DT Shaping
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Shaping
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
1
New cards
Hand tools
Tenon saw, Hacksaw, Coping saw, Piercing saw, Rasps, Planes, Chisels, Hand router, Gouges, Wheel brace and bit, Hand drill and twist bit, Abrasive papers
2
New cards
Tenon saw
Used for cutting straight lines when working with wood

3
New cards
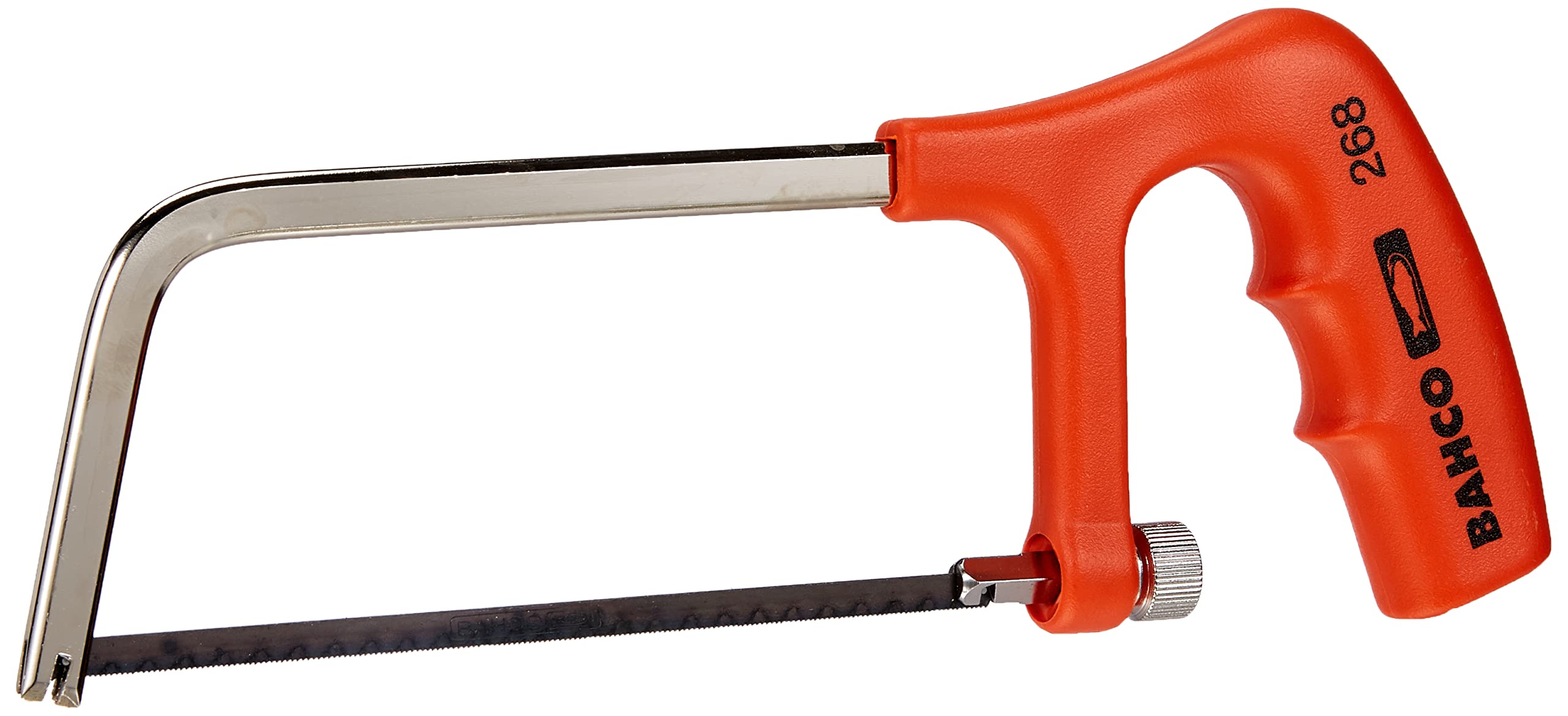
Hacksaw
Used on metals and plastics for cutting straight lines

4
New cards
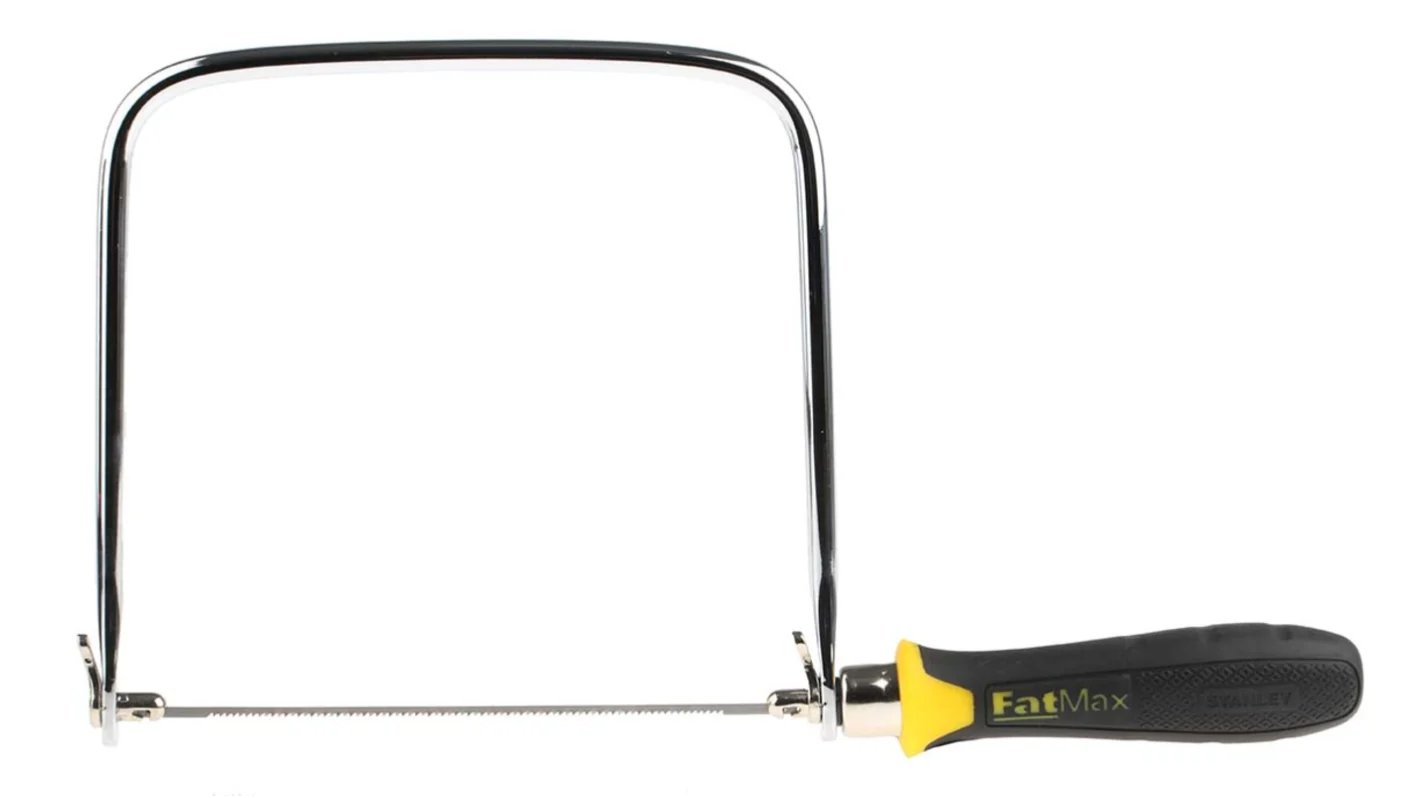
Coping saw
Used for cutting curved lines when working with wood or plastics

