CHEMISTRY QUARTER 1
1/175
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms

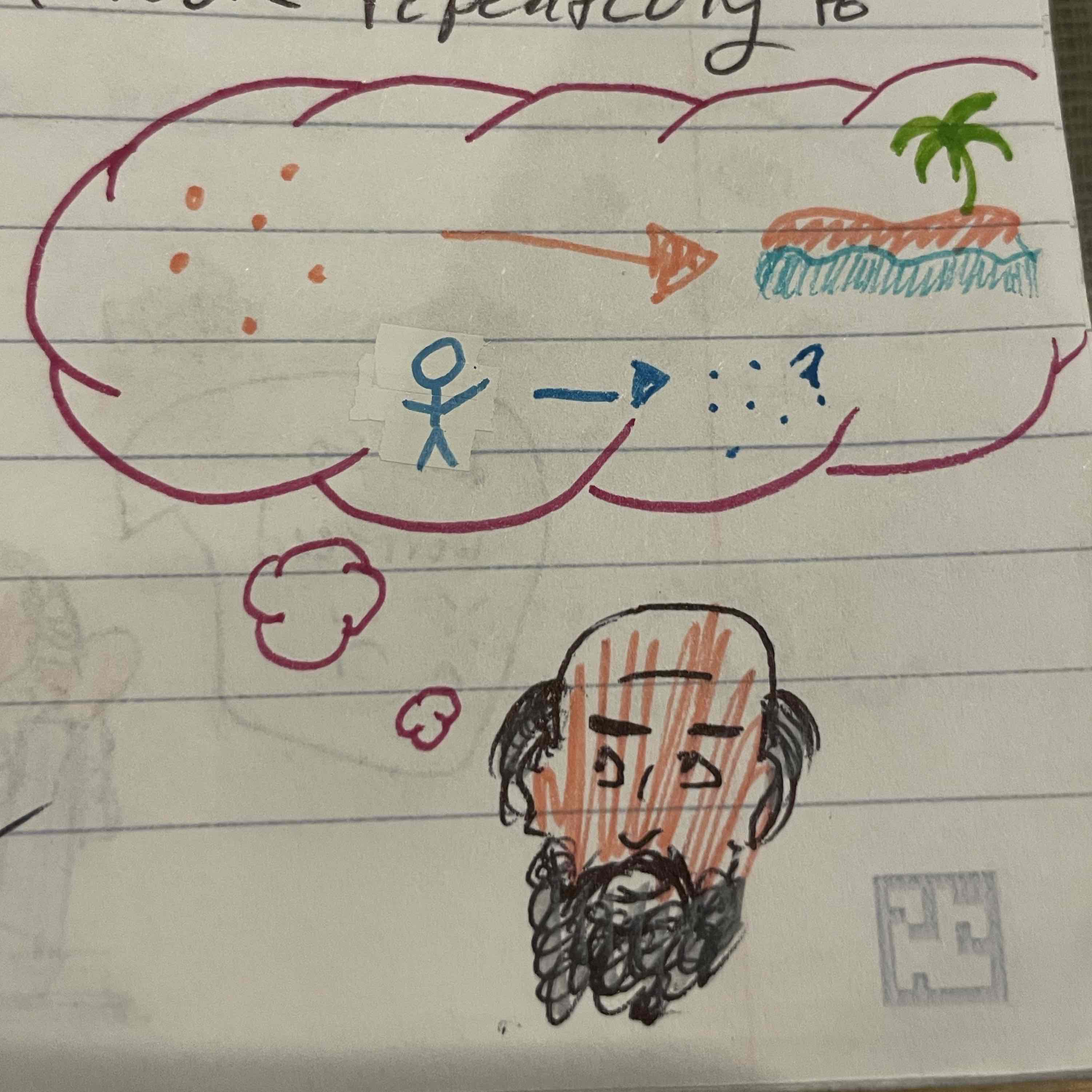
Democritus
Philosopher who was first to theorize that matter was composed of atoms

Joseph priestly
Prepared our oxygen, decomposed mercuric oxide, invented laughing gas/nitrous oxide


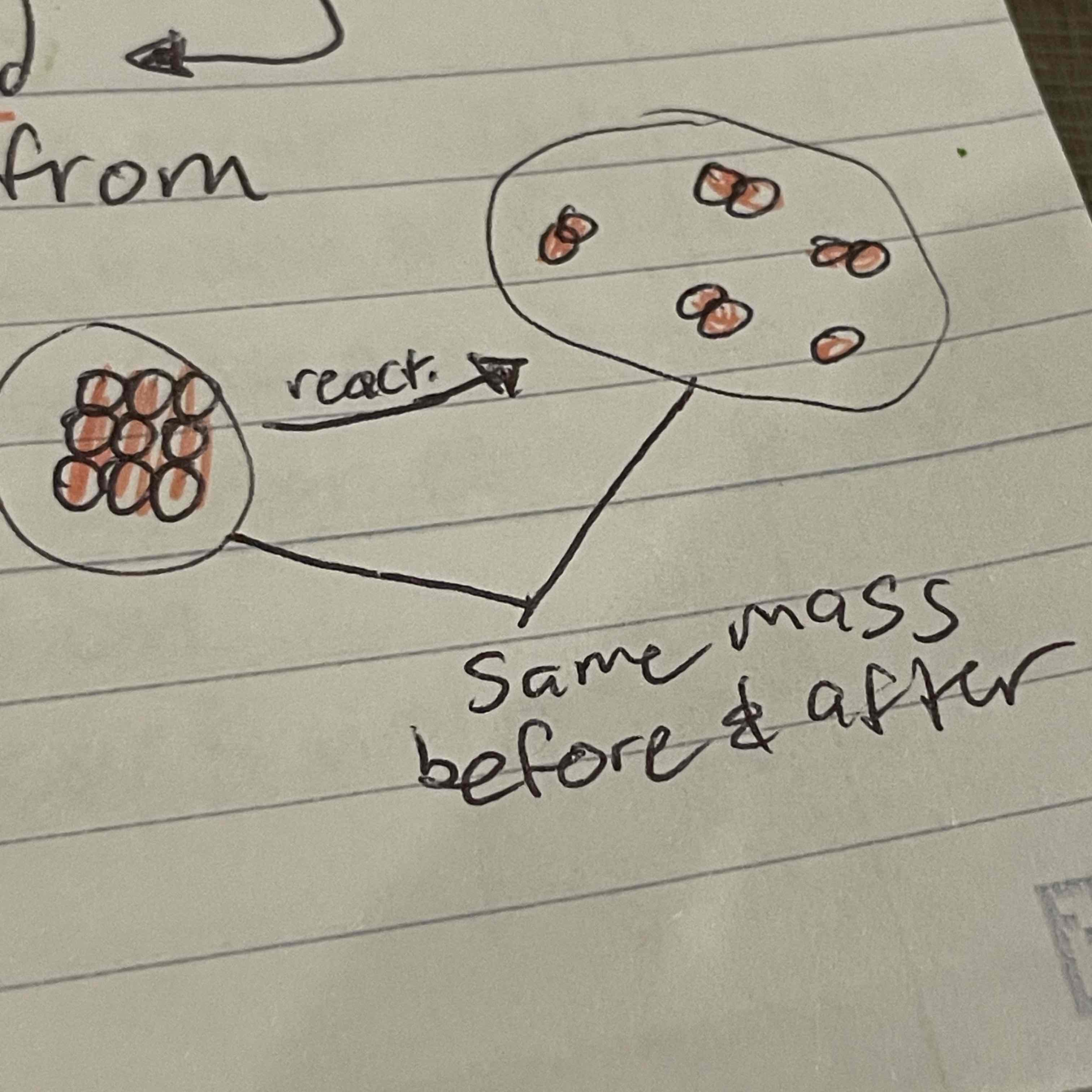
Anton Lavoisier
Observed that substances stopped burning when cut off from oxygen, realized that metals got heavier after burning, meaning the mixed with the air, came up with law of conservation of mass

