ABO BLOOD GROUP SYSTEM
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
001
ABO
Chromosome 9
A, B, AB, O
Give the appropriate answers.
ISBT number of ABO Blood group System
ISBT name
In what chromosome is ABO blood group found?
What are the 4 phenotypes?
[TRALI]: Transfusion-related Acute Lung Injury
Most common cause of death from transfusion reactions
Whole blood
Commercial anti sera
Antigen
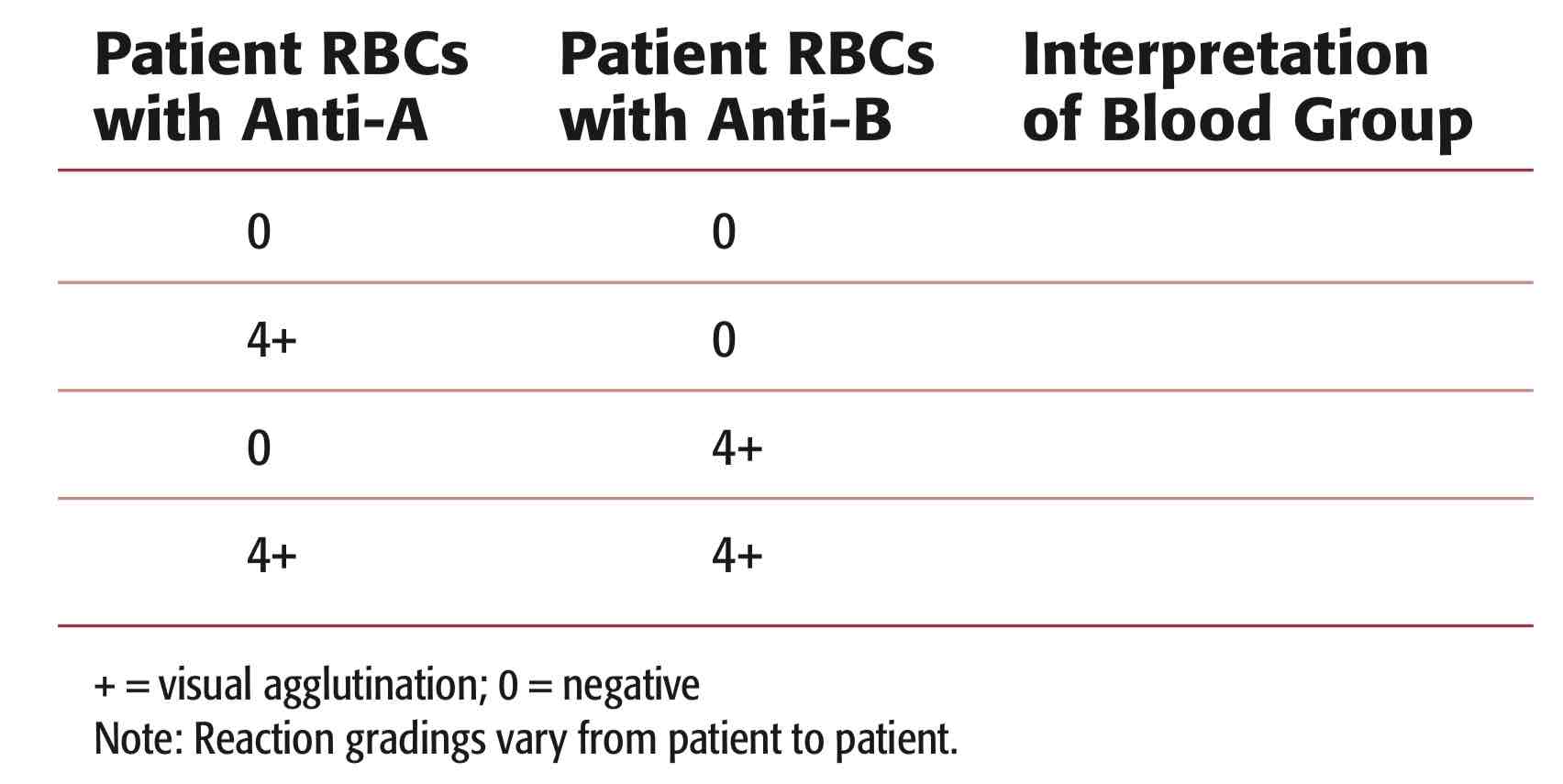
FORWARD TYPING.
