B cells
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
B cells are lymphocytes. What do B cells do?
Protect against infection by the production of antibodies
Presentation antigen to CD4 T cells through class II MHC (alongside macrophages and dendritic cells) (extracellular pathogen)
Regulation of the immune response by the production of cytokines. B cell derived cytokines are predominantly IL-10 and TNFa. IL-10-producing suppressive B cells are known as Breg
what are Breg cells?
IL-10-producing suppressive B cells are known as Breg
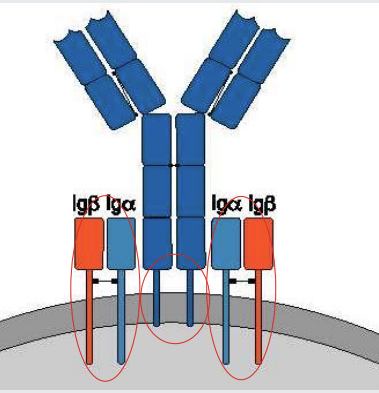
B cell receptor, Iga and Igb
The B cell receptor comprises an antibody molecule of 2 identical heavy chains and 2 identical light chains.
The antibody molecule has a transmembrane domain but no independent signalling capability.
B cell receptor signalling is dependent on Iga and Igb.
when the B cell receptor is cross linked - the signalling is initiated towards the nucleus
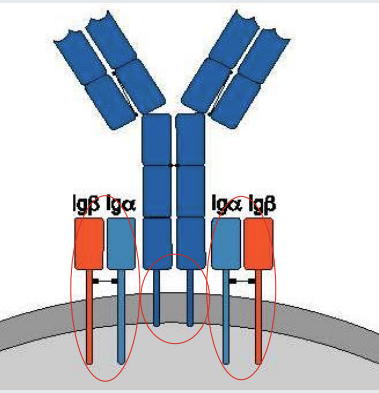
what is B cell receptor signalling is dependent on?
Iga and Igb.
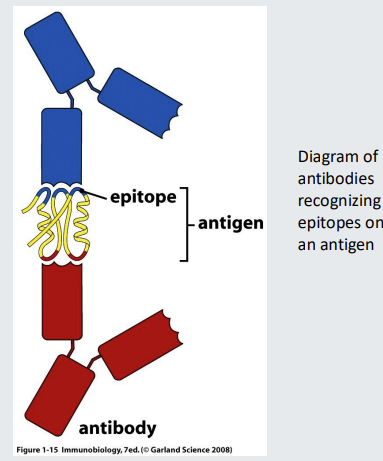
Antibodies recognize epitopes on the surface of antigens
Antibodies bind to the surface of antigens.
Binding occurs via the tips of the Y shapes that are highly variable between B cells.
A single antigen can have multiple epitopes on its surface that can be recognized by antibodies expressed by, or secreted by different B cells.
methods of antibody binding 2
Binding can be physical such as lock and key
physicochemical such as hydrophilic/ or electrostatic attractions.
Antibody structure - components
Antibodies comprise two identical heavy chains (base) and two identical light chains (flared out chains)
The heavy chains are joined together by disulphide bonds identified by the dotted oval
The light chains are joined to the heavy chains by disulphide bonds identified by dotted circles.
The ovals that are joined together to form the heavy and light chains structures are called domains
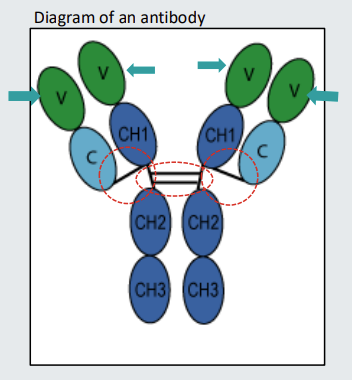
Antibodies have a hinge and Fab’ and Fc portions
The part of the antibody indicated with the dotted oval is the hinge. Some antibodies have longer hinge regions that enable them to bend- the longer the hinge the more bendy the antibody will be
The part of the antibody above the hinge is sometimes referred to as the Fab. The part of the antibody comprising the hinge and below is sometimes referred to as the Fc.