Joseph Proust
Came up with law of definite composition
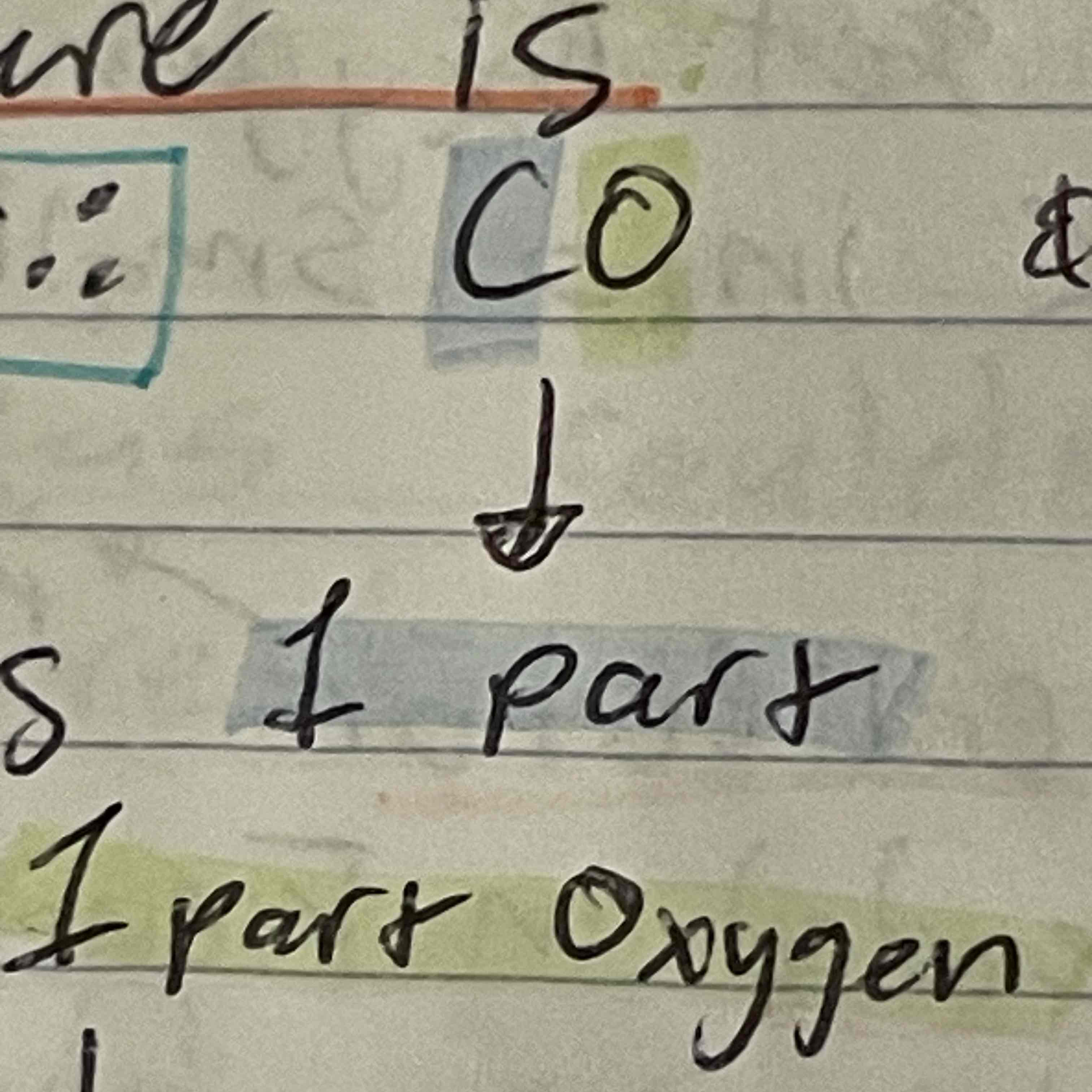

John Dalton
Summarized theories, came up with 4 postulates, described and predicted chemical behavior

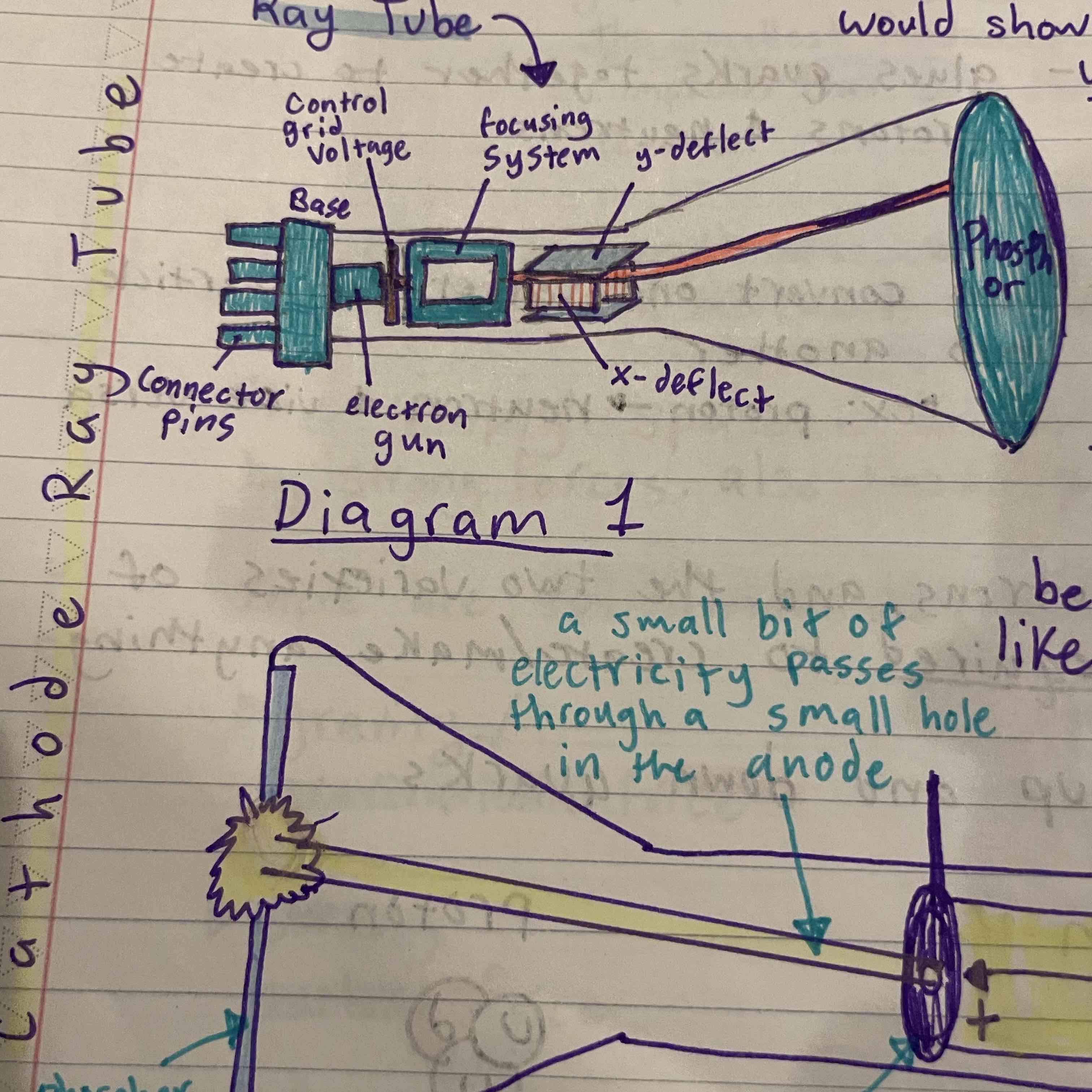
JJ Thomson
Discovered electrons using cathode ray tube, theorized protons

Rutherford
Gold foil experiment, concluded that atom is mostly empty space, theorized that positive charge and most of mass contained in the nucleus, discovered protons
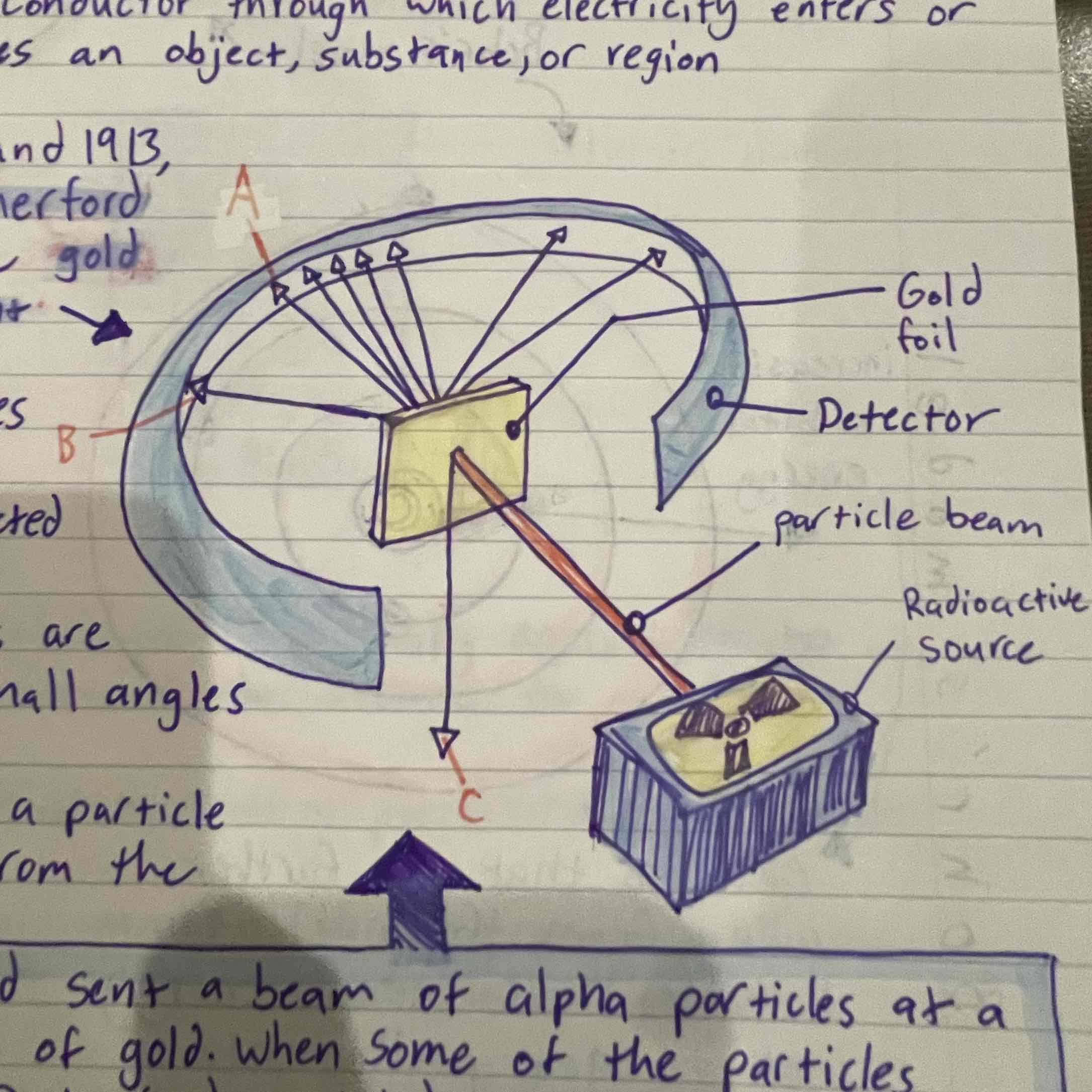
James Chadwick
Confirmed existence of neutron

