RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
inhalation
taking in air
exhalation
breathing out air
nostrils
two openings, where air is filtered
cillia
hairs in the nose than help capture dirt/dust
nasal cavity
warms up the air, inside the head
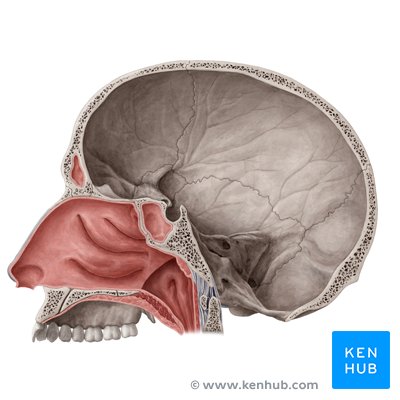
pharynx
divides into two passageways for air and food, also known as the throat
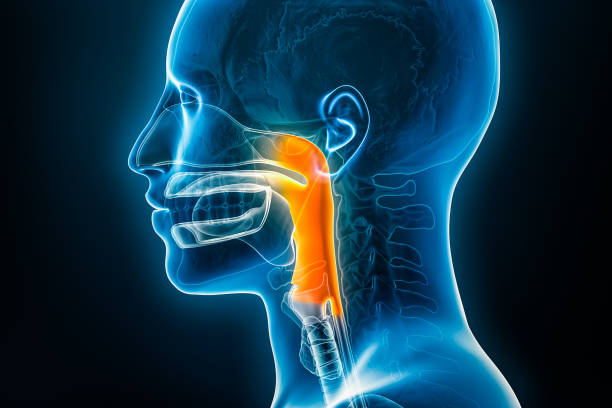
larynx
voice box below the pharynx
epiglottis
flap of tissue that stays open when you breathe, closes when you swallow food
vocal chords
two elastic ligaments in the larynx
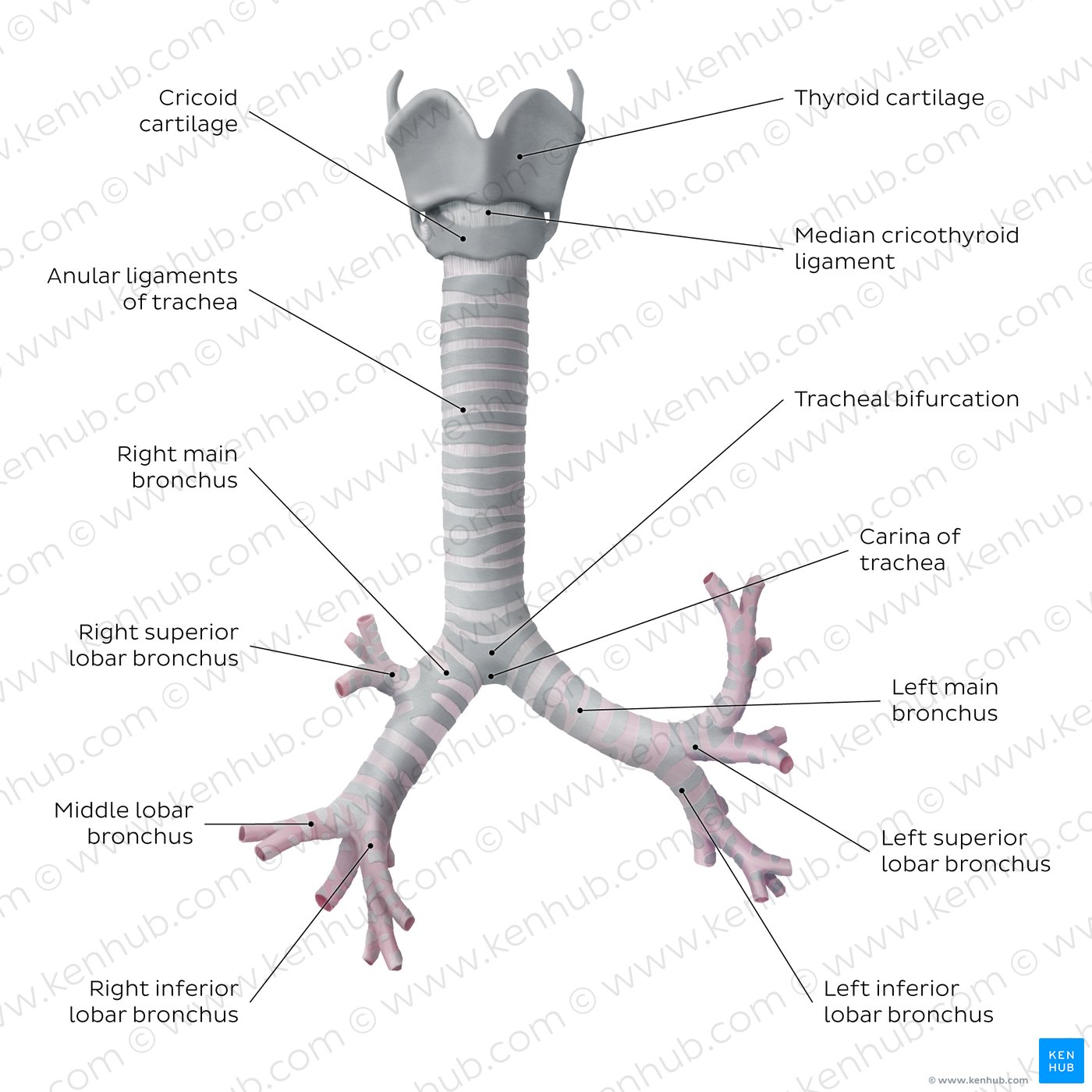
trachea
tubelike structure, also known as the windpipe
lungs
the main organs of the respiratory system, spongelike
lobes
the lungs are divided into sections called…
bronchi
when the trachea branches into two tubes, the left and right
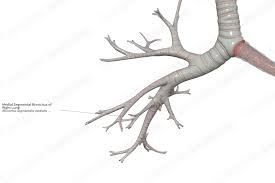
bronchioles
the bronchus divides into smaller branches into the lungs
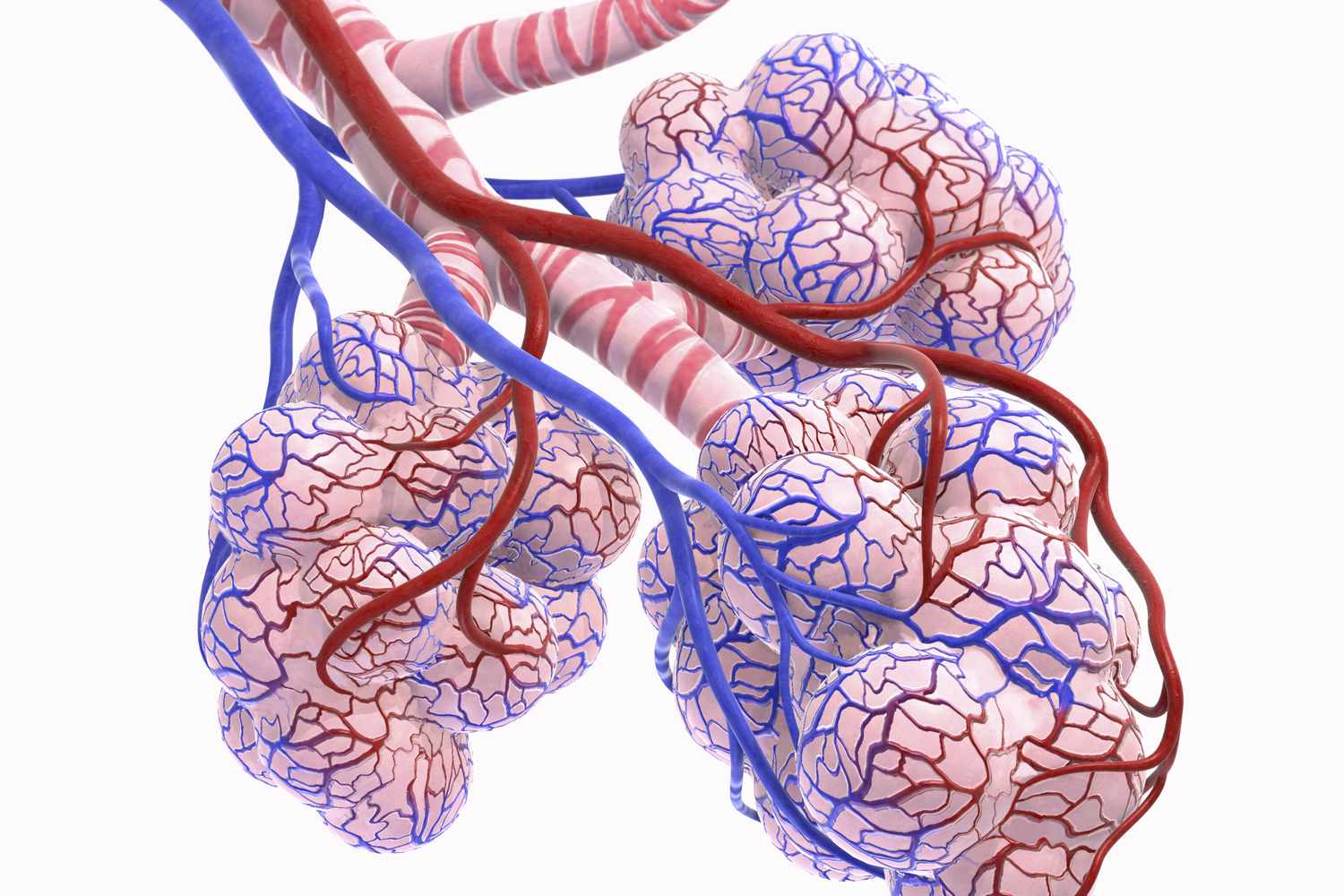
alveoli
tiny air sacs that inflate during inhalation and deflate during exhalation
air is drawn into the lungs by inhaling
the first step in inhalation
diaphragm contracts
second step in inhalation
rib cage moves up and down due to intercostal muscles contracting that pull upward
third step in inhalation
chest expands due to contractions
fourth step in inhalation
pressure inside alveolar cavities drop
fifth step in inhalation
diaphragm relaxes when inhaling
sixth step in inhalation
O2
oxygen
CO2
carbon dioxide
Asthma
chronic and allergic condition that makes the breathing airways narrow and swollen
Bronchitis
inflammation or swelling of the breathing passages between nose and lungs
Emphysema
long-term disease of the lungs caused by prolonged exposure to respiratory irritants. damages the alveoli of the lungs and breathing passages
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
associated with a group of diseases: emphysema, asthma, and chronic bronchitis. patients experience long-term obstruction of airflow that makes breathing difficult
Lung Cancer
caused by long-term exposure to tobacco smoke. tumors take up space in the lungs used for gas exchange