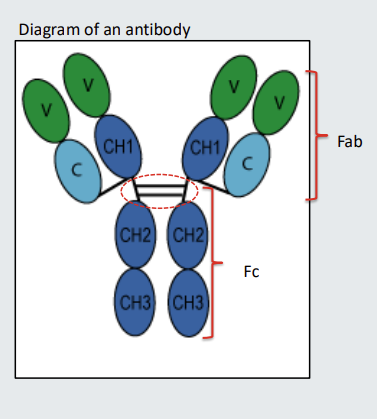
Fc receptor
Some cells, including macrophages and neutrophils, have receptors for antibody that bind the Fc. The receptors are called Fc receptors. The term Fc is often followed by the Greek letter for the class of antibody that the Fc receptor recognises. For example, an Fc receptor that binds IgG is an Fcg receptor. An Fc receptor that binds IgE is and Fce receptor
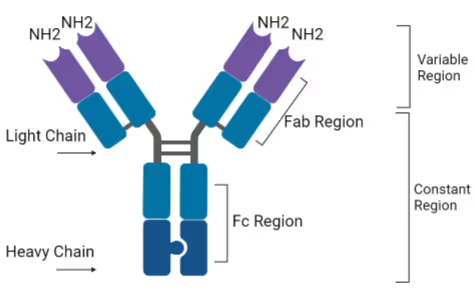
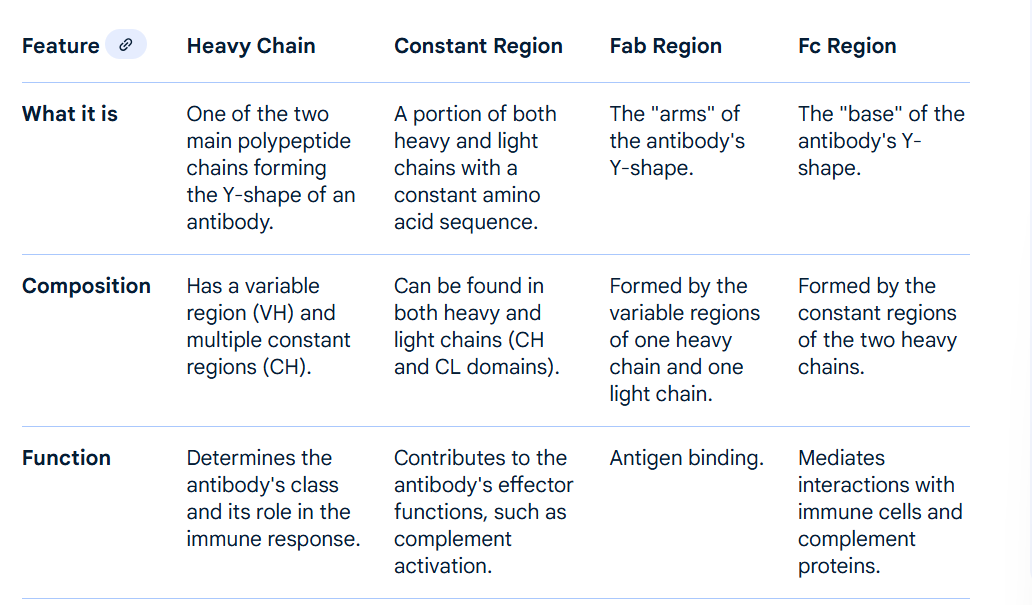
constant region , variable region and light/heavy chains
the constant region ma include some of the light chains
so the Fab is above the hinge, heavy and light, with constant and variable regions. but the fc is below the hinge, only heavy and only constant?
There are 5 immunoglobulin ‘isotypes’ or ‘classes’
The 5 different immunoglobulin ‘isotypes’ or ‘classes’ are IgG, IgM, IgD, IgA and IgE.
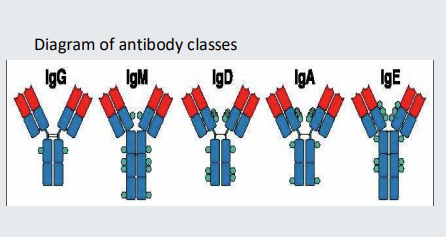
IgG
IgG in humans has 4 subclasses that differ in their constant region sequences that are encoded by different gene segments.
IgG subclasses are IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4 are numbered according to their abundance in human blood.
IgG1 is the most abundant IgG subclass
IgA
IgA in humans has 2 subclasses that differ in their constant region sequences that are encoded by different gene segments.
IgA in blood is mostly IgA1. IgA in gut can be either IgA1 or IgA2.
