BSC-111 Lab Practical #2
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Alternation of generations
Plants alternate two life stages. 
Haploid
n; has half of the complete set of chromosomes.
Diploid
2n; has a complete set of chromosomes.
Gametophyte
Produces gametes; in which egg cell production and fertilization take place.
Sporophyte
The asexual and diploid phase which produces spores. Dominant in vascular plants.
Gametes
A reproductive cell. Formed from gametophyte.
Spores
Formed from sporophyte via meiosis.
Mitosis
Cell nucleus splits into two identical daughter cells.
Meiosis
Single cell divides twice to form four haploid cells.
Zygote
A diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes.
Basic characteristics of seedless nonvascular plants
-Lack true leaves, seeds, and flowers
-Instead of roots, it’s hair-like structures.
Ex: Moss
Basic characteristics of seedless vascular plants
-Reproduce through unicellular haploid spores instead of seeds.
-Dominant diploid sporophyte generation.
Ex: Ferns
Why seeds and pollen represent an advantage for seed plants
Allows for plants to reproduce in the absence of water.
Basic characteristics of gymnosperms
-Don’t produce flowers
-Cones that contain spores
-Naked seeds/not enclosed in an ovary.
Basic characteristics of angiosperms
-Has flowers
-Enclosed ovary
-production of fruit
Distinguish between a monocot and eudicot on external features
Parts of a flower

Difference between pollination and fertilization
Pollination is the transferring of pollen from the anthers of stamens versus fertilization is the fusion of male and female gametes.
What is a double fertilization
Two male gametes meet with two female gametes.
Triploid endosperm is unique to…
angiosperms
A seed contains…
-A seed coat
-An embryo
-Endosperm (cotyledons, food)
Ovule becomes a…
Seed
Ovary becomes a…
Fruit
Basic functions of a plant leaf
To change sunlight into energy via photosynthesis
Basic functions of a plant stem
Transports water and other nutrients from the soil and roots all the way up to the leaves and other parts of the plant.
Basic functions of a root
For anchoring and absorbing nutrients
What is vascular tissue
Holds the xylem and phloem/ vascular system.
Xylem
Gives physical support, conveys water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. Is upwards.
Phloem
Downwards transportation with the plant, the sugars and other nutrients go down to the roots.
What ground tissue is
All tissue that isn’t dermal or vascular. Ex: parenchyma, collenchyma, schlerenchyma.
Monocot vs eudicot roots
Difference between primary and secondary growth
Primary growth = Increase in length of the shoot and roots.
Secondary growth = Increase in thickness or girth (hehe)
How to identify the age of a woody plant based on number of xylem rings (secondary growth)
By counting the annual rings within a plant
A plant leaf consists of a - and -
Petiole (counts the leaf to the stem) and blade (leaf body)
Upper epidermis
A single layer of cells containing few or no chloroplasts.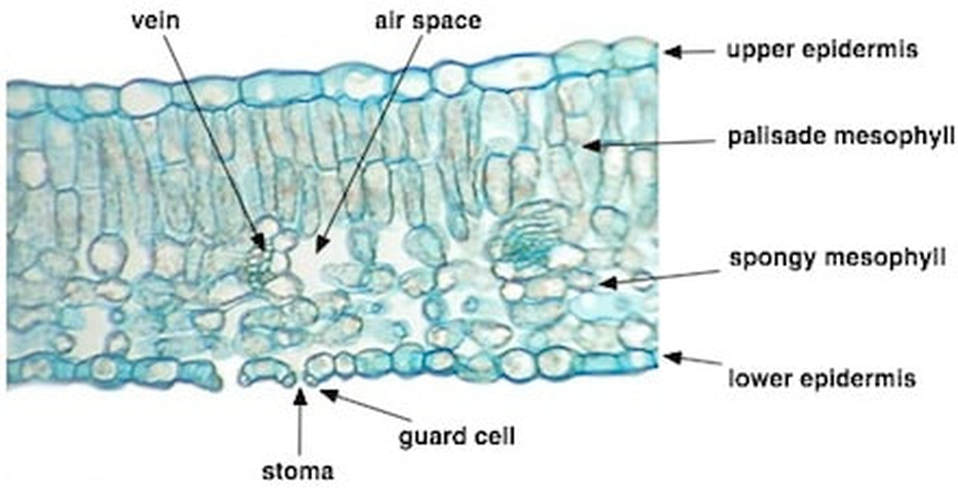
Lower epidermis with stomata
Regulates gas exchange and helps prevent water loss
Palisade mesophyll
Located inside the mesophyll; is where most of photosynthesis occurs in the leaf.
