IBDP BIO - AHL D3.3 Homeostasis
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
excretion
process of metabolic waste removal from an organism
performed by the excretory system (composed of kidneys, lung, skin, large intestine, liver)
mammals excrete nitrogen waste in the form of urea
describe the composition of urine
water + urea
osmoregulation
the process of regulating osmotic regulation
water is constantly being gained or loss and needs to be regulated in the body
osmotic concentration
concentration of solute particles per unit volume (measurement unit: osmoles per litre)
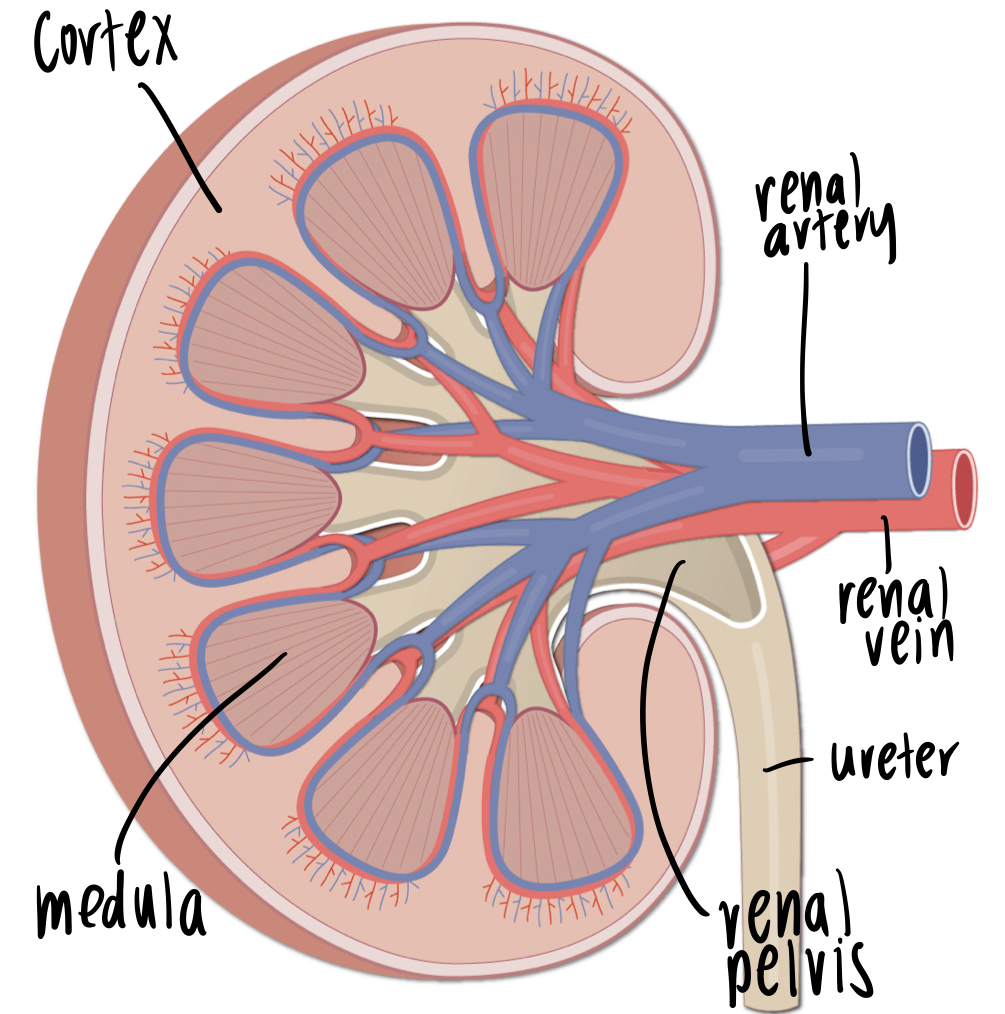
describe the process of excretion in the kidneys
blood enters via renal artery
blood is filtered (removal of metabolic waste) and exits via renal vein
urine exits renal pelvis via ureter towards bladder
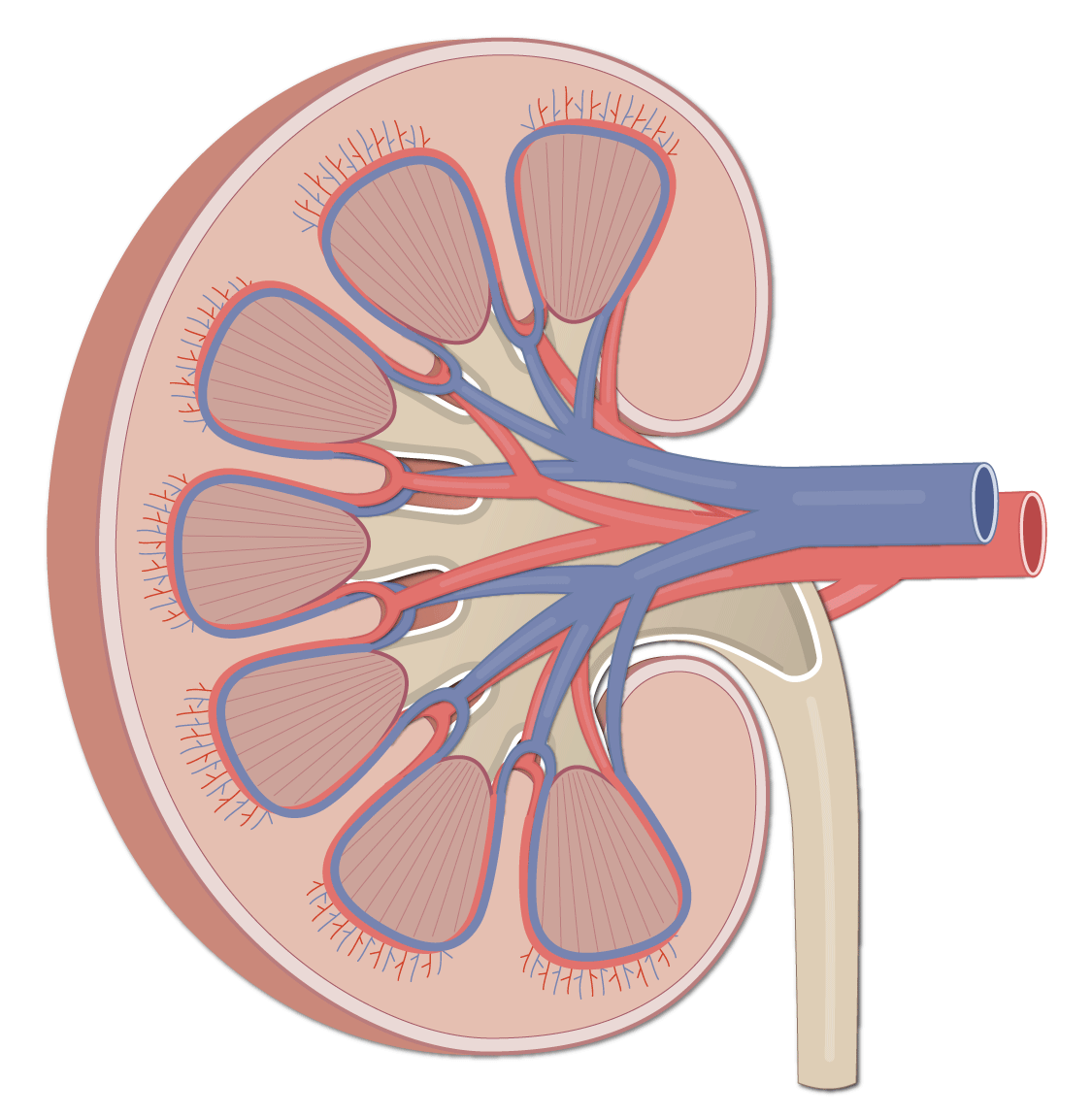
state the following structures of this kidney
