creatinine, Uric Acid, Urea, and ammonia, non protein nitrogen
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
nonprotein nitrogenous (NPN) compounds
Nitrogenous compounds
Not protein in nature
Derived from:
Dietary protein
Nucleic acids
Muscle mass
Hepatic deamination
Are processed in the liver
Eliminated by the kidney
Measure
Renal function
Hepatic Function
components of non-protein nitrogen
Urea Nitrogen 45%
Amino Acid 20
Uric Acid 20
Creatinine 5
Creatine 1-2
Ammonia 0.2
creatine/creatinine biochemistry
Synthesized mainly in the liver
From arginine and glycine
Transported to muscle
Converted to phosphocreatine,
a high energy source
Spontaneously converts to creatinine
Is then transported by plasma
Excreted by kidney
Excreted at a constant rate
Proportional to muscle mass
Removed from the plasma almost entirely by GFR
Excellent indicator of GFR
structure of creatinine
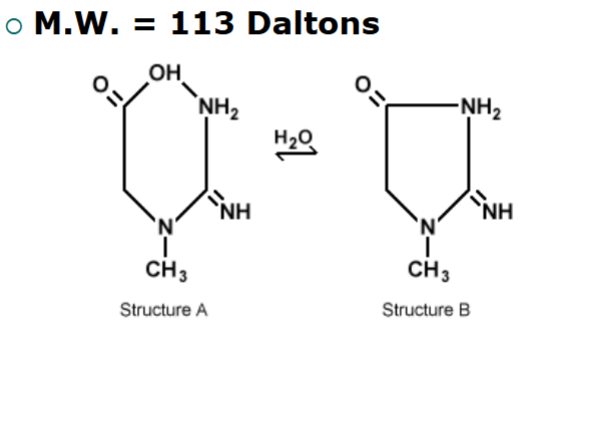
normal concentrations of creatinine
Serum or Plasma
0.6 - 1.2 mg/dl males (53-106 umol/L)
0.5 - 1.0 mg/dl females (44-88 umol/L)
ASCP Combined Adult Range: 0.8-1.2 mg/dL
Urine creatinine: 1-2 g/day
clinical significance of creatinine
Index of Kidney Function or (GFR)
Serum elevations:
Reduction of GFR
Kidney disease
Muscular dystrophy (Duchene's type)
Skeletal muscle atrophy
Starvation
Muscular Trauma, crushing injuries
Gigantism, Acromegaly
Myasthenia gravis
Poliomyelitis
Hyperthyroidism
check creatinine before giving nephrotoxic drugs
Methotrexate
Cisplatin
Cytoxan
Semustine
Mithramycin
Vancomycin
analytical procedures for creatinine
Jaffe Reaction
Principle reaction
Developed in 1886
Oldest Known chemical test principle to
date. OH-
Creatinine + picric acid creatinine-picrate
complex (red)
Measure Absorbance 520 nm
Original method required a Protein Free
filtrate prepared with TCA
interferences of creatinine
Non Creatinine Chromogens
Ascorbic acid
Pyruvate
Acetone and aceto-acetic acid
Alpha Ketoacids - Diabetic
Ketoacidosis
picric acid
Safety precautions
recommend storing
picric
Dry picric acid is
relatively sensitive to
shock and friction
picric acid can easily
form metal picrate salts
that are even more
sensitive and hazardous
TNT
kinetic Jaffe reaction
Spectrophotometric
Measures rate of change in
absorbance
Requires an initial reading
(baseline) A1
And an Endpoint reading A2
Measures increase of Absorbance at
500 nm (Delta Absorbance)
coupled enzymatic methods of creatinine
Enhanced specificity over Jaffe methods
Creatininase (creatinine aminohydrolase) Method
Encorporates enzymes, CK, PK, LD
(Creatininase aminohydrolase)
Creatinine + H2O Creatine
CK
Creatine + ATP Creatine Phosphate + ADP
PK
ADP + Phosphoendopyruvate ATP + Pyruvate
LD
Pyruvate + NADH Lactate + NAD+
