Parasitology Test 2
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
Helminths
some are free-living organisms in aquatic and terrestrial environments
others are parasites in most animals and some plants
most species have worms in them somewhere
general term meaning “worm”
multicellular eukaryotic invertebrates
tube-like or flattened bodies
bilateral symmetry
triploblastic
with endo-, meso-, and ecto-dermal tissues
play-helminths
“flat worms”
acoelomate
do not have body cavities
nemat-helminths
round worms
pseudocoelomate
body cavities not enclosed by mesoderm
segmented annelids
earthworms
coelomate
with body cavities enclosed by mesoderm
Platyhelminthes
flatworms
acoelomate
dorsoventrally flattened
bilaterally symmetric
organ systems
digestive
closed in trematodes
none in cestodes
reproductive— most are monoecious
excretory
neuromuscular
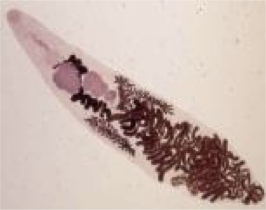
Trematodes
flukes
monogenea
flatworms ordinarily living as ectoparasites on single host throughout entire life cycle
mostly parasites of fish
direct lifecycles
digenea
alternation of sexual reproduction as internal parasite of vertebrate with asexual reproduction in mollusk
parasites of many types of animals
indirect lifecycles
mostly monoecious
cestodes— tapeworms
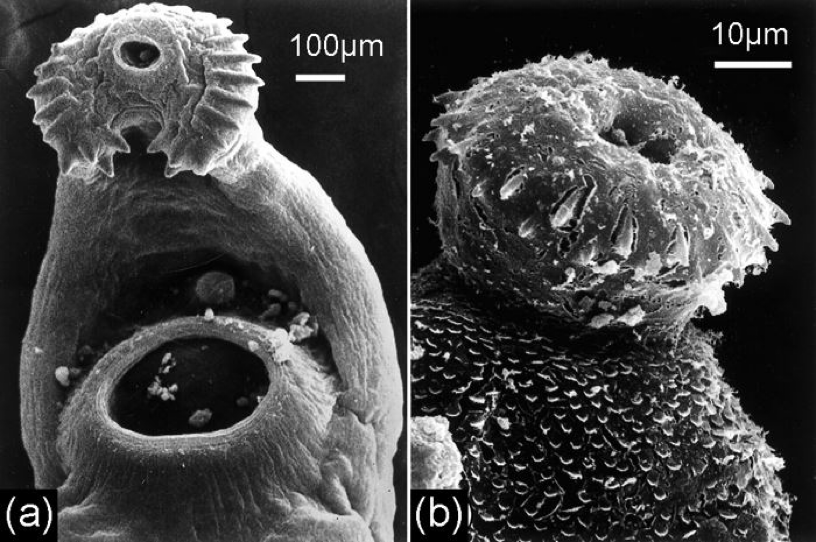
Trematodes— Monogeneans
may or may not have a weakly developed oral sucker
posterior end has larger posterior adhesive disk— opisthaptor
usually has hooks
anterior and dorsal excretory pores paired
simple life cycle
mainly found in the epithelial layers
Trematodes— Digeneans
organ systems
tegument
surficial covering of a multicellular organism
neuromuscular
digestive
reproductive
indirect life cycle
definitive host
first intermediate host
second intermediate host
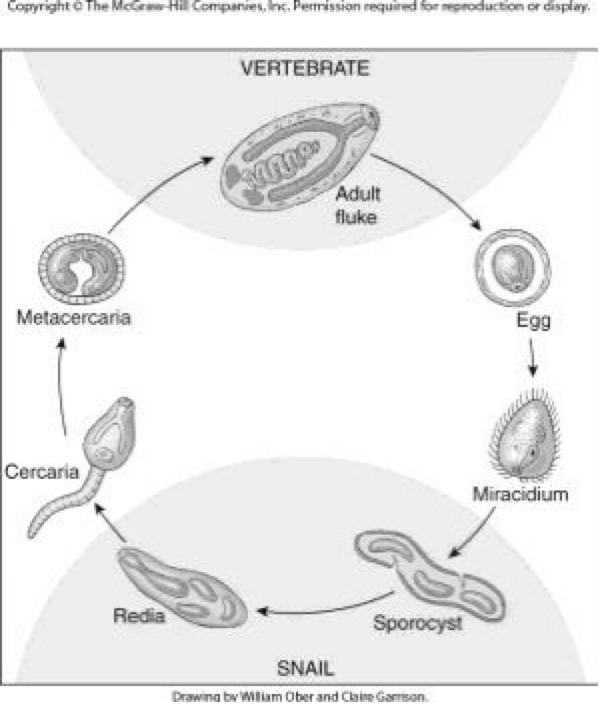
Digeneans— Life Stages
vertebrate (definitive host)
adult
environment
egg
miracidia (infect 1st intermediate host)
snail (1st intermediate host)
sporocyst
redia
environment
cercaria
mesocercariae
metacercariae (in 2nd intermediate host)
infect definitive host
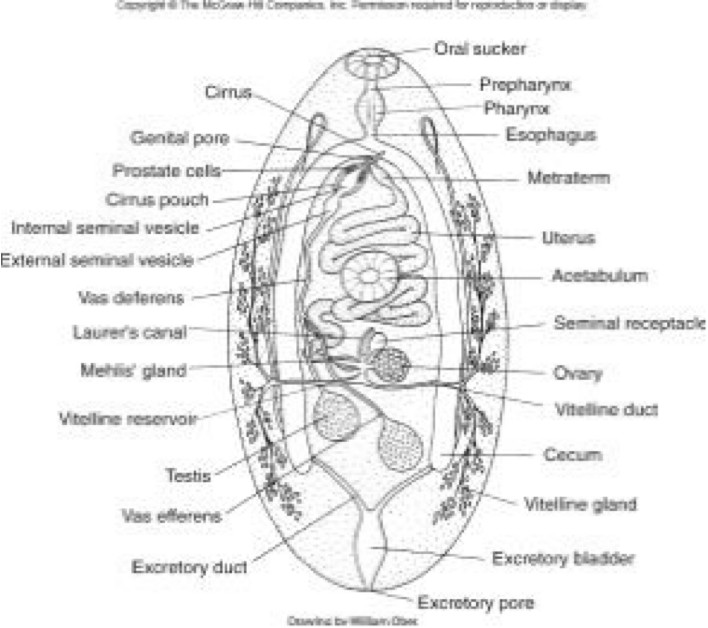
Digenetic Trematodes— Organ Systems
tegument— may have spines
