spherical central nuclei
Function of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Secretion and absorption
Location of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Kidney tubules
Ducts and secretory portions of small glands
Ovary surface
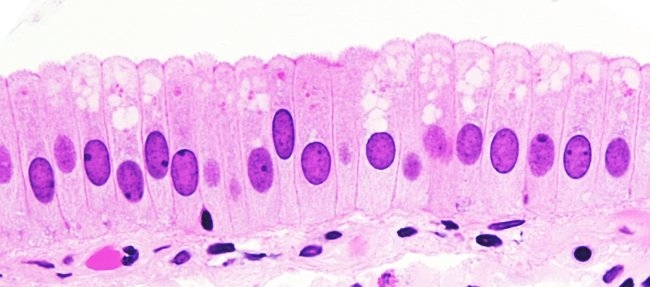
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Single layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei
Some bear cilia
May contain goblet cells
Goblet Cells
Mucus-secreting unicellular glands
Function of simple columnar epithelium
Secretion of mucus
absorption
ciliated type- propels mucus
Location of Nonciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
Lines most of the digestive tract
Gallbladder
Excretory ducts of some glands
Location of Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
Small bronchi
Uterine tubes
Some regions of the uterus
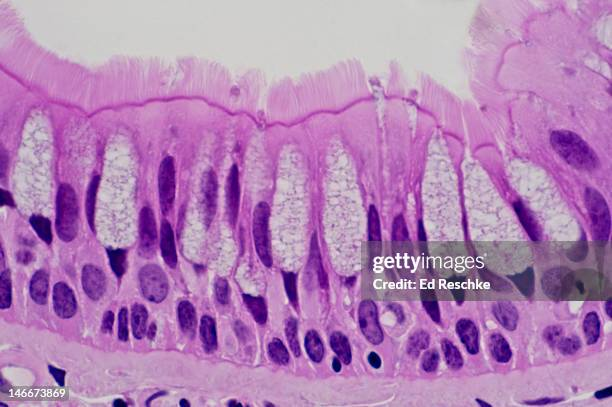
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Function of Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Secretion (particularly of mucus by ciliary action)
Location of Nonciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelial
Male sperm-carrying ducts
Large gland ducts
Location of Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelial
Lines trachea and most of the respiratory tract
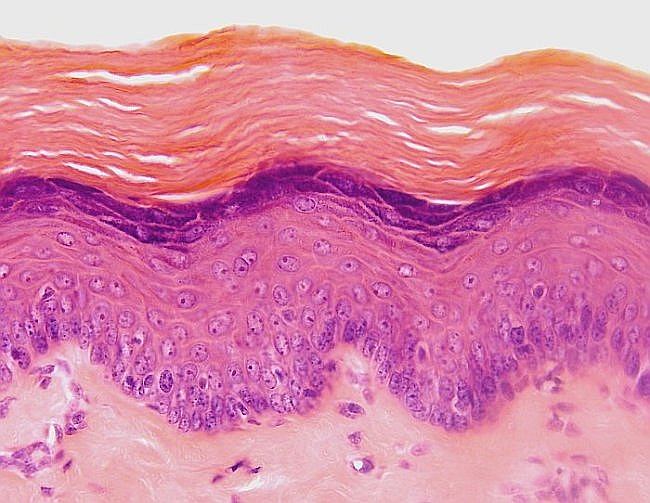
