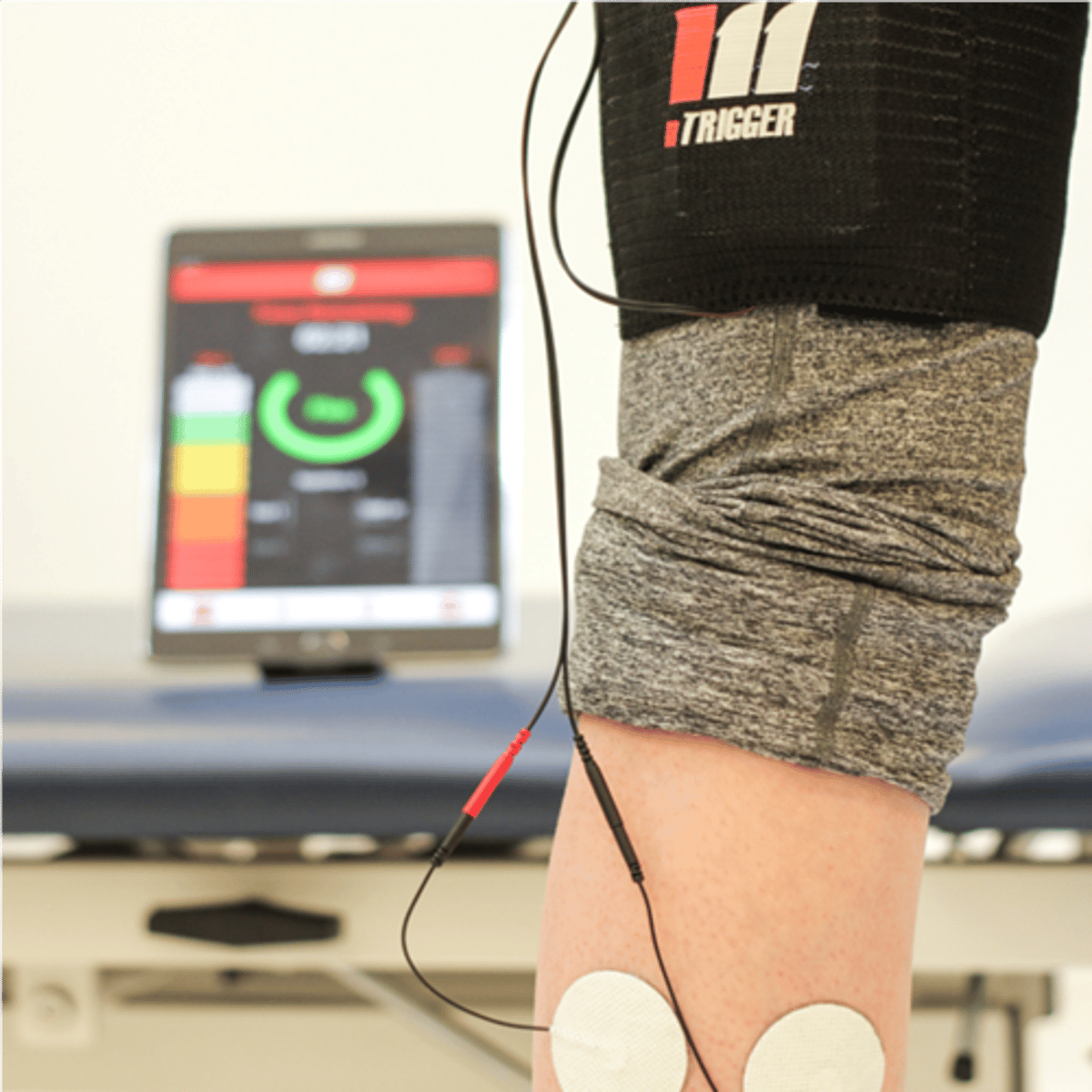
Biofeedback
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Electromyography