Measure the decrease of absorbance as NADH NAD+
Requires large sample, not routinely used
other couple enzymatic methods - creatinine
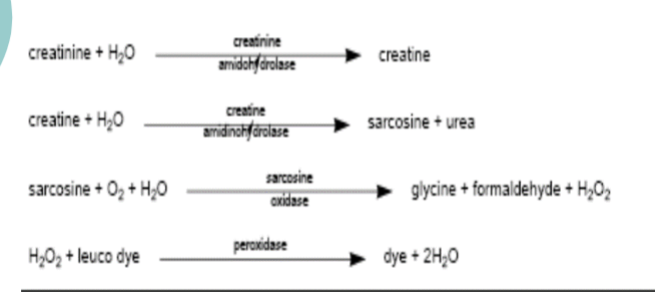
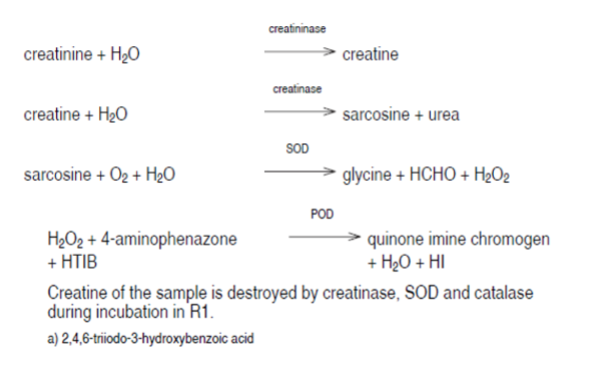
Creatinine aminohydrolase - H2O2 Methods
Creatininase
Creatinine + H2O → Creatine
Creatinase
Creatine + H2O → Sarcosine + Urea
Sarcosine Oxidase
Sarcosine + H2O + O2 glycine + formaldehyde+H2O2
H2O2 + phenol derivative + 4-aminophenazone →
benzoquinone immine dye
J & J Vitros CREAT
Principle
Creatinine diffuses to the reagent layer, where it is
hydrolyzed to creatine
The creatine is converted to sarcosine and urea by
creatine amidinohydrolase
The sarcosine, in the presence of sarcosine oxidase, is
oxidized to glycine, formaldehyde, and hydrogen peroxide
The final reaction involves the peroxidase-catalyzed
oxidation of a leuco dye to produce a colored product
Following addition of the sample, the slide is incubated.
During the initial reaction phase, endogenous creatine in
the sample is oxidized. The resulting change in reflection
density is measured at 2 time points
The difference in reflection density is proportional to the
concentration of creatinine present in the sample
Vitros CREAT
1. Upper slide mount
2. Spreading layer
(TiO2)
3. Reagent layer
• creatinine
amidohydrolase
• creatine
amidinohydrolase
• sarcosine oxidase
• peroxidase
• leuco dye
• buffer, pH 7.0
4. Support layer
5. Lower slide mount
Vitros CREAT rxn
Roche Cobas 501
creatinine clearance tests
Measurement of GFR
Clearance:
the amount of plasma that can be cleared of a
substance per unit time
Procedure
Hydrate the patient w 600 ml H2O
Void and discard urine
Begin 24 hr. collection from this time. Record time.
Collect urine /unit time
Collect blood specimen and assay for creatinine
calculation for creatinine clearance
Clcr = UV/P X 1.73/A
V = ml/min volume
U = urine creatinine
P = Plasma creatinine
A = Body surface area
reference ranges of creatinine clearance
105 ± 20 ml/min – Males
95 ± 20 ml/min – Females
Decreased GFR:
Impaired GFR
Kidney disease
uric acid biochemistry
Catabolism of nucleic acids
End product of purine metabolism
Adenosine and Guanine
Oxidation of xanthine by xanthine Oxidase
2/3 of uric acid is excreted by the kidneys, 1/3 stool
96.8 % of uric acid is present as monosodium urate
There are three disease states associated with
elevated uric acid levels:
Gout
Increased nuclear breakdown (leukemia, carcinoma)
Renal disease
clinical significance of uric acid
Elevated levels: Hyperuricemia
Gout
Leukemia
Decreased Kidney function - Renal failure
Lymphomas
Metastatic cancer
Multiple myeloma
Polycythemia
Hemolytic and Megaloblastic anemia
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
X-linked enzyme deficiency in purine biosynthesis.