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Function of Keratin in Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Forms a hard layer that forms dry membranes for protection
Location of Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelial Tissue
Epidermis
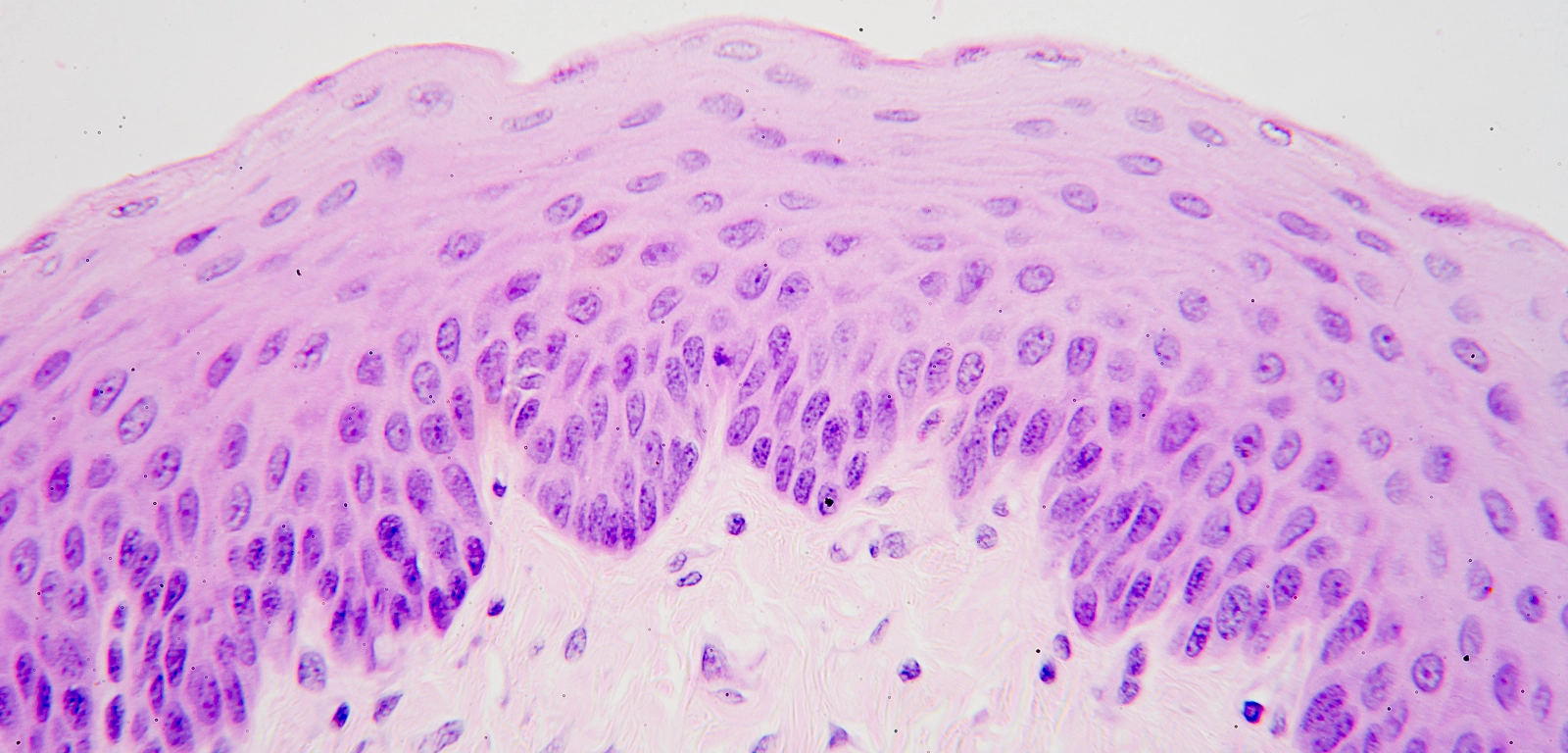
Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Function of no keratin in epithelial tissue
Forms moist linings
Location of Nonkeratinzed Stratified Squamous Epithelial Tissue
Moist linings of the esophagus, mouth, and vagina
Function of stratified squamous epithelial tissue
Protects underlying tissues that are subjected to abrasion, friction, or roughness
L
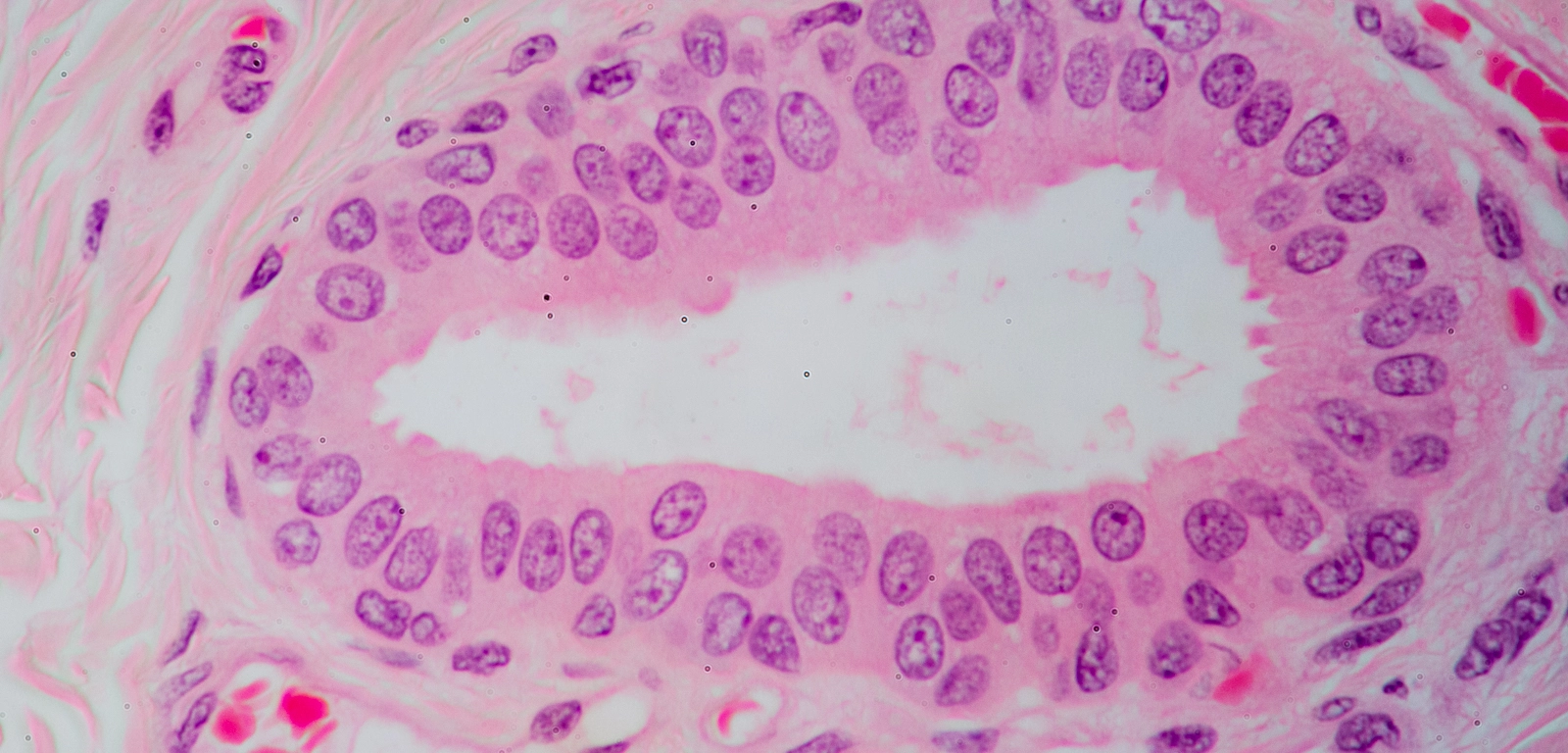
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Function of Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Protection
Location of Stratified Cuboidal Epithelial Tissue
Largest ducts of sweat, mammary, and salivary glands
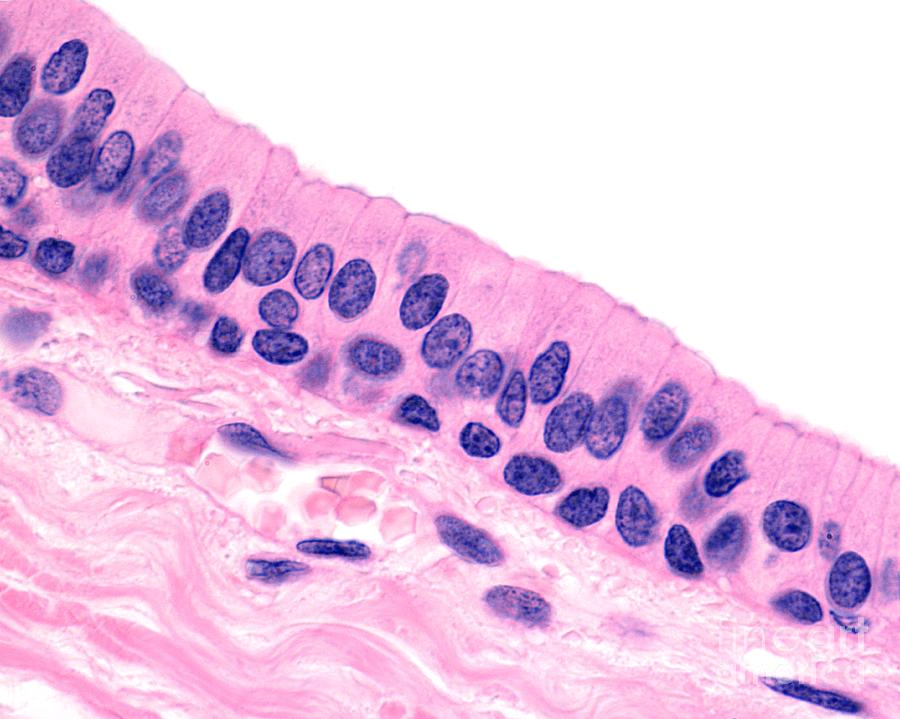
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Function Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Protection, secretion
Location of Stratified Columnar Epithelial Tissue
Very rare in body
Small amounts in male urethra
Some parts of large ducts of glands
Three special contact points and their location
Tight Junction
Desmosomes
Gap Junctions
Lateral surface
Tight Junctions