analysis of muscle electrical activity (physiologic signal)
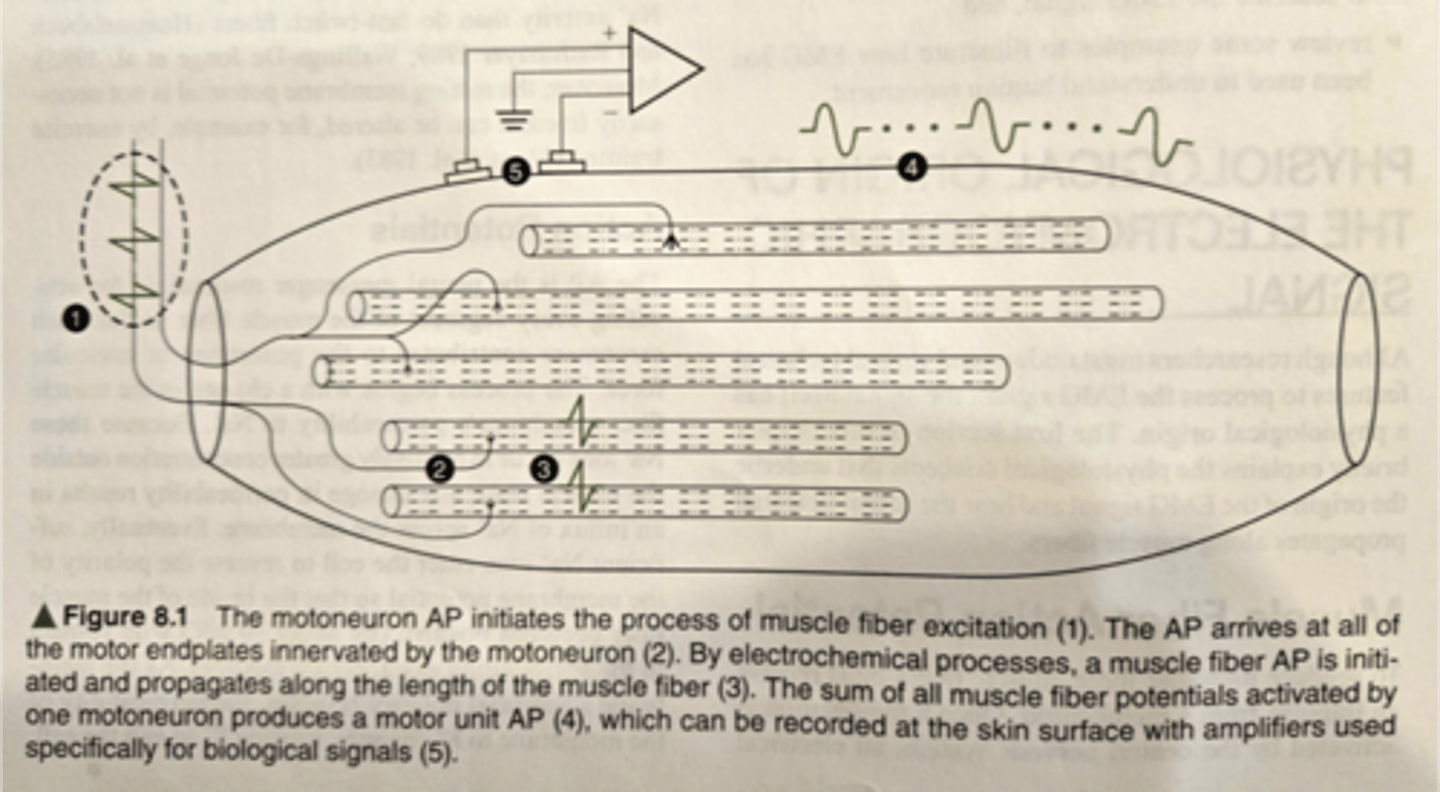
electrical signals of interest are?