5
New cards
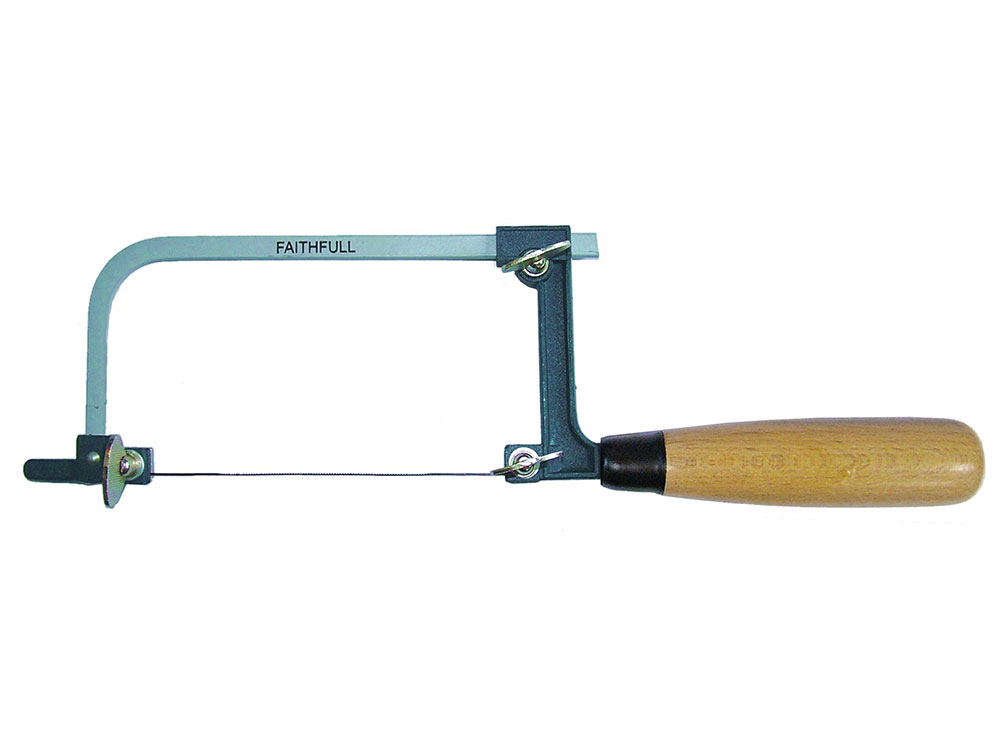
Piercing saw
Used to cut curved lines into metals and plastics

6
New cards
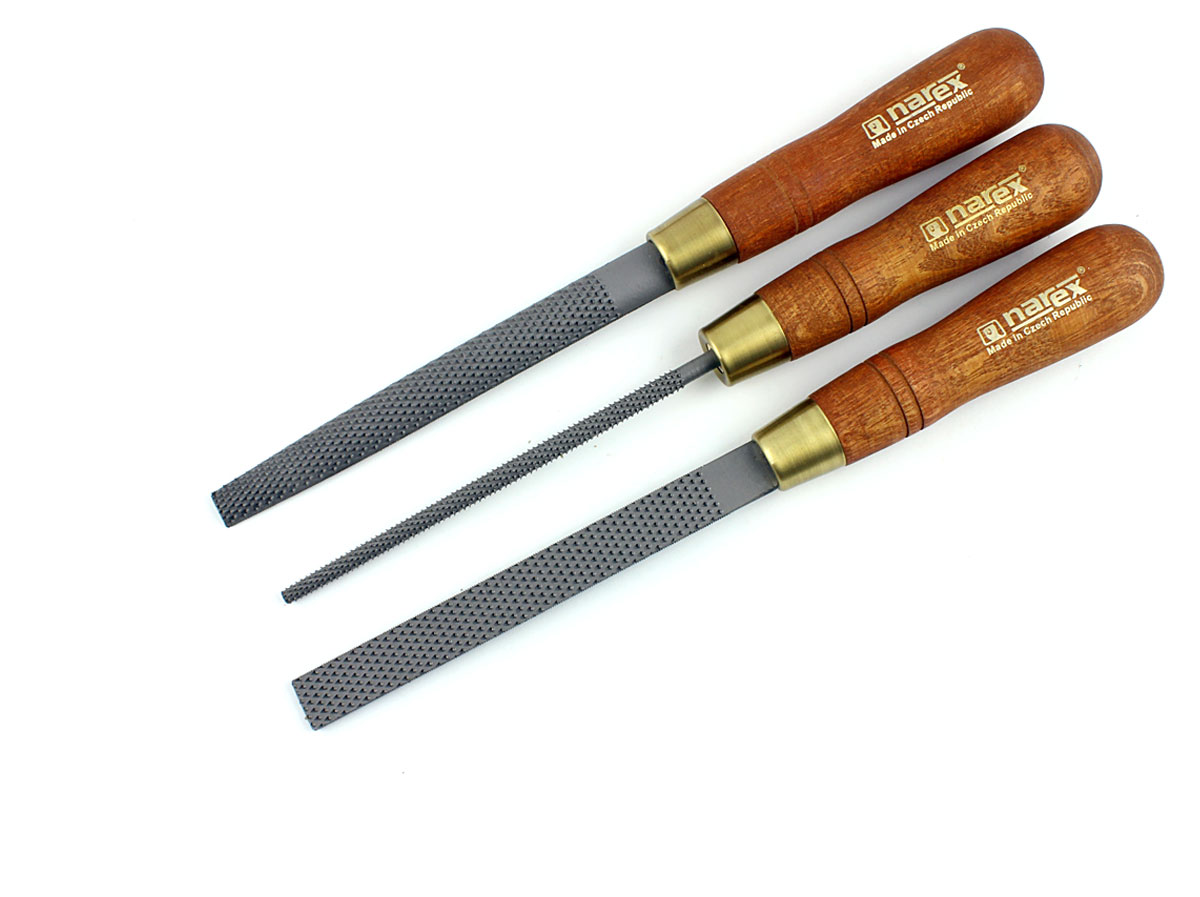
Rasps
Used to shape the edges of wood