What is the sample used?
What is the reagent used?
What is being detected?
Serum
Known reagent RBCs - A1 and B cells
RBC Suspension (3-5%)/Red cells
Antibodies
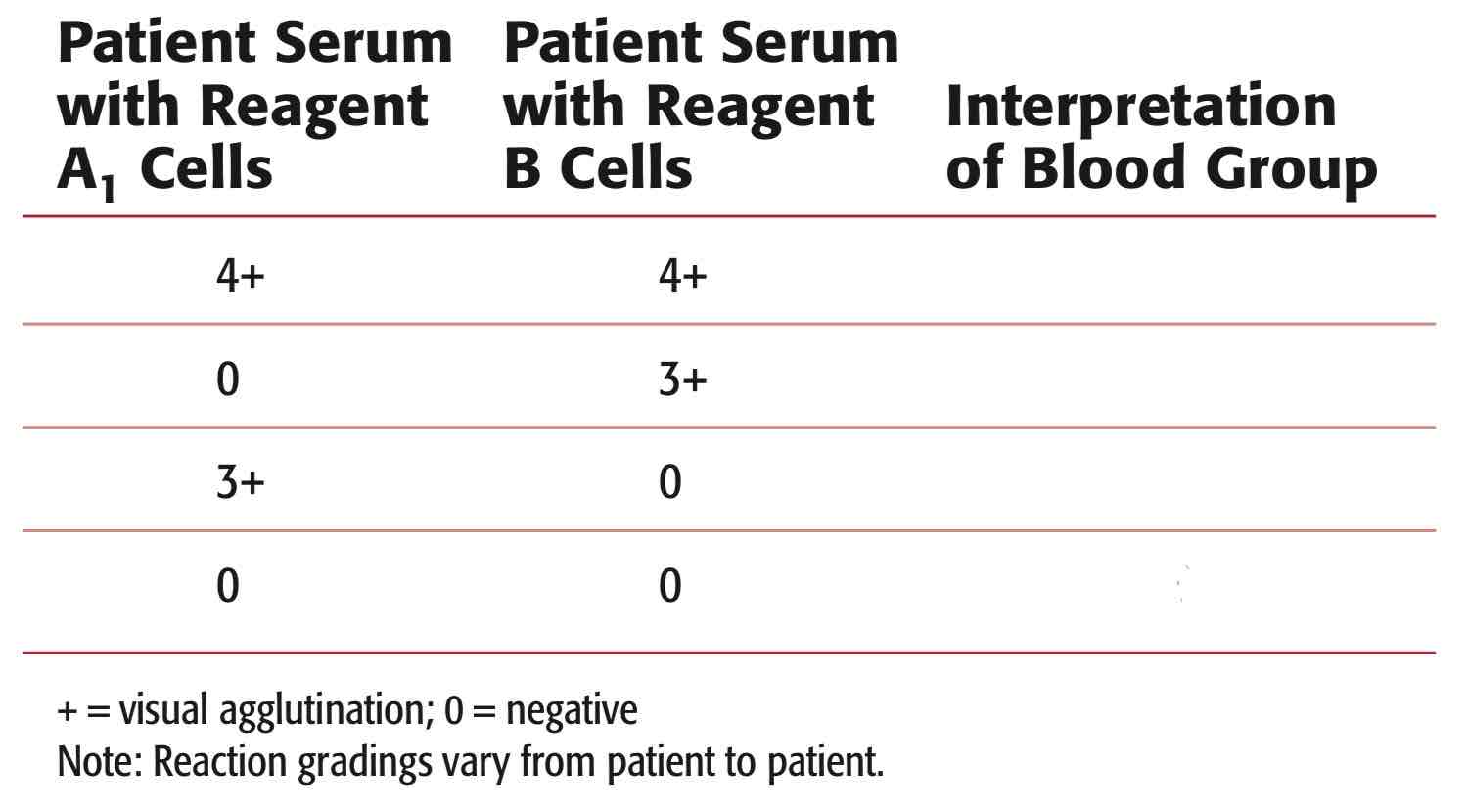
REVERSE BLOOD TYPING.
