AP Chem Units 1-5
1/428
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
429 Terms
Properties of Acids
- Tastes Sour
- Conducts an electrical current
- Reacts with Metals to form Gas
- pH of less than 7
- Turns Litmus Red
Properties of Bases
- Tastes Bitter
- Conducts an electrical current
- Feels slimy/slippery
- pH of more than 7
- Turns Litmus Blue
Arrhenius Acid
Produces H+ ions when dissolved in water
Strong Acids
HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4
C (CHOOPS)
Carbonates (CO3 2-)
H (CHOOPS)
Hydroxides (OH-)
O1 (CHOOPS)
Oxides (O)
O2 (CHOOPS)
Oxalates (C2O42−)
P (CHOOPS)
Phospates (PO4 3-)
S (CHOOPS)
Sulfides (S)
N (NAAA)
Nitrates (NO3-)
A (NAAA)
Acetates (C2H3O2-)
A2 (NAAA)
Alkali (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr)
A3 (NAAA)
Ammoniums (NH4+)
Arrhenius Base
Produces OH- ions when dissolved in water
Monoprotic Acid
acid with 1 acidic proton
Diprotic Acid
acid with 2 acidic protons
Triprotic Acid
acid with 3 acidic protons
Oxoacids
acidic proton is attached to an oxygen atom
Organic Acids
general formula of R-COOH
Bronsted Acid
substance that can donate a proton
Bronsted Base
substance that can accept a proton
Conjugate Acid
the particle formed when a base gains a hydrogen ion
Conjugate Base
the particle that remains when an acid has donated a hydrogen ion
Amphoteric
a substance that can act as both an acid and a base
Ex of Amphoteric
- H2O
- HSO4 -
- HPO4 2-
- H2PO4 -
Binary Acids
composed of hydrogen and a nonmetal
For Binary Acids, the...
greater the anion radius the smaller the attraction force on the H+ Ion (Smaller Radius = Weaker)
Oxoacid
an acid containing hydrogen, oxygen, and another element (HYO)
