Circulatory System
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Notes from APLab4 & 01/21 Lecture
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Heart
Pump that forces blood through the vessels
Heart and its surrounding blood vessels
Components of the circulatory system
O2, CO2, nutrients, and waste
Blood transports…
Base
The superior portion of the heart, slightly flat
Apex
Inferior portion of the heart, slightly pointy
Parietal pericardium
Thick membrane surrounding the heart
Visceral Pericardium
The layer of membrane that is contiguous with the heart
Atrium
2 thin walled chambers in the superior portion of the heart, collects blood from the body
Septum
Divides the heart longitudinally
Interatrial septum
Separates the atria
Interventricular septum
Separates the ventricles
Myocardium
The heart wall, cardiac muscle. “The muscular part of the heart”
Endocardium
Layer that covers the interior part of the chambers, smooth in texture to prevent formation of clots
Coronary vessels
Nutrition of the heart comes from:
Right and Left coronary arteries
These branches (arteries) come directly from the aorta and rest in the grooves (sulci) around the heart
Sulci
Grooves (seen around the heart)
Coronary sulcus
Encircles the heart between atria and ventricles
Anterior interventricular sulcus
Runs vertically between ventricles on the anterior side
Posterior interventricular sulcus
Runs between ventricles on the posterior side
Left coronary artery
Travels to the left side within the coronary sulcus
Anterior interventricular branch