What is the sample used?
What are the reagents used?
How are the reagents achieved?
What is being detected?
Hemolysis
Transfusion of incompatibe blood will immediately result in?
Human or Clerical Errors
What is the most common cause of ABO Hemolytic Transfusion reaction?
Karl Landsteiner (1901)
Alfred von Decastello and Adriano Sturli (1902)
Emil Von Dungern and Ludwik Hirszfeld (1911)
A1, A2, A1B, A2B, B, AB, O
DISCOVERY OF ABO BLOOD GROUP SYSTEM.
Discovered human ABO groups.
Discovered AB blood group.
Divided group A into 2 subgroups - A1 and A2
ABO system classified into 7 groups, which are?
Anti-A antisera
Tryphan blue dye
Anti-B antisera
Acriflavin dye
It is a monoclonal antibody antiserum containing IgM that is colored blue.
It contains?
A monoclonal antibody antiserum containing IgM that is colored yellow.
It contains?
O
A
B
AB
Determine the Blood Type using ABO Forward Grouping.
Bacteria and Pollen
What elements in nature are found to be chemically similar to A and B antigens?
Blacks
Asians
Group B (in ABO Blood Group) is found twice as frequently occuring in what race?
Asians
The subgroup A2 is rare in what race?
O
A
B
AB
Determine the Blood Type using REVERSE GROUPING.
Slide method - screening
Tube method - confirmatory
What are the two methods of determining ABO Blood Group?
What is their difference?
Avidity
Specificity
Specific agglutination titer
It refers to how fast the reaction is.
It refers to how the antibodies react with their corresponding antigen.
Means it is within the zone of equivalence.
IgM
Complement
Room or Cold temperatures
The ABO antibodies are predominantly (what immunoglobulin) that activate ___ and react at ___ temperatures.
Mother’s (maternal origin)
Most antibodies found in cord blood serum are of whom?
False. It is not valid because the antibodies only represent the ones of maternal origin. Forward grouping on cord blood is the only test that can be performed.
True or False. It is valid to do serum ABO testing for babies 3 to 6 months of age because all antibodies are of IgG maternal antibodes which reflect the antibodies of the infant.
Between 5 to 10 years of age
The peak of antibody production happens when?
Absent in the plasma
Present in the plasma
LANDSTEINER’S LAW.
If an agglutinogen is present on the RBC membrane, the corresponding agglutinin is?
If an agglutinogen is absent on the RBC membrane, the corresponding agglutinin is?
2+
Determine the Grade using Tube Method.
Numerous medium-sized clumps with reddish background.
4+
Determine the Grade using Tube Method.
One solid aggregate with clear background.
3+
Determine the Grade using Tube Method.
Several large clumps with clear background.
1+
Determine the Grade using Tube Method.
Numerous small-size clumps with reddish background.
Trace
Trace to 2+
Determine the Grade using Tube Method.
Numerous very small clumps with reddish background
Microscopic
DONATE — RECEIVE
A, AB — A, O
B, AB — B, O
A, B, O, AB — O
AB — AB, O
Determine to whom they can donate and from who they can receive blood.
