Openstax Biology 2eChapter 6
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
metabolism
term for all of an organism's chemical reactions
cellular respiration
metabolism of glucose

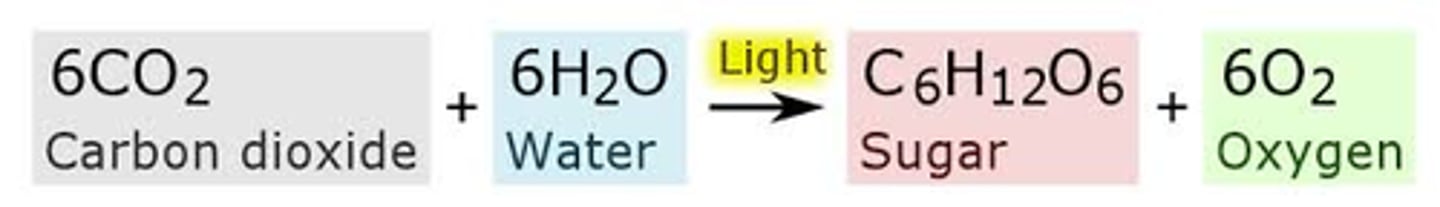
photosynthesis
production of glucose
metabolic pathway
begins with a specific molecule and ends with a product. (i.e. metabolic processes: photosynthesis and cellular respiration).
each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme
anabolic pathway
consumes energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones.
body builds molecules by forming bonds which store energy in the electrons of said bonds.
synthesis of protein from amino acids is anbolism
catabolic pathway
release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simple compounds.
body breaks down the molecule by breaking the bonds and releasing stored energy in electrons.
cellular respiration is an example.
energy
the ability to work. electrical, light and heat.
Kinectic energy
energy associated with objects in motion
potential energy
energy that has the potential to do work. stored energy.
chemical energy
potential energy in chemical bonds that is released when those bonds are broken.
exergonic
reactions that release energy
catabolic reactions release energy.
cellular respiration- metabolism of glucose
endergonic
requires energy
anabolic reactions require energy
photosynthesis- production of glucose requires energy.
aerobic
type of cellular respiration that contains oxygen.
anaerobic
type of cellular respiration that does not contain oxygen
activation energy
name of energy needed to start chemical reaction.
Law of Thermodynamics
study of energy and energy transfer.
in an open system energy matter can be transferred between system and its surroundings.
biological systems are open systems.
The First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed but it cannot be created or destroyed.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
During every energy transfer or transformation, some energy is unusable and is often lost as heat.
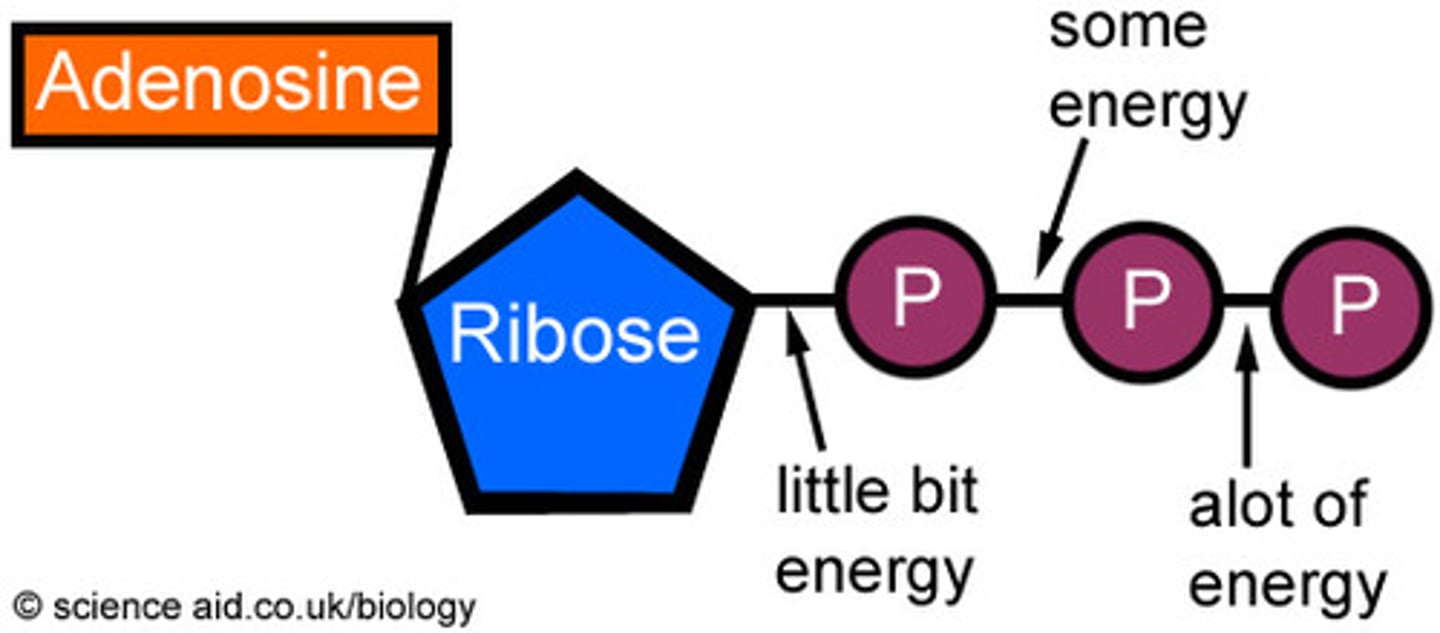
adenosine triphosphate
ATP, composed of ribose(a sugar), adenine (a nitrogenous base), and three phosphate groups.