proton number
Decides element of an atom, atomic number
Electrons
Negatively charged; decide behavior of the atom
Ions
Atoms with same # protons but diff numbers of electrons
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons; identified by mass number
Mass number equation
Proton # + neutron #
Atomic mass unit
1/12 mass id a carbon-12 atom; means that proton and neutron are very close but not exactly equal to 1
Atomic mass
Weighted average accounting for abundance of each isotope of an element that occurs in nature
average atomic mass calculation
(Mass of iso. 1 • [%abundance/100]) + (mass of iso. 2 • [%abundance/100)
Henri Becquerel
accidentally discovered radiation by setting uranium salts on a sealed photographic plate
Marie Curie
First to earn Nobel prizes in both physics and chem, named radioactivity, discovered radium, curium, and polonium
Radiation
penetrating rays and particles given off by a radioactive source
Nuclear radiation
occurs bc some nuclei are inherently unstable and the nucleus tries to obtain stability by emitting radiation during radioactive decay
Three main radiation types
alpha, beta, gamma
radioscope
any unstable nucleus
alpha particles
4He2+ ; made of 2 protons and 2 neutrons; have positive charge of 2
alpha radiation (α)
consists of helium nuclei
Beta radiation (β)
consists of electrons
Change caused by alpha radiation
Atomic mass drops by 4, atomic number drops by 2
changes from Beta decay
atomic number up by 1, mass stays the same
Changes from Gamma radiation
none
changes from electron capture or positron emission
Atomic number drops by 1, mass stays the same
What happens during electron capture?