A
B
O
AB
O, A, B, AB
O, B, A, AB
Frequency of ABO Blood Groups
Whites/ Blacks
Asians
Natural antibodies
These are naturally occurring antibodies that are present at birth. They do not require the presence of a foreign red blood cell to produce ABO antibodies. It is not a product of exposure.
ABO antibodies
IgM
These are non red blood cell stimulated due to environmental exposure. Also called Immune Antibodies.
It is mostly composed of?
IgG
This is the predominant antibody in Group O individuals
IgM
This is the predominant antibody in Group A and B individuals
Anti-A,B
A, B, and AB cells
This antibody is found in the serum of Group O individuals.
Which cells does it react with?
False. It is one antibody.
True or False.
Anti-AB is a mixture of anti-A and anti-B antibodies.
Anti-A
Group O and B individuals have this antibody.
Anti-A and Anti-A1
A1 antigen (not A2 antigen)
A2B subgroup by 22-30% (1-8% in A2)
None
ANTI-A ANTIBODY.
It can be separated into what components?
Anti-A1 agglutinates what antigen?
In which subgroup does it occur more?
Is there an anti-A2 antibody?
H antigen
The precursor structure on which A and B antigens are made.
A1 gene
This gene very efficiently converts all of H substance to A antigen. Hence, A1 and A1B individuals have Anti-H.
IgM cold agglutinin
Room temperature
Anti-H Antibody
What kind of immunoglobulin/ antibody?
Best reacts at what temperature?
Bernstein (1924)
He described that an individual inherits one ABO gene from each parent and that these two genes determine which ABO antigens are present on the RBC membrane.
Co-dominant alelle
Genes are inherited as ___ because there is 1 ABO mother and 1 ABO father.
Amorph
The O gene has no detectable antigen produced in response to its inheritance. It is referred to as?
Use punnett square
How to identify the blood type of the offspring?
Homozygous - AA
Heterozygous - AO
Give examples of homozygous and heterozygous genes.
Phenotype
Genotype
A, B, and O refers to?
AA, BO, and OO refers to?
Mendelian Law
The inheritance of genes follows what law?
Bernstein theory
This theory states that there is one locus on a chromosome at which any of three three alleles may be located.
6th week
RBC, WBC, platelets; salivary glands, pancreas, kidney, body fluids
37 weeks of gestation
2-4 years
ANTIGENS
Appear during what week of fetal life?
Can be seen in what cells and tissues?
When is it produced?
When is it fully expressed?
Chromosome 19
H genes can be seen in which chromosome?
H gene (chromosome 19)
Se gene (chromosome 19)
The presence or absence of the ABH antigens on the RBC membrane is controlled by the?
The presence or absence of the ABH antigens in secretions is indirectly controlled by the?
H genes - H and h alleles (h is amorph)
Se genes - Se and se alleles (se is amorph)
ABO genes - A, B, and O alleles (O is amorph)
What genes are present in ABO Antigen Genetics?
ABO, Hh, and Se genes
These genes do not code for the production of antigens. Instead, it produce specific glycosyltransferase that add sugars to a basic precursor substance.
Glycosyltransferase
Paragloboside / glycan
A transfer sugar
A precursor material where A, B, and H antigens originate
Type 2 precursor
Determine the type of precursor.
The terminal galactose is attached to the N-acetylglucosamine in a beta 1 → 4 linkage.
Type 1 precursor
Determine the type of precursor.
The galactose and N-acetylglucosamine is linked via beta 1 → 3 linkage.
FUT 1 (H)
FUT 2 (Se)
Chromosome 19
The FUT 1 (_) and FUT 2 (_) genes are closely linked and are located in what chromosome?
H gene
This must be inherited to form ABO antigens on the RBCs.
Se gene
This must be inherited to form ABO antigens in secretions.
C) a-2-L-fucosyltransferase
» due this, the immunodominant sugar is L-fucose.