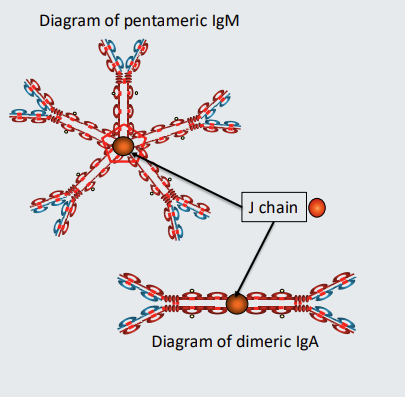
which antibodies can be polymeric?
IgM and IgA can be polymeric
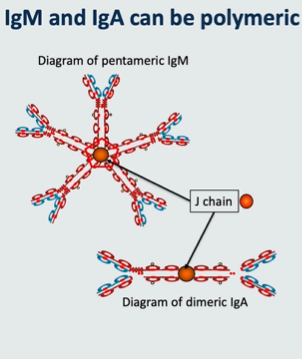
Polymeric antibodies
IgM in blood is pentomeric. It comprises 5 units of IgM held together by a molecule called J chain. ‘J’ stands for ‘joining’. Only when it’s in the blood is it pentameric - when it is on cell surface as part of a B cell receptor it is monomeric
IgA can be monomeric of dimeric. When IgA is dimeric the two units are also held together by J chain.
IgA1 and IgA2 subclasses can each be dimeric or monomeric. Therefore there are 4 different types of IgA
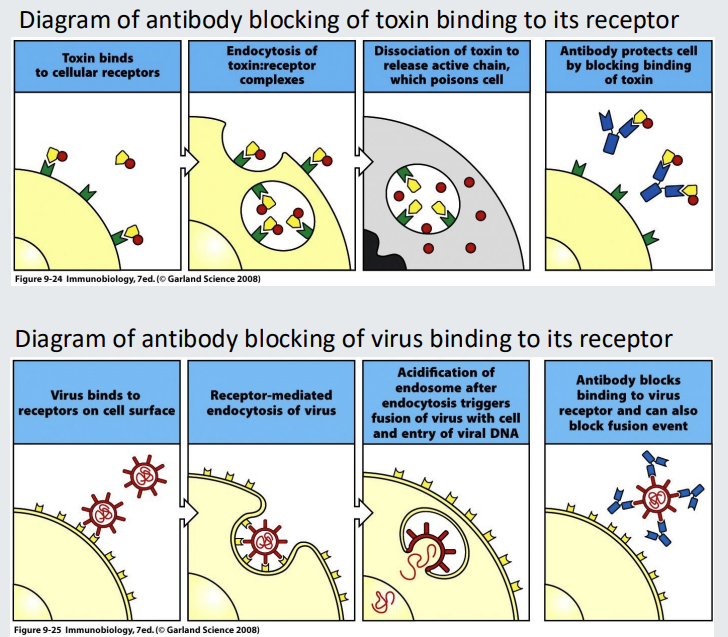
Functions of antibodies list 6
block receptors (binding to toxins or viruses)
complement activation
opsonisation
ADCC
Agglutination
Mast Cell Degranulation
functions of antibodies - blocking 2
Antibodies can function purely by binding to a target to prevent it binding to a receptor.
An example is blocking toxin from binding to toxin receptor.