For Oxoacids, as you increase the electronegativity of Y and the # of Oxygens...
Strength Increases
Why does adding more Oxygens to Oxoacids increase the strength?
the electron gets pulled closer to Y which weakens the OH bond which increases the strength of the acid
Conjugate Base Strength of Binary Acids
a small radius has a greater ability to attract and accept H+ Ions
[H+] = [OH-]
Solution is NEUTRAL
[H+] > [OH-]
Solution is ACIDIC
[H+] < [OH-]
Solution is BASIC
pH =
-log[H+]
Acid Percent Ionization
[H3O+] (eq)/[HA] (initial) x 100
Base Percent Ionization
[OH-] (eq)/[B] (initial) x 100
Generic Acid BCE
HA + H20 --> (or eq) H30+ + A-
Generic Base BCE
B + H20 --> (or eq) OH- + HB+
Common Ion Effect
a decrease in the solubility of an ionic compound caused by the addition of a common ion
2 Ways to make a Buffer
1-mix a weak acid and salt of its conjugate base or weak base and a salt of its conjugate acid (HA + MA)
2-add strong acid and partially neutralize a weak base or add strong base and partially neutralize a weak acid (B + HB)
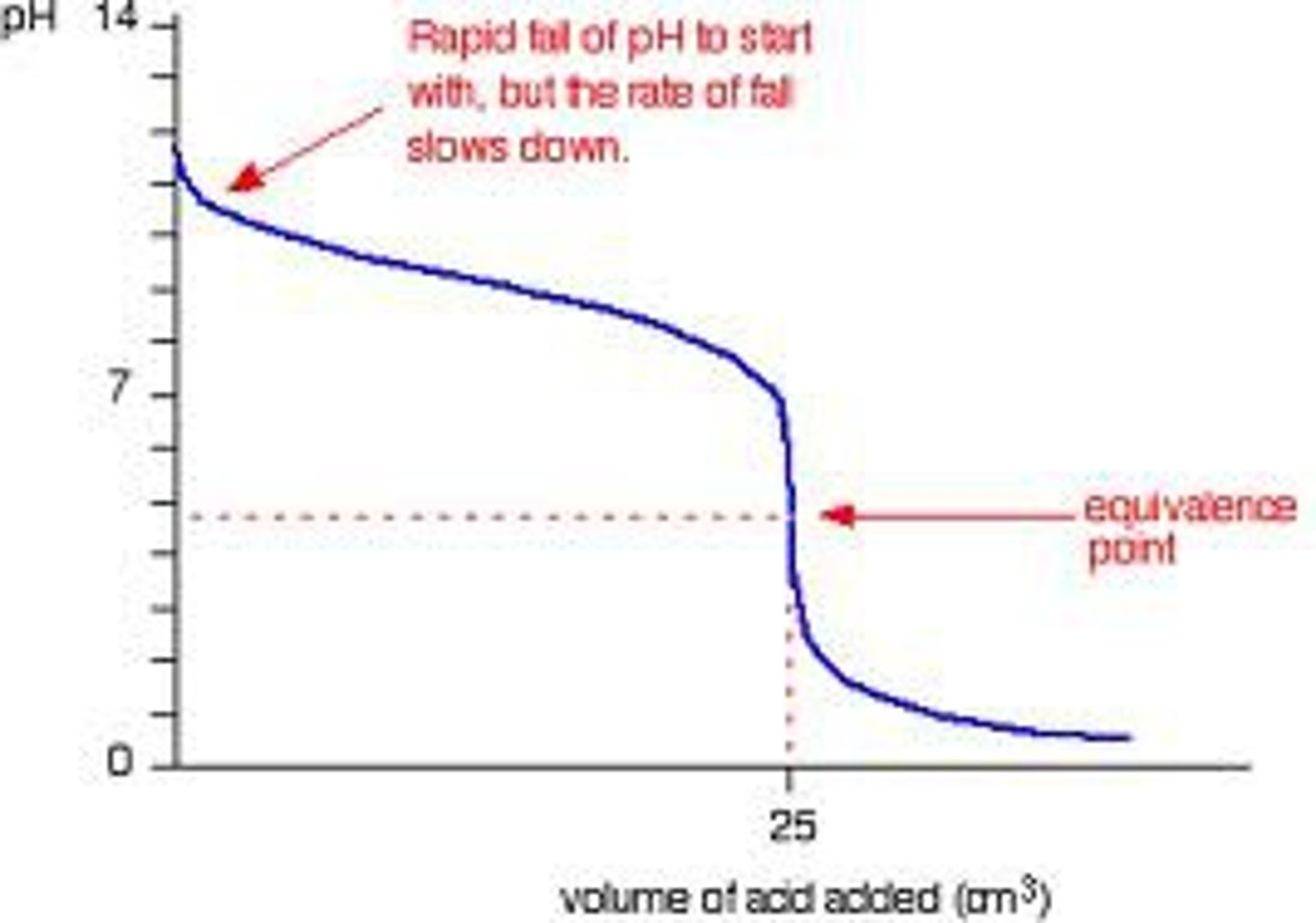
Weak Base + Strong Acid
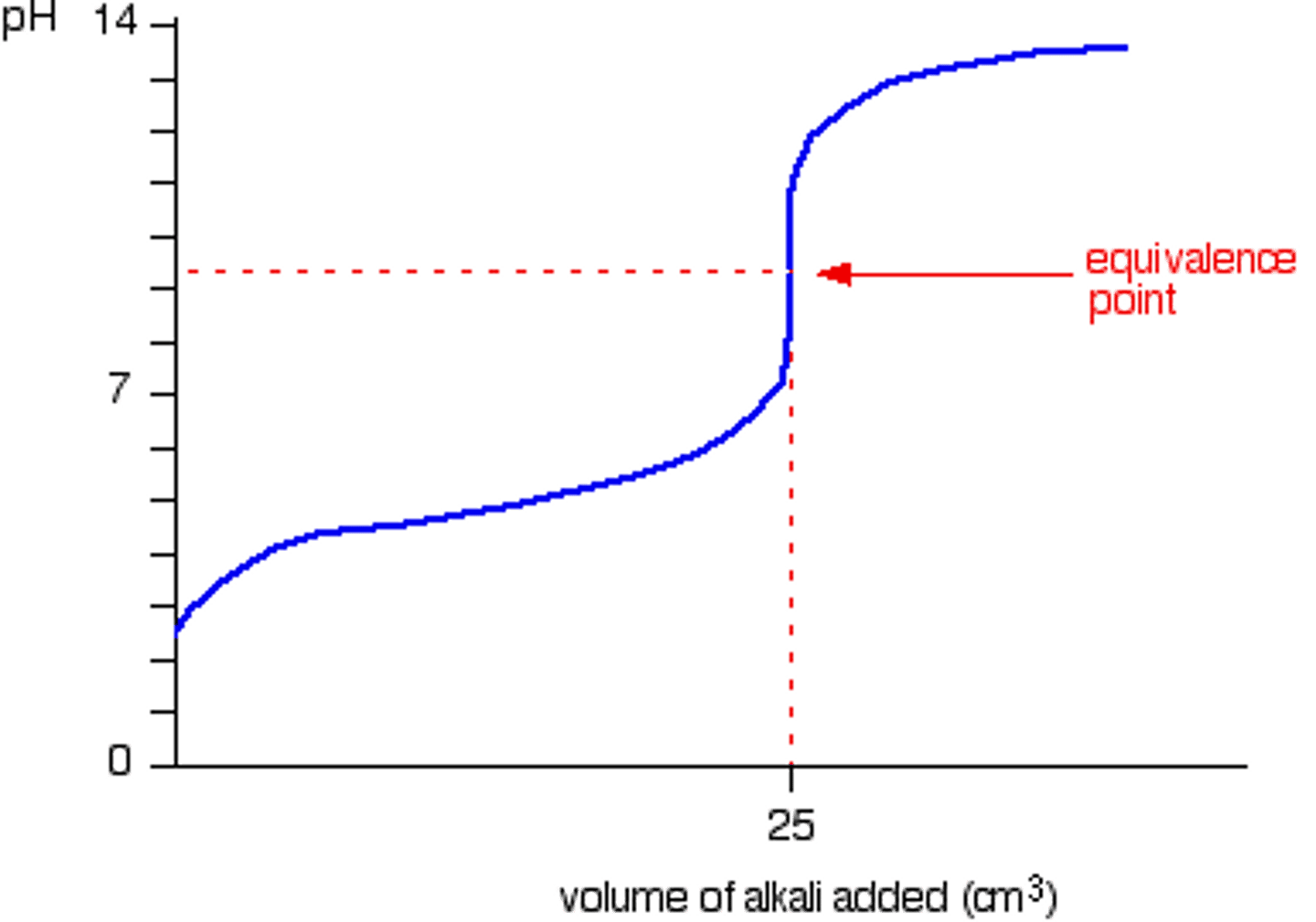
Weak Acid + Strong Base
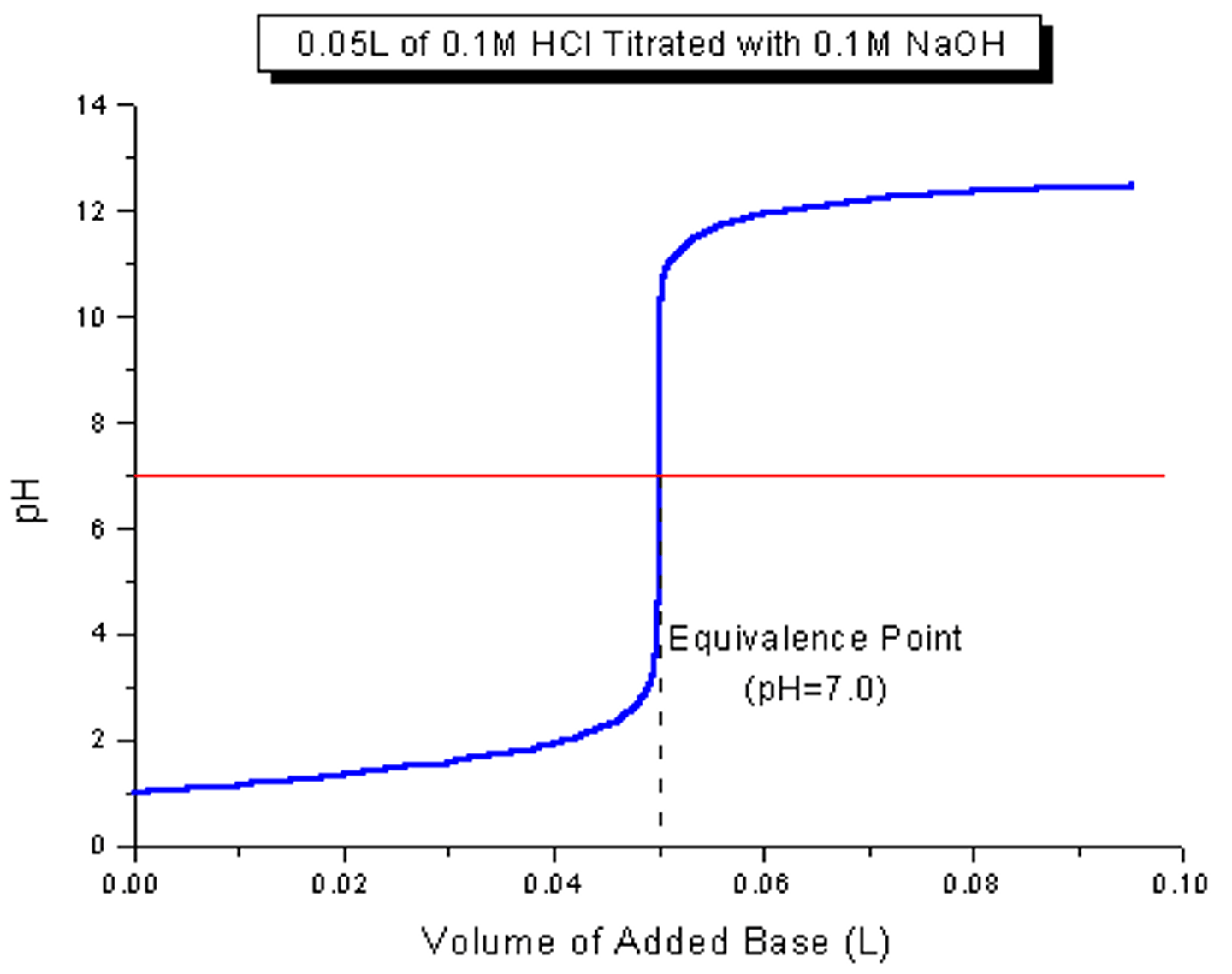
Strong Acid + Strong Base
Buffer Capacity
the amount of acid or base a buffer solution can absorb without a significant change in pH
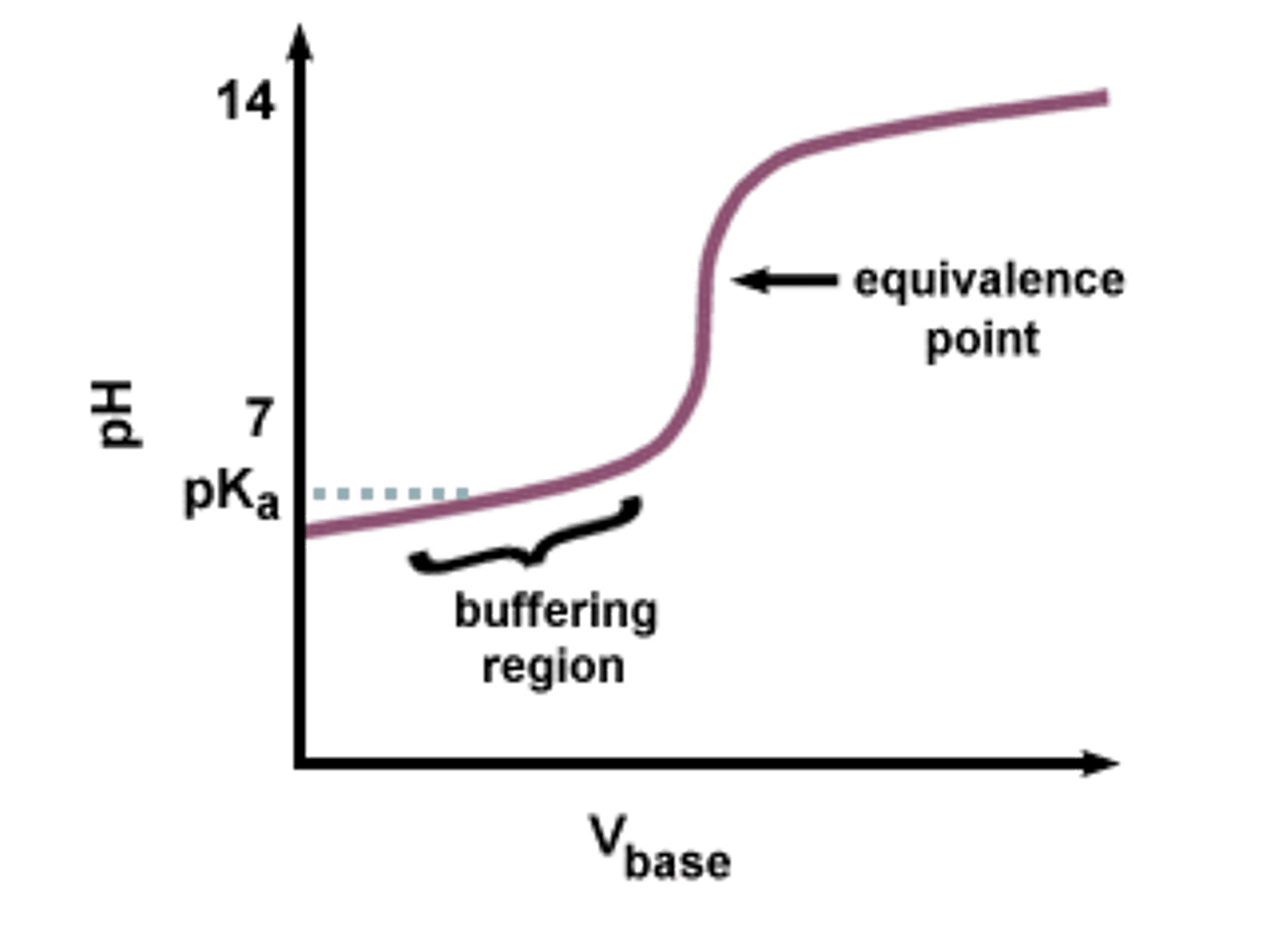
Buffering
Kinetics
determines how fast a reaction takes place or the rate of reaction
Example of a SLOW Reaction
Cgraphite -> Cdiamond
Example of a MEDIUM Reaction
4Fe + 3O2 -> 2Fe2O3
Example of a FAST Reaction
CH4 + 2O2 -> CO2 + 2H2O
Rate =
Change in an Observable Quantity/ Change in Time
Rate = Change in an Observable Quantity/ Change in Time =