Travels to the anterior side between the ventricles through the anterior interventricular sulcus. Supplies oxygen to the interventricular septum and the anterior walls of the ventricles
Right Coronary artery
Travels to the right side within the coronary sulcus
Circumflex Branch
Travels via the coronary sulcus on the posterior side
Marginal branch
Given rise from the right coronary arteries. Travels down the left anterior lateral part of the heart
Posterior interventricular branch
Goes to the posterior part and travels via the coronary sulcus and resides in the posterior intraventricular sulcus. Supplies oxygen to the interventricular septum and the posterior walls of the ventricles
Blood collected from the heart tissues —> coronary veins —> coronary sinus —> right atrium
Path of blood from heart tissues…
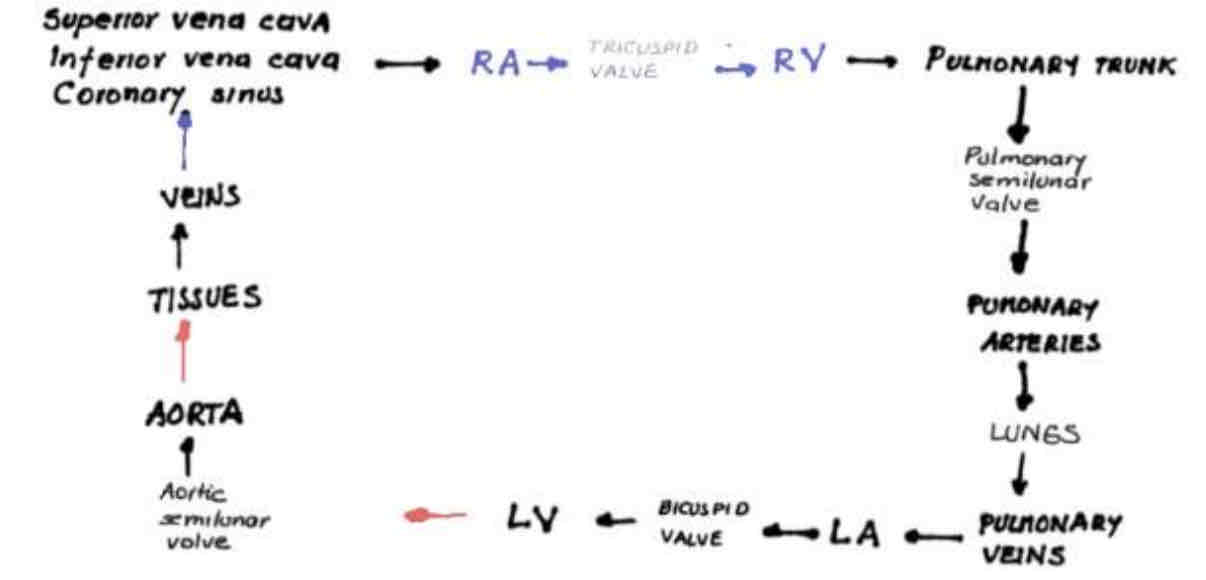
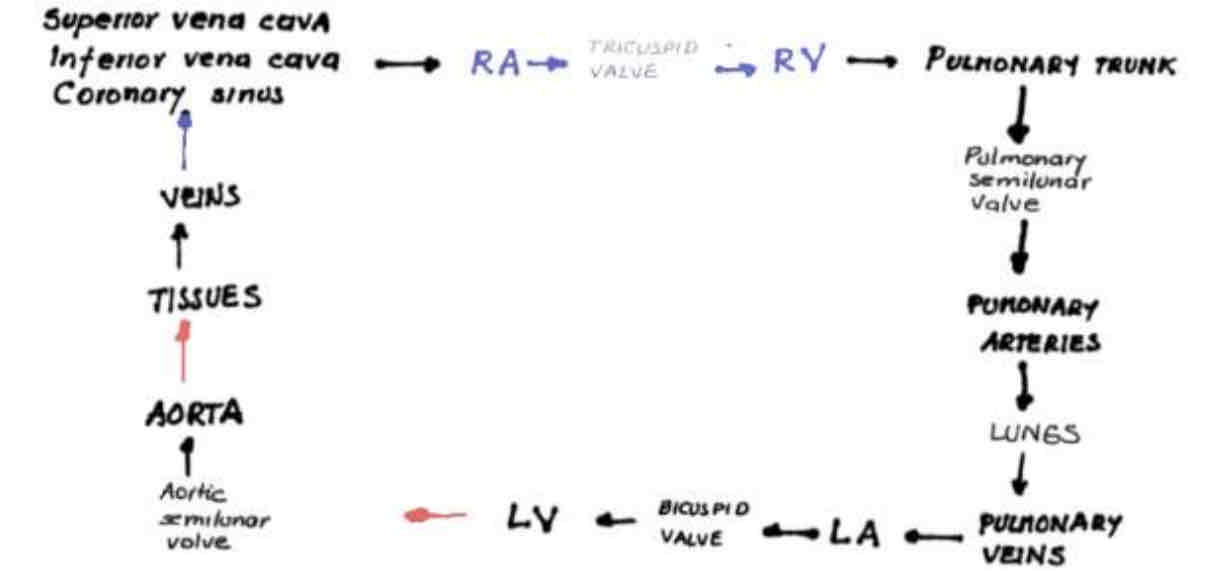
Superior/Inferior Vena Cava —> Right Atrium —> Tricuspid valve —> Right Ventricle —> Pulmonary Trunk —> Pulmonary Semiulnar Valve —> Pulmonary Arteries —> Lungs —> Pulmonary Veins —> Left Atrium —> Bicuspid Valve —> Left Ventricle —> Aortic Semiulnar Valve —> Aorta —> Tissues —> Veins —> Coronary Sinus
Circulation of blood through the heart…
Tricuspid Valve
Located on the right side, prevents back flow of blood during contraction (V)
Biscupid/Mitral Valve
Valve located on the left side
Chordae tendineae
Holds down valves by the inferior portion. Prevents atrial ventricular valves from inverting, embedded into papillary muscles (wall of the heart)
Pulmonary semilunar valve
Prevents backflow during relaxation on the side of the right ventricle
Aortic semilunar valve
