PSYCH 101 - Modules 1-9 Terms (Exam 1)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Correlation
when one variable tends to coincide with the other
extent of correlation lets us know how well one can potentially predict the other variable.
Behaviorism
emphasizes study of observable behavior as people are “conditioned” rather than studying the mind through introspection.
Freudian Psych
developed by Sigmund Freud — studies how unconscious mind and childhood experience affect our behavior.
Humanistic Psych
explores human growth potential
our needs
how our environments impact us
Random Sampling
a technique that ensures every person in a population of interest have equal chance to be selected for a study.
Confounding variable
a variable that potentially skews the results on an experiment
influencing both the independent and dependent variables.
Double-blind procedure
a research design where neither participants nor experimenters know who is receiving the treatment or placebo, reducing bias in results.
Standard deviation
number that illustrates how much scores differ from the mean (average) in a data set.
Range
number that represents how dispersed the scores are.
Statistically Significant
term concluding that the difference found in a sample isn’t by chance and can be applied to general population.
Not statistically significant
term concluding that the difference found in a sample IS by chance — can’t be applied to general population.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
the brain + the spinal cord = the body’s decision maker
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
gathers information from CNS and then transmitting it to other body parts.
Agonist
substance that promotes the increased production and release of neurotransmitters.
also act as natural neurotransmitter (mimicking) — like how opioid drugs give you a temporary “high”.