Change in [Products]/Change in Time = - Change in [Reactants]/ Change in Time
Instantaneous Rate
The rate given at a specific time
How to find Instantaneous Rate
Take the slope of the tangent line at time on the graph
Rate laws
how a rate changes as the initial concentration changes
k
Rate constant
[A]
mole per liter
When the exponents or "order" for a reaction is zero...
the concentration of a reactant has no effect on the reaction rate
0th Order Reaction
Rate=k
If [A] doubles in a 0th order, rate...
stays the same
When m=1
the rxn is 1st order with respects to A
If [A] doubles in a 1st order reaction, then rate...
doubles because they are directly related
1st Order Reaction
rate=k[A]
When m=2
the reaction is 2nd order with respects to A
2nd Order Reaction
Rate=k[A]2
Doubling [A] in a 2nd order reaction, the rate increases by...
4x because concentration is exponentially related to reaction rate
First Order Integrated Rate Law
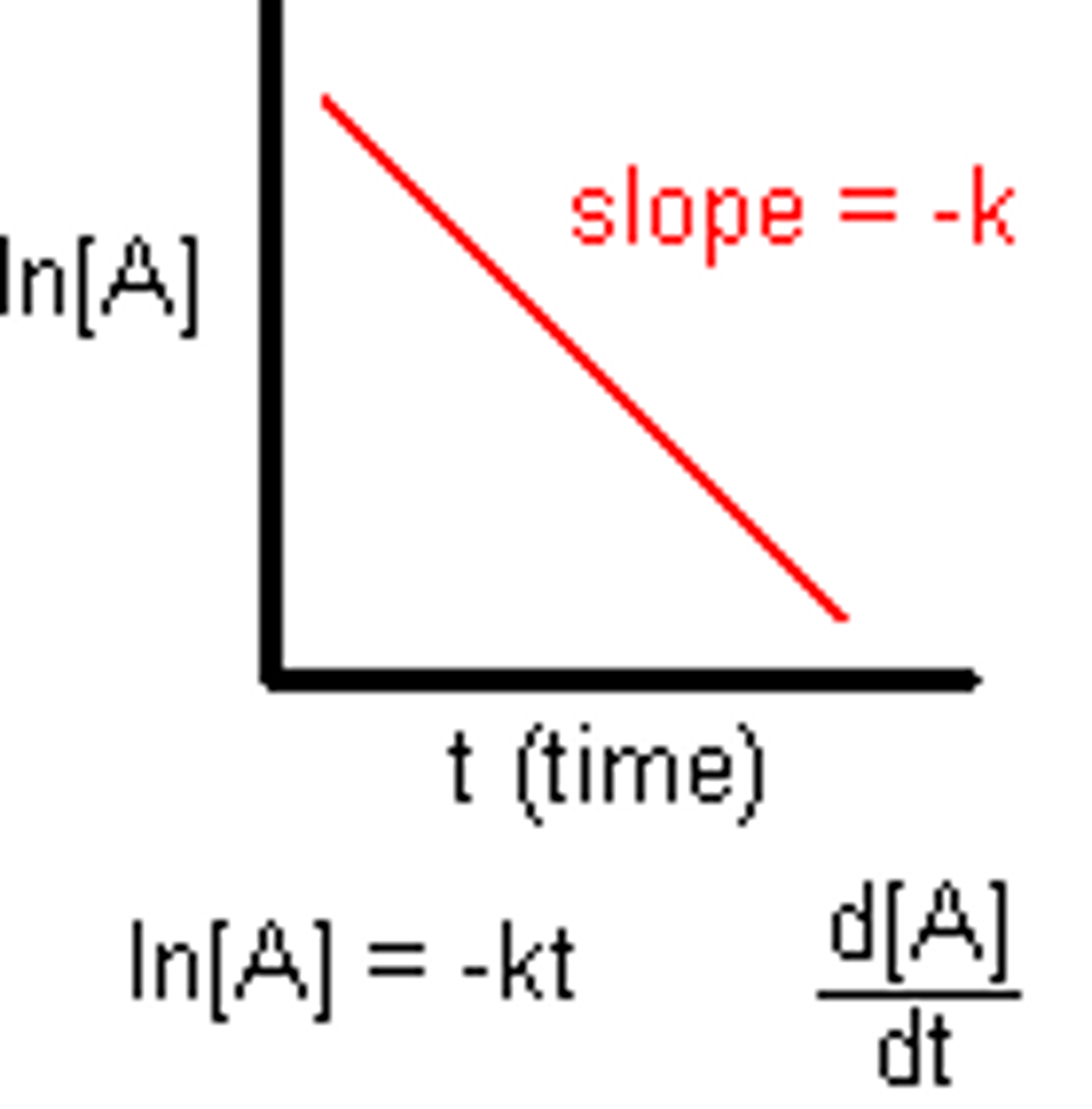
Second Order Integrated Rate Law
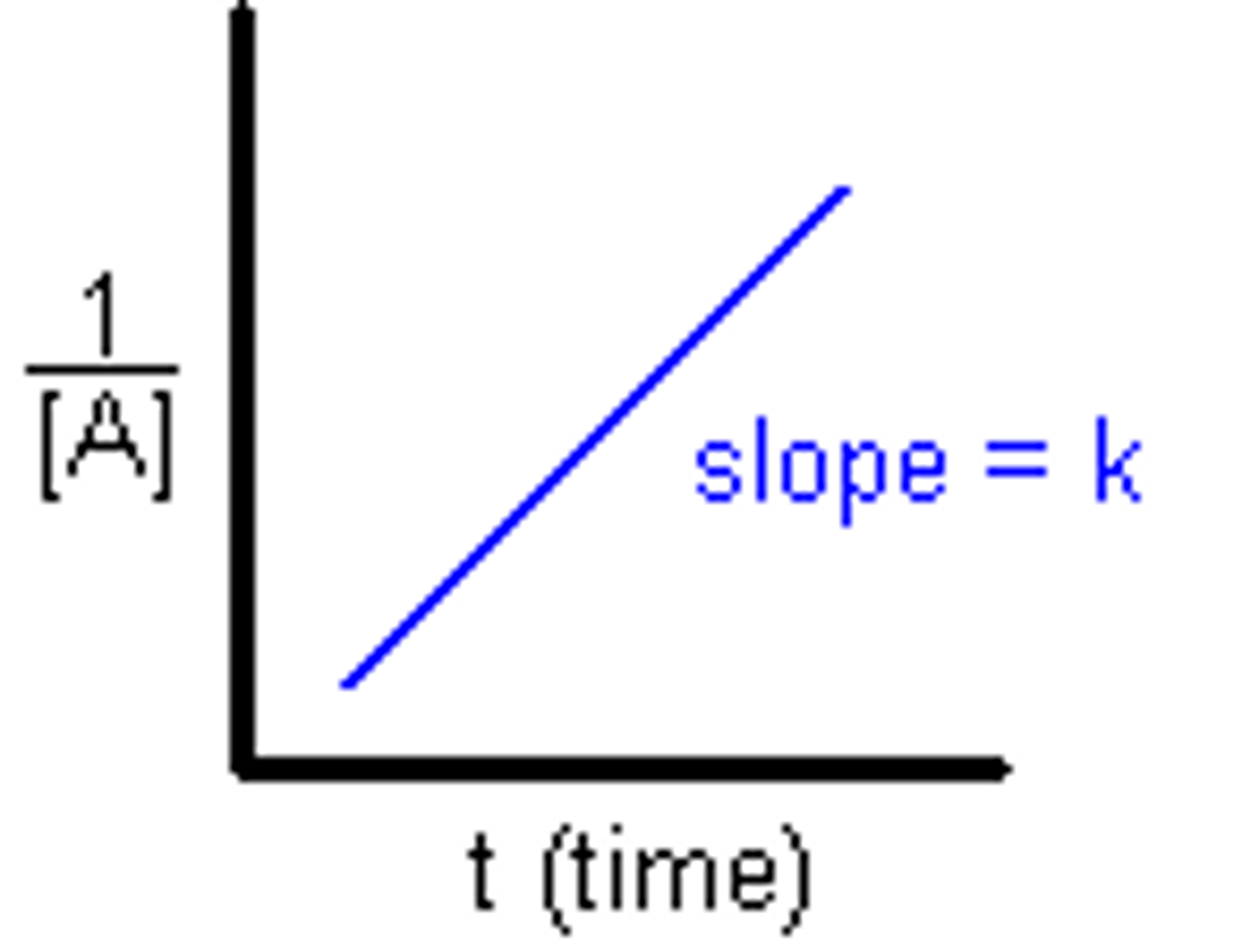
Zero Order Integrated Rate Law
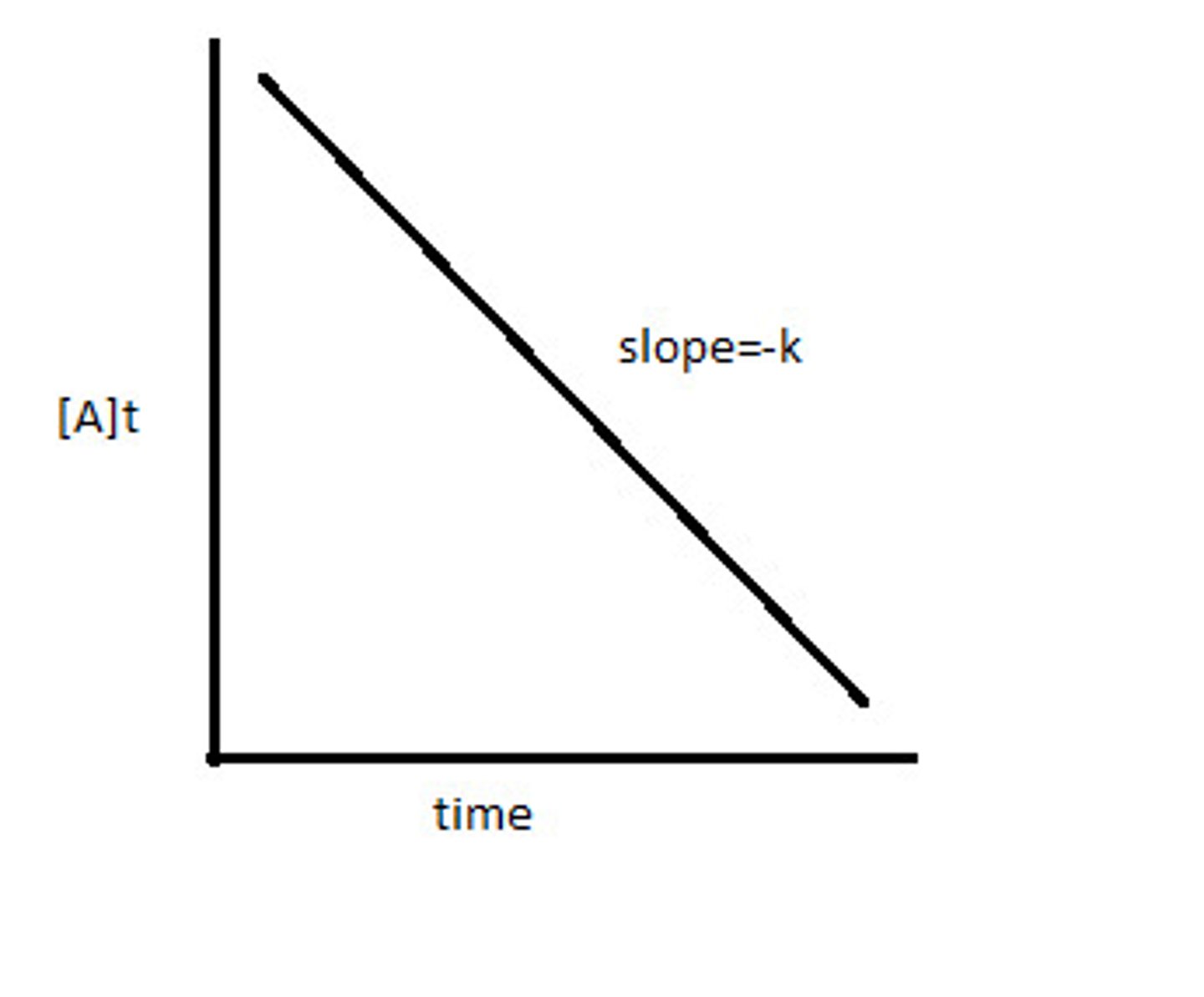
The Straightest Line...
Fits the Order
Collision Theory
The rate of the reaction is proportional to the numer of effective collisions
Factors that effect Orientation
Nature of the Reactants - Molecular Orientation
Temperature
Concentration
Catalysts
As temperature goes up, the nature of the reaction...
goes up since the numberof effe tive collisions goes up
How do you say when the number of effective collisions increases so the molecules require less energy to react?
Molecule's energy to overcome the energy barrier increases
Molecular Kinetic Energy Depends on...