neuromuscular
digestive
closed— mouth, gut, — no anus
feed on blood, mucus, tissue with mouth and pharynx
reproductive
monoecious
hermaphroditic
Digenetic Trematodes life cycle
indirect life cycle
definitive host
various vertebrates
1st intermediate host
almost always a mollusk
2nd intermediate host
various vertebrates
Metacercariae of adult Digenetic Trematodes
a tailless encysted late larva of a digenetic trematode
usually the form which is infective for the definitive host
Cercariae of Adults Digenetic Trematodes
a free-swimming larval stage
passes from an intermediate host (typically a snail) to another intermediate host or to the final vertebrate host
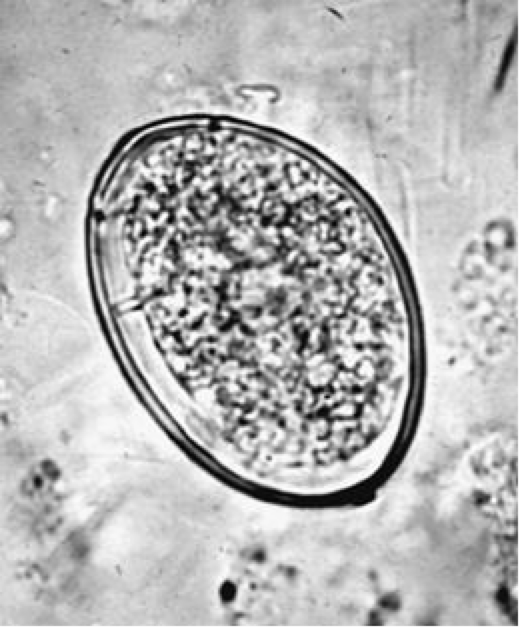
Eggs of Digenetic Trematodes
embryo encased in a capsule
most have an operculum— groove around one end of it
will open to release miracidium
variety of sizes, shapes, thickness, coloration
contain fully developed miracidia or only a few cells
most eggs hatch in environment
require water
also require certain O2 levels, temperatures, etc.
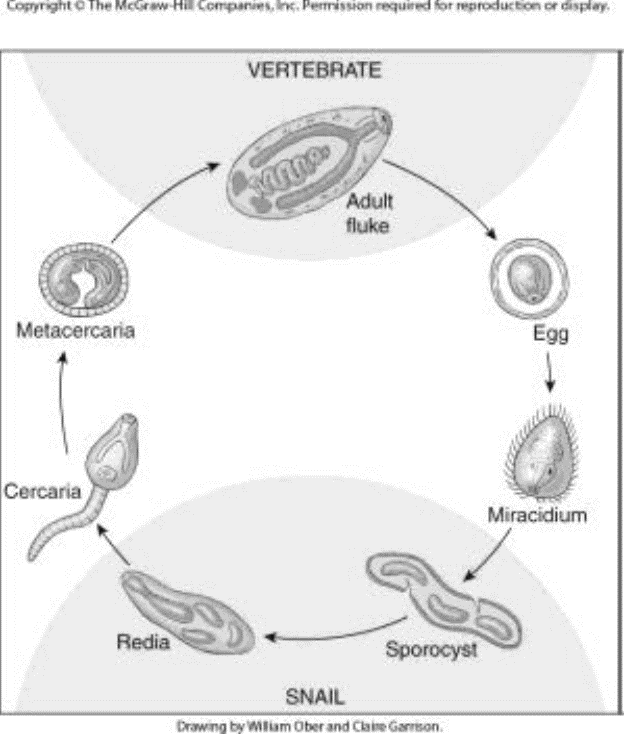
Miracidia of Digenetic Trematodes
free-swimming larval stage
tiny, ciliated organism
has penetration glands and apical glands
have germ cells in posterior region—will become sporocysts
usually hatch in water
must swim rapidly— survive only a few hours
must find a mulluscan host
attracted to mullusc by mucus → attaches with apical papilla, penetrates snail in about 30 mins
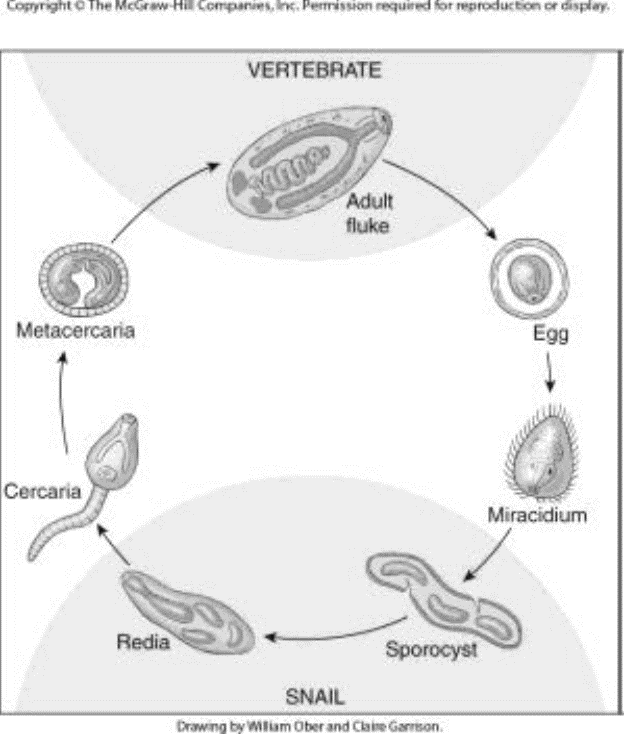
Sporocysts of Digenetic Trematodes within 1st Intermediate Host
result from metamorphosis of miracidia in snail host
NO digestive system
functions only to nurture developing embryos
next stage may be daughter sporocysts, redia, or cercariae
Redia of Digenetic Trematodes within first intermediate host
burst out of sporocyst or leave via terminal birth pore
migrate through host
feed on host tissue and other sporocysts
function to nurture developing embryos
next stage may be daughter redia or cercariae
Trematodes— Cercariae
juvenile stage released from first intermediate host
free swimming
most have tails for swimming
