Introduction to Sport Psychology Concepts
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Sport Psychology
The field within exercise science that examines how psychological factors influence athletic performance.
Managing anxiety
Using psychological principles to help optimize performance.
Dealing with stress
Using psychological principles to help optimize performance.
Improving focus
Using psychological principles to help optimize performance.
Improving performance during competition
Using psychological principles to help optimize performance.
Personality
Composite of characteristic individual differences that make us unique.
Trait Framework
Everything we do is a result of stable & enduring traits that predict how we act in a given situation.
Example of Trait Framework
If shy, will be timid when joining a new team.
Traits measurement
Traits can be objectively measured via inventories.
Interaction Framework
Personality traits and situational factors interact to determine how we act.
Example of Interaction Framework
A shy person joining a new team would react differently if team members were welcoming/inclusive vs suspicious/exclusive.
States
How a person feels at a particular point in time.
Influence of states
States can influence behavior but not determine it directly.
Personality Research
Identify personality characteristics of athletes vs non-athletes.
Athlete characteristics
Found athletes less anxious, more extroverted, more independent than non-athletes.
Issues in Personality Research
Inventory scales were created for clinical populations and may not be reliable or valid.
Definition of an athlete
How do you define an athlete? Non-athlete?
Motivation
Driving force for completing a task.
Components of Motivation
Consists of three parts: direction, intensity, and duration.
Direction of motivation
Where people invest their energy.
Intensity of motivation
How much energy is invested.
Duration of motivation
How long energy is invested at a given intensity.
Long term component of motivation
Success often drives motivation.
Definition of success
Depends on individual interpretation.
Achievement Goal Orientation
Self-referenced definition of success focusing on improvement and gaining new skills.
Ego Orientation
Success is defined by being better than others, focusing on winning.
Impact of orientations
Both orientations impact motivation.
Self-Determination Theory
You have a need for autonomy, which is key to intrinsic motivation leading to action.
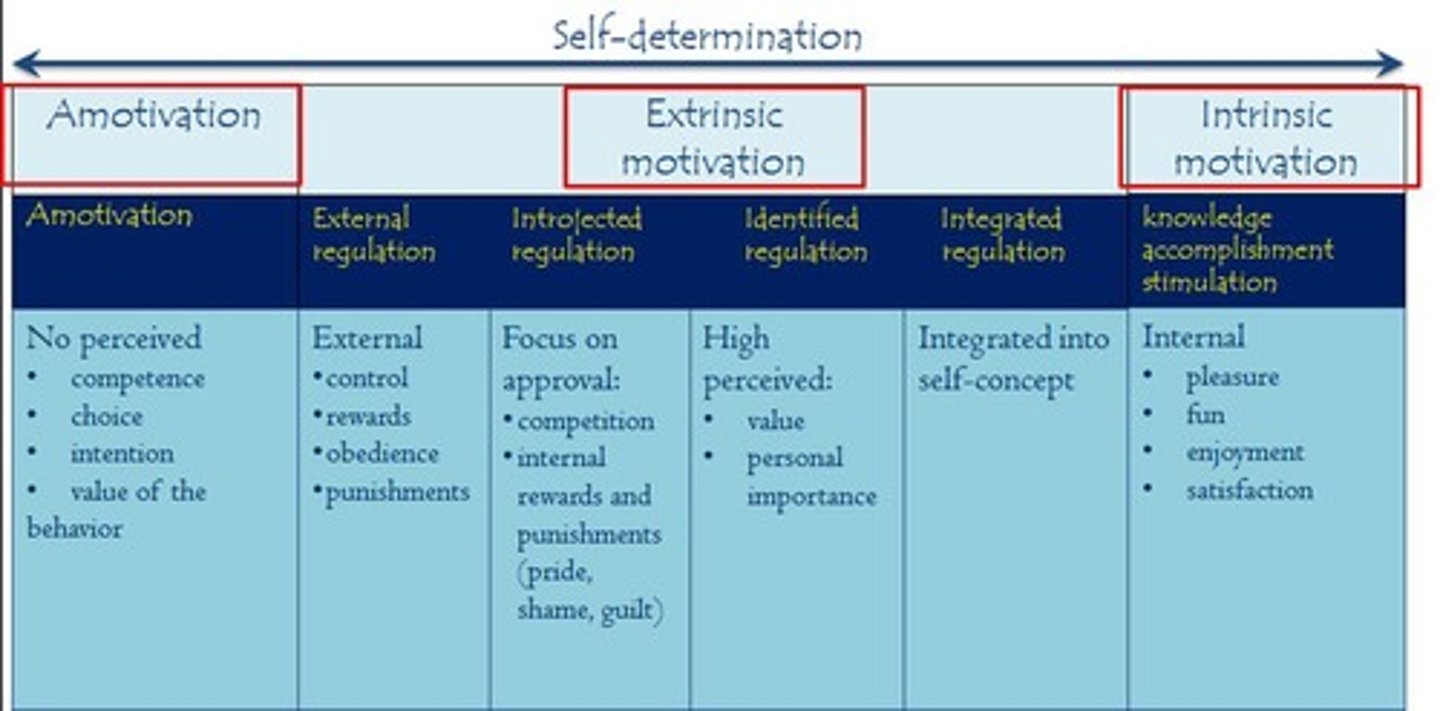
Three psychological needs
Autonomy, competence, and relatedness.