Temperature
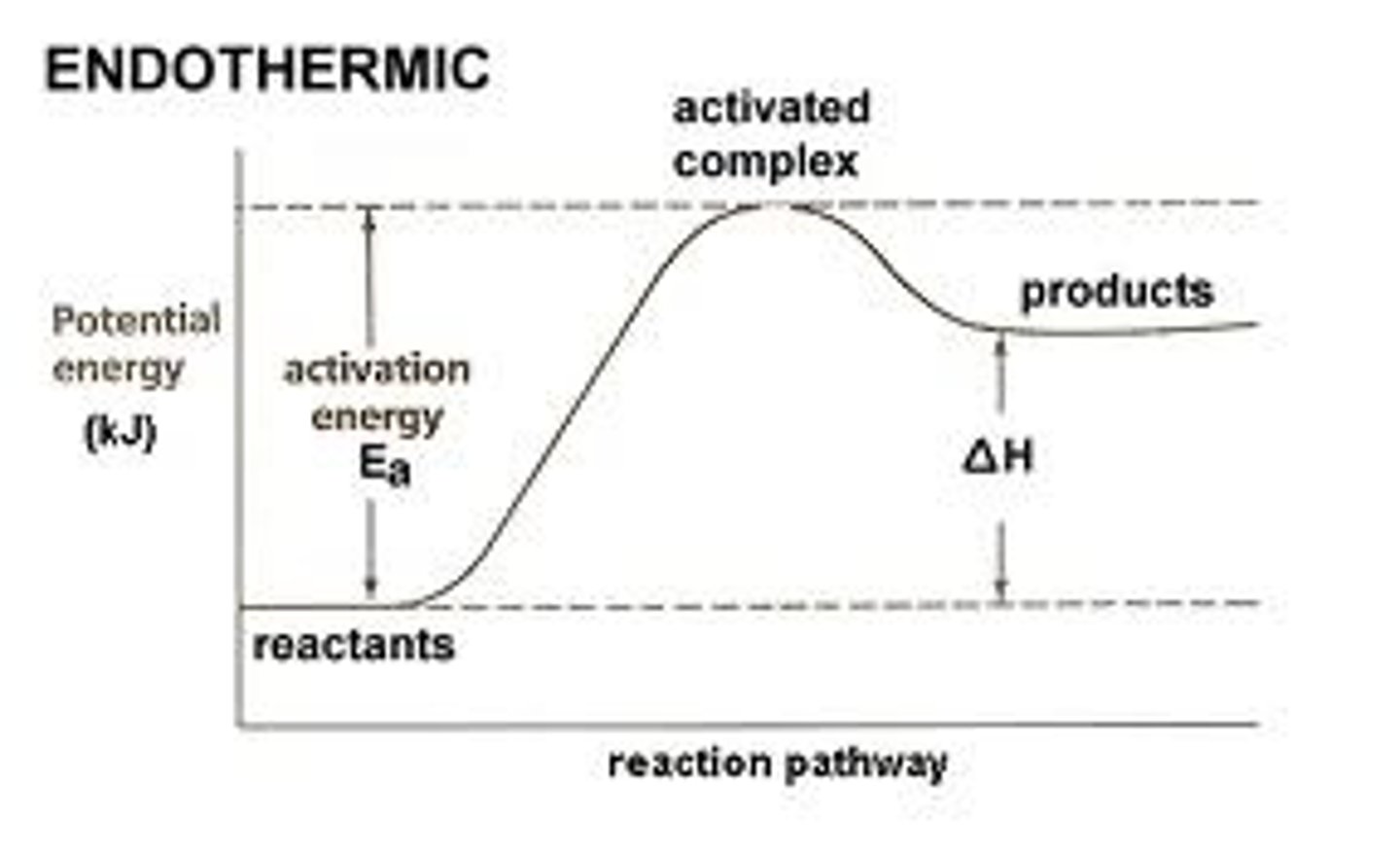
Potential Energy Diagram - Endothermic
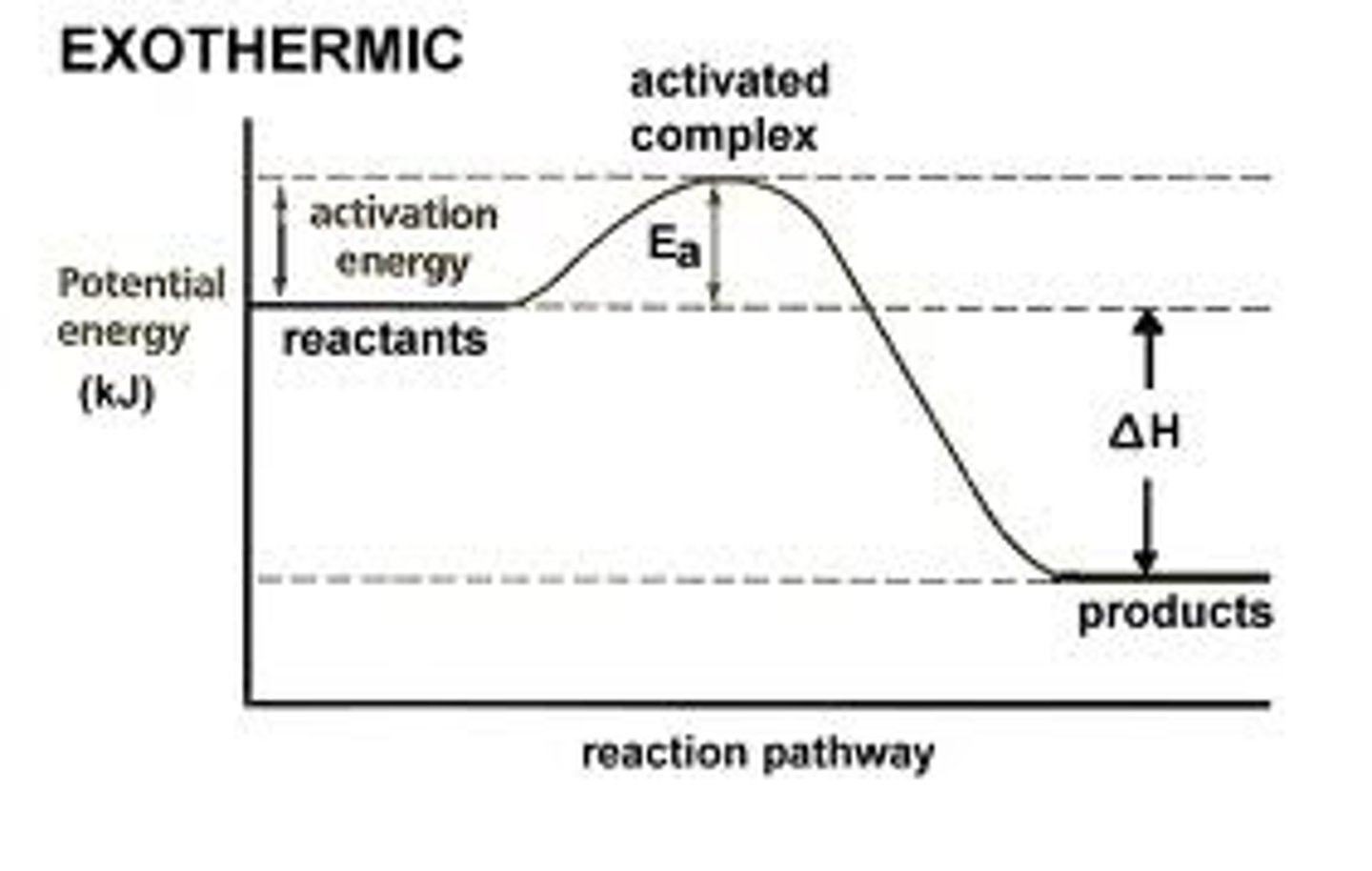
Potential Energy Diagram - Exothermic
Kinetics Diagram
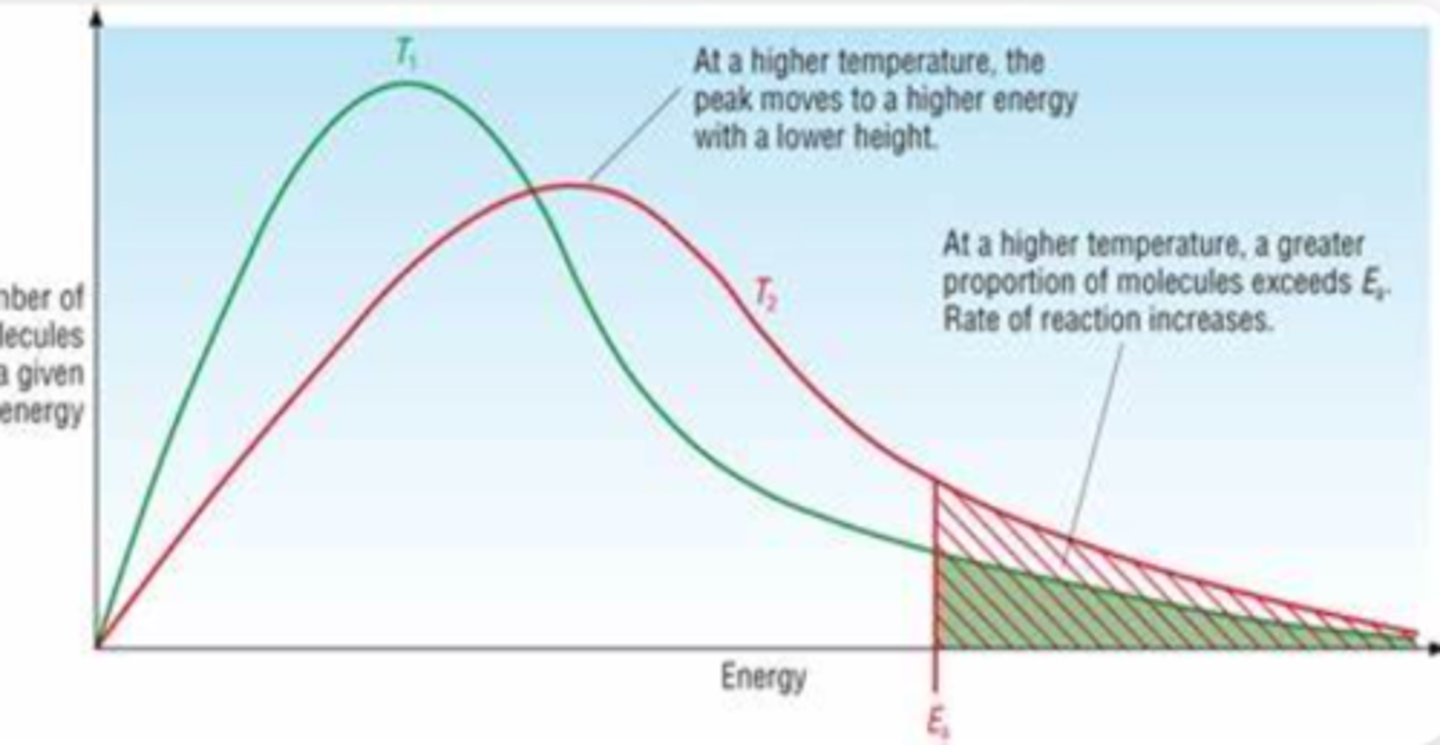
In General a reaction rate...
doubles every 10 degrees celsius
In a Kinetics Heat Diagram the hottest...
Is always the longest
As temperature increases the probability of finding molecules at higher energy...
increases
Concentration of Solids
As area Increases, effective collisions increases, rxn rate increases
Concentration of Gasses
As V decreases or P increases, effective collisions increase, rxn rate increases
Catalysis
lower the Activation Energy Barrier without becoming consumed or changed in the process
Mechanism
the sequence of steps the molecular level that control the speed of a reaction
Rules for Writing Mechanisms
1. The rate law of the slowest step determines the reactions overall rate law
2. The rate law of a step can be determined by looking at the equation
3. All the steps must add together to give the overall rxn (cross out intermediates)
Rates...
Change during the reaction
Rates are given... by the slope of the line
by the slope of the line
The Equation...
gives average rate over a time interval
Dynamic Equilibrium
Both are being made and destroyed at the same rate
When Slope = 0
equilibrium is achieved
Chemical Equilibrium
the state in which the concentrations of the reactant and products become constant over time
K =
Products/Reactants
K>>1
Lots of products
K<<1
Lots of reactants
K=1
equal amounts of reactants and products
Kc
[products]/[reactants]
Kp
pressure
Ksp
solubility product that are slightly soluble (solids excluded)