7
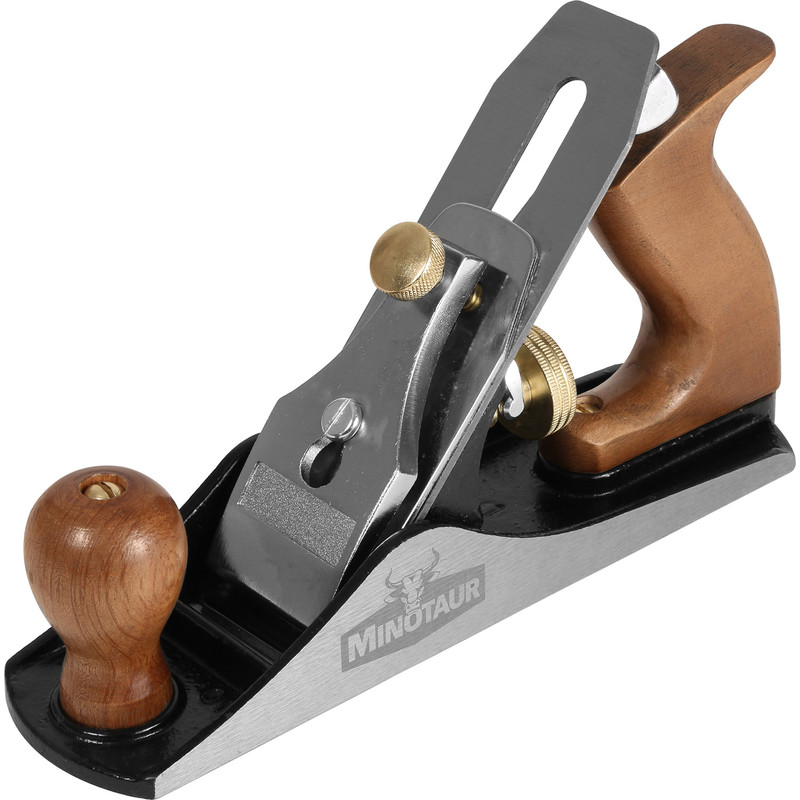
New cards
Planes
Shape the edges of different types of wood

8
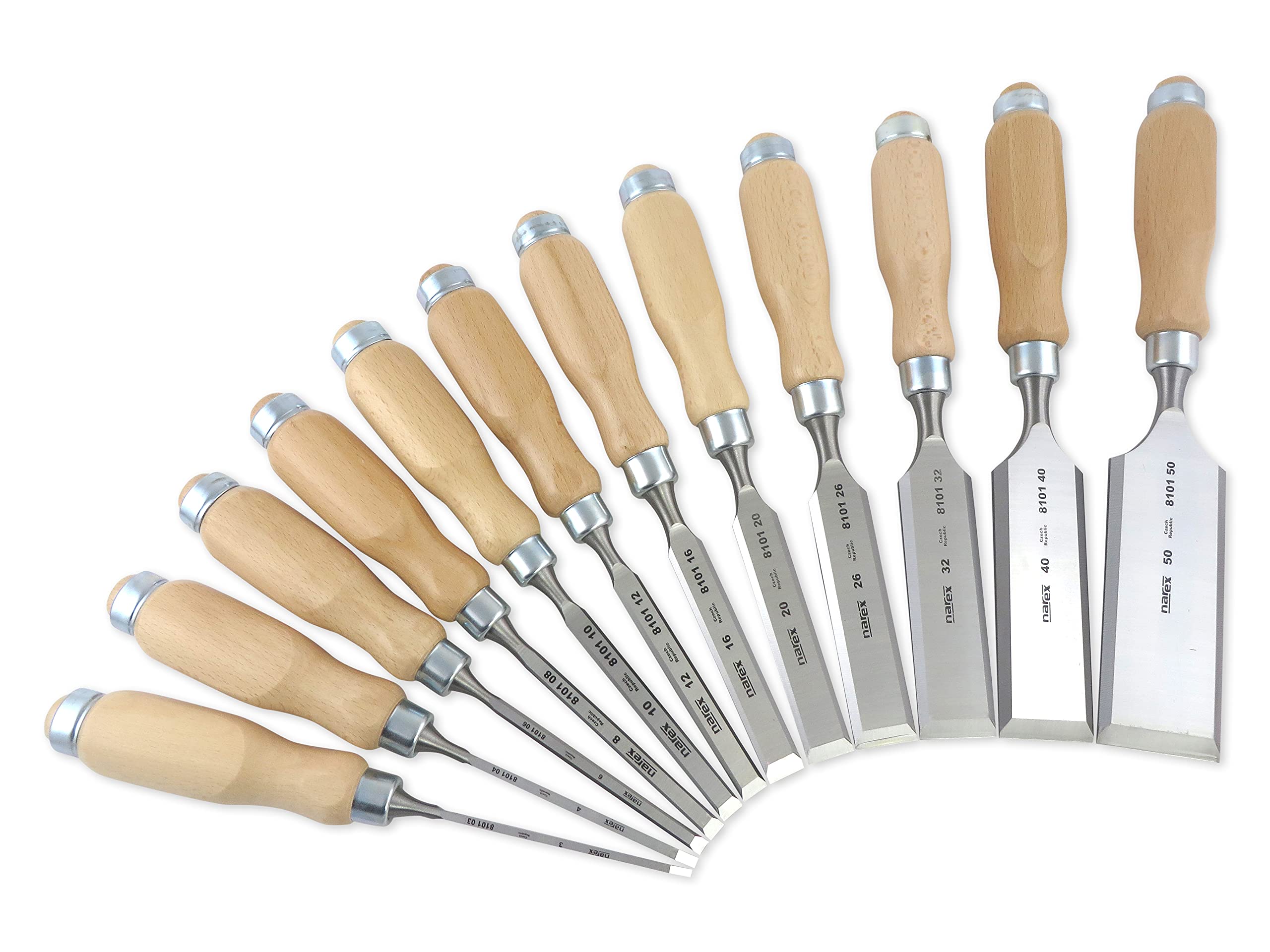
New cards
Chisels
Used for hollowing when working with wood

