Transport in animals
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is the circulatory system?
A series of blood vessels with a pump and valves to prevent backflow
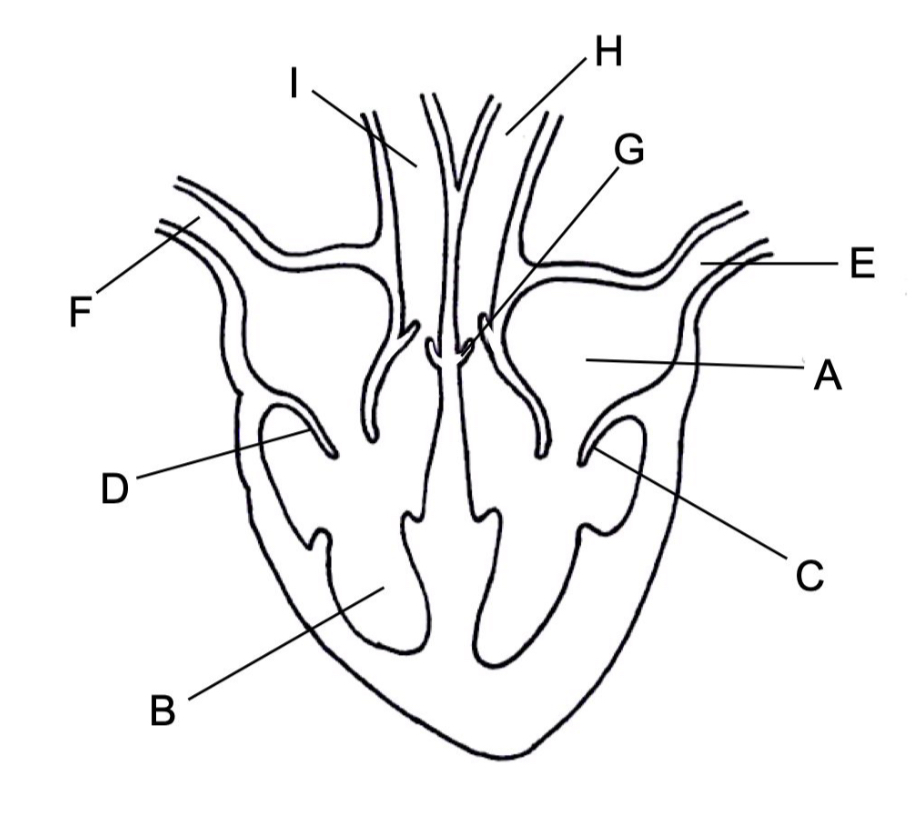
Identify the structures of the heart labelled in the diagram below
A ~ Left atrium
B ~ Right ventricle
C, D, G ~ Valve
E ~ Pulmonary vein
F ~ Vena cava
H ~ Aorta
I ~ Pulmonary artery
Show the direction of blood flow through the heart on the diagram below
Blue ~ Deoxygenated
Red ~ Oxygenated
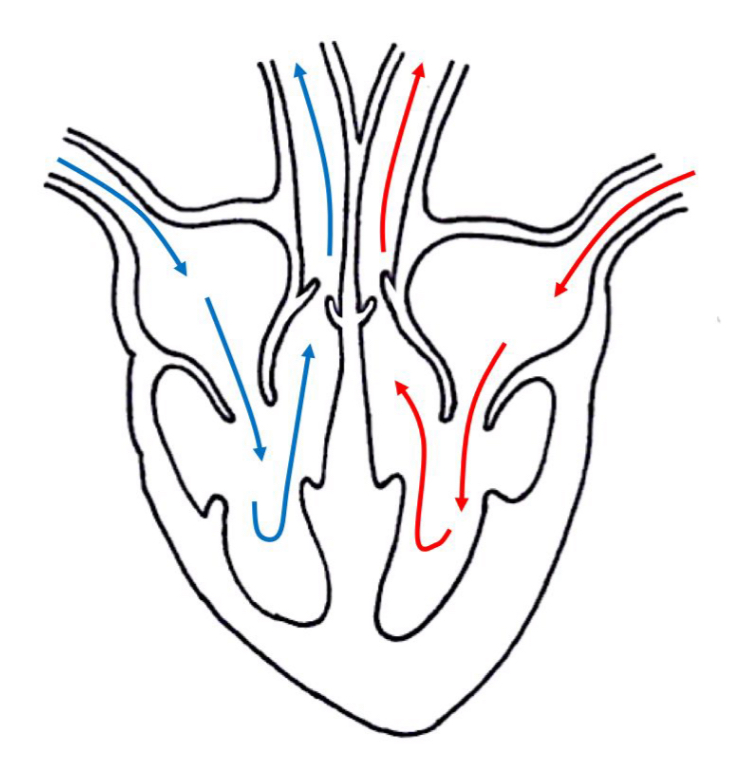
Describe the blood flow through the right side of the heart
Deoxygenated blood flows from the vena cava into the right atrium
The blood will the pass through the valve into the right ventricle
Lastly, the blood will pump out from the pulmonary artery and into the lungs
Describe the blood flow through the left side of the heart
Oxygenated blood will enter the left atrium from the pulmonary vein
The blood will then pumped through the valve and into the left ventricle
Lastly, the blood will be pump out to the body through aorta
What is the name of the wall that separates the right and left sides of the heart?
The septum
What type of muscle is the heart made of?
Cardiac muscle
What is the difference in function between veins, arteries and capillaries?
Veins ~ carry blood into the heart