Autonomy
Endorse & be the origin of one's own behavior.
Competence
Interact effectively in the environment and need optimally challenging activities.
Relatedness
Feel connected with, cared for, and close to others/community.
Arousal
Traditionally, activation (i.e. increased HR, BP, respiration rate)
Arousal
Can involve activation as well
Arousal in sport psychology
Degree of activation and intensity
Anxiety
Subjective feeling of unease, usually accompanied by high arousal
Anxiety
Excessive response to either a perceived or real threat that includes a variety of physical and emotional symptoms
Anxiety symptoms
Muscle tension, Dizziness, Over active Sympathetic response, Fear
Arousal and anxiety
Can have high arousal without anxiety
Trait Anxiety
When a person develops stress/anxiety
State Anxiety
When a person has a tendency to be stressed/anxious
Cognitive anxiety
Mental facet (worry, self-defeating thoughts)
Somatic anxiety
Physiological anxiety (sweaty palms, butterflies in stomach)
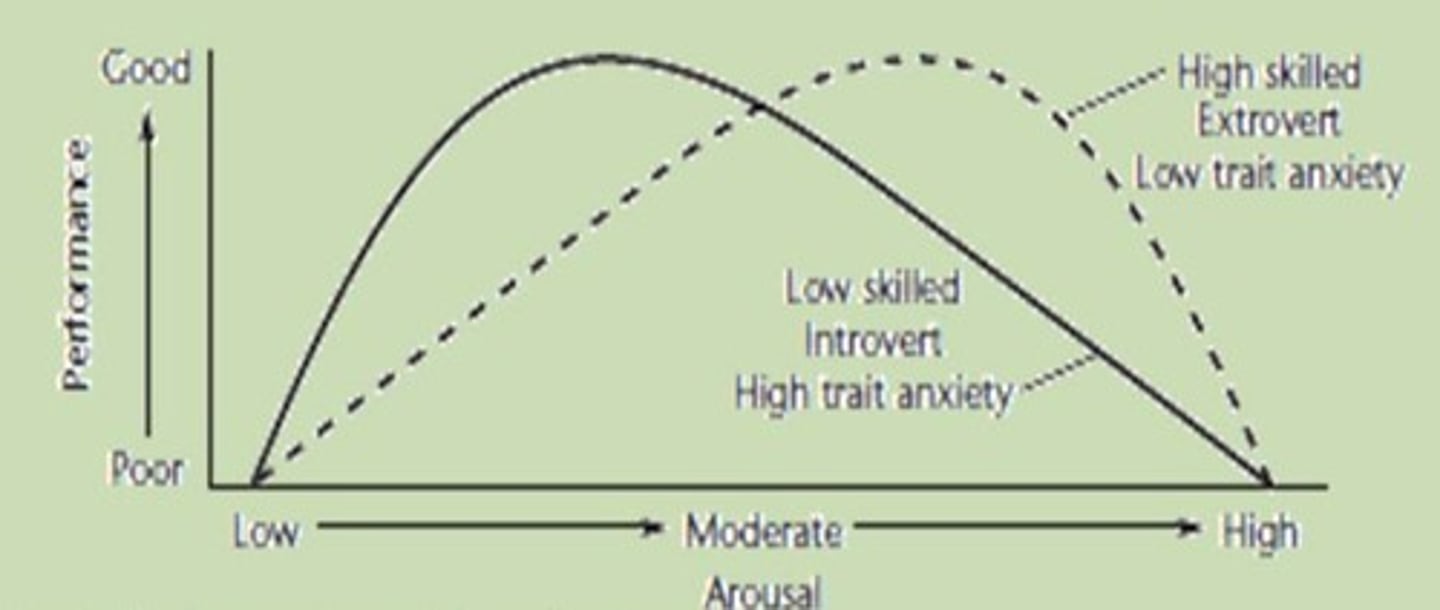
