Carbohydrates pt 2
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What do plants store carbohydrates as
Starch, stored as starch grains in chloroplasts
Note:
Does not dissolve meaning it does not affect water potential
Hold glucose molecules in chains that can be easily broken to be used in respiration
What does starch consist of
Two polysaccharides amylose and amylopectin
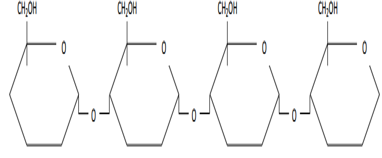
Amylose
Made up of a straight chain of alpha glucose molecules
Joined by 1-4 glycosidic bond
Forms a helix shape, this shape helps to make amylose compact for storage
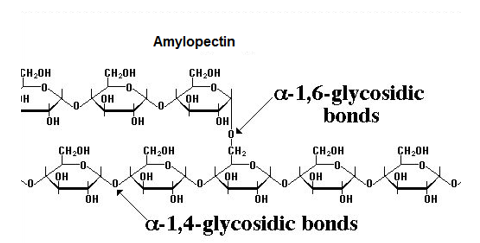
Amylopectin
Made up of a branched chain of alpha molecules
Branches occur due to having 1-6 glycosidic bonds alongside 1-4 bonds.
How come starch is insoluble
Starch is insoluble, this is because there hundreds of thousands of glucose units, and water molecules cannot easily surround such a huge molecule
Both amylose and amylopectin have many OH, the OH groups form hydrogen bonds between the chains, not with water
What are the advantages of branches in starches structure
By having branches this means there are more chain ends exposed this means enzymes can hydrolyse glucose faster, allowing release glucose quickly when needed
Allows the molecule to be stored compactly
What do animals store carbohydrates as
Glycogen, stored in the liver and muscle
Note:
Glycogen is less dense and more soluble than starch, this indicates a higher metabolic rate of animals
Glycogen forms due to high glucose blood levels and insulin is released
Do not dissolve so does not affect water potential
Hold glucose molecules in chains that can be easily broken to be used in respiration
What is the structure of glycogen
It is made up of many glucose units
Has 1-4 glycosidic bonds as well 1-6 glycosidic bonds, have more branches than amylopectin
What are the advantages of branches
As glycogen has more branches it makes it more compact for storage, branches also means there are more chains meaning there is quicker access to retrieve glucose through hydrolysis
What are the cell walls of a plant made of
Cellulose
Describe the structure of cellulose
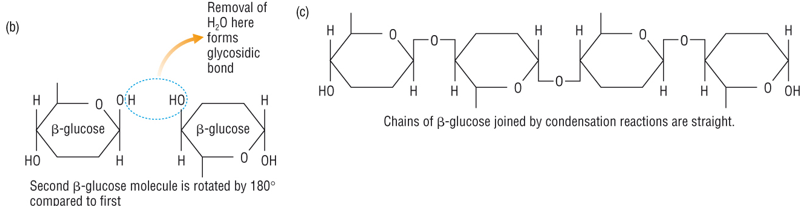
It is a polysaccharide which consists of long chains of beta glucose joined together by 1-4 beta glycosidic bonds.
The chains form rope-like microfibrils which are layered, as hydrogen bonds form between individual cellulose fibres
Microfibrils are held together by more hydrogen bonds to form microfibrils these are embedded in a polysaccharide glue called pectin