9
New cards
Hand router
Used for hollowing when working with wood

10
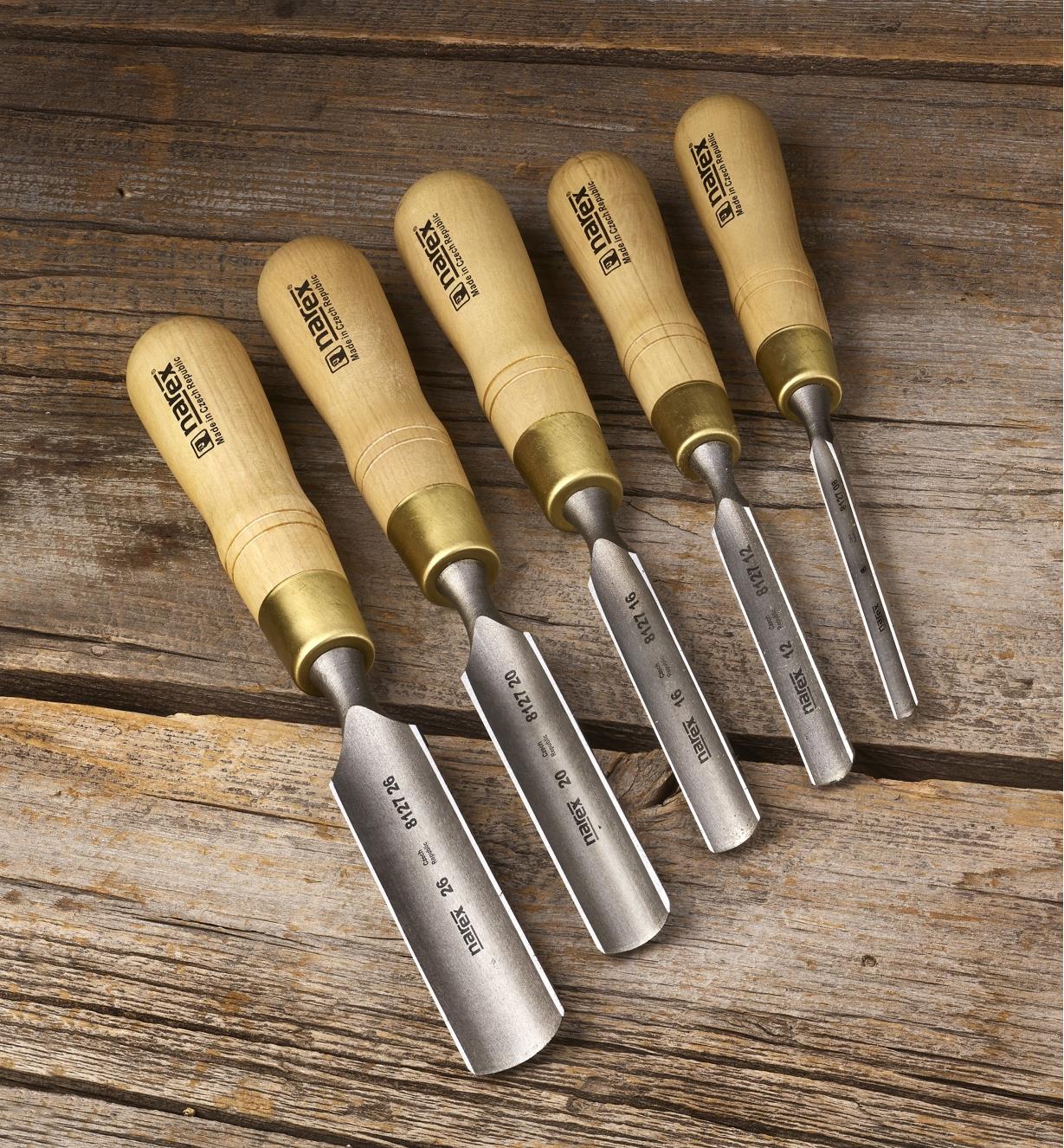
New cards
Gouges
Used for hollowing woods

11
New cards
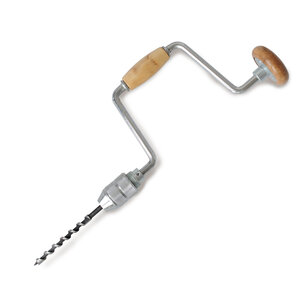
Wheel brace and bit
Drills holes into wood
12
New cards
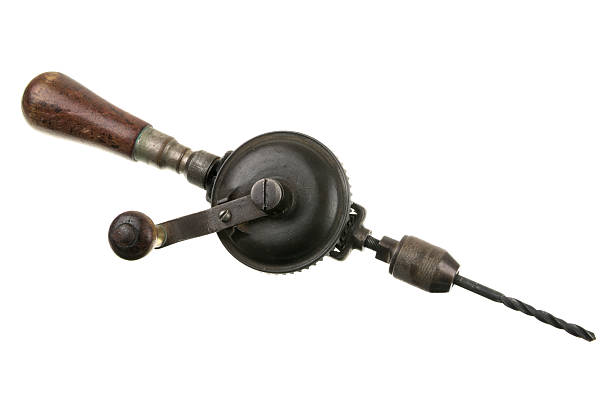
Hand drill and twist bit
Drill holes into both metals and plastics