motor unit action potentials
providing insight regarding control of voluntary/ reflexive movement
EMG typically used BLANK electrodes
surface electrodes
Fine-wire or needle electrodes can also be used (mainly for research or diagnostic testing)

larger and more superficial muscles produce more BLANK signals
more prominent
2 primary mechanisms to regulate muscle force
rate coding
recruitment
of additional motor units
EMG activity BLANK muscle force
DOES NOT EQUAL**
rate coding
rate at which the motor units are fired
EMG signals reflects BLANK activity under electrodes
summed
theres BLANK among muscles that are close to one another
crosstalk
ex: gastrocs and soleus
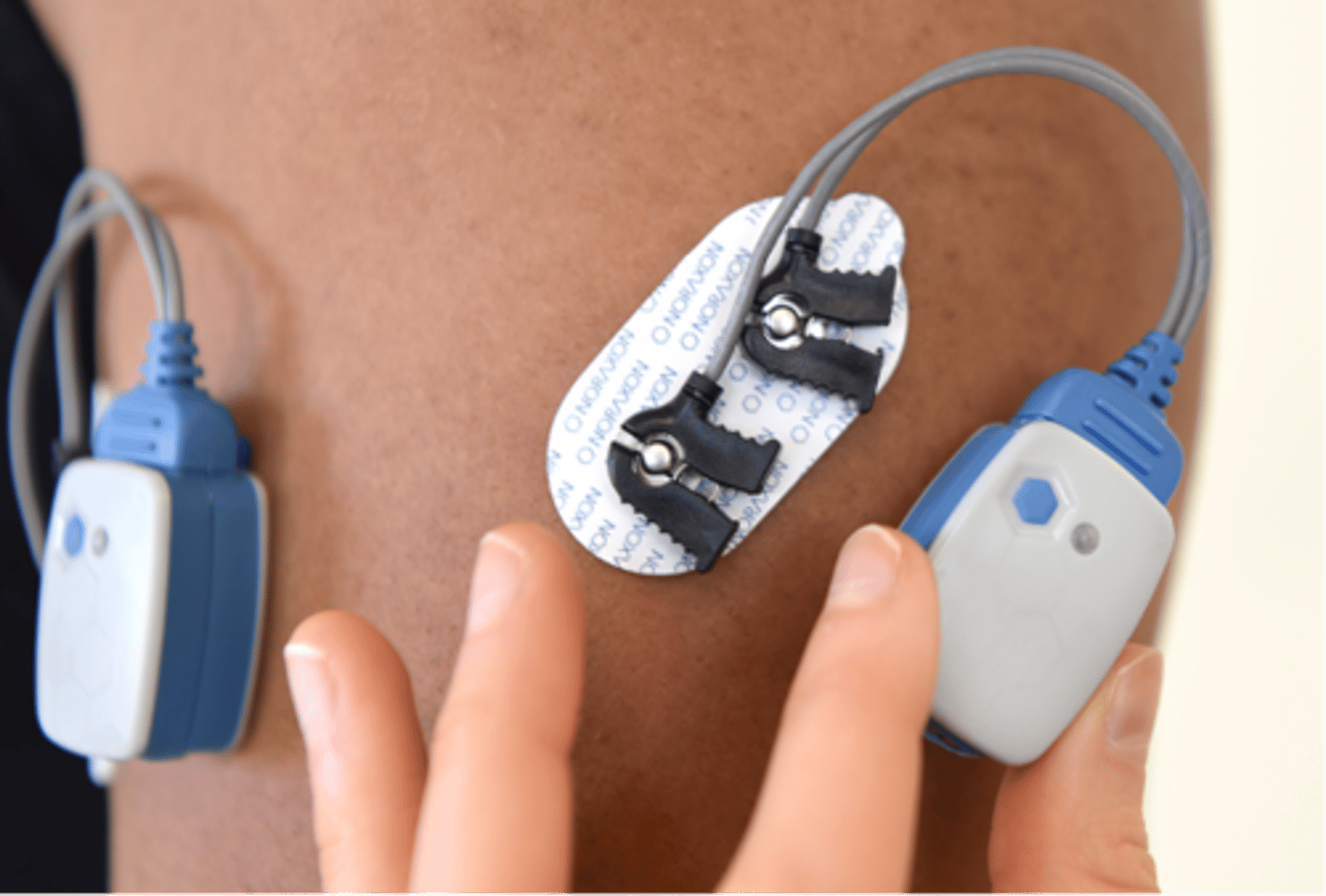
BLANK electrode arrangement typically used for surface EMG
bipolar
2 electrodes
common signal is attenuated*
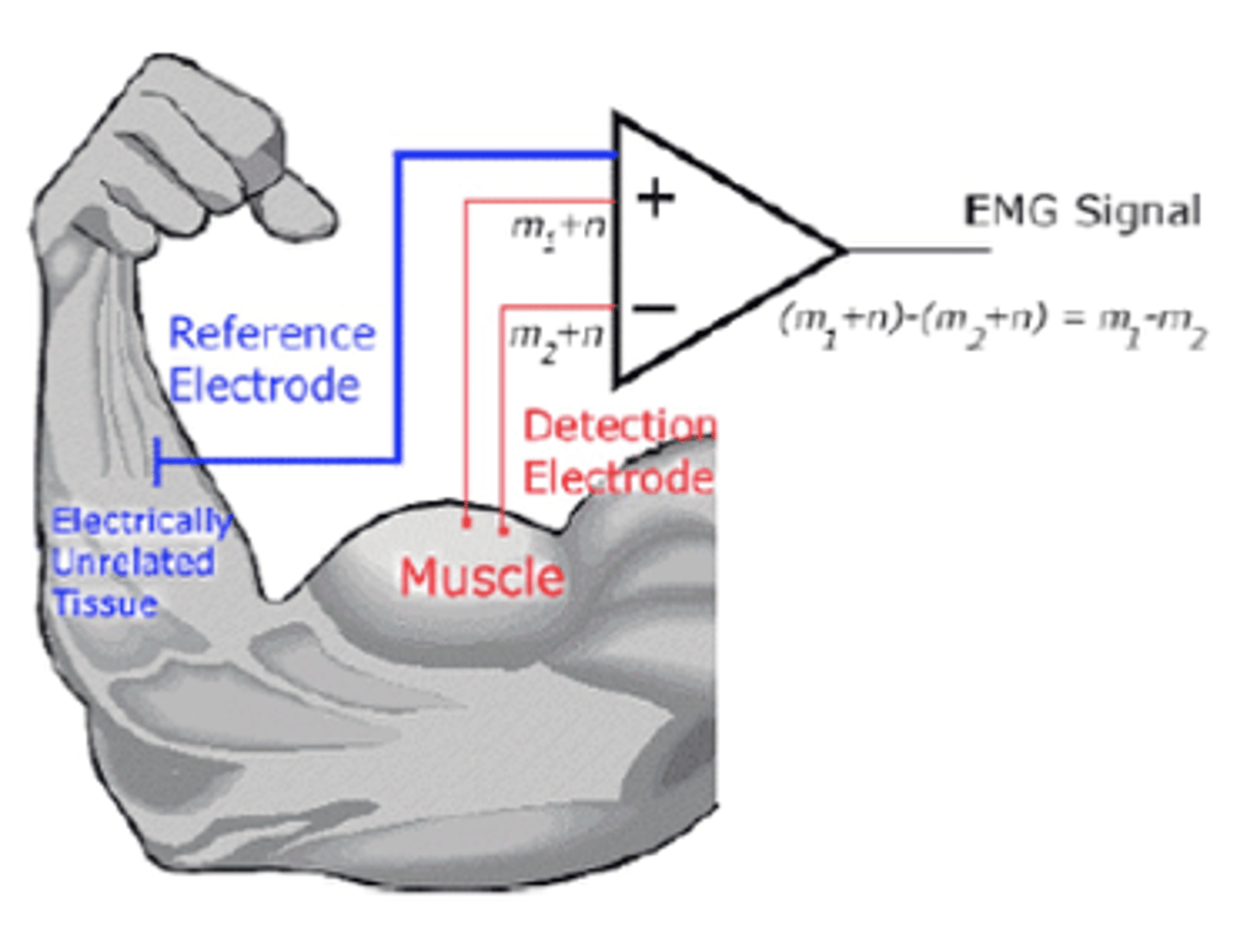
PLACE electrodes over area with BLANK, avoiding BLANK
muscle fibers
avoiding motor point (ex: tendon)
align electrodes BLANK to muscle fibers
parallel -@ muscle belly
harder with pennate muscles
EMG signal: Low frequency
movement artifact
movement of skin on overlying muscle
EMG signal: High frequency