have a mouth, oral sucker, penetration glands, digestive and excretory systems
find new host (usually second intermediate host) by chance
respond to stimuli
some penetrate definitive host
usually migrate in host for a period of time
Termatodes— Metacercariae
encyst— either in an intermediate host or on vegetation
lose their tails and undergo development
encyst on vegetation— little development, infective within hours
do not encyst in intermediate host, need several days of development
encyst in intermediate host— need weeks for development
after development— enter resting stage, infective to definitive host
allows for survival during unfavorable times
transports parasite from intermediate host to definitive host
Alaria americana
definitive host: canids
1st IH: aquatic snail (helisomid)
2nd IH: tadpoles
paratenic hosts
water snakes
have a mesocercariae
unencysted intermediate between cercariae and metacercarie (only one we talk about)
develop in 2 weeks
accumulate in 2nd intermediate host
eaten by paratenic host or definitive host
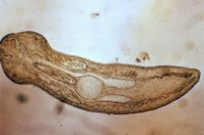
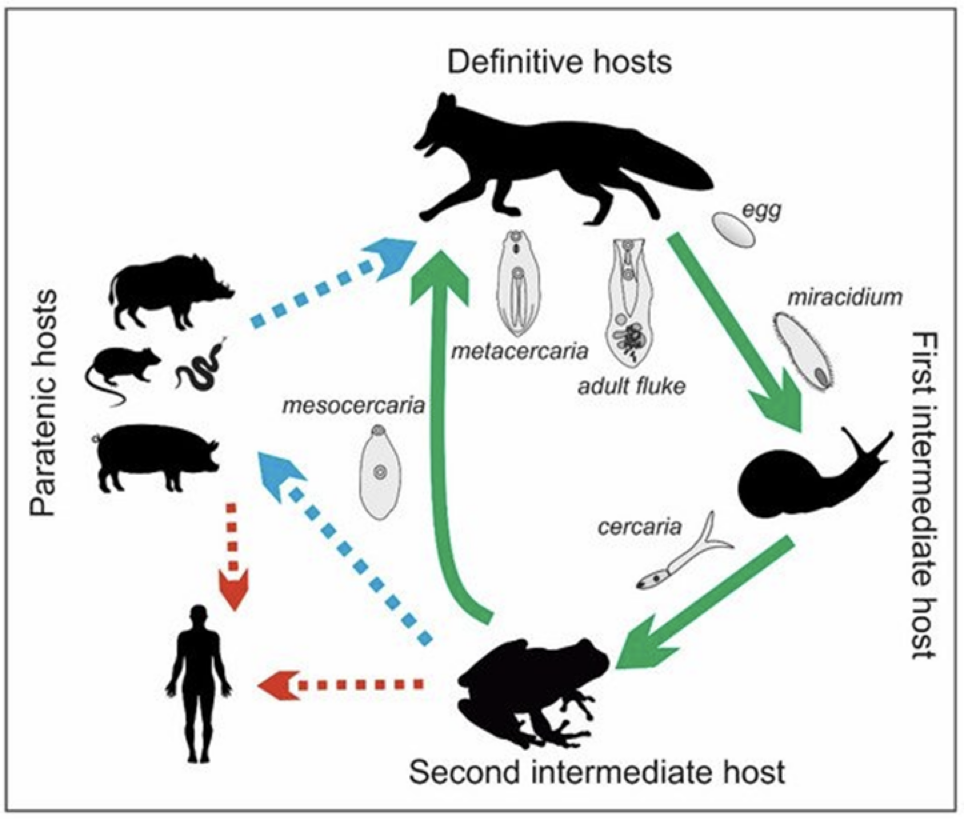
Alaria americana life cycle
adults in definitive host small intestine
miracidia penetrate snail (1st intermediate host)
cercariae penetrate tadpoles (2nd intermediate host)
tadpole/frog infected with mesocercariae can be eaten by either definitive host or paratenic host
paratenic host may accumulate many mesocercariae
definitive host eats paratenic host or 2nd intermediate host
humans can be infected by eating undercooked frog legs
human acts as paratenic host
Alaraia americana Pathogenesis
definitive host is canids
adults cause severe enteritis
death
2nd intermediate host— tadpole
mesocercariae, in high numbers, can cause disease
humans—rare
nearly every organ infected
hemorrhage, tissue damage, death
What is the most likely intermediate host for digenetic trematodes?
snails
What is the juvenile stage of trematode released from the first intermediate host?
cercariae
What is the definitive host for Alaria americana?
canids
Which species of Schistosoma is most likely to cause a UTI?
S. haetmatobium
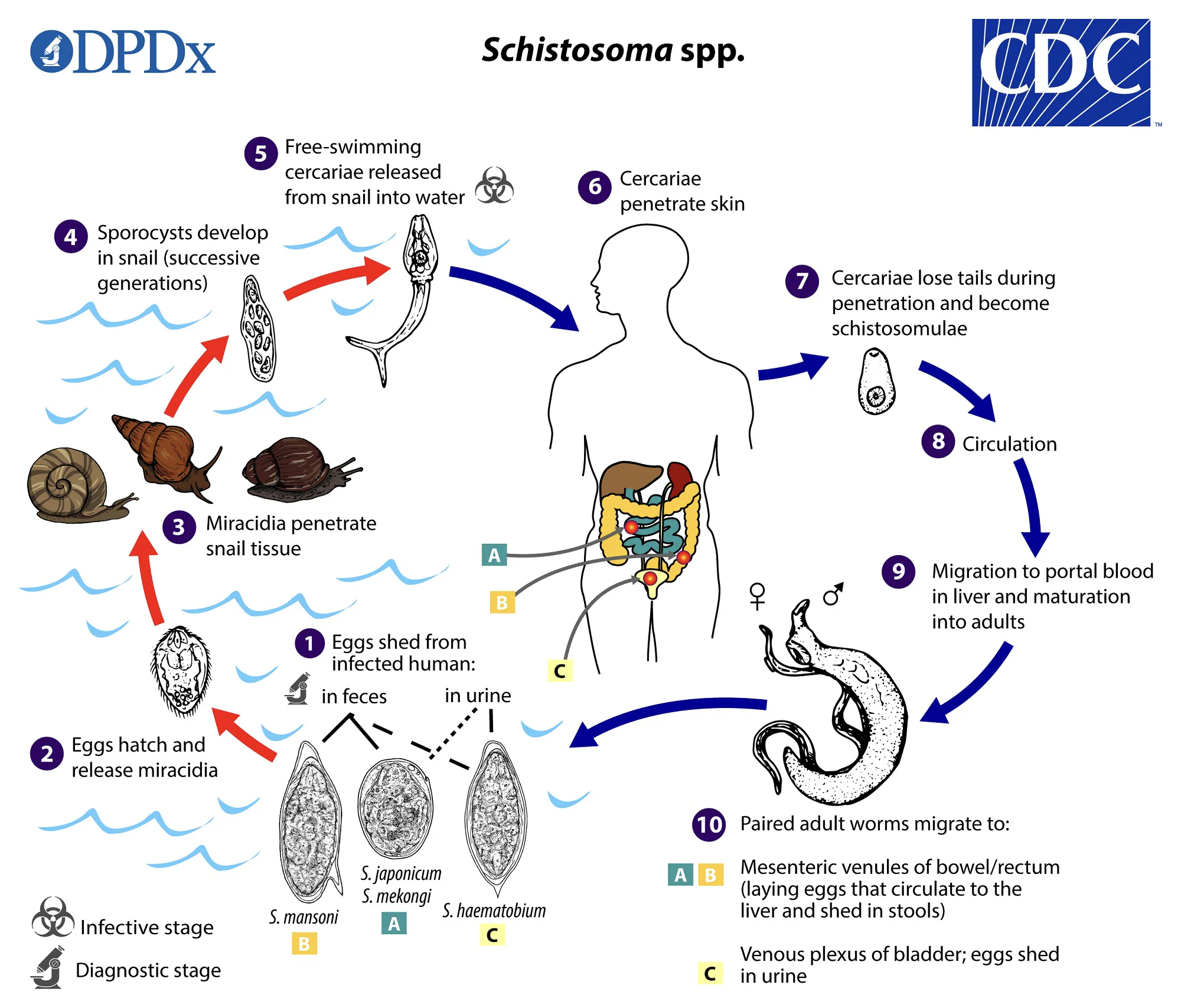
Schistosoma spp.