13
New cards
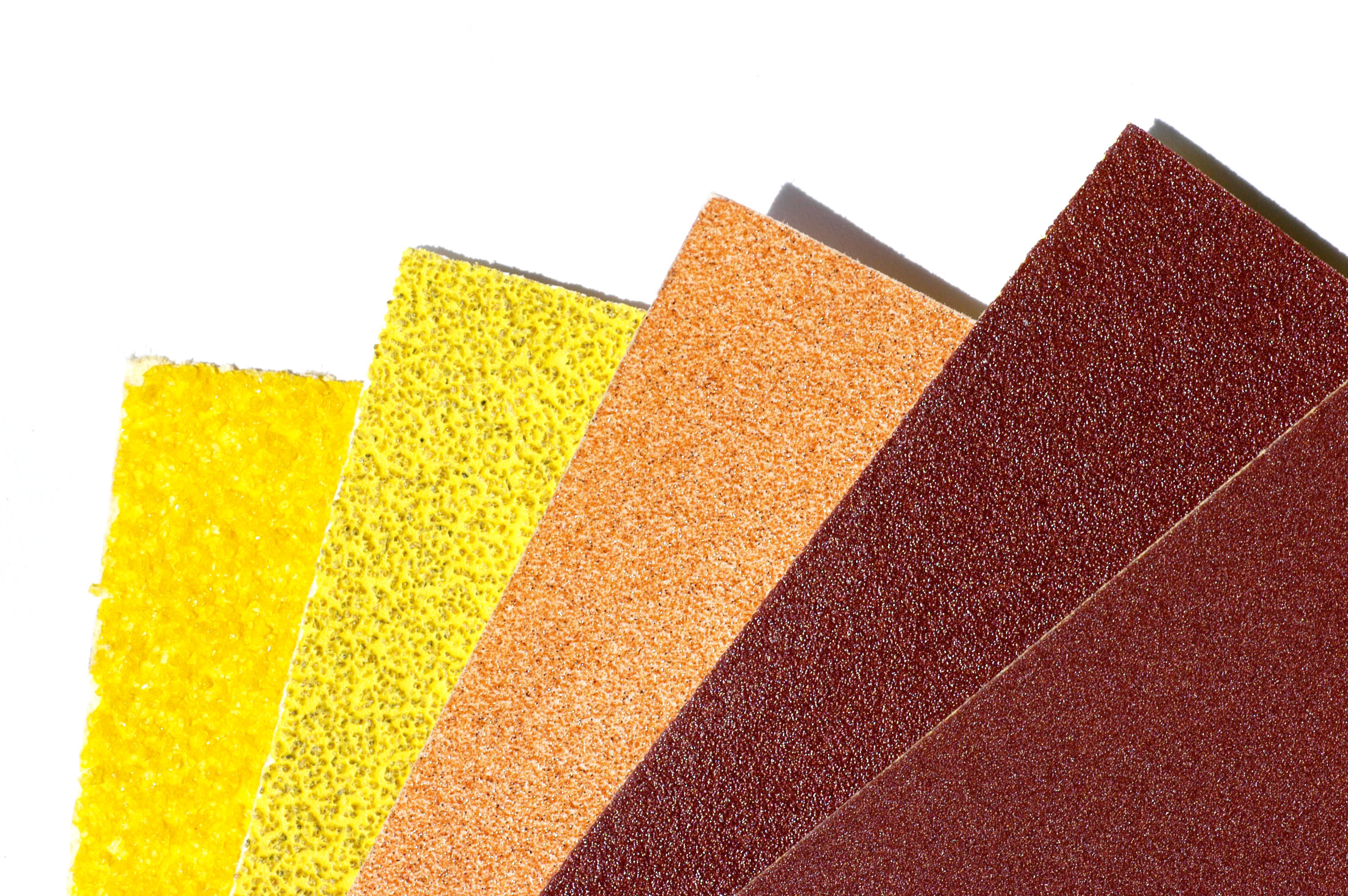
Abrasive papers
Used for smoothing surfaces when working with wood, metal or plastic

14
New cards
Machine tools
Circular saw, Bandsaw, Belt sander, Pillar/bench drill, Lathe, Milling machine
15
New cards
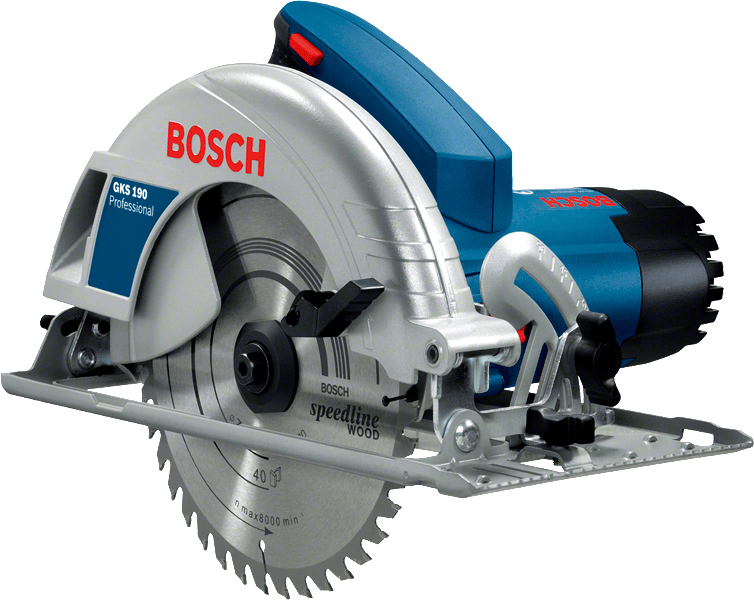
Circular saw
Cuts straight lines into woods and plastics

16
New cards
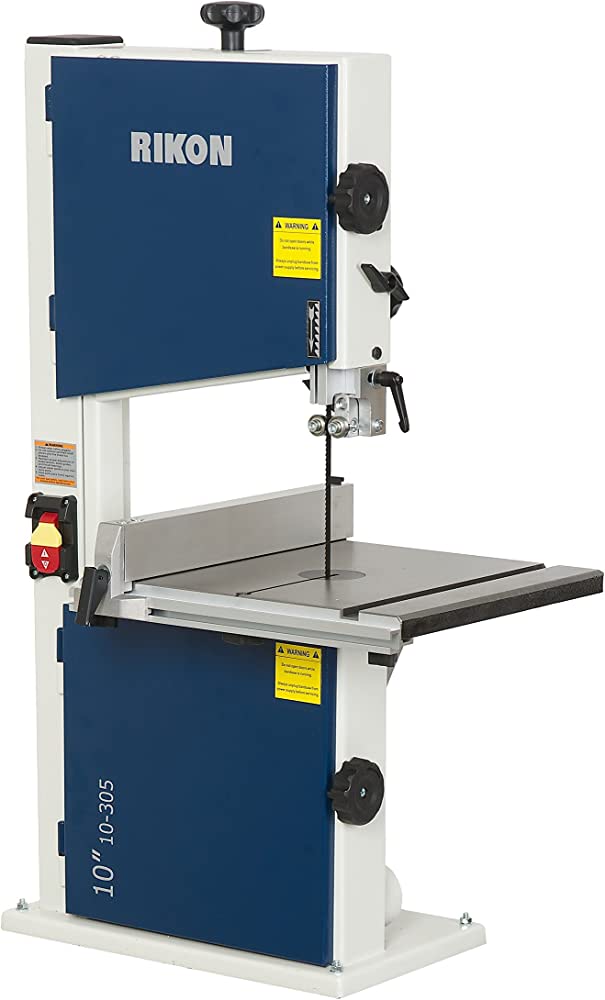
Bandsaw
Used for cutting curved lines when working with woods, metals and plastics