energy coupling
managing energy resources by using an exergonic process (release of energy) to drive an endergonic process (requires energy) one.
most energy coupling is mediated by ATP
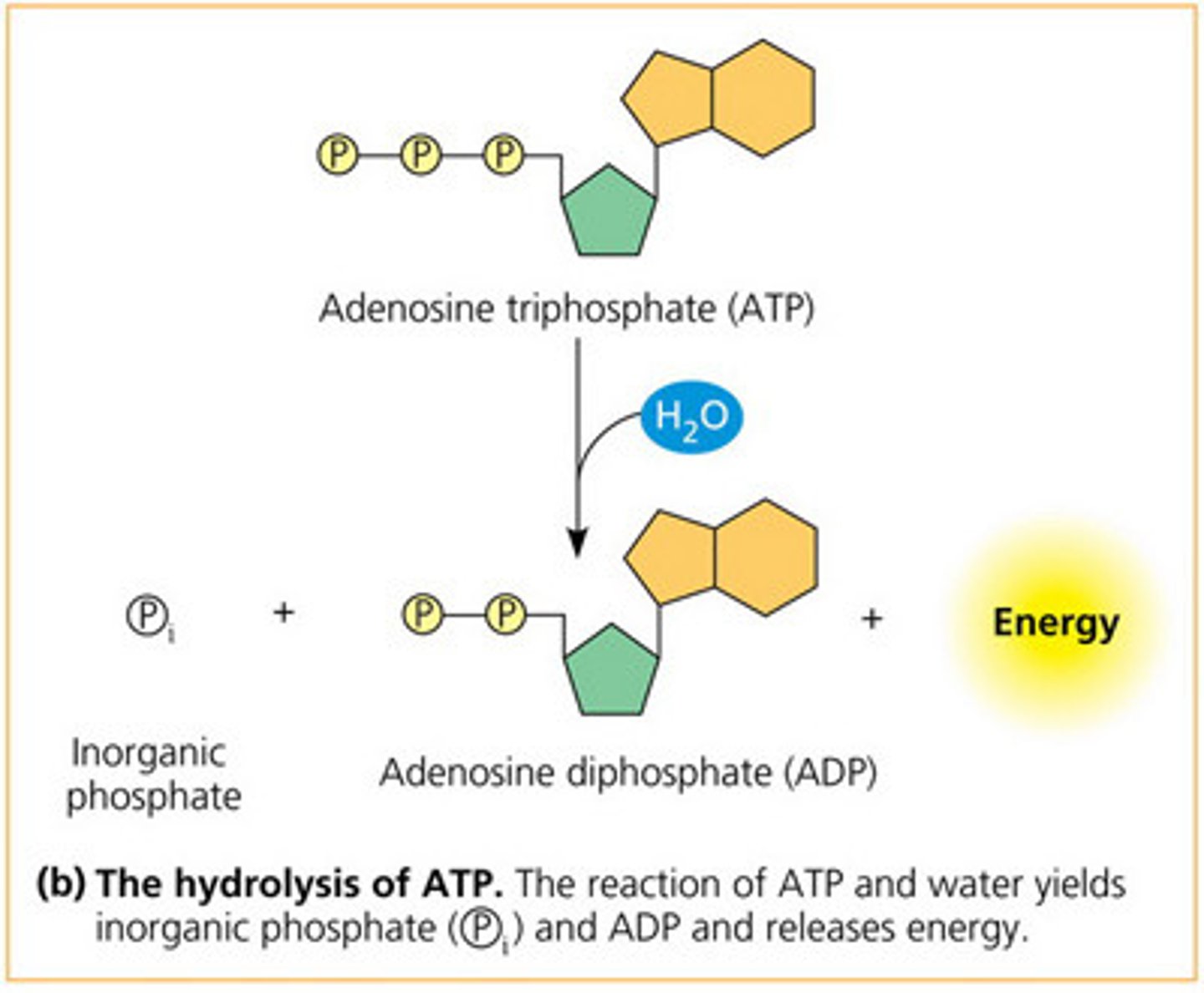
hydrolysis
breaks bonds in ATP phosphate groups.
energy is released as bonds are broken.
catalyst
chemical agent that speeds up reaction without being consumed by the reaction
enzyme
protein working as a catalyst
-ase
common suffix of enzymes
activation energy curve
enzymes catalyze reactions by lowering the required energy to speed up reaction that would occur eventually
substrate
chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds.