Proteins that connect/fuse walls of cells together
Prevents movement from in between cells
Desmosomes
Proteins that anchor cells together but does not prevent movement
Gap Junctions
Junctions that allow ions and small molecules to pass from one cell to the next for intercellular communication
Microvilli
Non-motile surface feature of the apical surface
increases surface area for absorption
supported by actin filaments
Found in absorptive cells (ex. small intestine)
Cilia
A type of microtubule that function to move things along the surface of a cell
Gland
A cell or organ that secretes fluid
Secretion
Aqueous fluids that usually contain proteins
Endocrine Glands
Secrete hormones
Hormones are released directly into ECF and then diffuse into blood stream without a duct
Effector organs can be near or far
Exocrine Glands
Secretions flow onto body surfaces or into cavities
Secretions act locally
Multicellular Exocrine Gland
Multiple cells form a gland that secretes products via a duct
Unicellular
Once-celled gland
What does the duct of a multicellular exocrine gland do?
Its a passageway for secretion
What does the glandular epithelium of a multicellular exocrine gland do?
Produces secretions
Functional Anatomy
Anatomy which emphasizes the structural characteristics of a body part that contribute to its function
Gross Anatomy
What we can see with the naked eye
Dissection
Where and what is the word anatomy derived from?
Greek “to cut apart”
Regional Anatomy
Certain part of the body
Systemic Anatomy
Studying by organ systems
Surface Anatomy
Studying by landmarks
Microscopic Anatomy
Needs magnification
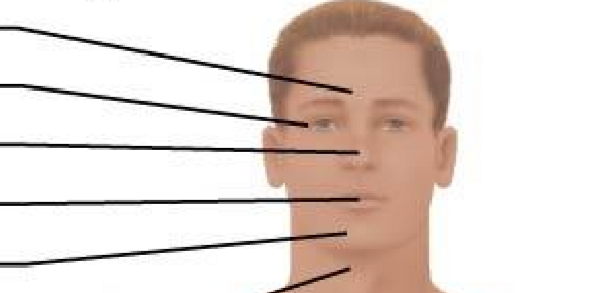
Anterior Axial Region: Cephalic (from top to bottom)
Frontal
Orbital
Nasal
Oral
Mental

Anterior Axial Region- Cervical
Neck
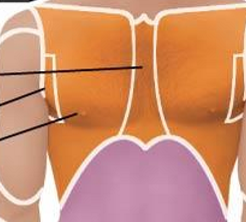
Anterior Axial Region- Thoracic
Sternal
Axillary
Mammary

Anterior Axial Region- Abdominal
Umbilical
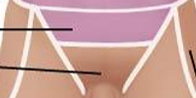
Anterior Axial Region- Pelvic
Pelvis
Inguinal
Anterior Appendicular Region- Pubic
Genitals
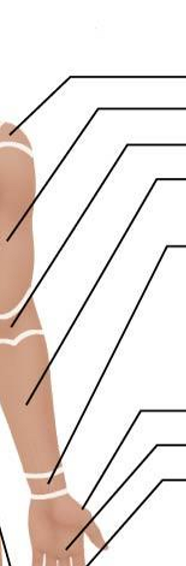
Anterior Appendicular Region- Upper Limb and Manus
Acromial
Brachial
Antecubital
Antebrachial
Carpal
Pollex
Palmar
Digital
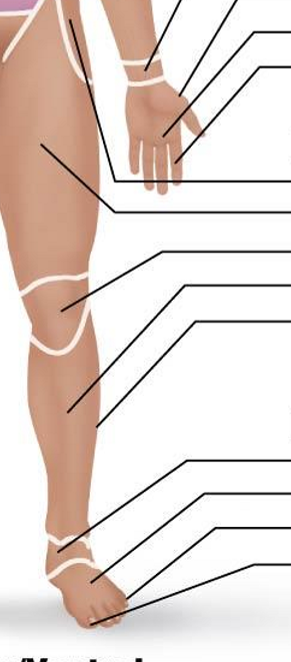
Anterior Appendicular Region- Lower Limb and Pedal (ignore the hand)
Coxal
Femoral
Patellar
Crural
Fibular or peroneal
Tarsal
Metatarsal
Digital
Hallux
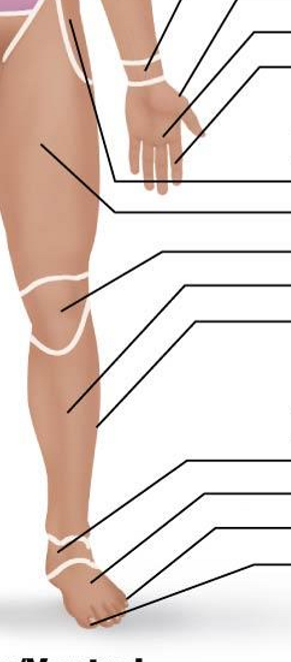
Posterior Appendicular Region: Upper Limb and Manus
Acromial
Brachial
Olecranal
Antebrachial
Metacarpal
Digital
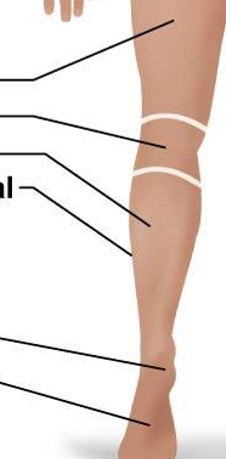
Posterior Appendicular Region: Lower Limb and Pedal
Femoral
Popiteal
Sural
Fibular or peroneal
Calcaneal
Plantar
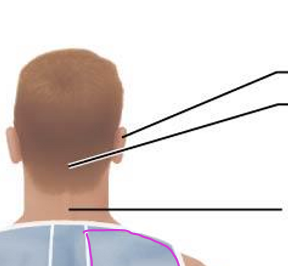