Another example is blocking a virus preventing it from binding to its receptor
complement activation
IgG and IgM can ‘fix’ complement when they bind to a surface (of a bacterium for example). This initiates the complement cascade that results in the production of proinflammatory molecules and formation of the membrane attack complex
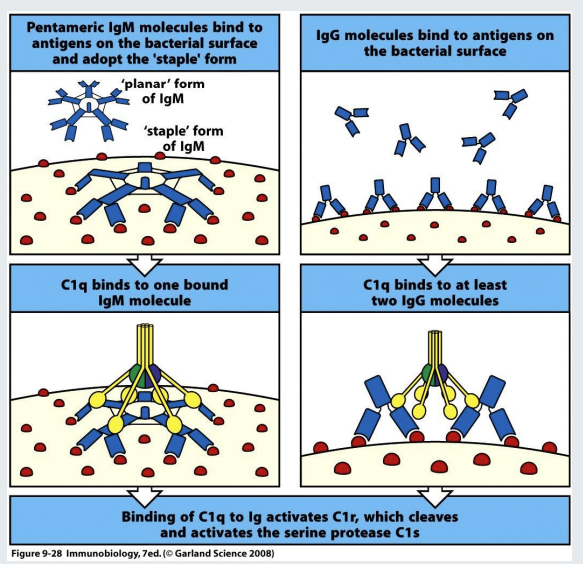
planar → staple conformation of IgM →C1q is able to identify the change in conformation
C1q can also recognise bound IGg - binds to at least 2
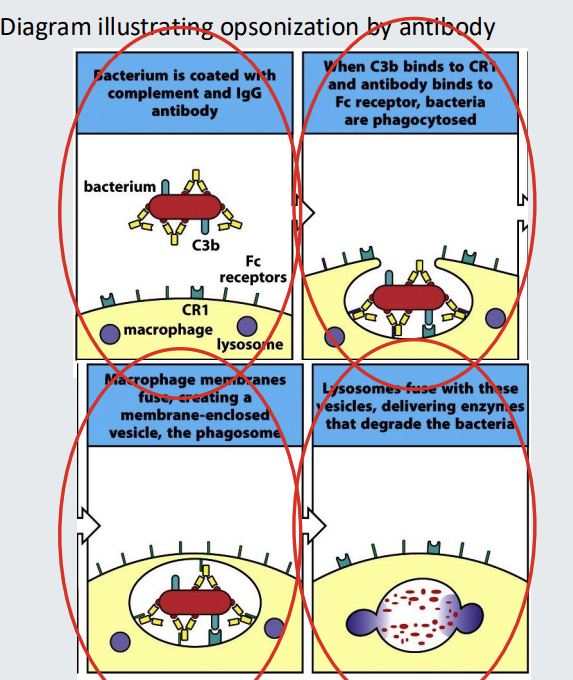
opsonisation
The binding of IgG to the surface of a pathogen can make the pathogen more visible to phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils.
The bound IgG can be recognized by Fcg receptors of phagocytes.
This facilitates phagocytosis.
The antibody can be referred to as an opsonin
The antibody coated target is said to be opsonized.
The process is called opsonization.
Complement C3b can also be an opsonin.
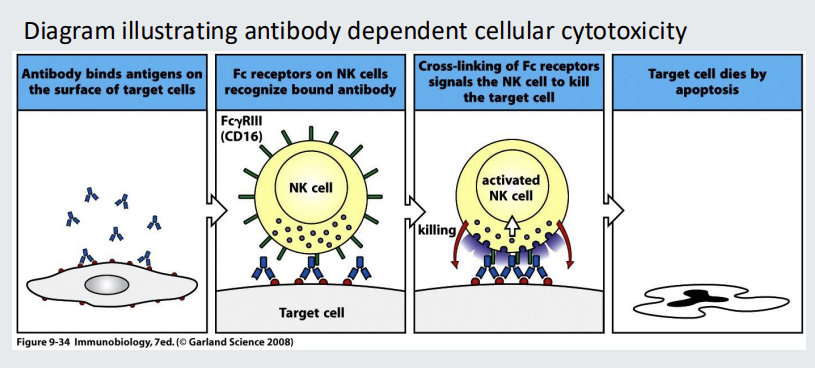
Functions of antibodies: 4. ADCC
ADCC stands for ‘antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity’ IgG antibody bound to a target cell can be recognized by Natural Killer (NK) cells via their Fcg receptors The NK cells with cross-linked Fc receptors can the secrete cytotoxic granules into the synapse, resulting in the death of the target cell.
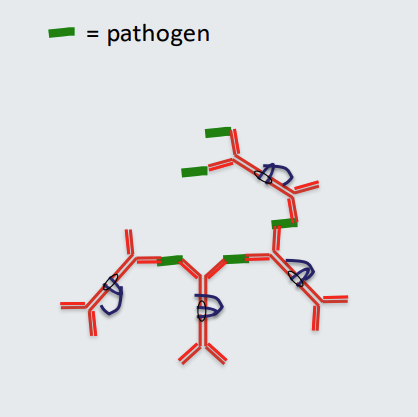
Functions of antibodies: 5. Agglutination
Polymeric antibodies with multiple binding arms (polymeric IgA has 4 binding arms) can cross link pathogen resulting in formation of a lattice.
This can ‘disarm’ the pathogen. Polyclonal IgA antibodies can be actively secreted at mucosal sites such as the gut, eyes and mouth and are at relatively high concentration in mucus, saliva and tears compared to other antibodies.
IgA antibodies are transported across epithelia by secretory component that binds to the J chain.
