Semantics Lecture Notes
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on lecture notes about semantics, word meaning, sense relations, lexical ambiguity, and lexicology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Semantics
Studies the meaning or meaning potential of words, phrases, and sentences.
Lexical meaning
Word meanings that are typically concrete.
Example:
Word: "Snake"
Lexical meaning: A long, legless reptile.
Figurative meaning: A dishonest or sneaky person (not lexical).
Grammatical meaning
Abstract meanings related to grammar, such as tense, plural, and voice.
Word: "cats"
Lexical meaning: the animal "cat"
Grammatical meaning: plural (more than one cat)
Word: "running"
Lexical meaning: the action of running
Grammatical meaning: present participle/verb form used in continuous tense
Sense
All elements contained in our conventional understanding of a concept associated with a word.
dog is “a domesticated carnivorous mammal, which typically has a long snout, an acute sense of smell, non-retractile claws, and a barking, howling, or whining voice” Oxford English Dictionary Online, s
Semantic Core
a set of keywords that describe the main topic of a website or page.
Structuralism
the idea that we understand things by looking at the structure behind them
Words get meaning not just by themselves, but by how they relate to other words in the language
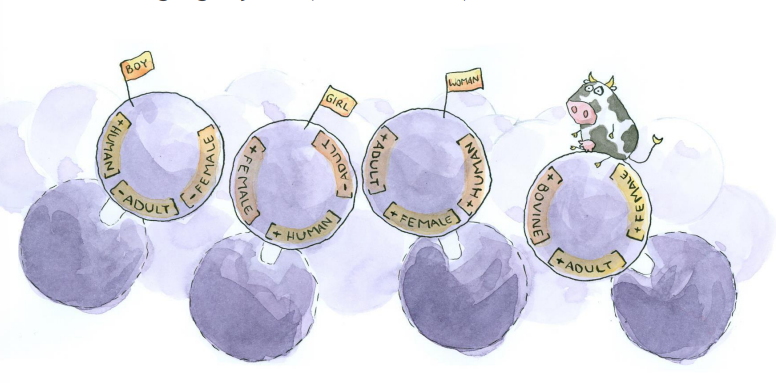
Intension
Equals the 'sense' of a word; contains all semantic features that make up a dictionary definition; a word's abstract/systematic meaning.
Cow = [+bovine] [+ adult] [+ female]
Denotation
Core meaning, intensional + extensional meaning, sense (what it means) + reference(what it points to).. The dictionary defenition.
link between a word and the world
Extension
All the things a word can point to in real life—some words refer to just a few items, others to many.
e.g Word: “Fruit”
Extension: All individual fruits in the world: apples, bananas, cherries, mangoes, etc.
Reference
The use of a word in its conventional sense to refer to an object in the real world or a possible world of fiction.
Referent
Entity (or entities) referred to (or “picked out”) by an expression in a particular context
Ranging Reference
Variable(indexcal) reference
identical reference and yet different sense
no referent
Variable (indexical) reference
Referent changes depending on context.
example: the pope; here; tomorrow
Identical reference and yet different sense (Reference)
different forms are used to pick out one and the same real-world entity
example: Morning Star and Evening Star (planet “Venus”
No referent
Some expressions that have no referent in the real world, but have sense and denotation.
example: dragon (sense and denotation)
Connotation
Peripheral/additional meanings (i.e., contextual, emotional, evaluative, stylistic meanings. The deeper meaning- what we associate with the word. e.g The rose - love, beauty, or passion.
Types of Connotation: Stylistic
Stylistic connotations
neutral style → default
“low” style
high” style
Stylistic connotations
expressive meaning a word adds because of the tone it brings, not just its basic meaning.
Example:
"Childlike" vs "Childish"
Both mean “like a child” (similar lexical meaning).