Spongy mesophyll
Allows for the interchange of gases that are needed for photosynthesis.
Basic characteristics of Kingdom Animalia
-Can move/locomotion
-Lack a cell wall
-Heterotrophic
-Reproduction is normally sexual
-Multicellular/eukaryotic
-Sensory and excretory organs
-Body symmetry
What are the three body parts found in all mollusks
Head, muscular foot, visceral hump
Where are the three body parts found on a squid
Where are the beak and pen found
 Beak is found between the tentacles/arms.
Beak is found between the tentacles/arms.
What is the pen and beak made of?
Chitin
What is the purpose of an ink sac?
Defense against predators
What is the purpose of a funnel/siphon?
To expel/flow water for locomotion, feeding, respiration, and reproduction.
Where is the funnel/siphon located on the squid?
Underside of the mantle, between the eyes, below the mantle collar.
What structure does a squid use to breathe?
Gills
How does the term segmented apply to the earthworm?
Ring-like segments called annuli
What does hermaphrodite mean as it applies to the earthworm?
They have both male and female reproductive organs.
General characteristics of the Phylum Arthropoda
-Exoskeleton
-Jointed appendages
-Body is segmented
-Bilaterally symmetrical
-Open circulatory system
What does arthropod mean?
An insect, spider, or crustacean.
A crayfish is a crustacean. A grasshopper is an insect.
What does segmentation mean
The division into separate parts or sections.
The term applies to crayfish and grasshoppers with the sections of their body.
What class is the crayfish apart of?
Crustacea
What and where is the carapace?
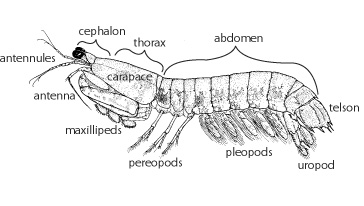 The carapace is on the backside of the crayfish. Another word for protective shell.
The carapace is on the backside of the crayfish. Another word for protective shell.
What is the exoskeleton made of?
Chitin!
The function of uropods
High contractility and breaking of adhesion at the rear. 
How many legs are found on a crayfish
Four pairs of walking legs; ten legs total bc pair of claws.
What structure does a crayfish use to breathe?
Gills; beneath their carapace.
How would you distinguish between a male and female crayfish?
Between the simmerets. Female has a hole, male has L-shaped appendages.
What class is the grasshopper apart of?
Hexapoda
What is the exoskeleton made of?
Chitin
Where is the tympanum? What is it used for?
Just above and behind the hind leg of the grasshopper. It detects vibrations for listening.
How many wings are found on a grasshopper?
Two pairs
How many legs are found on a grasshopper?
Six legs
How does a grasshopper breathe?
Tracheae; openings in the thorax and abdomen called spiracles.
How would you distinguish between a male and female grasshopper?
Its behind; the female has a longer abdomen that ends with a four pointed tip called an ovipositor. Male is shorter and is curved.
The 10% rule as it applies to levels in a food chain
Only 10% of the energy consumed is passed onto the next trophic level.
What is bioremediation and how it can help reduce pollution
Its the use of living organisms such as microbes and bacteria; decomposers, to decontaminate affected areas. It’s beneficial for just eating up or reducing pollution because it removes contaminants.