IgA has a specific role in regulating microbial populations due at least in part to its ability to coat and agglutinate bacteria
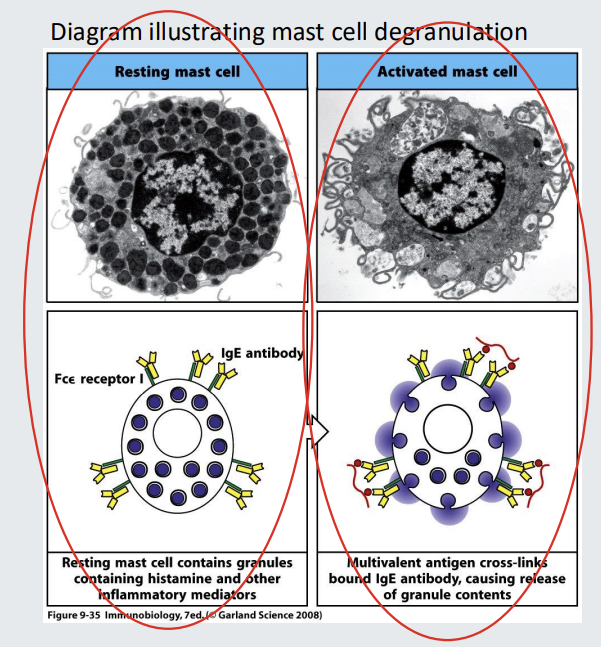
Functions of antibodies : 6. Mast Cell Degranulation
Mast cells contain granules each containing proinflammatory molecules including histamine. Mast cells have receptors for IgE (Fce receptors).
IgE can bind to the Fce receptors of mast cells and so long as the IgE is not cross linked, there will be no consequences.
If the IgE bound to the Fce receptors of mast cells becomes cross linked (via antiGEN or allegen), the mast cell will become activated and granules released resulting in a characteristic ‘allergic’ reaction.
the antibody variable region
the tip of the antibody Y shape is the variable region
the variable region consists of → variable, diiversity and joining
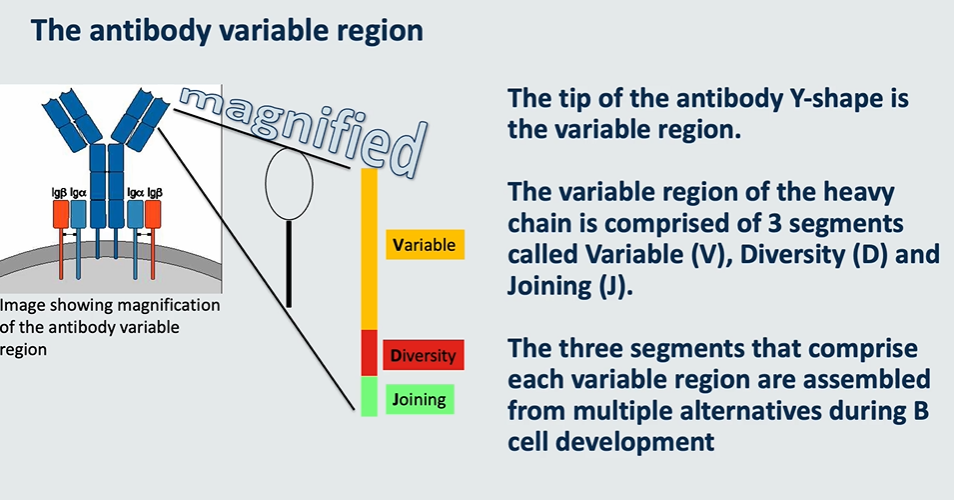

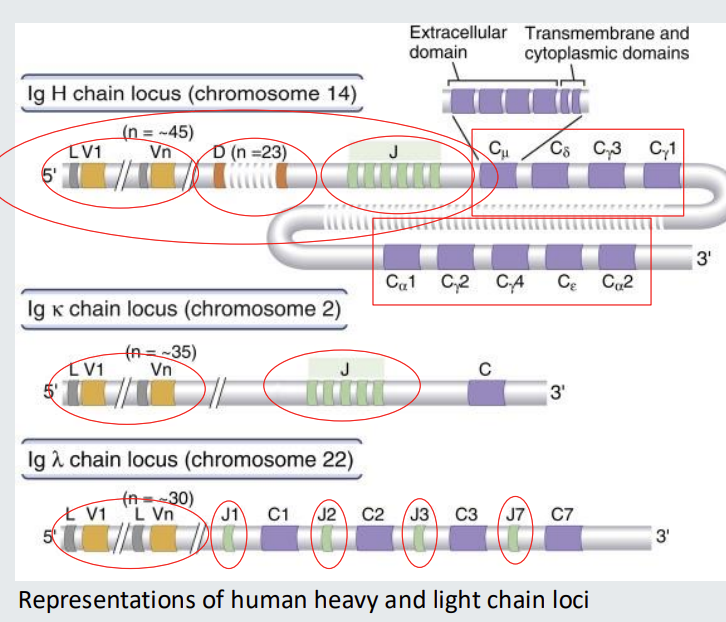
Illustration of immunoglobulin heavy and light chain loci
Immunoglobulin variable region genes before commitment to become a B cell comprise multiple alternatives for each of V (Variable), D (Diversity) and J (Joining) segments.