But:
Childlike = positive (innocent, pure) → positive stylistic connotation
Childish = negative (immature) → negative stylistic connotation
“low” style(Types of Connotation: Stylistic)
colloquial, e.g., buddy, pal “friend”
slang, e.g., trippin’ “losing control”
vulgar, e.g., c*nt
high” style(Types of Connotation: Stylistic)
formal, e.g., capacity, (to) contemplate, (to) elicit
Literary or poetic, e.g., (to) breathe “live”
archaic, e.g., spouse “husband or wife”
foreign, e.g., zeitgeist, (to) encore “repeat”
Expressive Connotations + Subtypes
Express a speaker’s emotional attitudes towards a concept.
derogatory, e.g., chick “woman”, benchwarmer
taboo, e.g., c*nt, arse, f*ck, sh*t
euphemistic, e.g., restroom “toilet,” gosh “god”
jocular, e.g., bugrake “comb”, (to) go belly-up “die”
appreciative, e.g., lady, elegant
Contextualization
Word meanings that alter somewhat in context.
hot day (literal day that is elevated in temperature)
hot iron (brand name for type of weightlifting activity)
hot chocolate (drink)
disambiguation
Single: “unmarried” or “one only” Single book cannot mean “unmarried book”
Synonymy
Two different phonological words with the same or very similar meanings.
Antonyms types
Complementary antonymy
Gradable antonymy
Converseness
Directional opposition
Complementary antonymy
Either/or relationship between two terms of a pair of semantic opposites.
Examples
Dead and alive
Live and die
Asleep and awake
male and female
Gradable antonymy
show opposite meanings but can vary in degree
Opposite of one word not necessarily synonymous with the other → not large is not necessarily smalHot and cold → hot–warm –tepid–cool –cold, etc.(lukewarm, scalding hot, freezing cold, etc.)

Converseness ( Antonymy)
Senses that represent different ways of looking at the same action or relationship
Parent and child: parent can’t be without a child
Teacher and pupil
Buy and sell
Directional Antonymy
Pairs of senses express a change of direction, especially motion into different directions
examples
Come and go
Fall and rise
Push and pull
Hyponymy
Word relationship of super-/subordinated meanings
“animal” is a hypernym of “dog.” - hyponym
Co-hyponyms
hyponyms of same superordinate sense
Meronymy
Word relationship of part/whole meanings.
Example: “wheel” - meronym of “car holonym.
e.g. nose is a part of face → obligatory
collar is a part of shirt → not obligatory, but common
cellar is a part of a house → optional
Exhaustive Options
all choices are included — nothing is missing.
What’s your favorite fruit?
And you list:
Apple
Banana
Orange
Something else
Homonymy
Two words that overlap in form, but differ in meaning.
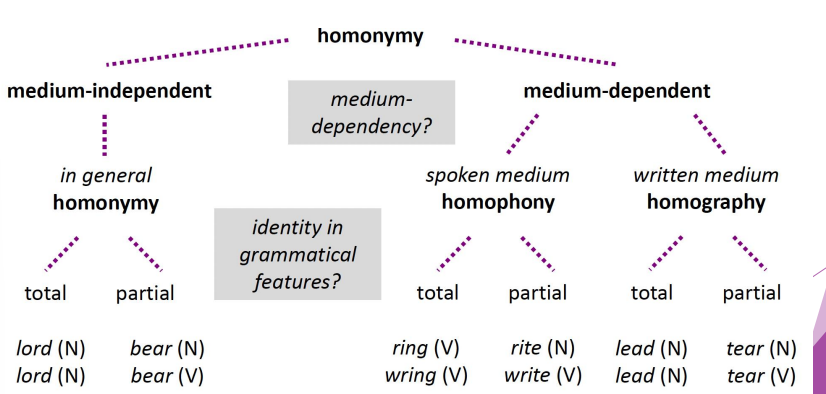
Polysemy
Multiple senses of the same phonological word that is judged to be etymologically related.
a sole (“a kind of fish”)
a sole (“part of a shoe”)
Synchronic perspective
Studying something at one point in time, ignoring its history or changes over time.
Diachronic perspective
Studying something over time, looking at how it changes and develops through history.
i.e., traceable, although shared origin dates back considerably (polysemy)
Lexicology
Mental Lexicon and Representative Vocabularies.
Personal vocabulary
active
pasive
vocabulary of a language
size hard to assess
Active Vocabulary
Personal vocabulary that is active.
Passive Vocabulary
Personal vocabulary that is passive.
semantic change-denotation (Gradual Lexical Change)
semantic widening, e.g. barn (barley house > general farm storage)
semantic narrowing, e.g. starve (to die > to die from lack of nourishment)
semantic change–connotation (Gradual Lexical Change)
pejoration (worsening of connotation), e.g. lewd (orig., meant of the people)
amelioration (improving of connotation), e.g. knight (orig., boy)
Folk Etymology
Coming to wrong conclusions about origins and meanings of words.