Genetic quiz 4
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is the relationship between the degree of crossing over and the distance between two genes?
A) It is direct: as the distance increases, the frequency of recombination increases.
B) It is direct: as the distance decreases, the frequency of recombination increases.
C) It is indirect: as the distance increases, the frequency of recombination doubles.
D) There is no correlation.
E) It is indirect: as the distance decreases, the frequency of recombination doubles.
A
If complete linkage occurs, we expect ________.
D) to see only parental phenotypes in the F2 of the appropriate test cross
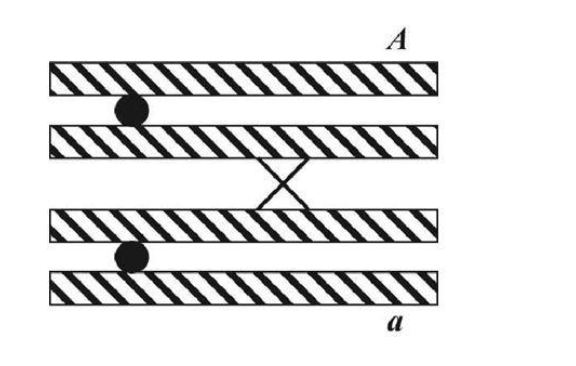
Below is a diagram during crossing over in prophase I of meiosis. Based on the outcome of this cross over event will the A and a alleles of this gene segregate during meiosis I like normal? Why or why not?
Yes because homologs still separate so A and a go into different cells
True-breeding parents (AAbb and aaBB) are crossed. A test cross of the F1 produces the progeny ratios below. How far apart are the A and B genes?
Progeny ratios: 0.11 AB, 0.13 ab, 0.38 Ab, 0.38 aB
Recombinants are AB and ab
0.11+0.13= 24cM
The cross GE/ge × ge/ge produces the following progeny:
GE/ge 404
ge/ge 396
gE/ge 97
Ge/ge 103
a) Why would you suspect that these genes are linked?
b) Which of these progeny are recombinant?
c) What is that map distance (in cM) between locus G and E
parental -> recombinants -> not 1:1:1:1 linked.
gE/ge and Ge/ge.
97+103/1000= 20cM.
Assume that a cross is made between AaBb and aabb plants and that the offspring occur in the following numbers: 106 AaBb, 48 Aabb, 52 aaBb, 94 aabb. Why would you suspect that these genes are linked? Calculate the map distance in cM between gene a and gene b.
Not 1:1:1:1 genes are linked.
48+52/300 = 33 cM
In the snail Cepaea nemoralis, an autosomal allele causing a banded shell (b) is recessive to the allele for an unbanded shell (B). Genes at a different locus determine the background color of the shell; here, yellow (y) is recessive to brown (Y). A banded, yellow snail is crossed with a homozygous brown, unbanded snail. The F1 are then crossed with banded, yellow snails (a testcross).
a. What will the results of the testcross be if the loci that control banding and color are linked with no
crossing over? Write the progeny phenotypes and expected proportions.
b. What will the results of the testcross be if the loci assort independently? Write the progeny
phenotypes and expected proportions
c. What will the results of the testcross be if the loci are linked and 20 m.u. apart? Write the progeny phenotypes and expected proportions
1:1 unbanded brown and banded yellow
1:1:1:1 unbanded brown/yellow and banded brown/yellow
40% unbanded brown/banded yellow
10% unbanded yellow/ banded brown
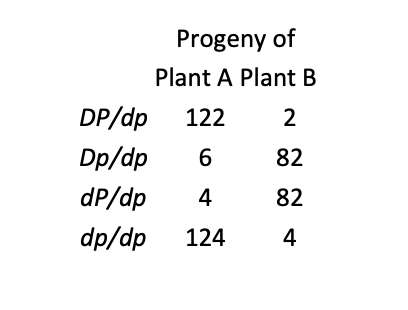
In tomatoes, tall (D) is dominant over dwarf (d) and smooth fruit (P) is dominant over
pubescent fruit (p), which is covered with fine hairs. A farmer has two tall and smooth tomato plants, which we will call plant A and plant B. In two separate crosses, the farmer crosses plants A and B with the same dwarf and pubescent plant and obtains the following numbers of
progeny:
a. What are the genotypes of plant A and plant B?
b. Are the loci that determine the height of the plant and pubescence linked
c. What is the percent recombination between genes P and D? Do a separate calculation for
each cross
d. Explain why different proportions of progeny are produced when plant A and plant B are rossed with the same dwarf pubescent plant.
Plant a: DP/dp Plant b: Dp/dP
Yes
both 4%
One plant has alleles in cis arrangement, the other in trans

Below is a map of three X-linked genes in Drosophila:
List all possible gamete genotypes and their expected frequencies from a female of genotype
a + c / + b + .
a + c = 36%
+ b + = 36%
a b + = 4%
+ + c = 4%
a + + = 9%
+ b c = 9%
a b c = 1%
+ + + = 1%
Genes A and B are located 10 cM from each other on a chromosome. Gene C is located 25 cM from gene A and 15 cM from gene B. Assuming that I = 0, what is the probability that the trihybrid ABC/abc will produce an AbC gamete?
0.75%

The recessive alleles k (kidney-shaped eyes), c (cardinal-colored eyes), and e (ebony bodycolor) identify three genes on the same chromosome in Drosophila. Females with kidney-shaped, cardinal-colored eyes were mated with ebony males. The F1 were all wild-type. When F1 females were testcrossed with ebony males with kidney-shaped, cardinal-colored eyes, the following progeny phenotypes were obtained:
a) Determine the order of genes and the map distances between them.
b) How much interference in double-recombination is there?
k-c-e
k-e= 7cM
c-e= 15cM
k-c= 22cM
60%
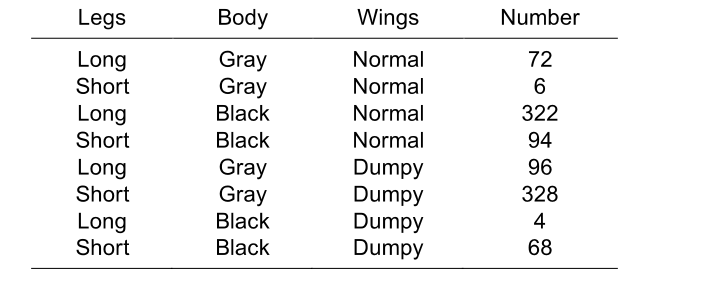
Dumpy wings (d), short legs (s), and black body (b) are linked autosomal recessive traits in Drosophila. Wild-type flies have normal wings, long legs and gray bodies. A cross is done between a phenotypically wild-type female and a short, black dumpy male, yielding a total of 1000 progeny (a prolific mother!) with the following phenotypes and numbers
a) What is the genotype of the father in this cross?
b) List the genotypes of the mother's gametes that produced each class of offspring.
c) What was the genotype of the mother in this cross?
d) Determine the relative order of the d, s, b loci on the chromsome.
e) What is the map distance between the d and s loci? Between d and b? Between s and b?
f) What is the value of the coefficient of coincidence (interference) in this cross?
g) If the mother in this cross had been mated to a male having the same genotype with respect to these three traits, what fraction of their progeny would have black bodies?
1. sbd/sbd
2. ———
3. sbd/+++
4. s - d - b
5. d-s= 10cM
d-b= 16cM
s-d= 6cM
6. 0.29
7.75%