Toxemia of pregnancy and lactic acidosis
Starvation, increased tissue breakdown
Purine rich diet
Alcoholism
Lead poisoning
significance of uric acid
Hypouricemia
Decreased levels
Secondary to severe liver disease
Fanconi’s syndrome
(defective tubular reabsorption)
Wilson’s disease
Treatment with Xanthine oxidase
inhibitor drugs
(Allopurinol)
reference ranges - uric acid
4.0 - 8.5 mg/dl (males)
2.7 - 7.3 mg/dl (females)
determination of uric acid
Two Methods in current use:
Phosphotungstic acid (PTA)
Uricase methods
PTA
principle
Na2CO3 /OH-
Uric Acid +H3PW12O40 + O2 → Allantoin +CO2 + Tungsten Blue
Measure Absorbance at 710 nm
Nonspecific, requires protein separation
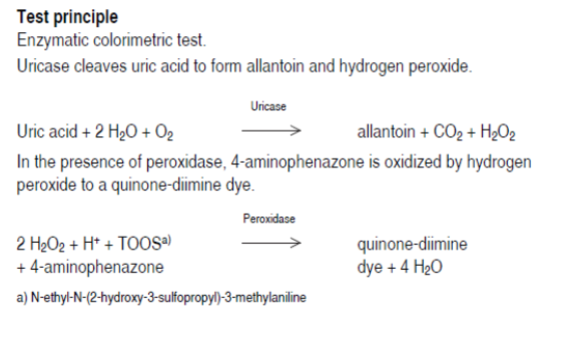
enzymatic methods - uricase
Principle:
uricase
Uric acid +O2 → Allantoin +H2O2 +CO2
Measure decrease of Absorbance at 293
nm
As uric acid is converted to allantoin (non
UV absorbing)
Candidate for reference method
Hemoglobin and xanthines interfere
couple enzymatic determination of uric acid
Very popular/ automated
Enzymatic methods are highly
specific Catalase
H2O2 +CH2OH → H2CO3 +H2O
H2CO3 + 3 C5H8O2 + NH3 → 3H2O + Colored
Compound
automated methods
Differential Absorption
Uricase Principle
UA absorbs light @ 293 nm
Allantoin is non-absorbing
Measure decreased of
Absorbance/time
Candidate for reference
methodology
johnson and johnson vitros analyzer
Dry slide (film)
Technology
Uric acid migrates
through the scavenger
layer
Oxidized by uricase to
allantoin and H2O2
H2O2 reacts with
peroxidase and Dye to
produce a chromogen
Measured by
Reflectance
colorimetry
Incorporates
Ascorbate oxidase to
eliminate interference
due ascorbic acid
Roche Cobas 501 principle for uric acid
high performance liquid chromatographic procedure
Reversed-phase chromatography
Spectrophotometric detection at
280 or 235 nm
Ion-exchange separation
Followed by amperometric detection
Using thin-layer flow-through
electrochemical cell
interfering substances in uric acid determinations
Ascorbic acid
Glucose
Glutathione
Acetaminophen
Caffeine
Theophylline
urea
Biochemistry
Major product of protein metabolism
Deamination of amino acids to ammonia (NH3 )
Ornithine or Krebs cycle
Synthesized in the liver from CO2 and NH3
Transported by the plasma
Filter by the glomerulus
Smaller amounts by skin and GI
Up to 40% is reabsorbed by the renal tubules
plasma levels
Affected by renal function
Protein content of diet and level of protein catabolism
Historically measured based on nitrogen level, some
assays still measure Urea nitrogen
Conversion of BUN to urea:
Atomic Weight of nitrogen is 14 g/mol
molecular weight of urea=60.06 g/mol (60 Daltons)
urea contains 2 nitrogen atoms per molecule (2x14=28)
Mol wt. Urea / At. Wt. N2 = 60/28 = 2.14
Urea = BUN mg/dl X (2.14)
urea cycle
Takes place in the mitochondria and the
cytoplasm of the liver cells
Produced from the conversion of arginine to
ornithine
Carbamyl Phosphate Synthetase (CPS)
Enzyme responsible for converting NH3 to Carbamyl
Phosphate used in the urea cycle
CPS
NH3 + CO2 + H2O + 2ATP → Carbamyl Phosphate
clinical significance of urea (BUN)
Useful in assessment of Renal Function
Elevated Urea in the blood is termed azotemia
Very high Plasma Urea accompanied by renal
failure is termed Uremia or uremic syndrome
Prerenal azotemia (Reduced renal blood flow)
Congestive heart failure
Shock, hemorrhage
Dehydration
Renal azotemia
Acute and chronic renal failure
Glomerulonephritis, tubular necrosis
Post renal azotemia
Blockage of urine flow below the kidney
Obstruction, calculi, tumors, pregnancy
Congenital abnormalities, Urinary tract infection
BUN/CREAT ratio
Aids in differentiating causes of azotemia
Normally 10-20:1
Non renal conditions...
Will elevate urea greater extent than creatinine
As a result, the BUN/CREAT ratio will be elevated
Elevation of BUN/CREAT ratio...