signal noise
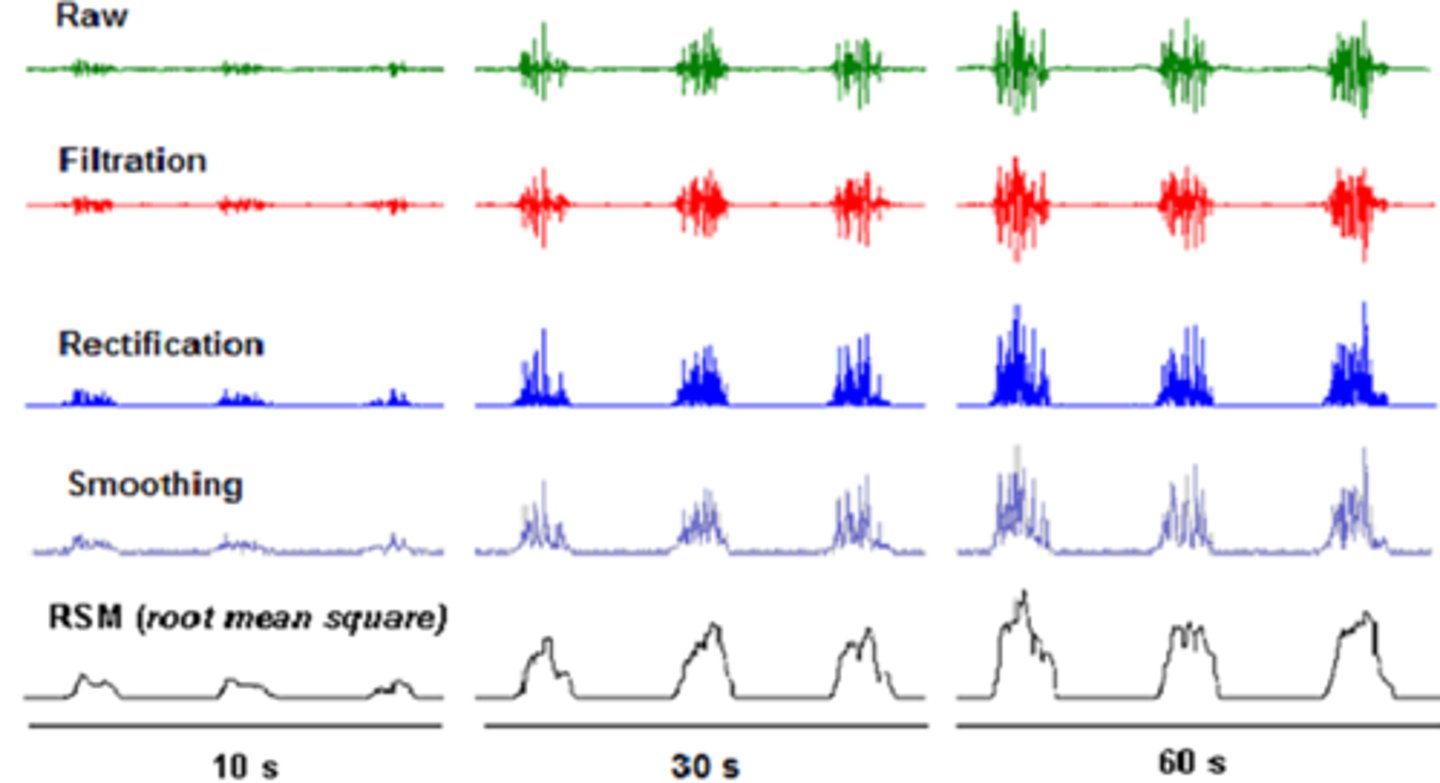
rectify EMG signal ?
'smooth' it; oscillating between positive and negative, from a noisy raw signal to a clean one
Analysis: what are we looking at when looking at EMG signal ?
EMG amplitude and/pr muscle onset-offset timing
OR
signal frequency
BLANK often used to analyze muscle activity levels
mean or peak EMG amplitude
Rectify signal so all values are BLANK
positive
full wave rectified
Biofeedback is usually trying to one of 3 things
facilitate a muscle contraction or inhibit muscle activity, or retrain muscle recruitment pattern