Prevents backflow during relaxation on the side of the left ventricle
Pulmonary Trunk
Exits the right valve and branches into Right & Left pulmonary arteries
Artery
Blood vessel leaving the heart
Vein
Blood vessel entering the heart
Pulmonary veins
Set of 4 veins (two from each lung) located superiorly to left atrium
Left Ventricle
Thickest portion of the myocardium is in this location due to this portion pushing blood to every part of the body through the Aorta
Capillaries
Smallest blood vessels, where the tissues are located
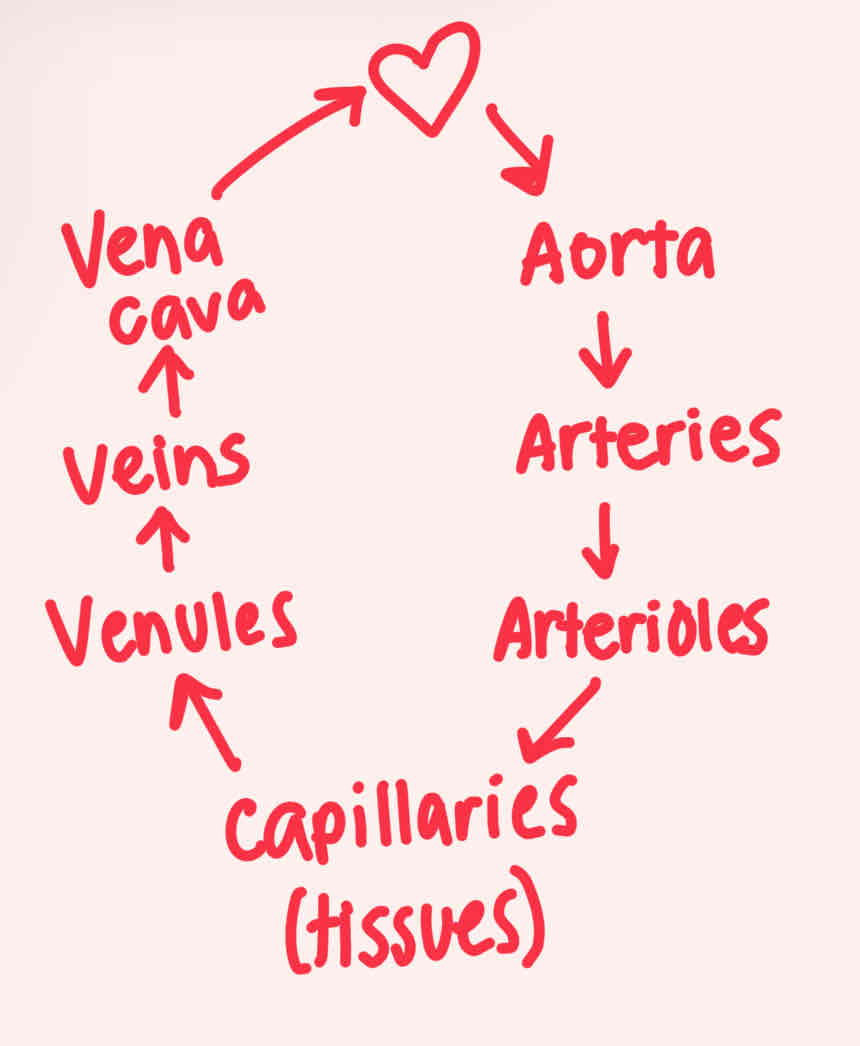
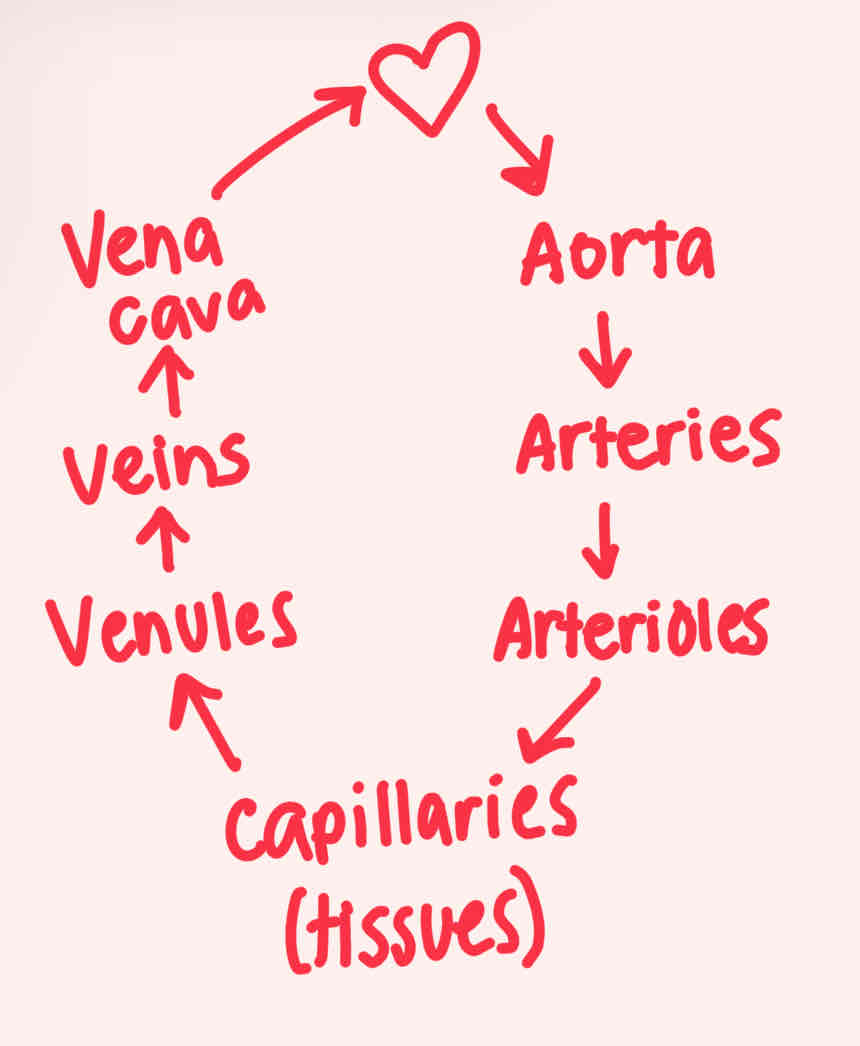
Aorta —> Arteries —> Arterioles —> Capillaries (tissues) —> Venules —> Veins —> Vena Cava
Blood flow cycle to the body
Heart murmur
Caused by back flow of blood through the ventricular valves
Valves slamming shut
Heartbeat is the sound of…
Tamponade
Accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space, prevents heart from expanding and contracting normally
Left Subclavian Branch
Branch on the left side of the aortic arch, going under the clavicle
Left common carotid
Branch of the aortic arch giving rise to the left external and internal carotid
Left external carotid
Goes to the left side of the head and face
Left internal carotid
Goes to the left side of the brain
Innominate Artery/Brachio-cephalic
Asymmetrical branch of the aortic arch, gives rise to the right subclavian and right common carotid (which gives rise to the right external and internal carotid)
Right external carotid
Goes to right side of head and face
Right internal carotid
Goes to right side of brain