unique among trematodes
causes schistosomiasis (snail fever)
major disease in tropics
200 million people infected
dioecious
sexual dimorphism
females— long and slender
males— short and stout
mate in blood circulation
non-operculated eggs
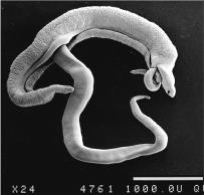
Schistosoma spp. — pathology
eggs
cause major pathology
migrate through tissue
pass through veins to get to lumen of bladder or intestine
mechanism unknown
granuloma formation
immune response: WBCs “wall off” eggs
granulomas trapped in vessels
may occlude vessels
Schistosoma spp. — Distribution
about 85% of world’s cases in Africa
prevalence rates can exceed 50% in local populations
schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium distributed throughout Africa
Schistosoma haematobium
throughout Africa
only S. haematobium in areas of middle East
Schistosoma japonicum
Indonesia
parts of China and Southeast Asia
Schistosoma spp.— Life cycle
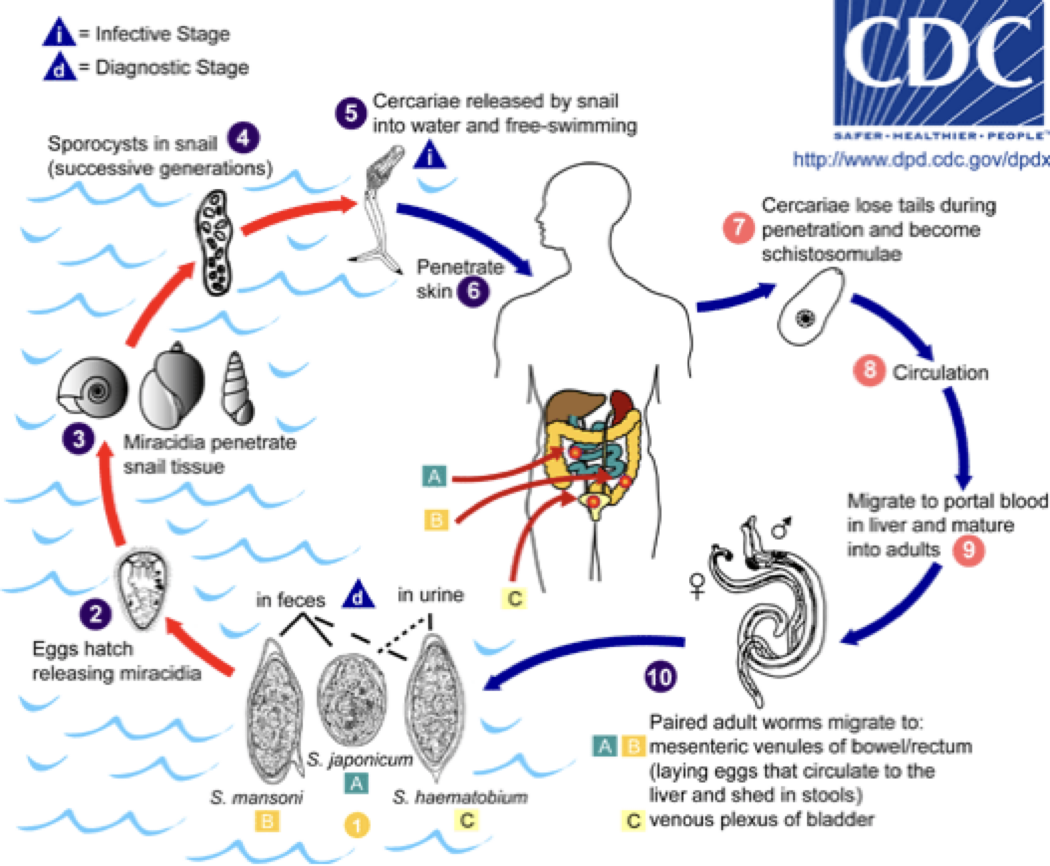
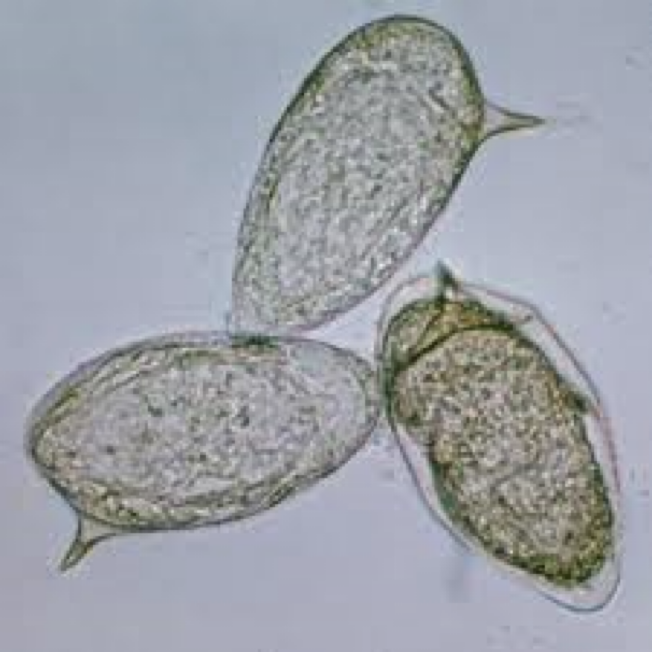
Schistosoma mansoni
distribution
throughout Africa
not in US— do not have snail host
definitive host is humans
first intermediate host is aquatic snails
eggs— large lateral (subterminal) spine
adults— reside in veins of large intestine

Schistosoma mansoni pathology
penetration of skin by cercariae
dermatitis (1-4 days)
swelling, itching, allergic reaction
migration (3-4 weeks)
through lungs
fever, cough, difficulty breathing
through liver
hepatitis
acute stage (egg production)
chills, fever, malaise, abdominal pain and tenderness, diarrhea, bloody stool
chronic stage
granuloma formation— hallmark symptom of Schistomiasis
hepatosplenic schistosomiasis
intestinal schistosomiasis
Katayama syndrome
Clay Pipestem Fibrosis
Hepatosplenic schistosomiasis
liver and spleen enlargement
granulomas in liver
jaundice
Intestinal schistosomiasis
colitis, abdominal cramps, granulomas
Katayama Syndrome
severe reaction to eggs
fever, chills, abdominal pain, cough
not seen in every case
Clay Pipestem Fibrosis
portal vein surrounded by granulomas
portal vein major blood supply for liver
often fatal
Schistosoma japonicum
distribution
indonesia, parts of china and southeast asia
humans and mammals are definitive host
aquatic snail is intermediate host
domestic animals are reservoir host
eggs are in the small lateral spine
adults reside in veins of small intestine
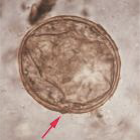
Schistosoma japonicum pathology
same as S. mansoni
Katayama Syndrome— more common
cerebral schistosomiasis
diagnosed by eggs in feces
treated with praziquantel
Cerebral schistosomiasis
eggs enter brain (smaller spine)
granulomas in brain
neurological signs
lethargy, seizures, vision problems
