Tectonic hazards
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Location of volcanos and earthquakes
majority happen along the narrow bands of plate margins
found on both land and sea
earthquakes are found at all types of plate margins
there is anomalies to this due to hot spots
Hazards of a Volcano
Tephra
Nuées Ardennes ( Phyroclastic flows)
Tsunami
Lava flow
Flooding
Acid rain
Lahara
Volcanic gases
Primary effects of a volcano
Tephra
Nées Ardennes
Lava flow
Volcanic gases
Secondary effects of a volcano
Tsunami
Flooding
Acid rain
Lahara
Tephra
The term tephra defines all pieces of all fragments of rock ejected into the air by an erupting volcano. Most tephra falls back onto the slopes of the volcano, enlarging it
Nuées Ardennes (Pyroclastic flows)
A pyroclastic flow is a hot (typically >800 °C, or >1,500 °F ), chaotic mixture of rock fragments, gas, and ash that travels rapidly (tens of meters per second) away from a volcanic vent or collapsing flow front. Pyroclastic flows can be extremely destructive and deadly because of their high temperature and mobility.
Tsunami
Several types of volcanic activity can displace enough water to generate destructive tsunamis, including: Pyroclastic flows (flowing mixtures of rock fragments, gas, and ash) Submarine explosions relatively near the ocean surface. Caldera formation (volcanic collapse)
Lava flow
Lava flows are outpourings of molten rock from a vent onto Earth's surface during an effusive volcanic eruption. Fluid basaltic lava flows may travel great distances from their vent. But more viscous (less fluid) types of lava are not able to travel as far, and form shorter and thicker lava flows
Flooding
Devastating floods caused when volcanoes erupt beneath glaciers and ice caps, creating huge volumes of meltwater. They are common in Iceland. Occurs at: Constructive plate margin volcanoes (cinder cone, fissure eruption) They can also occur when the lava flows and large debris ejected from the eruption can block stream and creek beds causing the water to build up and flow in a new direction.
Acid rain
the term 'acid rain' refers to rainfall containing strong acids. These can originate from both natural sources (especially volcanic emissions) and anthropogenic sources (especially fossil fuel combustion).
Lahara
A lahar is a hot or cold mixture of water and rock fragments that flow quickly down the slopes of a volcano. They move up to 40 miles per hour through valleys and stream channels, extending more than 50 miles from the volcano. Lahars can be extremely destructive and are more deadly than lava flows.
Volcanic gases
Volcanic gases are gases given off by active volcanoes. These include gases trapped in cavities in volcanic rocks, dissolved or dissociated gases in magma and lava, or gases emanating from lava, from volcanic craters or vents. Volcanic gases can also be emitted through groundwater heated by volcanic action.
Why people still live in ears that has volcanic activity:
Economic - farming in that area will be lucrative, tourism, mineral extraction and geothermal energy
Social - The threat may not be great enough to leave and it may not be viable to move people, building will keep them same
Protection against volcanos
Planning evacuation areas and removing the people most at risk from tectonic hazards is vital in reducing vulnerability. Hazard mapping allows local areas to limit access to the danger zones and prevent buildings near to potential hazards from being built. Retrofit buildings.
Monitoring volcanos
Scientists use a wide variety of techniques to monitor volcanoes, including seismographic detection of the earthquakes and tremor that almost always precede eruptions, precise measurements of ground deformation that often accompanies the rise of magma, changes in volcanic gas emissions, and changes in gravity.