in heavy chain locus there are 45 different options for V - different sequences but all code for V
23 different options for D
6 different options for J
then there are different constant regions

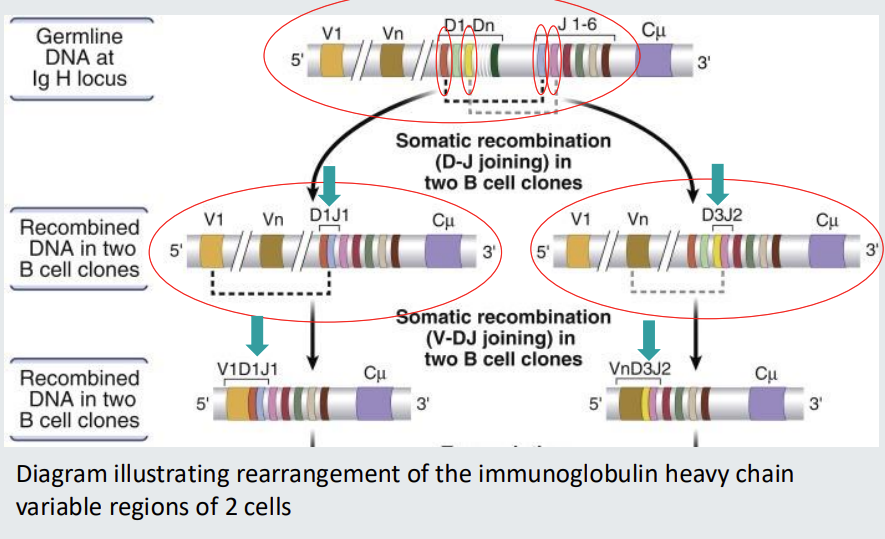
Assembly of unique B cell receptors
Single gene segments from multiple alternatives in the germline assemble to form a unique receptor sequence.
Maths behind BCR variability
*heavy chain diversity
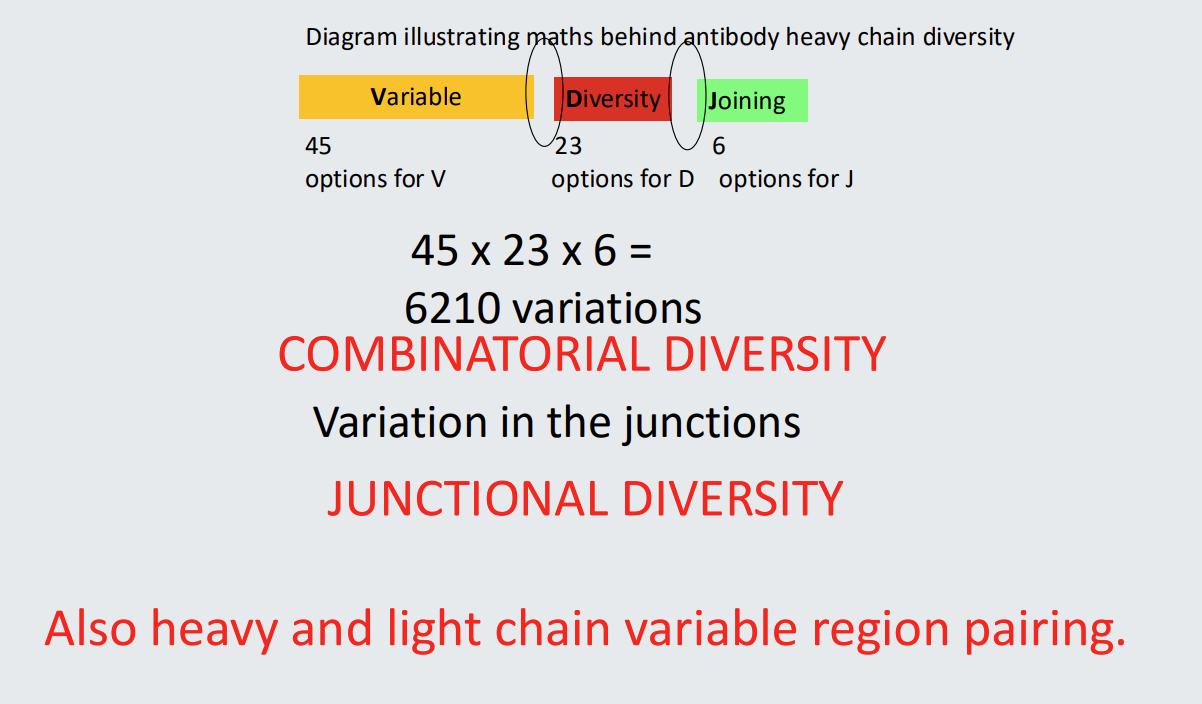
junctional diversity
variation in the junctions - the actual mechanisms that pairs the segments together → introduction of random nucleotides as a form of glue
how is variation increased by light chain and heavy chain diversity?