speech impairment
Schistosoma haematobium
distributed throughout Africa, areas of Middle East
humans is definitive host
aquatic snail is intermediate host
chimpanzees and baboons are the reservoir hosts
eggs have terminal spines
adults reside in veins of urinary bladder
can be in uterus, prostate, etc.
Schistosoma haematobium
same as S. mansoni but less severe
urinary schistosomiasis
major cause of bladder cancer in Nile region
hepatosplenomegaly— children
pulmonary
rapid breathing, cough, cyanosis (bluish skin, low oxygen in blood)
Urinary Schistosomiasis
hematuria (blood in urine)
frequent urination
bacteria in urine
Schistosoma spp. epidemiology
main source of infection
human waste, urine, in water with intermediate host
people at risk:
low economic and education levels related to sanitation
more common in 10-20 years old
males are more infected than females
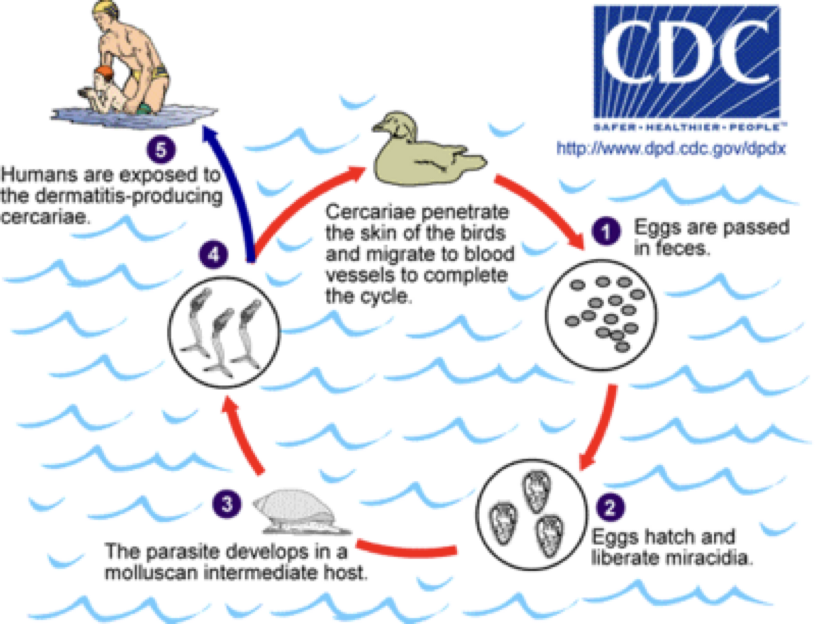
Schistosome Cercarial Dermatitis (Swimmer’s Itch)
caused by avian schistosomes
humans are a dead-end host
cercariae penetrate skin; unable to complete migration
immune system kills cercariae
cercariae release antigens
causes inflammatory response
purulent-filled lesion
severe itching
not serious health problem
more common in Great Lakes region
Fasciola hepatica— sheep liver fluke
known for 100s of years
first trematode life cycle described
one of the largest trematodes
30 mm long by 13 mm wide
DH— ruminants, humans
IH0— aquatic snail
RH— sheep, cattle, rabbits
human cases in europe, africa, south america
few cases in US
parasite common in areas of south and west
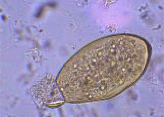
Fasciola hepatica— in humans
maturation
metacercariae to adult flukes ~ 3-4 months
adult flukes are large
reside in large biliary ducts of mammalian host
eggs passed out of bile ducts with bile
enter intestines and exit with feces
Fasciola hepatica— pathology
liver migration (metacercariae)
feed on liver cells and blood
necrosis
parasites in bile ducts (adults)
inflammation, edema, anemia
stimulate growth of fibrous tissue in duct walls
cirrhosis
jaundice
heavy infections
gallbladder damage
anemia
erosion of bile ducts
large liver abscesses
death
migrate juveniles
ulcers in ectopic locations
eyes, brain, skin, lungs
Fascioloides magna
large
DH— cervids (deer, elk, etc.), cattle, sheep
IH— snail
degree of pathogenicity depends on host
sheep
extensive damage
migration leads to hemorrhage and peritonitis
no capsule around fluke
cervids
less damage, limited migration
form capsule around fluke
Fasciolopsis buski
DH— swine and humans
IH— aquatic snail
life cycle similar to F. hepatica
common in Asia
infects small intestine
pathology seen in small intestine