Indicates Pre-renal Azotemia or Urea elevation
Post renal azotemia
Decreased BUN Levels
Primary renal azotemia
Renal disease
Acute tubular necrosis
analytical methods for urea
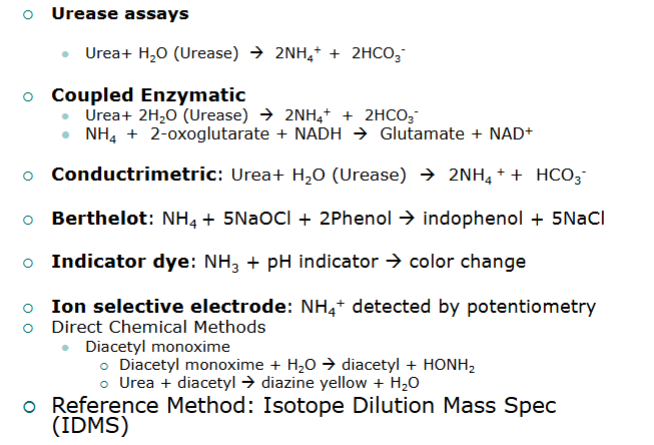
urease/GLDH method

vitros BUN
Principle:
A drop of patient sample is deposited on the
slide and is evenly distributed by the spreading
layer to the underlying layers
Water and nonproteinaceous components then
travel to the underlying reagent layer, where
the urease reaction generates ammonia.
The semipermeable membrane allows only
ammonia to pass through to the color-forming
layer, where it reacts with the indicator to form
a dye.
The reflection density of the dye is measured
and is proportional to the concentration of urea
in the sample.
1. Upper slide mount
2. Spreading layer
(TiO2)
3. Reagent layer
• urease
• buffer, pH 7.8
4. Semipermeable
membrane
5. Indicator layer:
ammonia
indicator
6. Support Layer
7. Lower slide mount

Roche/Hitachi Cobas 501 test principle for urea
reference levels - urea nitrogen
ASCP Combined Adult Range: 6-20
mg/dl (2.1-7.1 mmol/L)
Interferences
Fluoride or citrate inhibits Urease reaction
Low protein, high carbohydrate diet-falsely
lower
Urea is quite susceptible to bacterial
decomposition, especially urine
ammonia, NH3 biochemistry
Arises - deamination of amino acids-protein
Digestive and bacterial enzymes on proteins
Release from metabolic reactions occurring in
skeletal muscle
Consumed by hepatic parenchymal cells in the
production of urea
In severe liver disease, Parenchymal cells are
damaged
NH3 levels rise
Plasma levels of NH3 are not dependent on renal
function, but on liver function
metabolism
Hepatic Portal vein delivers the ammonia
to the liver
Enzymes convert the NH3 to urea
Combines with H+
Ammonia cannot be excreted by kidney
Elevations of ammonia are neurotoxic
Often associated with hepatic
encephalopathy (hepatic coma)
clinical significance of urea
Hepatic Failure
Hepatic encephalopathy
(hepatic coma)
Reye’s Syndrome
Viral disease treated with aspirin in young
children and teens can lead to Reye’s disease
Acute metabolic disorder of the liver
Severe Liver Disease (most common)
Impaired Liver circulation
Genetic enzyme deficiencies
Involving urea cycle enzymes
specimen handling requirements
Proper specimen handling is utmost importance
Ammonia levels can rise rapidly in whole blood
Venous specimens should be obtained without
trauma
Place on ice immediately
Li-Heparin or EDTA plasma is preferred
specimen
ammonia testing considerations
For best results, assays should be completed
ASAP to prevent in-vitro deamination
Hemolysis must be avoided, red cells contain 2
- 3 times plasma levels
Smoking should be avoided for several hours
before sample is drawn
Glassware and reagents must be free of
ammonia contamination
analytical methods
Ion Exchange Resin Absorption
Cation exchange resin (Dowex 50)
Elution of NH3 with NaCl
Quantitation by Berthelot reaction
Manual, time consuming procedure,
not available for automation
Gives slightly higher results
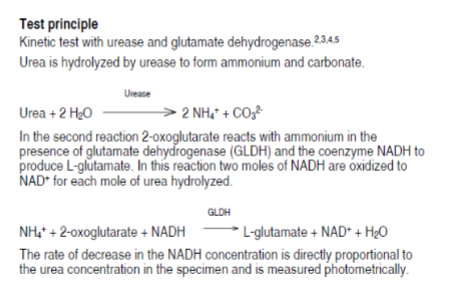
coupled enzymatic method
Principle:
Glutamine dehydrogenase (GLDH)
GLDH
NH4+ + 2-oxoglutarate + + NADPH → Glutamate + NADP+ + H2O
Measure decrease of Absorbance at 340 nm
as NADPH is reduced to NADP+
Most commonly used on automated systems
Good precision and accuracy
ammonia ion selective electrode
Diffusion of NH3 through a selective
membrane into NH4Cl solution.
Measures change of pH as NH3 diffuses
across selective membrane
Measured potentiometrically
Problems with membrane stability
reference ranges for urea
Adult:
19-60 ug/dl or (11-35 umol/L)
Newborn:
68-136 ug/dl or 64-107 umol/L