4.4 Genetic diversity and adaptation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is genetic diversity?
Number of different alleles of genes in a population
What are alleles and how do they arise?
Variations of a particular gene (same locus) → different DNA base sequence
Arise by mutation
What is a population?
A group of organisms of the same species in a particular space at a particular time
That can (potentially) interbreed (to produce fertile offspring)
Explain the importance of genetic diversity
Enables natural selection to occur
As in certain environments, a new allele of a gene might benefit its possessor
By resulting in a change in the polypeptide (protein) coded for that positively changes its properties
Giving possessor a selective advantage (increased chances of survival and reproductive success)
What is evolution?
Change in allele frequency (how common an allele is) over many generations in a population
Occurring through the process of natural selection
Explain the principles of natural selection in the evolution of populations
Mutation: Random gene mutations can result in [named] new alleles of a gene
Advantage: In certain [named] environments, the new allele might benefit its possessor [explain why] → organism has a selective advantage
Reproduction: Possessors are more likely to survive and have increased reproductive success
Inheritance: Advantageous allele is inherited by members of the next generation (offspring)
Allele frequency: Over many generations, [named] allele increases in frequency in the population
Name the 3 types of adaptations
Anatomical
Physiological
Behavioural
Describe the Anatomical adaptation
Structural / physical features that increase chance of survival
Describe the Physiological adaptation
Processes / chemical reactions that increase chance of survival
Describe the Behavioural adaptation
Ways in which an organism acts that increase chance of survival
Name the 3 types of selection
Directional Selection
Stabilising Selection
Disruptive Selection
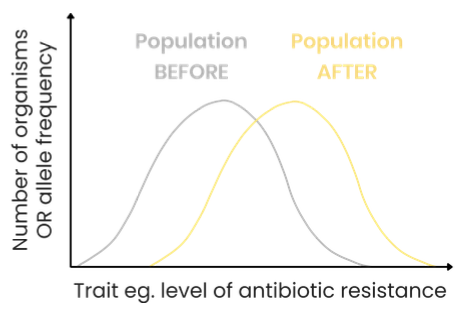
Directional selection
E.g. antibiotic resistance in bacteria
Organisms with an extreme variation of a trait, e.g. bacteria with high level of resistance to a particular antibiotic
Environment: Often a change, e.g. antibiotic introduced
Increased frequency of organisms with alleles for extreme trait
Normal distribution curve shifts towards extreme trait
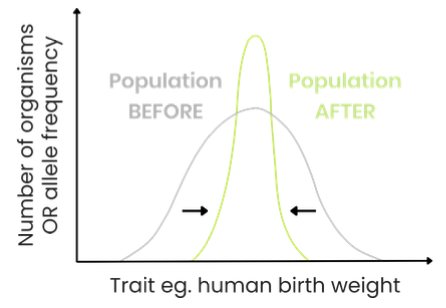
Stabilising Selection
E.g.Human birth weight
Organisms with a modal variation of a trait e.g. babies with an average weight
Environment: Usually stable
Increased frequency of organisms with alleles for average trait
Normal distribution curve similar, less variation around the mean
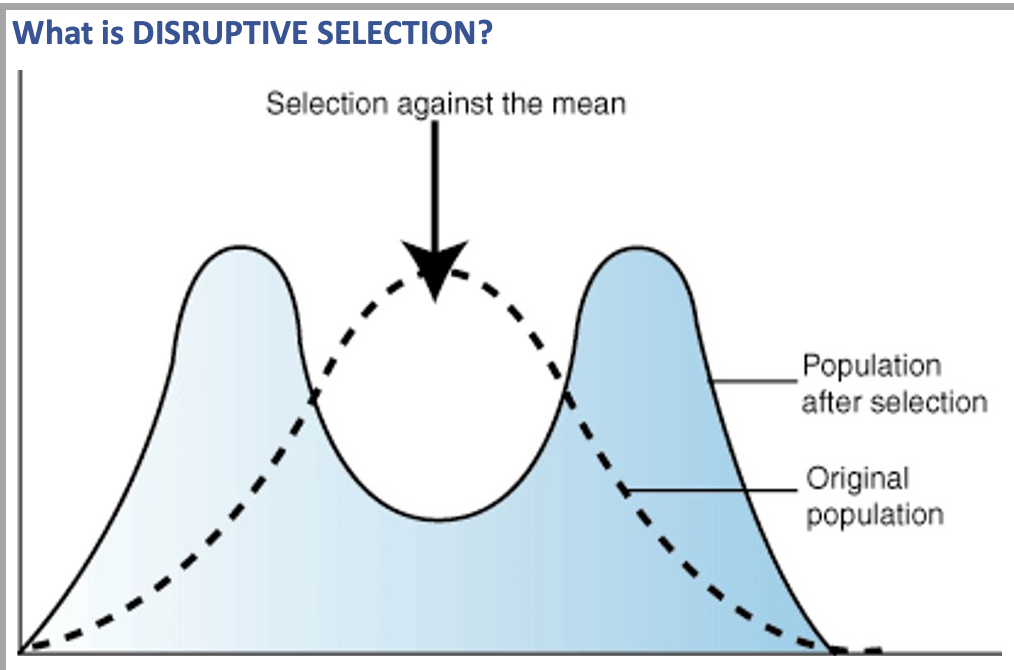
Disruptive Selection
Favours extreme phenotypes at intermediate expense
Important in bringing evolutionary change
Caused by a change in environmental conditions (eg. Seasonal temp changes).
Example: In an environmental with black and white rocks. White rabbit lives: camouflaged; Grey rabbit dies: seen by predator; Black rabbits lives:camouflaged