Determine the glycosyltransferase of H gene.
a) a-3-D-galactosyltransferase
b) a-3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase
c) a-2-L-fucosyltransferase
B) a-3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase
» the immunodominant sugar is N-acetyl-o-galactosamine.
Determine the glycosyltransferase of A gene.
a) a-3-D-galactosyltransferase
b) a-3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase
c) a-2-L-fucosyltransferase
A) a-3-D-galactosyltransferase
» the immunodominant sugar is D-galactose.
Determine the glycosyltransferase of B gene.
a) a-3-D-galactosyltransferase
b) a-3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase
c) a-2-L-fucosyltransferase
RBC → Glucose → Galactose → N-acetylglucosamine → Galactose
The precursor substance contains?
Type 2 chains
ABH antigens are derived from what chains?
Type 1 and 2 precursors
Blood group substances in secretion are made from?
At least one FUT 1 (H) genes and two O genes.
Individuals who are blood group O has these genes.
a-2-L-fucosyltransferase
Oligosaccharide chain on the terminal galactose
Type 2 chains
H genes elicits the production of this enzyme.
It transfers L-fucose to the?
What chain type is it involved in?
L-fucose
Blood Group O
This sugar is responsible for the H specificity.
This ABO Blood Group has the highest concentration of H antigen.
h alelle
hh allele
Bombay
This allele of the H gene is quite rare.
This allele of the H gene is extremely rare
This refers to a phenotype that lacks normal expression of ABH antigens because of hh genotype.
hh genotype
This H genotype does not elicit production of a-2-L-fucosyltransferase
Transferase
The A gene tends to elicit higher concentrations of what enzyme than B gene?
B enzyme
When both A and B genes are inherited, this enzyme competes more efficiently for the H substance, causing more amount of antigenic site.
Seven
» 6,7 is dominant
» most genes are in exon 7
How many exons does the ABO gene have?
Sese (FUT2) genes
This gene codes for the production of a-2-L-fucosyltransferase that modifies the type 1 precursor substance in secretions to form H substance.
Blood Group Substances
These are soluble antigens (A,B,H) that can be found in secretions.
H and Se genes
ABO Antigens in secretions is controlled by?
Secretor
Nonsecretor
If the Sese or SeSe genotype is inherited, the person is called?
If the sese genotype is inherited, the person is called?
Glycoproteins
Group A individual that is a secretor will secrete ____ carrying A and H antigens.
Secretors (Sese or SeSe)
It secretes A,B, or H substances in saliva and other body fluids corresponding to the person's blood type.
ABH antigens on RBCs
ABH Soluble Substances
ABH Antigens on RBCs
ABH Soluble Substances
ABH Antigens on RBCs
Determine if ABH ANTIGENS ON RBCS or ABH SOLUBLE SUBSTANCES.
The enzyme produced by the H gene acts as primarily on type 2 chains.
The substances are glycoproteins.
Type 2 chain refers to a beta 1 → 4 linkage in which the number one carbon of the galactose is attached to the four carbon of N-acetylglucosamine.
Type 1 chain refers to a beta 1 → 3 linkage in which the galactose is attached to the three carbon of N-acetylglucosamine sugar.
They can be glycolipids, glycoproteins, or glycosphingolipids.
Silent
The O gene is a ___ allele. It does not alter the structure of the H substance. Hence, it has more H antigen sites.
O → A2 → B → A2B → A1 → A1B
List down the cells from the greatest amount of H antigen to the least amount of H.
Von Dungern
He described two different A antigens based on reactions between group A RBCs and Anti-A and Anti-A1.
A2
Both A1 and A2
Between A1 and A2, who does not react with anti-A1 lectin reagent?
Between A1 and A2, who reacts with anti-A reagent (anti-A plus anti A1)?
Lectins
These are seed extracts that agglutinate human cells with some degree of specificity.
Dolichos biflorus
Bandeiraea simplicifolia/ Griffonia simplicifolia
Ulex europaeus
Determine the lectin.