inflammation and mucous secretion at attachment site
blockage, ulcers, hemorrhage, abscesses, chronic diarrhea, death
prevention
boil vegetables
cease use of nightsoil as fertilizer

Ribeiroia ondatrae
DH— carnivorous birds and mammals
hawks, eagles, falcons
1 IH— aquatic snail
2 IH— fish and amphibians
cause of recent frog deformities
cercariae attracted to limb bud region in tadpoles
cause limb deformities as tadpoles metamorphose
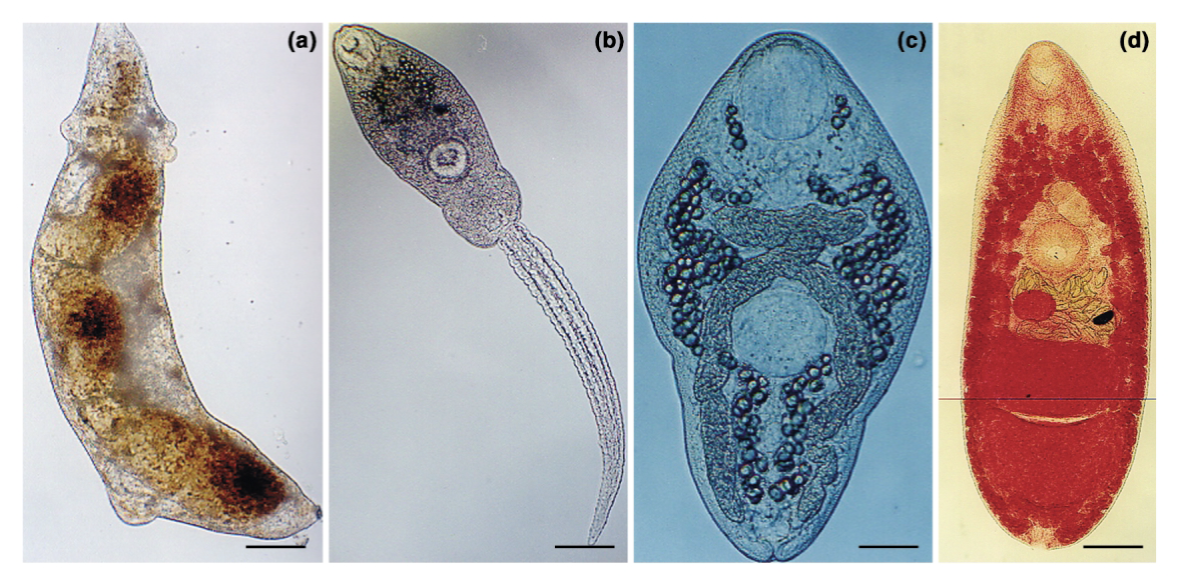
Dicrocoelium dendriticum
DH— sheep, cattle, goats, pigs, cervids
localizes to the bile ducts
1 IH— land snail
2 IH— ants
life cycle does not require water
ex of parasite manipulating host behavior to enhance transmission
distributed throughout Europe, Asia, North America, Australia
Paragonimus westermani
DH— mammals
felids, canids, mustelids, viverrids, humans, swine
mustelidae— otters, ferrets, badgers, and weasels
viverridae— civets, oyans, genets
1 IH— aquatic snail
2 IH— crabs, crayfish
PH— various mammals and birds
distributed throughout Asia, Africa, South and Central America
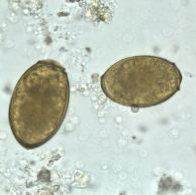
Paragonimus westermani pathology— pulmonary infections
rarely fatal
inflammatory response leading to granuloma formation
difficulty breathing, chronic cough, sputum streaked red (blood) or brown (eggs)
Nanophyetus salmincola
dog salmon poisoning disease
example of hyperparasitism
zoonotic
DH— mammals (dogs, humans, others)
1 IH— aquatic snails
2 IH— fish (salmon!) and crustaceans
distributed throughout Pacific Northwest US and Siberia
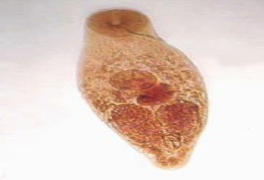
Dog Salmon Poisoning
caused by rickettsial organism
affects canids
rapid and severe disease
fever, swelling of face, eye discharge
depression, anorexia, thirst
vomiting, diarrhea
enlarged and hemorrhaging lymph nodes
death 10-14 days after first signs— 90% mortality without treatment
Chlonorchis sinesis
Chinese Liver Fluke
DH— humans, other mammals
1 IH— aquatic snail
2 IH— fish, crustaceans
RH— dogs, cats
distributed throughout Asia and other countries where people consider raw fish a delicacy

Clonorchis sinesis pathology
erosion of epithelial lining of bile ducts
mucous production, inflammation
necrosis of liver cells
occlusion of bile ducts
eggs can cause granulomas and gallstones
cancer of bile ducts
liver
Where in the body are immature Fasciola hepatica released?
inappropriate; change to triclabendazole
a 20 year old college student is diagnosed with Fasciola hepatica. They are prescribed praziquantel. Which is true about their treatment?
lungs
Where in the host does Paragonimus westermani develop into adults?
eating raw fish
Which of the following is most likely to result in Chlonorchis sinesis?