by the combination of heavy and light chain diversity - this makes additional combos

B cell responses can be…
T dependent or T- independent
T-dependent B-cell responses
T-dependent B-cell responses require the antigen to have a protein component.
isotype switched, high affinity antibodies, memory B cells, long lived plasma cells
needs T cell receptor to help cross link antigen
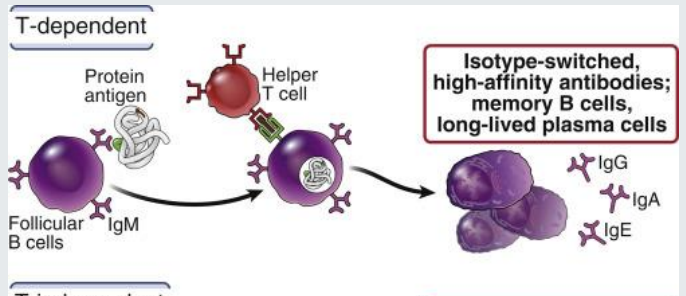
T-independent B-cell responses
T-independent B-cell responses depend on antigens having repeat subunit structures so that they can cross-link the B cell receptor - without T cell help
mainly IgM, low affinity antibodies, short lived plasma cells
do not increase in affinity based on repeated exposure
The germinal centre response - Tdependent
Centroblasts divide rapidly in the germinal centre and undergo somatic hypermutation of antibody variable region genes.
They have no antibody on their cell surface.
Centroblasts mature into relatively non dividing centrocytes and re-express antibody.
Centrocytes will sample antigen stored by STROMAL cells called follicular dendritic cells IF their antibody has sufficient affinity.
Centrocytes able to sample antigen, process and present it to T follicular helper cells (in form of C2 MHC) and acquire help to survive.
Centrocytes with low affinity antibody cannot compete for antigen do not receive a T cell survival signal and die.
A Darwinian process of survival of the fittest.
Affinity maturation - generation of high affinity antibodies
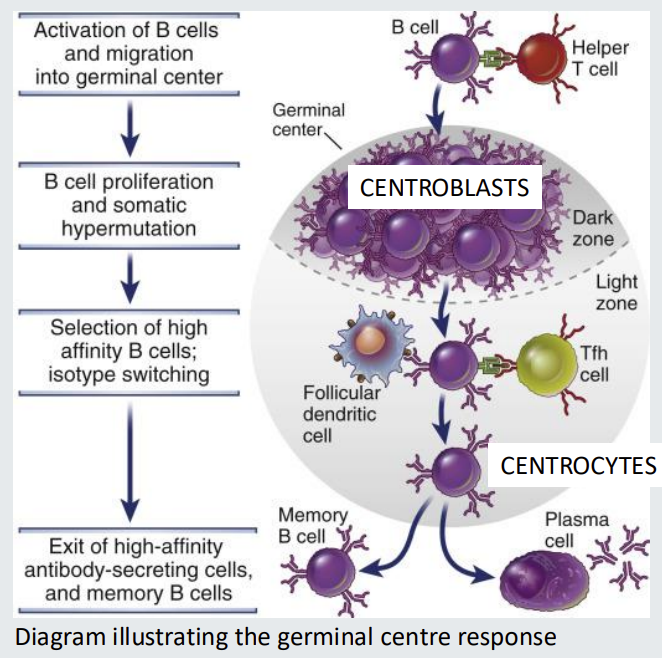
Germinal centre response generates memory cells and plasma cells
Memory B cells can reside in tissues and circulate in blood.