Planning against volcanic hazards
Have a planned evacuation route and having access to emergency food and water supply
Predicting volcanos
Volcanos are predictable, meaning that there can be an approximate through thermal imaging of when they are going to erupt
Plate margins include:
Oceanic - continental destructive
Continental - Continental destructive
Oceanic - Oceanic destructive
Oceanic - Oceanic constructive
Continental - continental constructive
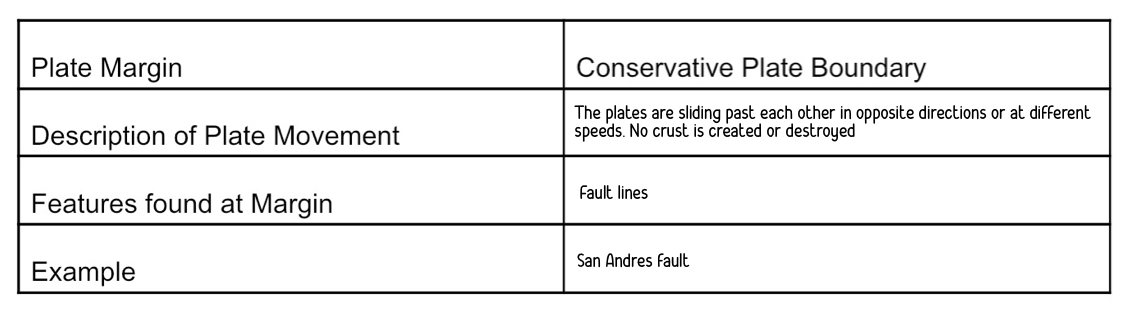
Conservative
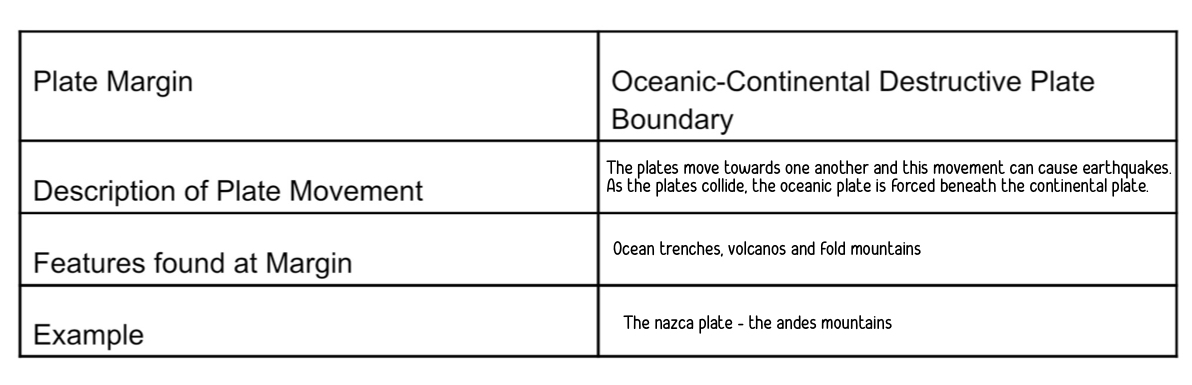
oceanic - continental destructive