A lectin that agglutinates A1 and A1B.
A lectin that agglutinates B cells.
A lectin that agglutinates O cells and other ABO blood groups depending on the amount of H antigen available.
ABO subgroups
They differ in the amount of antigen present on the RBC membrane.
They are the result of less effective enzymes (not as efficient in converting H antigens to A or B antigens).
A1 and A2
» they both strongly react with anti-A reagent.
What are the subgroups of A?
A subgroups
This subgroup is naturally occuring, IgM, cold reactive that is not clinically significant unless it reacts at 37 degrees celsius.
It can cause ABO discrepancies in both forward and reversed grouping.
Can cause crossmatch incompatibilities
Reacts with anti-A1
A2 gene
A2 and A2B
This gene doesn't convert the H3 & H4 to A very well. Hence, there is few of their antigen sites.
These individuals may produce an anti-A1.
A3
These red cells cause mixed field agglutination when polyclonal anti-A or anti-A,B is used. They may contain anti-A1.
Mixed field agglutination
This appears as small agglutinates with a background of unagglutinated RBCs.
Decreased number of A antigen sites per RBC resulting in weak or no agglutination with anti-A
Varying degrees of agglutination by anti-A, B
Increased variability in the detectability of H antigen resulting in strong reactions with anti-H
Presence or absence of anti-A, in the serum
What are the characteristics of weaker A subgroups?
A,end
Ax
Am
Ael
DETERMINE THE A SUBGROUP.
Displays weak mixed field agglutination with anti-A and anti-AB. No glycosyltransferase is detected.
Do not agglutinate with anti-A but agglutinates with anti-AB. It does not produce anti-A1.
Displays weak to no agglutination by anti-A and anti-B. It is inherited as a rare allele and does not produce anti-A1.
It is unagglutinated by anti-A and anti-AB reagents. It is a rare gene at ABO locus. Only contains H substance in the saliva.
Am and Ay
Ael
A3, Am, Ay
Am
DETERMINE THE A SUBGROUP.
Have no anti-A1 reaction.
Have some anti-A reaction.
Have A,H substance in saliva.
Have A transferase in serum.
Bel
B3
B, B3, Bm
Bx, Bel
Bm, B3
Bm
DETERMINE THE B SUBGROUP.
It is unagglutinated by Anti-B and Anti-AB. An extremely rare phenotype that is described as unique mutation in the exon 7 of B gene.
Displays mixed field agglutination that is the most frequent weak B phenotype.
Has B,H substances in the saliva.
Has unexpected anti-B (no B glycosyltransferase).
Has weak positive B glycosyltransferase
More frequent in Japan.
OH — anti-A, anti-B, anti-AB
Oh — null phenotype, has inheritance of hh
Bhende, 1952
Other bombay individuals
What is true phenotype?
What is bombay phenotype?
Bombay was found by who in what year?
Who can donate blood to bombay individuals?
False. They do not have H, A, or B antigen but they are Blood/Cell Group O.
True
MODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE.
Bombay can have H, A, or B antigen that indicates they are Blood Group O.
Bombay RBCs are NOT agglutinated with anti-A, anti-B, or anti-H (no antigens present).
False. They do not have H, A, or B antigen but they are Blood/Cell Group O.
True
MODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE.
Bombay can have H, A, or B antigen that indicates they are Blood Group O.
Bombay RBCs are NOT agglutinated with anti-A, anti-B, or anti-H (no antigens present).
Bombay
True Type O
Between True Type O and Bombay, who has antibodies against O cells?
Between True Type O and Bombay, who has anti-H antigens?
Parabombay phenotype
A rare phenotype wherein there is compete lack of H antigen or small amounts of H antigen is present.
The H antigen is weakly expressed.
Hangover
Criminality
Good teeth
Associtions of blood group specificity with terminologies:
(__) for A group
(__) for B group
(__) for O group