Performance-Arousal Curve
Relationship of arousal (stress) for performance
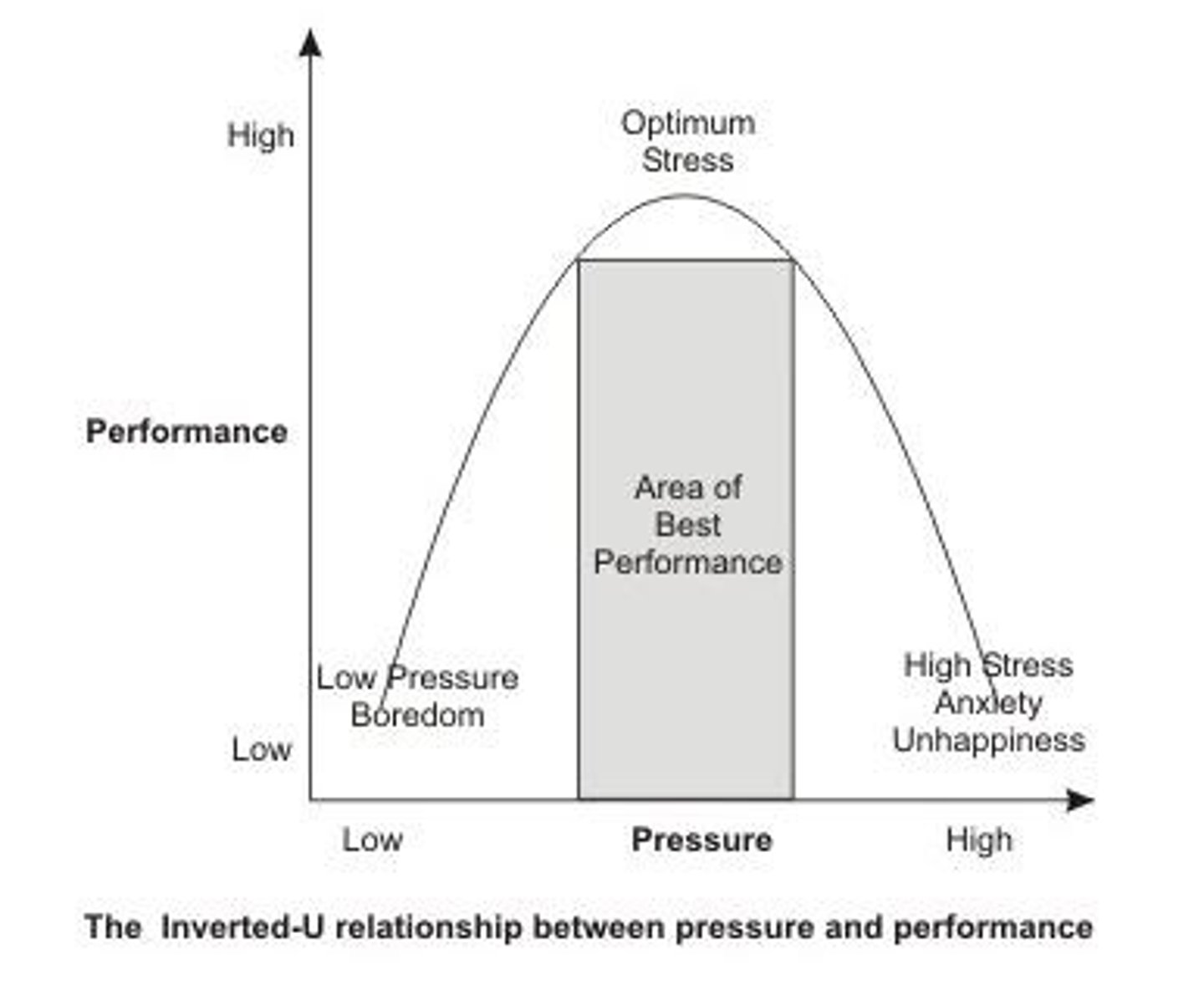
Performance-Arousal Curve
Individual differences in Curve
Performance-Arousal Curve
Optimal level of arousal (excitation) for performance
Imagery
Creating a mental representation of a situation using all of your senses
Imagery perspective
First person perspective
Imagery usage
Used regularly in competitive sports but can be used in almost any sport
Benefits of Imagery
Allows 'practice' without physical execution
Imagery benefits
Can improve performance
Imagery practice
Athletes can see & feel themselves performing the way they want to
Imagery and skill acquisition
Can facilitate the learning of a new skill
Imagery for control
Can help control anxiety
Imagery effectiveness
The more vivid, the more brain is convinced the image is real
Guided imagery
Need to picture good performance vs all of the mistakes
Overtraining
Period characterized by higher than normal training volume/intensity accompanied by fatigue.