Can be IgM+ or class switched - not D.
Have antibody variable regions genes that are mutated by somatic hypermutation - they acquired this when they were at the centroblast stage of development
Plasma cells home to bone marrow or gut. Can be IgM+ or class switched - just not D. Have antibody variable regions genes that are mutated by somatic hypermutation
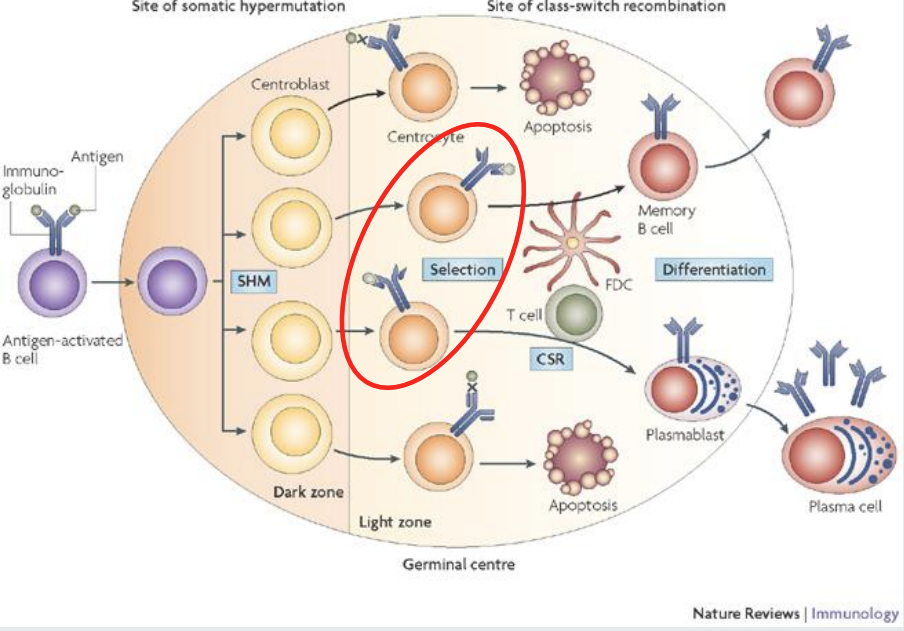
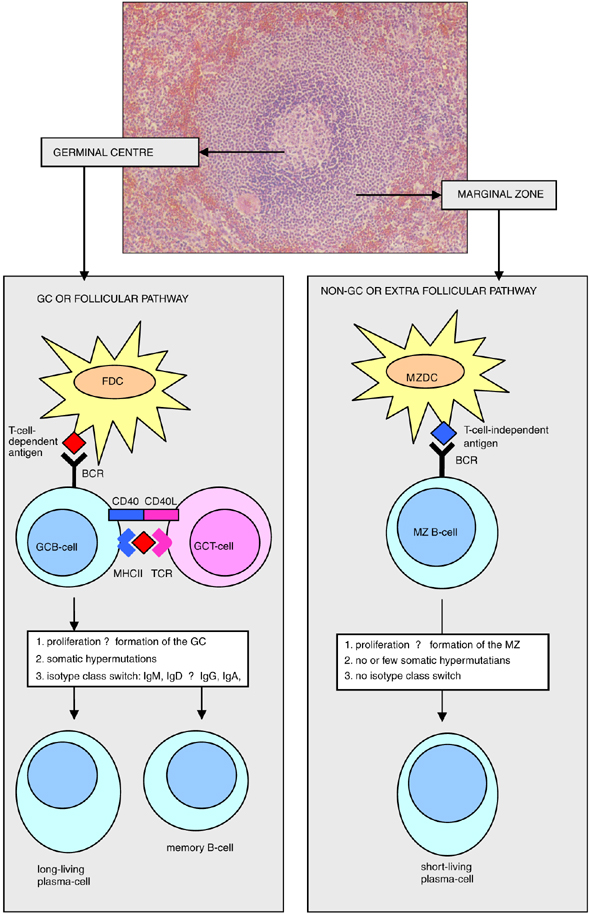
note that T independent B cell response cant produce memory B cells nor can they class switch - so why are they there then? -?
LOs