An atom pulls an electron to a proton to create a neutron
What happens during positron emission
a proton breaks down into a neutron and a positron
positron
+1e
electron
-1e
alpha particle
4H2+
beta particle
-1e1-
band of stability
plot of number of protons and neutrons in relation to one another
section of band of stability on top
beta decay
band of stability bottom section
electron capture and positron emission
causes beta decay
too many neutrons
causes positron emission or electron capture
too many protons
half life
time it takes for ½ of a sample to decay
transmutation
changing element of an atom
induced transmutation
changing element of an atom on purpose in a lab
mass defect
when the mass of a nucleus is less than the sum of the masses of protons and neutrons
cause of nuclear chain reaction in nuclear reactors (what happens/what key parts are involved & what they do)
neutrons fired out that hit radioisotopes on other rods
amplitude
wave’s height from zero to crest
wavelength
distance between crests
frequency
number of wave of cycles to pass a given point per unit of time
quantum
minimum amount of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom
radioactive wave frequency in relation to gamma ray frequency
radioactive waves have a lower frequency
photon
massless particle that carries a quantum of energy and moves with a wavelike motion
quantum model
Bohr’s model of an atom, which stated that electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed levels
erwin schrodinger
produced quantum mech. model
parts of quantum mechanical model
electron cloud, energy levels, and energy sublevels
s orbitals
can hold 2 electrons, circle shape
p orbitals
can hold 6 electrons, dumbbell shape
d orbitals
can hold 10 electrons, double dumbell shaped
aufbau principle
each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available
4 postulates of Dalton’s Atomic theory
all elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms, atoms of the same element are chemically identical and atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element, atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios, chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged; atoms are never transmuted during a chemical reaction
strong nuclear force
holds protons and neutrons in the nucleus; attractive force between subatomic particles that are incredibly close together; has short range
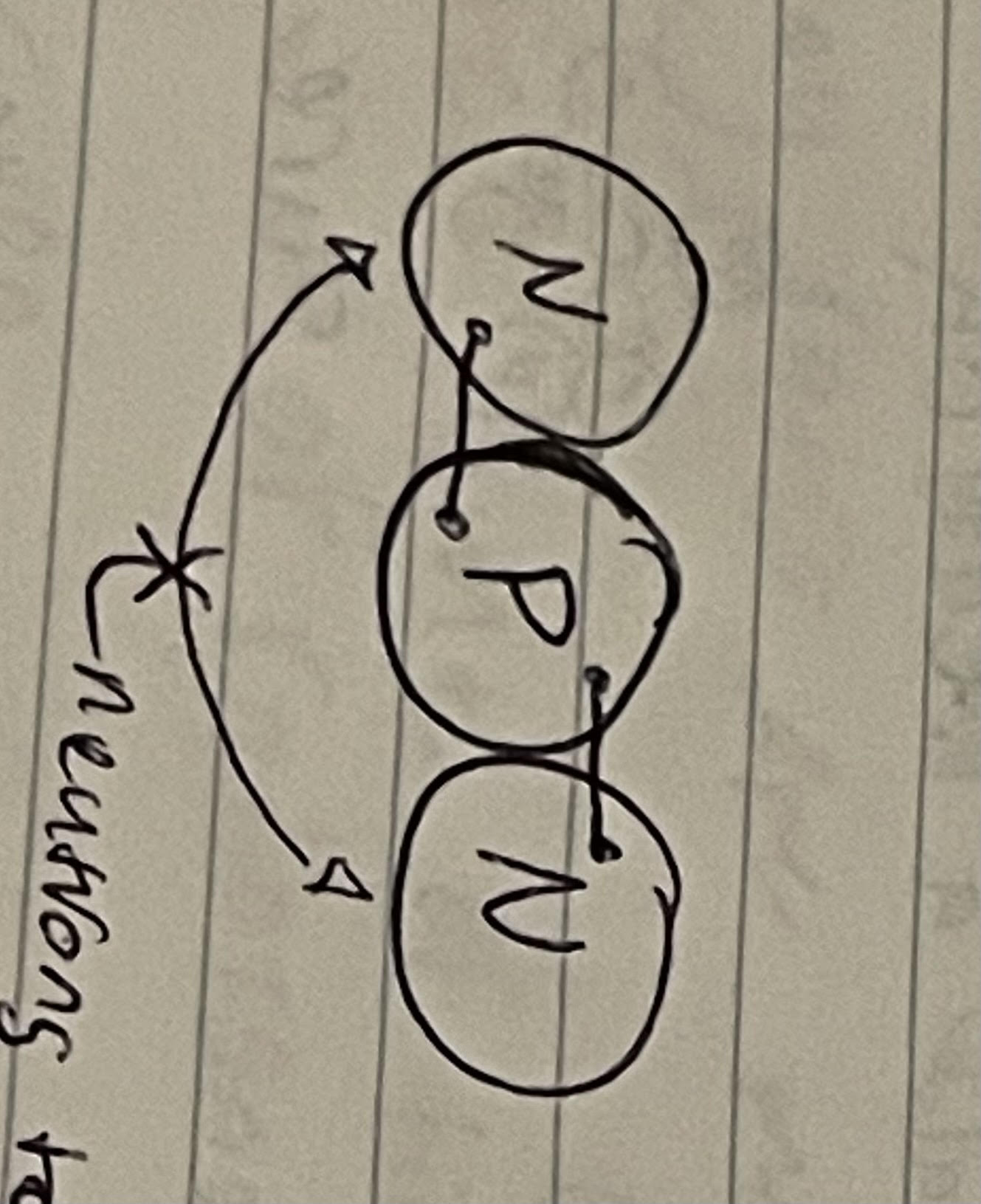
the reason that these neutrons are not attracted to each other by strong nuclear force