Posterior Axial Region: Cephalic and Cervical
Otic
Occipital
Cervical/neck
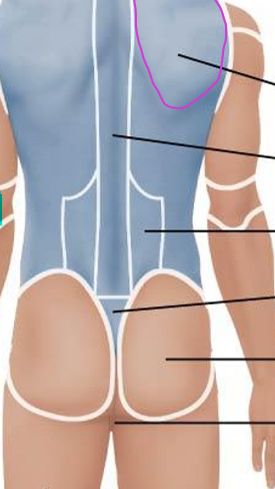
Posterior Axial Region: Dorsal
Scapular
Vertebral
Lumbar
Sacral
Gluteal
Perineal
Dorsal Body Cavities (& what each holds and does)
Cranial: contains and protects brain, formed by cranial bones
Vertebral canal: contains and protects spinal cord, formed by vertebral column
Meninges
Layers of protective tissue that line the cranial cavity and vertebral canal
Specific to dorsal cavities
Ventral Body Cavities
Thoracic Cavity
Abdominopelvic Cavity
Body Membranes
Mucous membranes
Serous membranes
Mucous Membranes
Lines cavities that are open to the outside environment
Cells secrete mucous
Serous Membranes
Lines cavities that are closed to the outside environment
Cells secrete serous fluid
thoracic and abdominal cavities
Two layers of serous membrane
Visceral Layer: touches the organ
Parietal Layer: touches the body wall
continuous with one another
Main structural components of a cell
Plasma membrane
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Cholesterol
Found among the lipid tails of the bilayer
Provides structure for the plasma membrane
Hydrophobic
Glycolipids/Glycoproteins
Only found in layer facing ECF
Recognizes specific sequences of cells
Carbohydrate/sugar chain
Sticky- good for cell adhesion
Two membrane proteins
Integral proteins
Peripheral proteins