Antagonist
substance that blocks the production and release of neurotransmitters (decreasing neurotransmitter action).
Sympathetic Nervous System
arouses energy
ex: accelerates heartbeat when you have an important interview, initiates sweating to cool you down.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
calms the aroused energy
ex: decreasing heartbeat, lowering blood sugar
Sensory Neurons
carry messages and sensory receptors to the CNS (to be processed).
Motor Neurons
promote movement
carry directions from CNS outward to glands & muscles.
Interneurons
processes information between sensory input and motor output.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
records & reads out electrical waves in our brain’s neurons.
measured on the surface (through the scalp, so indirect).
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
measures magnetic fields (+ their strength) from brain’s electrical activity.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan
utilizes radioactive form of glucose to display brain activity
records at the surface in great detail and timing.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
uses magnetic fields & radio waves to show brain structure & its tissue.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
comparing previous + sequential MRI scans to reveal blood flow, brain function, & brain structure.
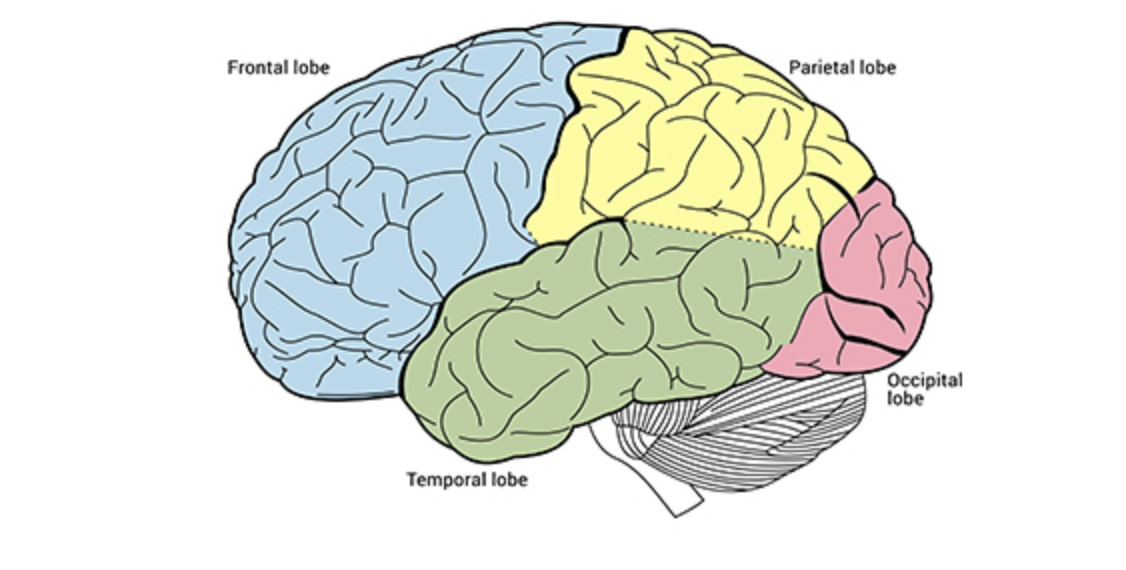
Frontal Lobe
The hugest lobe, in the very front
involved in planning, critical thinking, decision-making
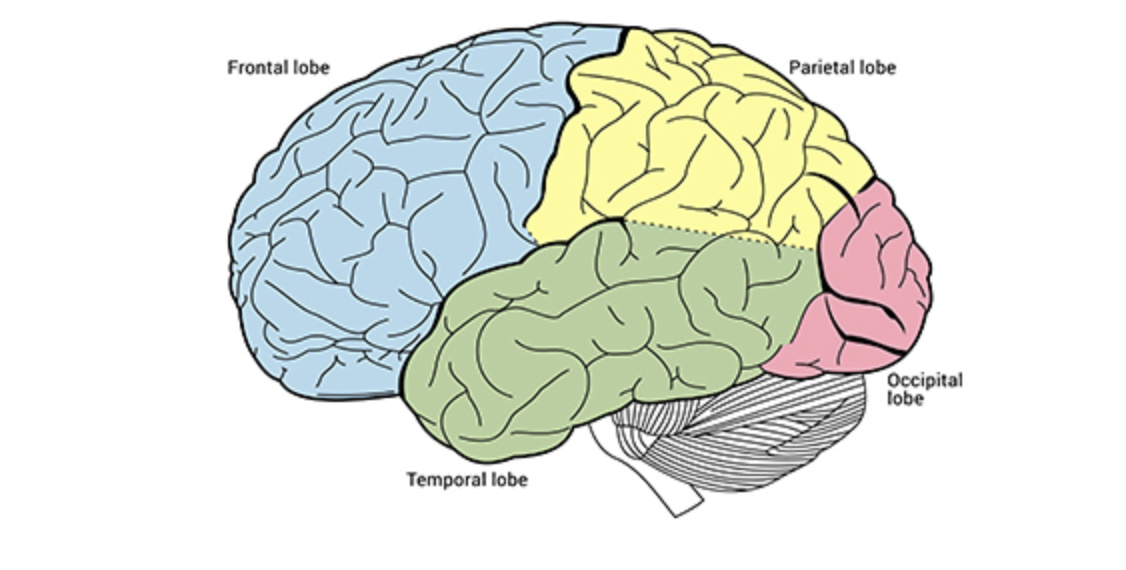
Parietal Lobe
processes sensory information (touch, temp, pain)
top middle
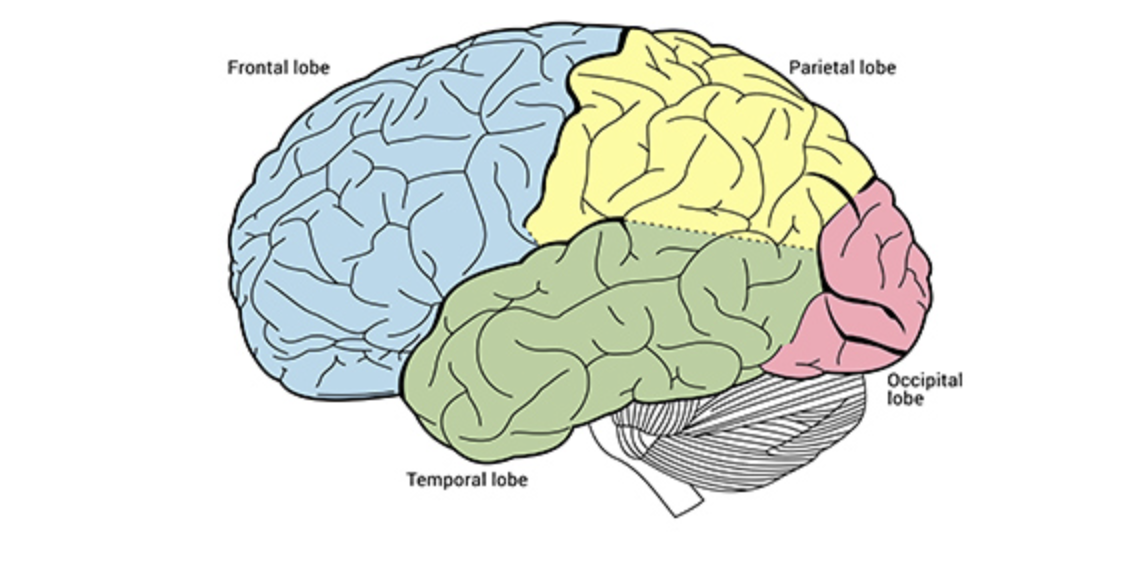
Temporal Lobe
functions also in processing sensory information like hearing, memory, and language)
bottom middle
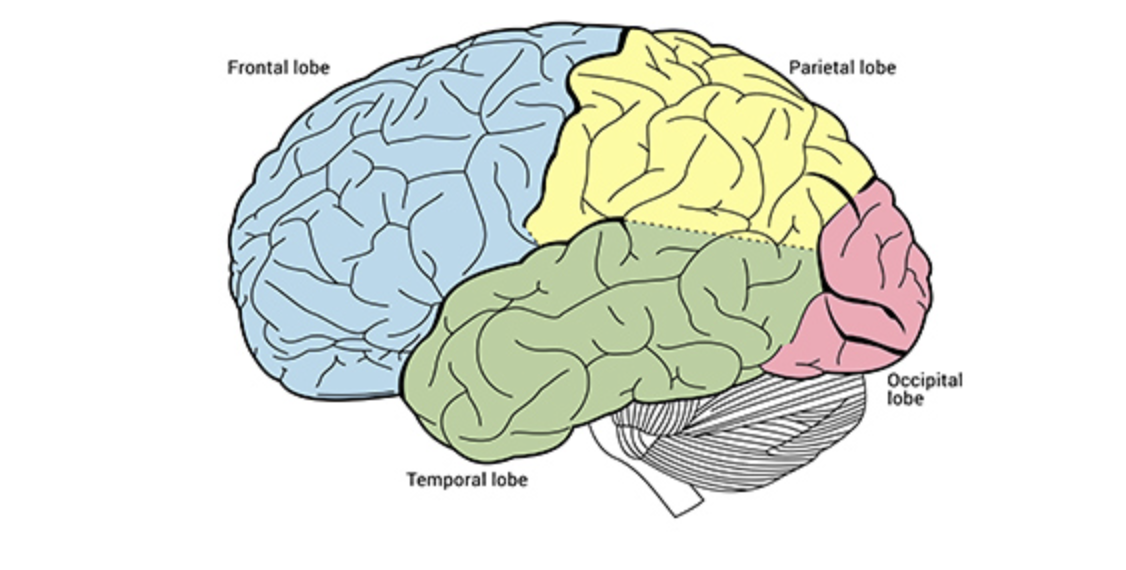
Occipital Lobe
functions in vision
in the very back of brain