the neutrons are too far apart
forces provided by protons?
attractive & repulsive (they repel each other)
forces provided by neutrons
attractive forces
what force wins over strong nuclear force?
repulsion; proton repulsion takes over when there are too many neutrons in between protons
more neutrons → _____ ______ between things→ _______ takes over → _____
bigger distance, repulsion, instability
most stable nuclei are here
in smaller atoms (at. # < 20)
most stable nuclei have this proton to neutron ratio
1:1
What happens when atoms get bigger and protons get farther apart?
their electrostatic repulsion overpowers strong nuclear force, and more and more neutrons are needed to achieve stability
maximum ratio for a stable nucleus
1.5:1 (1.5 is an average, bc. you can’t actually have half a neutron)
amt. of stable isotopes that atoms have
1 (most of the time)
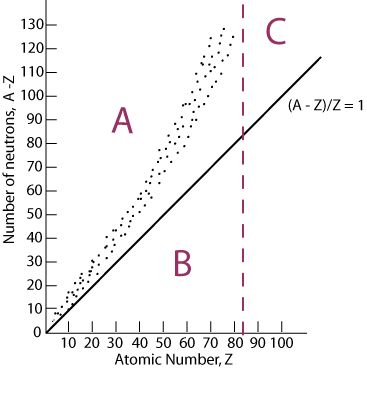
Band of stability
plot of the # of protons in relation to the # of neutrons; where an isotope is found on the band of stability can be used to predict what type of decay can occur
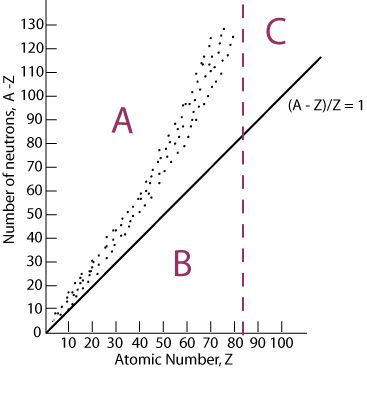
type of decay most likely to happen if an isotope falls in section A of the graph
beta
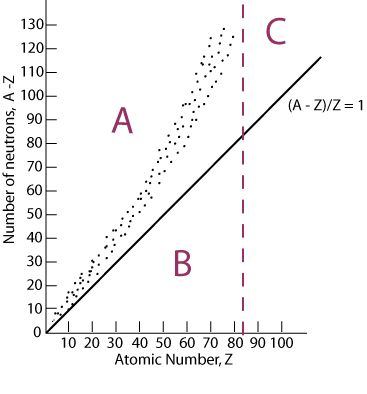
type of decay most likely to happen when isotope falls in section C of the graph
Alpha decay
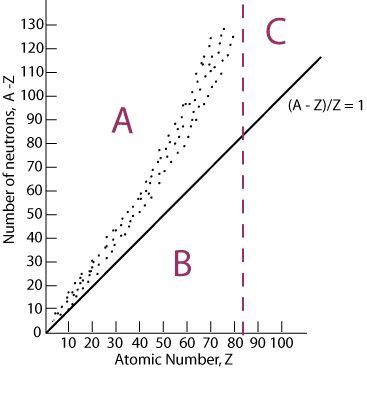
type of decay most likely to occur when isotope falls into section B of the graph
Electron capture or positron emission
cause of beta decay
too many neutrons (converts neutron into proton & electon)
cause of positron emission and electron capture
too many protons → balances charges
cause of alpha decay
need to get rid of both neutrons and protons
reason that there are radioisotopes left when they are continuously decaying
every isotope has its own decay rate, some seconds or minutes, some millions of years
half-life
used to measure radioactive decay rates; amount of time that it takes for ½ of a sample of radioisotopes to decay
transmutation
conversion of an atom of one element to an atom of another element; goal of alchemists for centuries; occurs through radioactive decay and induced transmutation
induced transmutation
where change is caused in the nucleus by bombarding it with other subatomic particles; artificial transmutation
transuranium elements
elements following uranium of periodic table; do not occur in nature; produced by induced transmutation; all highly radioactive
mass defect