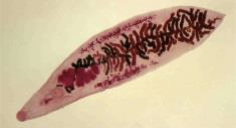
Cestodes
dorso-ventrally flattened
segmented
no digestive system
monoecious
live in intestines of most vertebrates
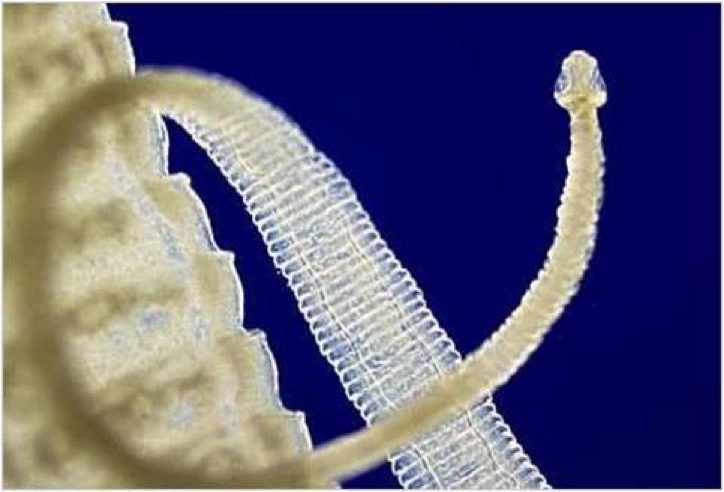
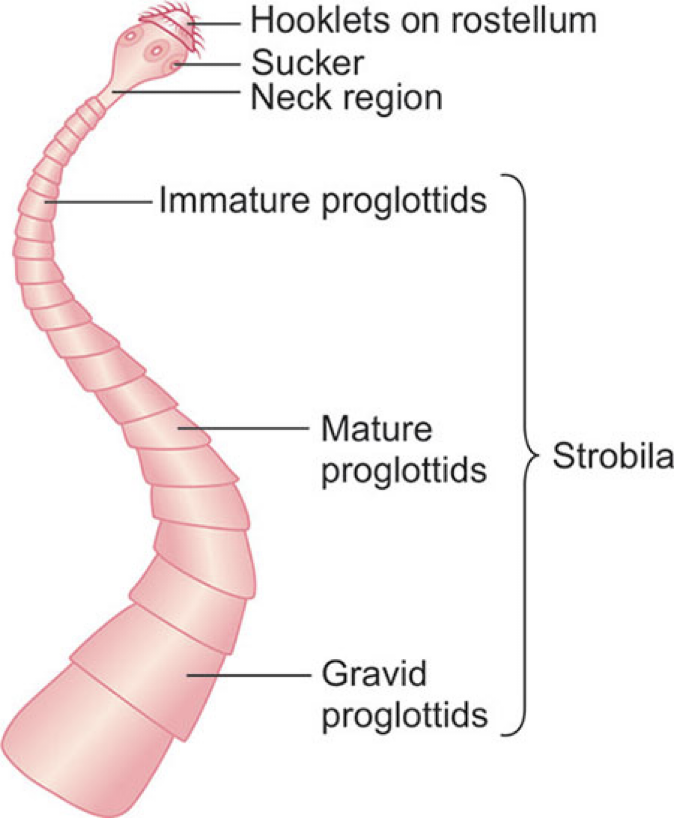
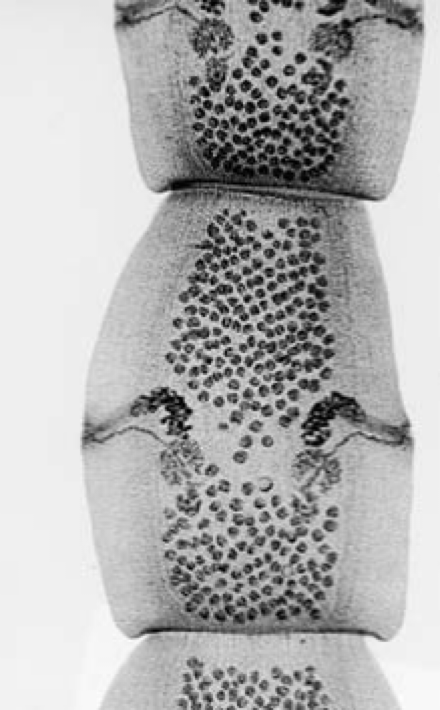
Structures of Cestodes
Scolex- head
may have attachment organ
suckers
hooks
simple or missing
neck
undifferentiated area
produces new segments
stroblia
sum of proglottids
proglottid
“segment”
contains male and female organs
Cestode Reproduction
occurs through genital pore
exchanges spermatozoa
fertilizes other proglottids in the strobila
can also fertilize proglottids in other worms
fertilization of the same proglottid segment is rare
strobilation
new proglottids move toward posterior end
maturing as they descend
as they reach posterior end of stobila → reproduction and egg formation have taken place
result is gravid proglottid
Cestode Egg Release
may pass gravid proglottids with eggs
results in proglottids in feces
proglottid may disintegrate and release eggs
results in eggs in feces
Pseudophyllidean
procercoid
crustacean ingests ciliated coracidium
procercoid develops in body cavity of crusteacean
plerocercoid
develops from procercoid in 2nd IH that ingested infected crustacean
Cyclophyllidean
cysticercus
coenurus
cysticercoid
hydatid cyst
unilocular
multilocular
one or other will occur in IH; which one depends on cyclophyllidean species
Cysticerus
fluid filled body; one scolex, grossly visible, invaginated ex. Tania sp
Coenurus
fluid filled body; many scolices, invaginated, up to a baseball size
Cysticercoid
solid bodied, 1 scolex, invaginated
Hydatid cyst
fluid filled; many scolices, invaginated, up to a basketball size
Unilocular
internal budding to produce internal daughter cysts (also contain scolices)
Mulitlocular
external budding to produce external daughter cysts (also contain scolices)— can metatasize
Diphyllobothrum latum Fish Tapeworm
DH— fish-eating mammals and humans
canine, felines, mustelids, pinnipeds, bears, humans
1st IH— copepods (crustacean)
2nd IH— fish
up to 10 m
shed up to 1 mil eggs/day
scolex has bothria (two longitudinal grooves used in attachment to intestinal wall)
distributed throughout Scandinavia, Baltic States, Western Russia, United States, Great Lakes Area
Pacific Northwest
Diphyllobothriasis Pathology
DH
asymptomatic
vague symptoms
abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, weakness
anemia
Finnish people
parasite absorbs vitamin B12
treatment of parasite usually resolves anemia
Diagnosis
eggs in stool
Treatment
Niclosamide and Praziquantel
Diphyllobothriasis
control of D. lactum
humans infected by eating raw or undercooked fish
cook fish thoroughly (especially imported fish)
At risk:
communities that dispose of sewage in lakes, rivers— leads to higher prevalence in fish
use of human waste as fertilizer
Spirometra mansonoides
human acts as accidental 2nd IH
transmission to humans from accidental ingestion of copepods infected with procercoids
migrate from intestine, become plerocercoids
ingestion of raw/undercooked amphibians, reptiles, birds, or mammals infected with plerocercoids
use of poultices made from frogs/snakes on open skin wounds, mucous membranes
plerocercoid migrates into human
Sparganosis
rarely, spargana can proliferate
split longitudionally or bud
results in 1000s of worms and honeycombed organs
North America
Spirometra mansonoides
DH— cats
may live up to 10 years
Treatment
surgical removal
praziquantel
Taenia saginata
beef tapeworm
length: 3-5 m, up to 20 m
scolex has 4 suckers, no hooks
DH— humans
IH— cattle
Taenia saginata Pathology
most are asymptomatic or have vauge symptoms
abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea
dizziness, headache
sometimes..