17
New cards
Belt sander
Used to shape the edges of woods and plastics as well as smooth the surfaces of metals and woods

18
New cards
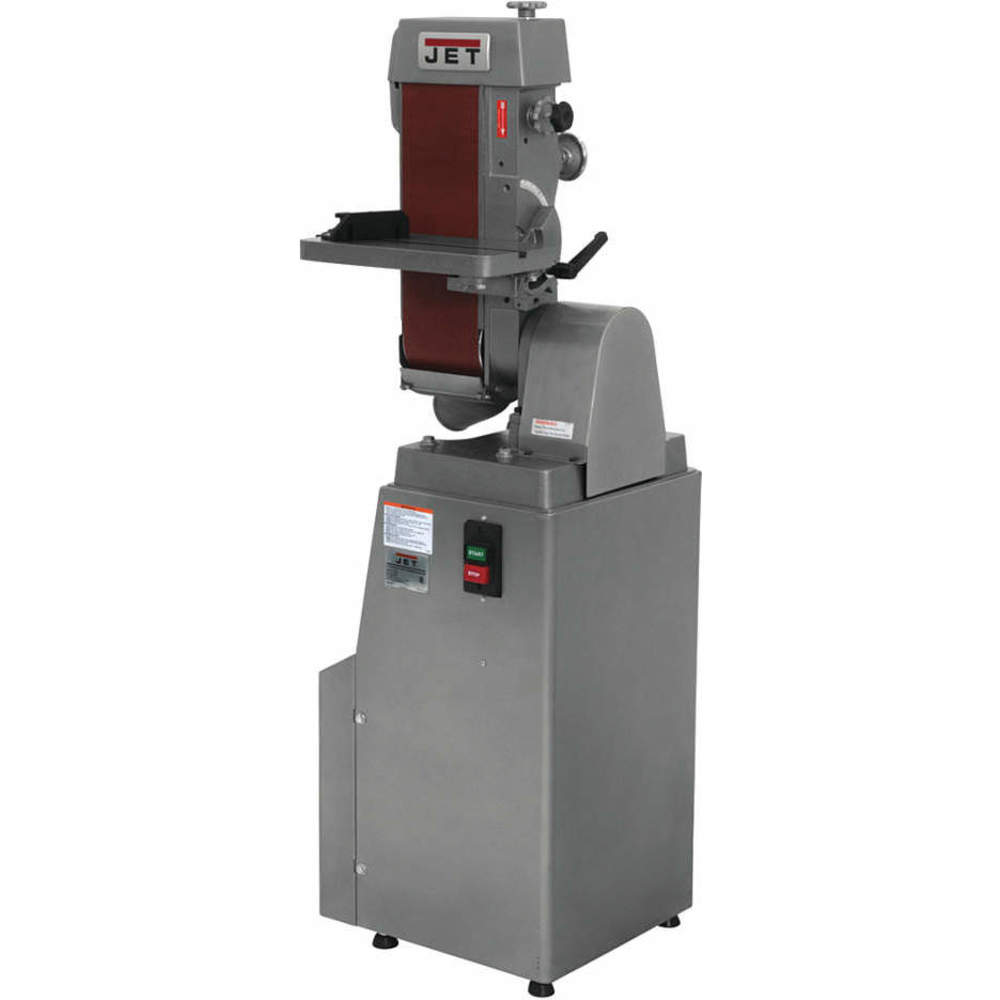
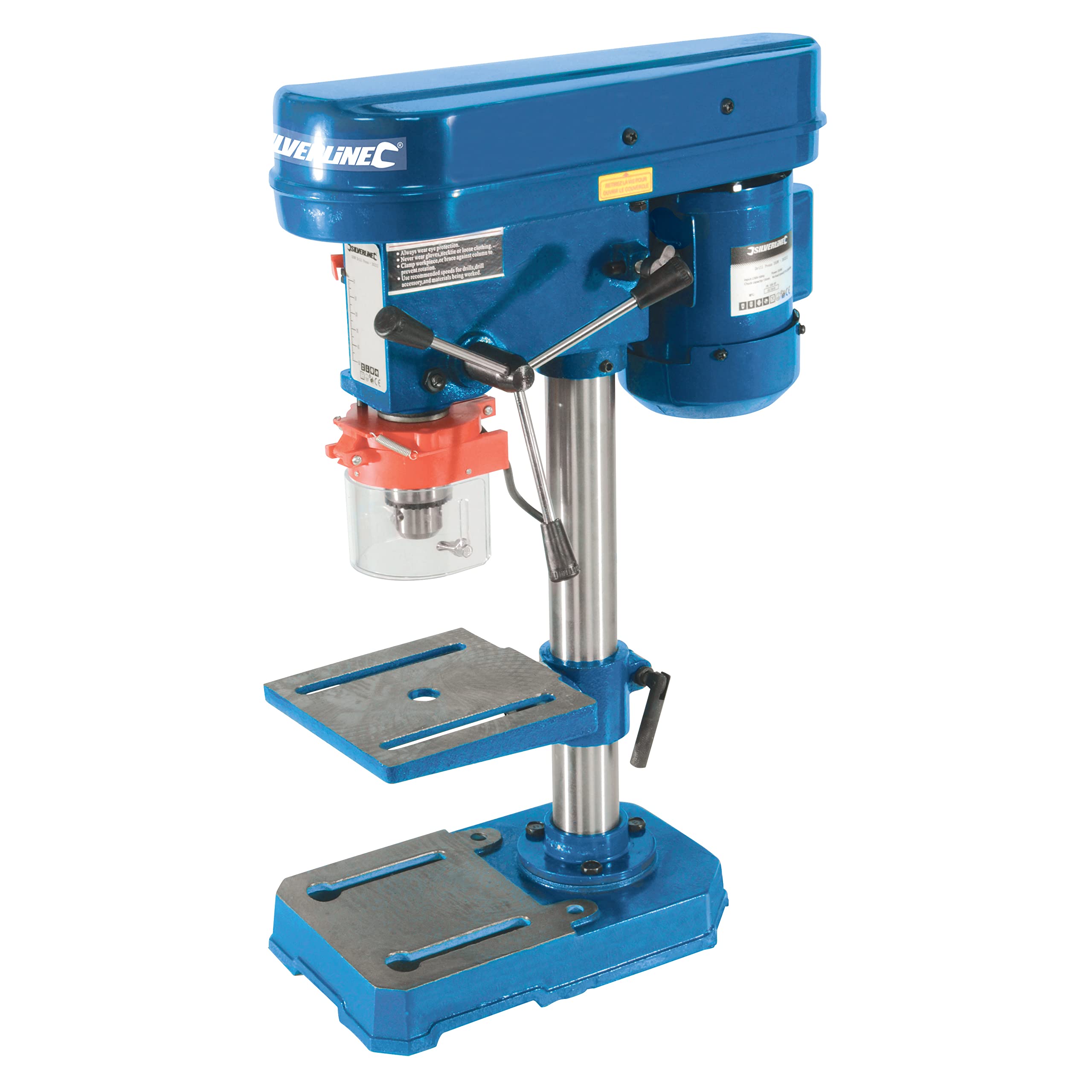
Pillar/bench drill
Drills holes into woods, metals and plastics