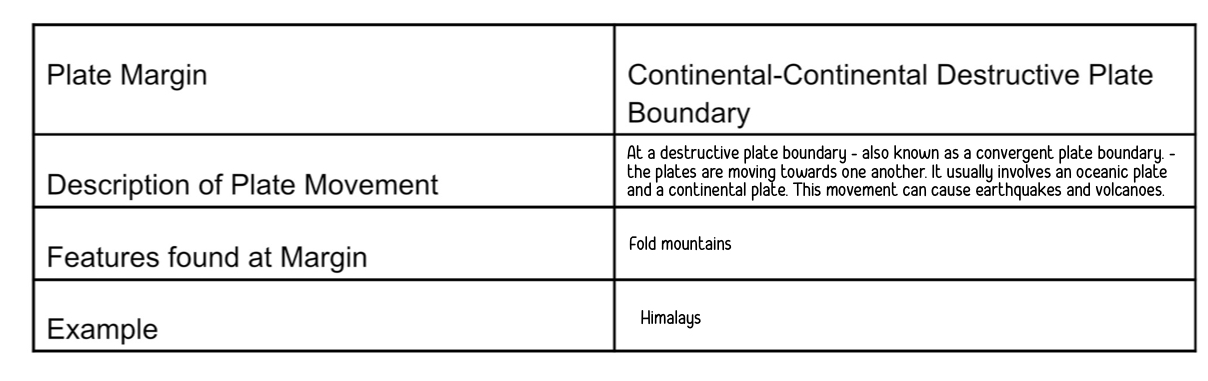
continental - continental destructive
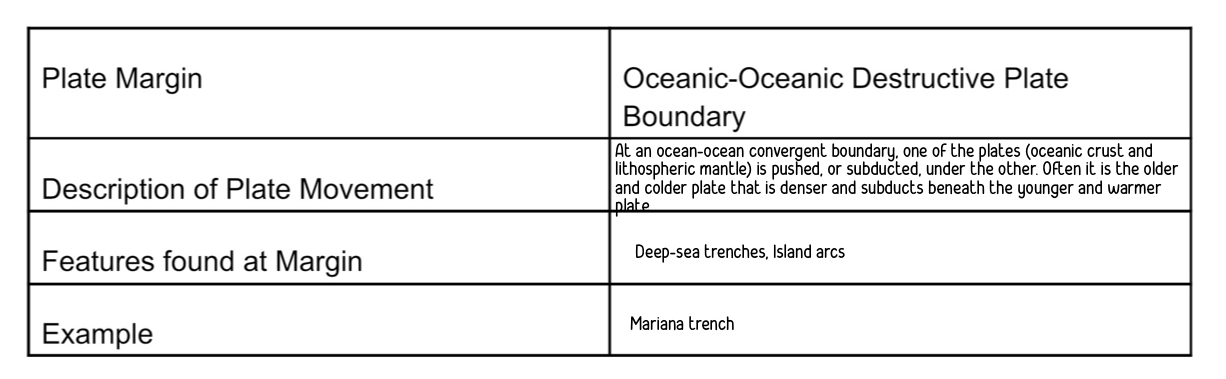
oceanic - oceanic destructive
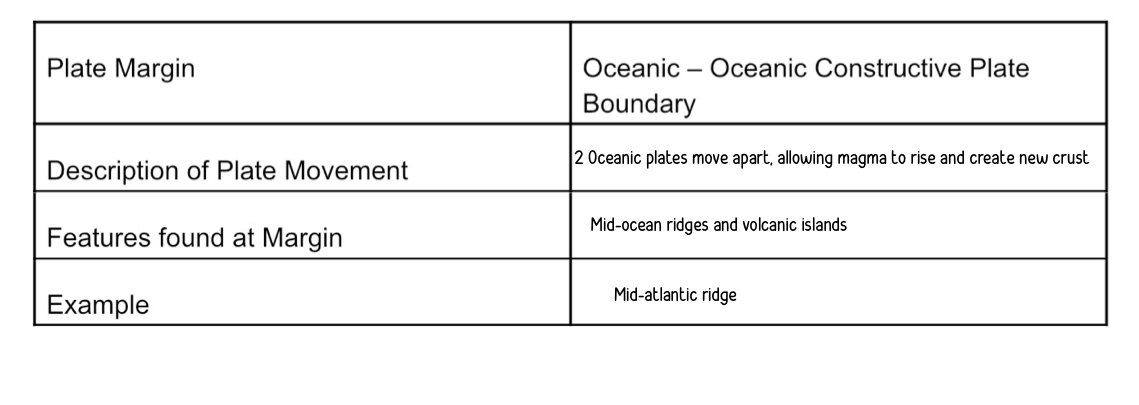
oceanic - oceanic constructive
continental - continental destructive
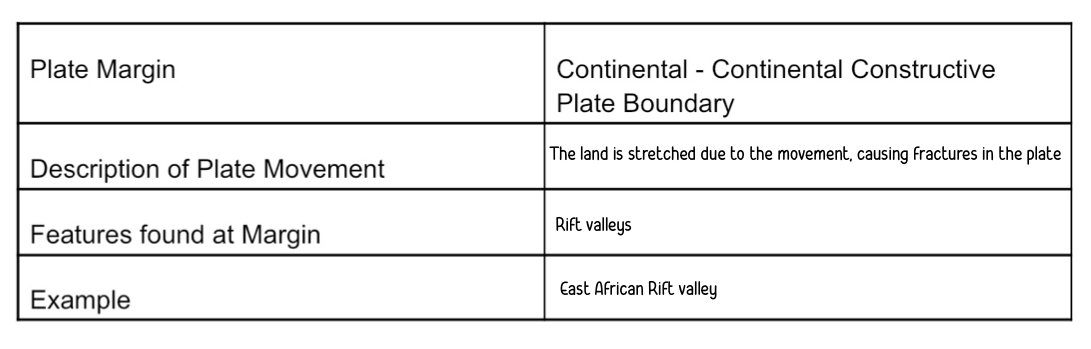
conservative
Hot spots
Plumes of hot magma rising from deep within the mantle, creating areas of intense volcanic activity away from plate boundaries. As the tectonic plate moves over the stationary hotspot, a chain of volcanic islands or seamounts can form, such as the Hawaiian islands.