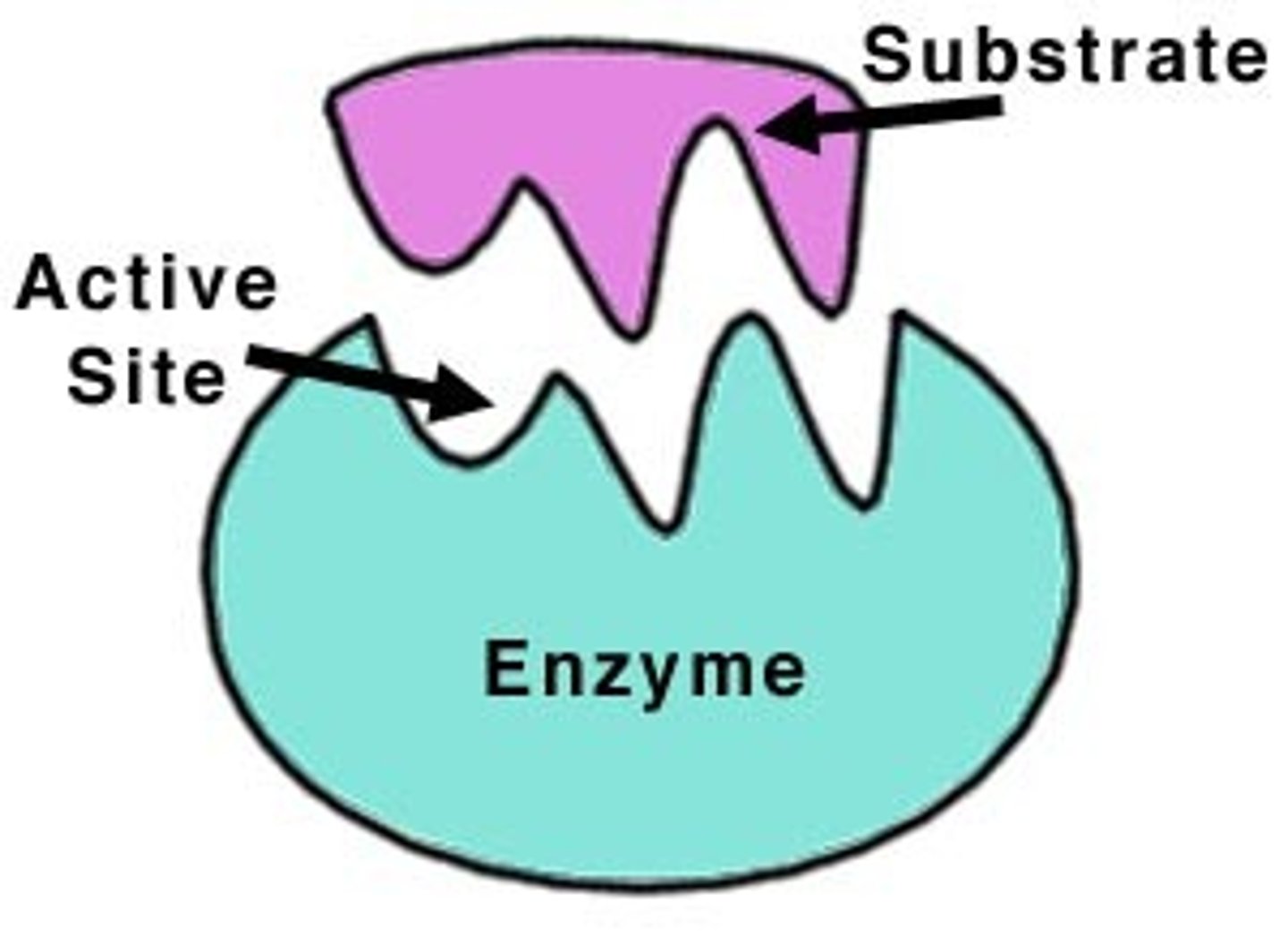
active site
location within enzyme where substrate binds.