19
New cards
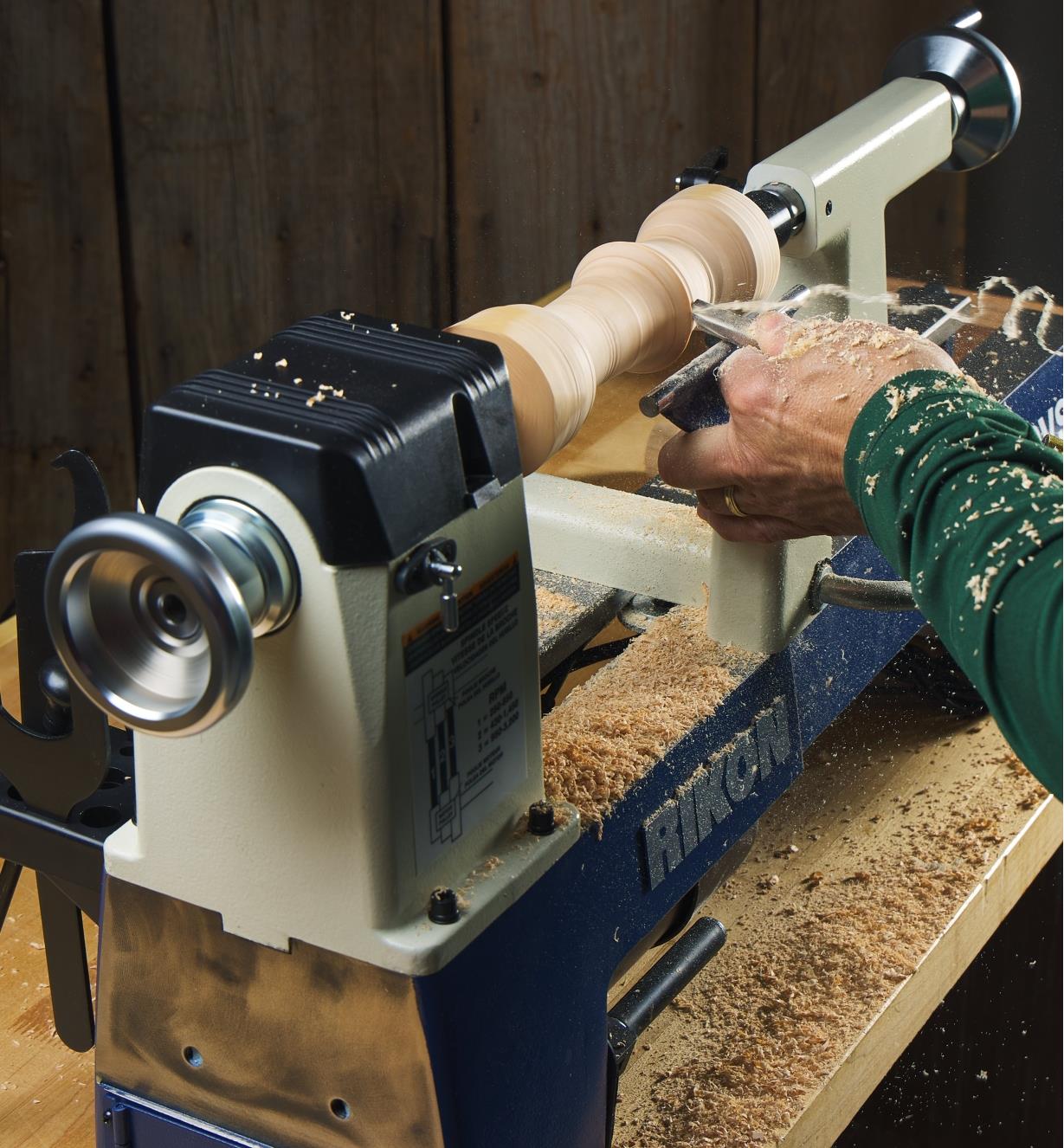
Lathe
Shapes the edges of wood

20
New cards
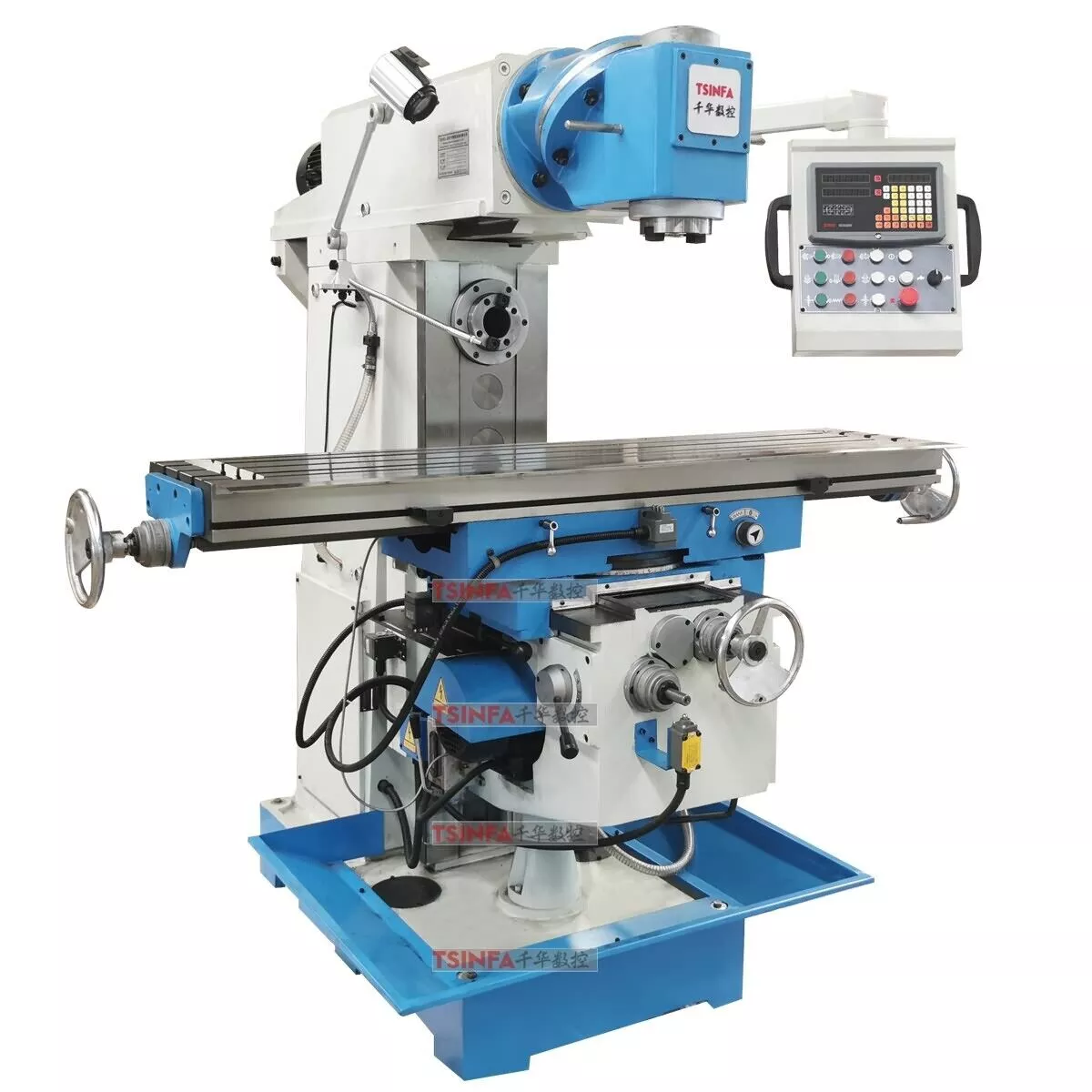
Milling machine
Used for hollowing metals and plastics

21
New cards
Drilling
A method used for making a hole all the way or partially through a material
22
New cards
Elements of a hole
Pilot hole, Clearance hole, Tapping, Countersunk hole, Counterbored hole
23
New cards
Pilot hole
Smaller than the screw being used, so that the thread cuts in and holds
24
New cards
Clearance hole
Larger than the thread and shank of a screw, so that the screw does not grip or ‘bite’ into the sides, allowing the two pieces to pull together
25
New cards
Tapping
Usually used with metals, where a screw-thread is added to the inside of a pilot hole, using a tool called a ‘tap’, so that it accepts a machine screw
26
New cards
Countersunk hole
An indentation at the top of a hole to accept a countersink headed screw, with the screw head being level with the surface, usually with a 90 degree inclusive angle
27
New cards
Counterbored hole
A large diameter recess at the top of a hole to accept a cheese or fillister headed screw, with the screw head being recessed below the surface
28
New cards
Deforming processes
Steam bending, Lamination, Press forming, Vacuum forming, Blow moulding
29
New cards
Steam bending
Strips of hardwood are heater in a steam chamber until the wood is pliable enough to easily bend around a former to create a specific shape
30
New cards
Lamination
Thin sheets (veneers) of hardwoods are layered with strong adhesive and pressed in a former until the adhesive cures
31
New cards
Press forming
Sheet materials are presses between a male and female former, until they cool, to take on a new shape. Some materials need to be heated to become ‘plastic’ (malleable) prior to forming, or in the case of metals they can be annealed
32
New cards
Vacuum forming