cortex, medulla, renal artery, renal vein, renal pelvis, ureter
nephron
specialised functional units that perform filtration, excretion, osmoregulation
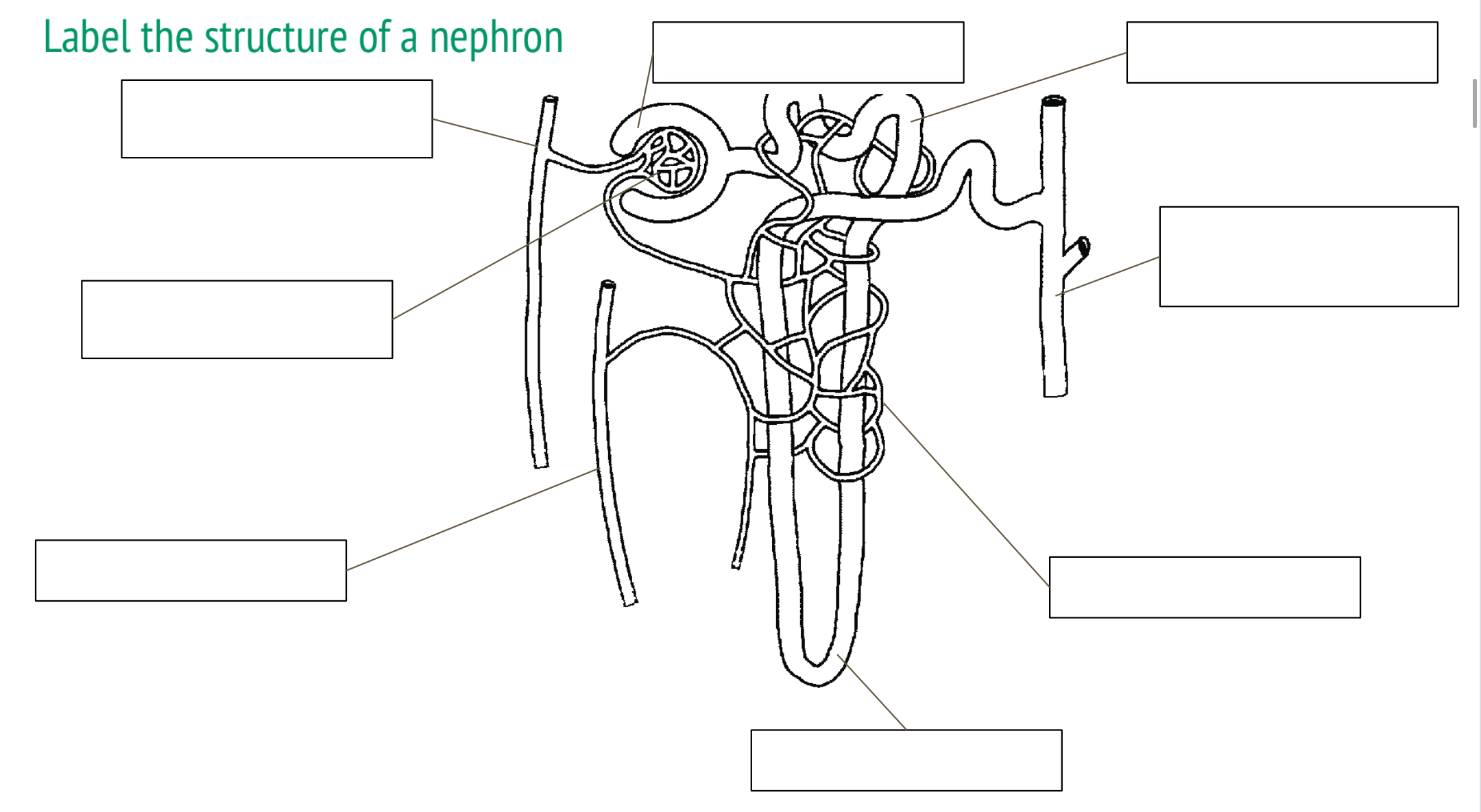
label the structure of a nephron
bowman’s capsule, proximal convolute tubule (PCT), collecting duct, vasa recta, loop of henle, renal vein, glomerulus
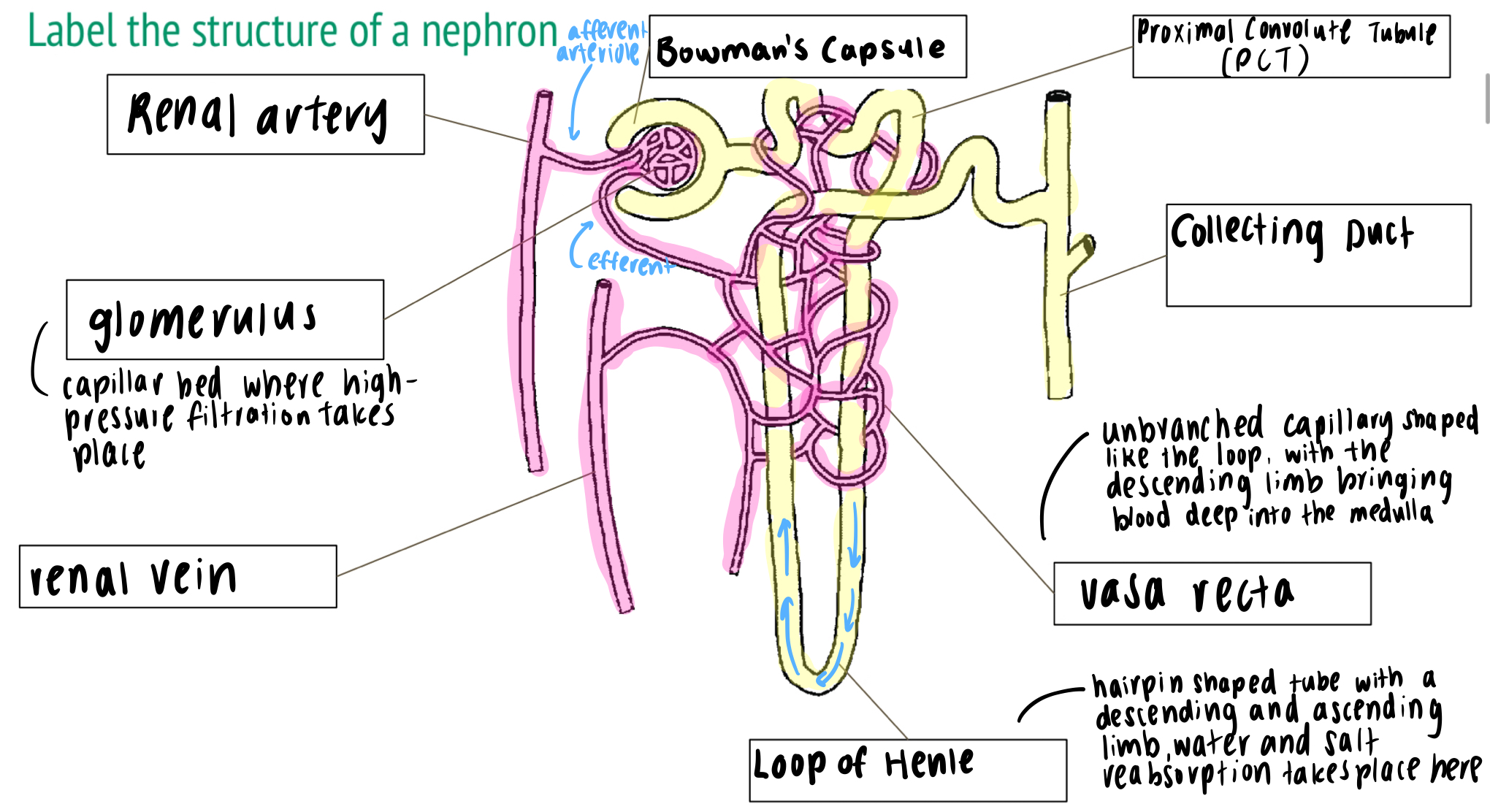
describe the functions of the nephron
ultrafiltration (filters out good useful materials, e.g. minerals and vitamin)
selective reabsorption (reuptake of useful materials)
osmoregulation (balance solute concentration)
describe the movement of blood in the bowman’s capsule
filtration of blood occurs under high pressures in the glomerulus (capillary network)
blood enters via afferent arterioles and exits via efferent arterioles
bowman’s capsule collects the filtrate (solutes filtered out from blood plasma)
distinguish between an afferent and an efferent arteriole.