intestinal obstruction
delirium
loss of appetite
psychological issues
Taenia saginata Diagnosis and Treatment
cannot diagnose based on eggs
need scolex and proglottid morphology
PCR—RFLP
ELISA
treatment
Niclosamide and praziquantel
Taenia solium
pork tapeworm
DH- humans
IH- swine
length 2-3 m, up to 10 m
scolex— rostellum with 4 suckers and 2 rows of hooks
distributed throughout Mexico, Central and South America, Africa, India, China, Eastern Asia
Taenia solium pathology
most are asymptomatic or have vague symptoms:
Ab pain, diarrhea, nausea
dizziness, headache
sometimes have:
intestinal obstruction
delirium
loss of appetite
psychological issues
Taenia solium Cysticercosis Pathology
signs depend on infection site
skeletal muscle, skin, liver
Taenia solium Cysticercosis Pathology
signs depend on infection site
skeletal muscle, skin, liver
few signs
eye
damage to retina, etc
vision loss
CNS
epilpsy (most common)
necrosis, blindness, paralysis, hydrocephalus, etc
Taenia solium Diagnosis and Treatment
diagnosis in DH
presence of eggs/proglottids in feces, antibody tests
diagnoses in IH
signs, imaging, antibody tests
treatment with praziquantel
not for CNS or eye cysticerci
worm death → severe inflammatory response → death of host
surgery
Taenia solium Prevention/Control
early detection and treatment of infection with adults T. solium
personal hygiene
prevent spread of eggs within household
prevent contamination of food and water
do not use human sewage as fertilizer
Echinococcus granulosus
adults very small
DH— mainly canids
IH— many, exp. herbivores
cystic echinococcosis in humans
areas where herbivores are raised with our near carnivores
transmitted in definitive host when dogs feed on organs of butchered animals
transmitted in intermediate host when herbivores ingesting eggs in feces from infected dogs
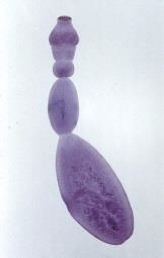
Echinococcus granulosus pathology
IH (including humans)
may not see signs for months to years
crowds and disrupts function of organs
extent of pathology depends on location of cyst
accidental rupture of hydatid cyst
Echinococcus granulosus diagnoses
DH— detect eggs in feces
IH— detect hydatid
Treatment of Echinococcus granulosus
drugs for inoperable cysts; Albendazole, Prazinquantel
surgery
Echinococcus multilocularis
small, morphology like E. granulosus
DH— mainly canids (foxes)
IH— rodents
smaller DH/IH host range than E. granulosus
tend to cycle in wild populations
alveolar echinococcosis in humans
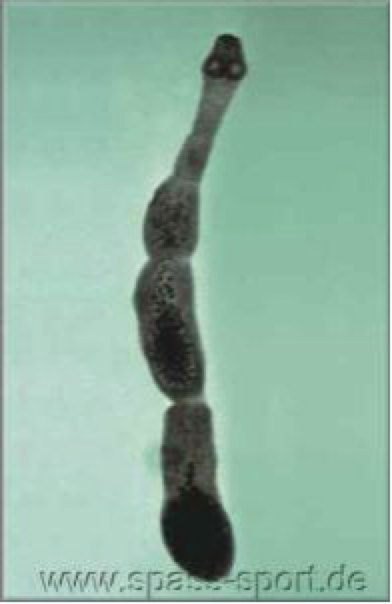
Echinococus multilocularis distrubution
Boreal (sub-artic)
Europe
Asia
North America
Echinococcus multilocularis Transmission
life cycle similar to E. granulosus
DH
ingestion of infected rodent IH
IH
rodents ingest eggs shed in DH feces
humans— accidental ingestion of eggs
Echinococcus multilocularis Pathology
multilocular hydatid cyst
thin outer wall
grows and infiltrates host tissues
faster growing than unilocular cyst
Echinococcus multilocularis epidemiology
diagnosis
DH— detect eggs in feces
IH— detect alveolar hydatids
treatment
albendazole
surgery— often inoperable
control
avoid dog feces in endemic areas; thorough washing of fruits/veggies; regular deworming of dogs; education
Dipylidium caninum
“cucumber tapeworm”
worldwide, common
DH— dogs, cats, humans
IH— fleas
adults ~ 18 inches long
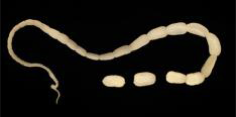
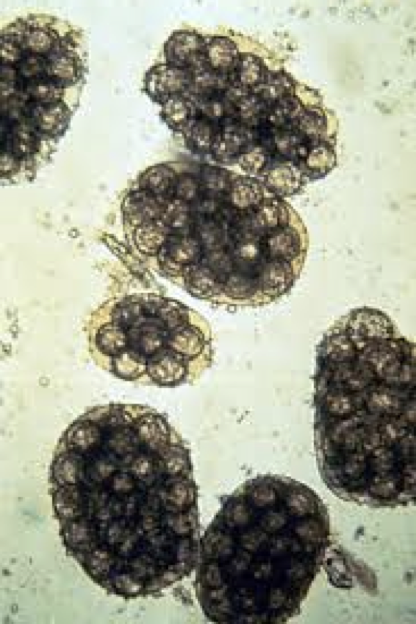
Dipylidium caninum epidemiology
pathology
signs and symptoms rare
diagnosis
characteristic proglottids or egg packets in feces
treatment
praziquantel
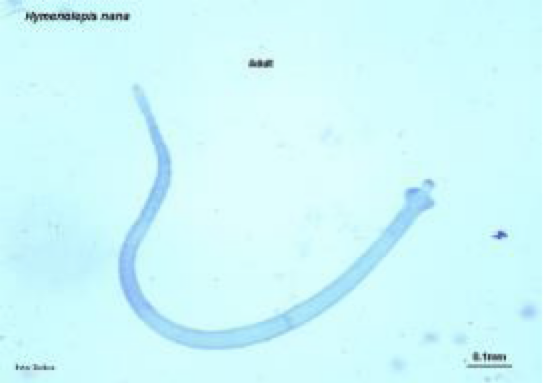
Hymenolepis nana
dwarf tapeworm
worldwide
very common cestode in humans
especially children
DH— rodents and humans
IH— fleas and beetles
rostellum with one row of hooks
adults ~ 40 mm long
Rostellum
fleshy protuberance of the scolex of a tapeworm, which may or may not bear hooks