Plastic sheets are heated to their elastic state, then a former is pressed into the sheet and the air below is evacuated. The external pressure presses the plastic onto the former
33
New cards
Blow moulding
Tubes of plastic are heated and fed through a mold. The air is blown into the tube, forcing it to expand out and form against the mould.
34
New cards
Addition
The process of shaping materials by combining or joining them, for instance using screws, nails, nuts and bolts, and adhesives. Joining methods can be classified as temporary or permanent, with particular methods being used with different materials
35
New cards
Deforming
The process of subjecting a material to a stress that changes its shape. Typically heat is applied to materials to bring them into the ‘elastic’ zone, where they can be deformed
36
New cards
Reforming
The process of changing the shape of a material, typically by melting and pouring or injecting the molten material into a mould
37
New cards
Resistant material
A material that requires force in order to be worked of shaped
38
New cards
Wastage
The process of cutting away material to leave the desired shape
39
New cards
Reforming processes
Injection moulding, Extrusion, Sand casting, Die casting
40
New cards
Injection moulding
Plastic beads are heated to their plastic state and injected into a mould to form complex shapes
41
New cards
Applications of injection moulding
Toys, consumer goods (mobile phone cases)
42
New cards
Extrusion
The material is heated to its plastic state and pushed through a ‘die’ to create components or parts with a fixed cross-sectional profile
43
New cards
Applications of extrusion
Pipes, tubes, beams and rods
44
New cards
Sand casting
Non-ferrous metal (iron, brass, aluminium) is melted and poured into a mould made of a special sand
45
New cards
Applications of sand casting
Engine blocks, gas and water valves
46
New cards
Die casting
The metal is melted and forced into a hardened tool steel mould (or die)
47
New cards
Applications of die casting
Toys, brackets, engine parts