when the mass of a nucleus is less than the sum of masses of the protons and neutrons; accounted for my einstein’s E=mc² equation where energy and mass can be converted between each other
result of breaking apart or bringing together nuclei
infinitesimally small amounts of matter being converted into huge amounts of energy
fission
breaking down of smaller nuclei after being bombarded with neutrons; produces extra neutrons
Uranium
used for fission; biggest naturally occurring element; biggest thing that we can get from the ground; unstable & breakable
product of one fission reaction
3 new neutrons, which can then cause three new fission reactions, producing 4 neutrons → cause of chain reactions in nuclear reactors
how a nuclear reactor works
fissionable material is shaped into fuel rods which are placed into coolant. As the rods exchange neutrons, more and more energy is released, which heats the coolant which heats the water and causes steam to turn turbine. Rods are placed close together so that neutrons can potentially hit radio isotopes on another rod and continue reacting; gaps in between rods allow control rods to be placed between fuel rods to stop or slow the chain reaction
reasons why not to use more nuclear fission if it is so efficient
cost, safety and protection of workers, production of dangerous waste, location specifics, chernobyl disaster fears
Fusion
when 2 or more small nuclei are forced to combine and form a bigger nucleus and huge amount of energy
attractive qualities of fusion
small nuclei used as fuel are incredibly abundant, products significantly less radioactive than fission, not self-sustaining (won’t explode), everyone has the resources, could bring military in middle east home, could reduce climate change, could provide energy for desalination, won’t have to pay for gas
electromagnetic radiation
energy moving through space like a wave
red light is ____ frequency, purple light is ____ frequency
lower, higher
wavelength _____ as energy/frequency ______
increases, decreases
speed of all electromagnetic radiation
light
photoelectric effect
electrons emitted from the surface of a metal when light of a certain frequency or higher shines on surface
Max Planck
studied metals & wavelengths given off at different temperatures
quantum
minimum amt. of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom
photon
massless particle that carries a quantum of energy & moves with wavelike motion; bundles of energy; make up light in a beam
Einstein said that everything moves in a ______ motion
wavelike