Stage 1 Sleep
“beginning of sleep”
brain activity declines (sometimes accompanied by dream-like hypnogogic sensation)
Stage 2 Sleep
time of memory organization (day memories being moved to long-term cortex) and bodily slow down (heart rate, muscles, breathing)
Stage 3 & 4 Sleep
deep slowing (heart rate, breathing, brain activity) + memory traces replaced with long-term/more important memories
Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep
time of rapid eye movement
extremely relaxed postrual muscles (which maintain balance and posture) = going immobile
associated with positive improvements (mood, brain development)
long-term dreams connected to old ones & general knowledge
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
tiny part of hypothalamus
regulates circadian rhythm (daily wake/sleep schedule) by controlling other brain parts
ex: the pineal gland which secretes melatonin to signal “it’s time to sleep”
Thalamus
egg-shaped sensory information router
takes info from all senses except smell & leads this info to brain parts that deal with senses.
Amygdala
almond-shaped
enables aggression and fear in individuals and animals
Hypothalamus
below thalamus
governs bodily maintenance (hunger, thirst, body temp)
Motor Cortex
Somatosensory Cortex
Hippocampus
processes explicit memory
damage to it can prevent one from making new memories
Endogenous Attention
Voluntary, goal-driven focus of attention.
Exogenous Attention
Involuntary shift of attention triggered by external stimuli
Inattentional blindness
not seeing something unusual, but obvious, because your mind was somewhere else.
Specialization of left brain hemipshere
left half of brain
processes language + regulates emotion
guides motor activity of right side of body
Specialization of right brain hemipshere
right half of brain
controls left side of body (movement, sensation, creativity, music ability)