afferent arteriole has a large and wide lumen, facilitating entry of blood, and efferent arterioles has a narrow and small lumen, creates high hydrostatic pressure within the glomerulus
difference in diameter creates high pressure for ultrafiltration
podocytes
cells of the epithelial lining (lining of a surface) of bowman’s capsules
wraps around capillaries and form filtration slits
high pressure within capillaries (porous) - size selective
prevents red and white blood cells and other large proteins from entering filtrate
allows solutes such as urea, toxins, amino acids, salts, glucose and water into filtrate
epithelium
outer lining of a surface or inner lining of a cavity
endothelium
inner lining of blood vessels
ultrafiltration
blood enters glomerulus via the afferent arteriole and exits via the efferent arteriole
the difference in diameter creates high pressure within glomerulus - ultrafiltration of solutes from blood into filtrate
capillaries are fenestrated
podocytes wrap around capillaries and form filtration slits to prevent blood cells from entering filtrate
filtrate collected in bowman’s capsule and continues to proximal convoluted tubule
reabsorption of selective solutes
indirect active transport, and requires membrane proteins in the proximal convoluted tubule wall
sodium potassium pumps actively transport Na+ out of the PCT into blood, helps maintain low concentration of Na+ in PCT cell
sodium diffuses passively from filtrate into PCT cell through the cotransporter proteins, also transports glucose and amino acids from filtrate
passive diffusion of glucose and amino acids from PCT cell back into blood
water moves passively via osmosis
adaptations of the PCT structure
contains many mitochondria to power active transport, PCT wall is only one cell thick to decrease diffusion distance from filtrate to blood, PCT cells are connected by tight junctions to prevent leaking of larger materials, tight junctions adhere with cells and decreases the chances of solutes leaking into the blood stream, microvilli to increase surface area to maximise diffusion and reabsorption
effects of filtrate during osmoregulation
filtrate from the PCT travels down descending limb of loop of henle then back up ascending limb, active transport of sodium ions out of filtrate in ascending limb, active transport of sodium ions out of filtrate in ascending limb into fluid filled medulla region, creates high osmotic concentrations in medulla, filtrates continues to collecting duct
collection of urine during osmoregulation
final reabsorption of water from filtrate in collecting ducts, water passively exits filtrate into medulla through aquaporin channels, high Na+ concentration in medulla maintained by ascending limb, concentrated filtrate collects in renal pelvis and exits kidney via ureter into bladder
osmoreceptors
located in the hypothalamus, detects changes in solute concentration in blood
functions of the osmoreceptors
dehydration or high sodium levels result in high solute concentration in blood detected by osmoreceptors to stimulate release of antidiuretic hormone from pituitary gland, increases the number of aquaporins present in collecting duct membrane, higher water reabsorption from filtrate
increase in ADH levels
vesicles fuse with collecting duct cell membrane, aquaporins insert into cell membrane, water reabsorbed from filtrate
decrease in ADH levels
cell membrane invaginates, aquaporins stored back into vesicles