Excessive training
Leading to prolonged fatigue and frequent illness.
Multiple signs and symptoms
Indicators of overtraining.
Overuse Injuries
Injuries resulting from excessive training.
Hormonal changes
Alterations in hormone levels due to overtraining.
Increased Cortisol
Elevated cortisol levels as a result of overtraining.
Heart rate changes
Variations in heart rate associated with overtraining.
Decreased Heart Rate recovery
Slower recovery of heart rate after exercise due to overtraining.
Decreased Heart Rate Variability
Reduced variability in heart rate as a sign of overtraining.
Increased Resting Heart Rate
Higher resting heart rate indicative of overtraining.
Performance decrement
Reduction in performance compared to known benchmarks.
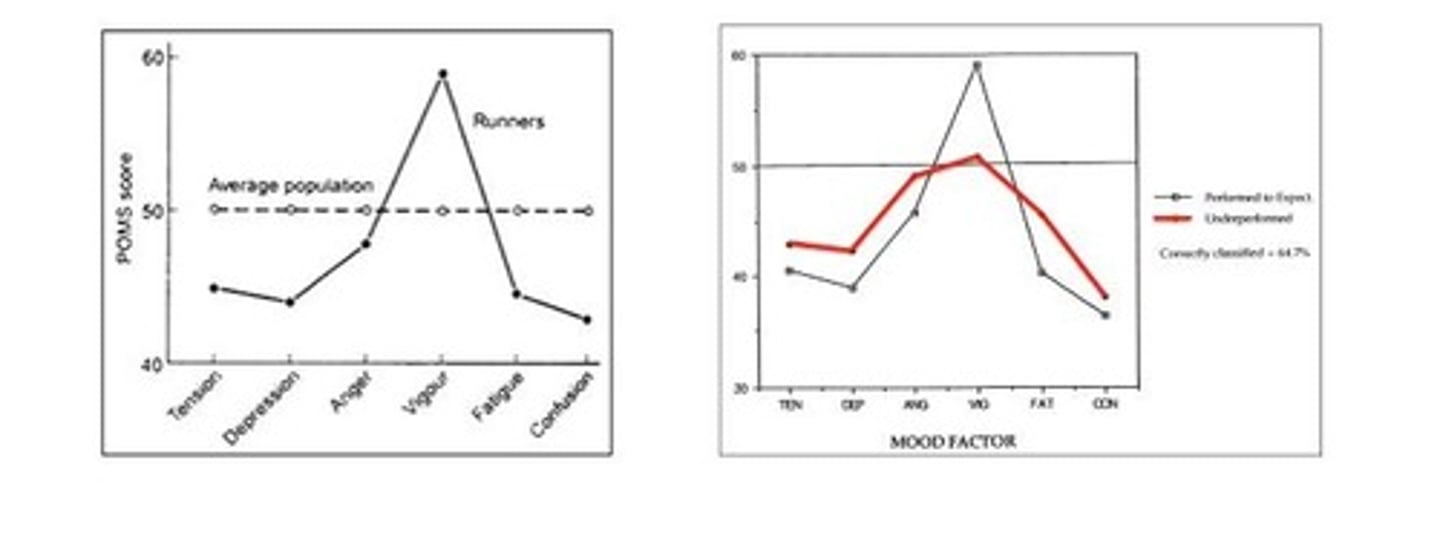
Profile of Mood States Questionnaire
A tool used to assess mood states in athletes.
Flow State
An intrinsically rewarding state where everything seems to click into place, even during extreme challenges.
Almost Autopilot
A feeling of being in complete control without trying, characteristic of flow state.
Unambiguous feedback
Clear and direct feedback that contributes to achieving flow.
Total and complete concentration
Intense focus on the task at hand experienced during flow.
Paradoxical Performance
Occurrence of inferior performance despite striving and incentives for superior performance.
Choking
Deterioration of performance when in high pressure situations.
Focus on the outcome
Concentration on results rather than the process can lead to choking.
High anxiety
Elevated stress levels that can contribute to choking.
Narrowing attention
Focusing too narrowly can lead to performance issues.
Overactive physiological response
Increased physiological reactions that can hinder performance.
Increase in muscle contraction
Heightened muscle tension that slows intended movements.
Acute coping strategies
Immediate techniques to manage performance anxiety.
Mindfulness training
Practice that helps athletes stay present and focused.
The Yips
Impediment affecting the execution of fine motor skills during sporting performance.

Uncontrollability of movements
Loss of control over fine motor skills, worsened by psychological distress.