Arteries ~ carry blood away from the heart
Capillaries ~ flow close to tissues for gas exchange
Describe the structure of arteries
Thick walls made of muscle and elastic tissue and a small lumen to transport blood under high pressure
Describe the structure of capillaries
They have thin walls about one cell thick to allow the easy exchange of substances at the tissue
Describe the structure of veins
Lesser muscle and elastic tissue compared to the arteries. They have large lumen as the blood pressure are low, and they also have valve to prevent backflow

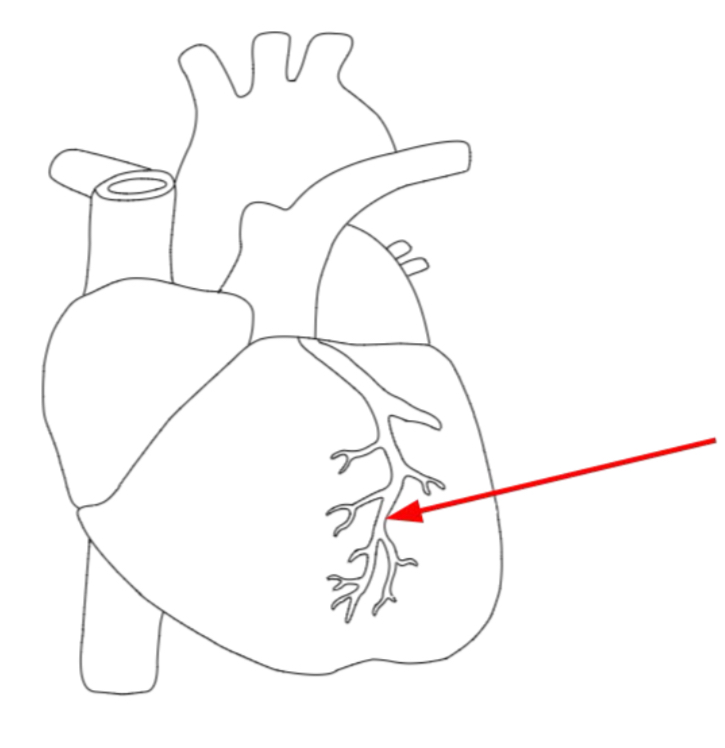
Name the artery and state its purpose
It is pulmonary artery and it supplies heart muscle with blood
Name the blood vessels that supply the lungs with blood
Pulmonary artery
Name the blood vessels that takes blood away from the lungs
Pulmonary vein
Name the main blood vessels that takes blood away from the heart
Aorta
Name the main blood vessels that takes blood to the heart
Vena cava
Name the blood vessels that takes blood to the kidneys
Renal artery
Name the blood vessel that takes the blood away from the kidneys
Renal vein
Name 4 component of the blood
Red blood cells
White blood cells
Plasma
Platelets
Name 2 types of the white blood cells
Lymphocyte
Phagocyte
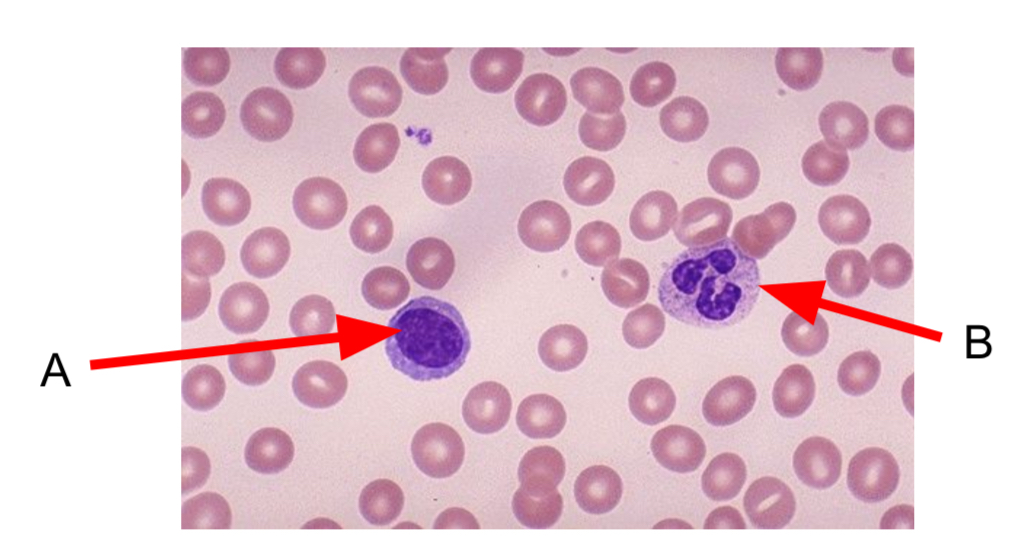
Identify cell A and cell B
A ~ Lymphocyte
B ~ Phagocyte
What is the function of platelets?
Blood clotting
What is the purpose of blood clotting?
preventing excess of blood loss
Preventing the entry of pathogens through wounds
What is the function of red blood cells?
Transporting oxygen to tissues using haomoglobin
State 2 functions of white blood cells
Produce specific antibodies
Phagocytosis (engulfing pathogens)
What is the function of plasma?
Transporting substances like ions, soluble nutrients, hormones and carbon dioxide in the blood
Give 3 ways of measuring the activity of the heart
ECG
Pulse rate
Listening to the sounds of the valve
State the effect of physical exercise on heart rate
It increases heart rate
Explain the effect of physical exercise on heart rate
Muscular contraction requires energy from respiration
More respiration requires more oxygen and more carbon dioxide
Heart would pump faster to provide more oxygen to the muscle (for respiration) and remove carbon dioxide quickly
What is coronary heart disease (CHD)?
Blockage of coronary artery
6 common risk factors for coronary heart disease
Smoking
Poor diet
Lack of exercise
Stress
Genetic predisposition
Gender
How can coronary heart disease be prevented by altering lifestyle choices?
Exercise regularly
Control diet:
Eat less saturated fats (饱和脂肪)
Eat more fruits and vegetables
Eat less salty foods
Stop smoking / drinking