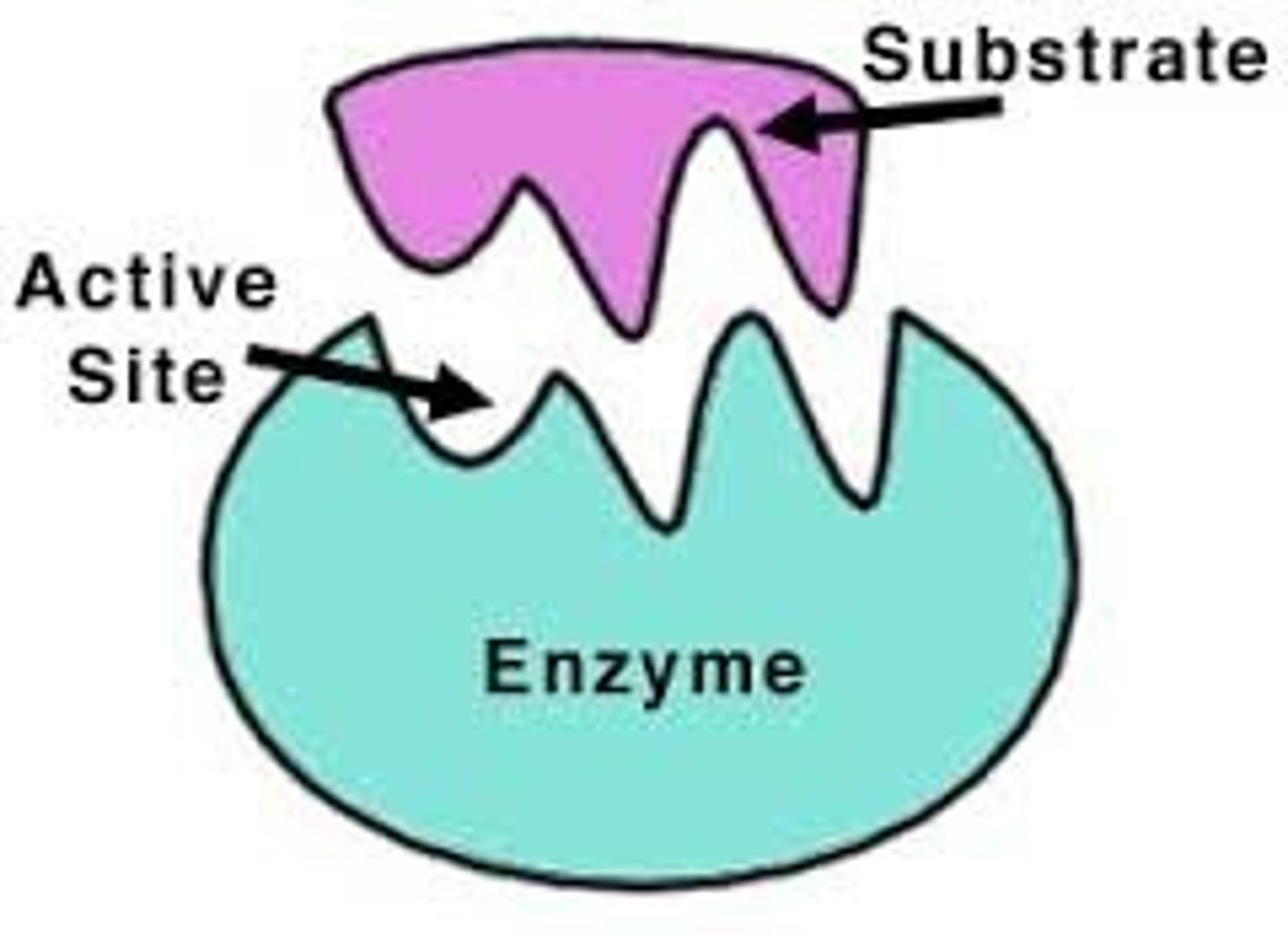
enzyme specificity
complimentary fit between the shape of active site and substrate shape.
induced fit
enzymes change shape due to chemical interactions with substrate. the change brings chemical groups of the active site into positions that enhance their ability to catalyze the reaction.
chemical chaos
result if a cell's metabolic pathways were not tightly regulated
competitive inhibitors
bind to the active site of an enzyme, competing with the substrate
non-competitive inhibitors
bind to another part of an enzyme, causing the enzyme to change shape and making the active site less effective.
inhibitors can be toxins, poisons, pesticides
cofactors
non-protein enzyme helpers.
may be inorganic (such as metal in ionic form) or organic
coenzyme
organic cofactor
includes vitamis
coenzymes
ATP
NADH
FADH2
feedback inhibiton
effect of a product of a reaction sequence to decrease its further production by inhibiting the activity of the first enzyme in the pathway that produces it
transition state
a high-energy intermediate state of the reactants during a chemical reaction that must be achieved for the reaction to proceed