Week 2 - Self Study - Anatomy & Physiology: Diencephalon to Spinal Cord (Pages 1-3)
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering diencephalon components, basal nuclei, brainstem, cerebellum, spinal cord and vertebral column, and spinal cord internal anatomy.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
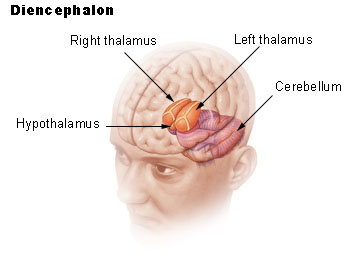
What are the three main components of the diencephalon?
Thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus.
What is the primary role of the thalamus?
Acts as a relay station for most sensory input (except olfaction) to the cerebral cortex and relays motor info from cerebellum and basal nuclei to the motor cortex.
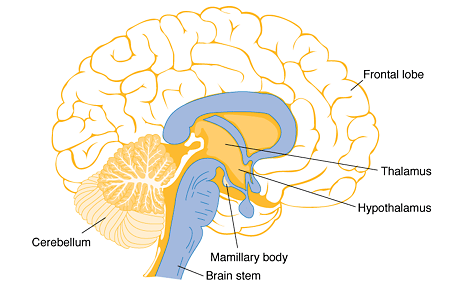
Where is the hypothalamus located, and what does it connect to?
Inferior and slightly anterior to the thalamus; connected to the pituitary gland via the infundibulum.
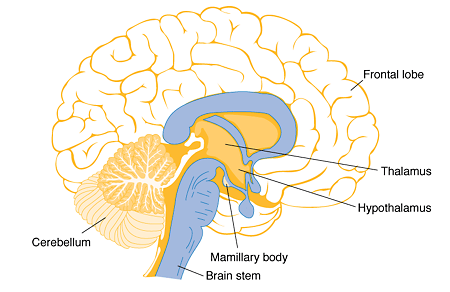
What are the main functions of the hypothalamus?
Regulates homeostasis and visceral activities by integrating sensory info and initiating responses; links the autonomic nervous system, endocrine system, and limbic system.
What gland is contained in the epithalamus and what does it secrete?
Pineal gland; secretes melatonin, regulating circadian rhythms.
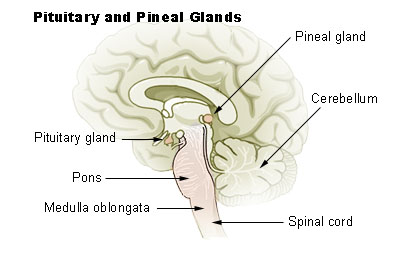
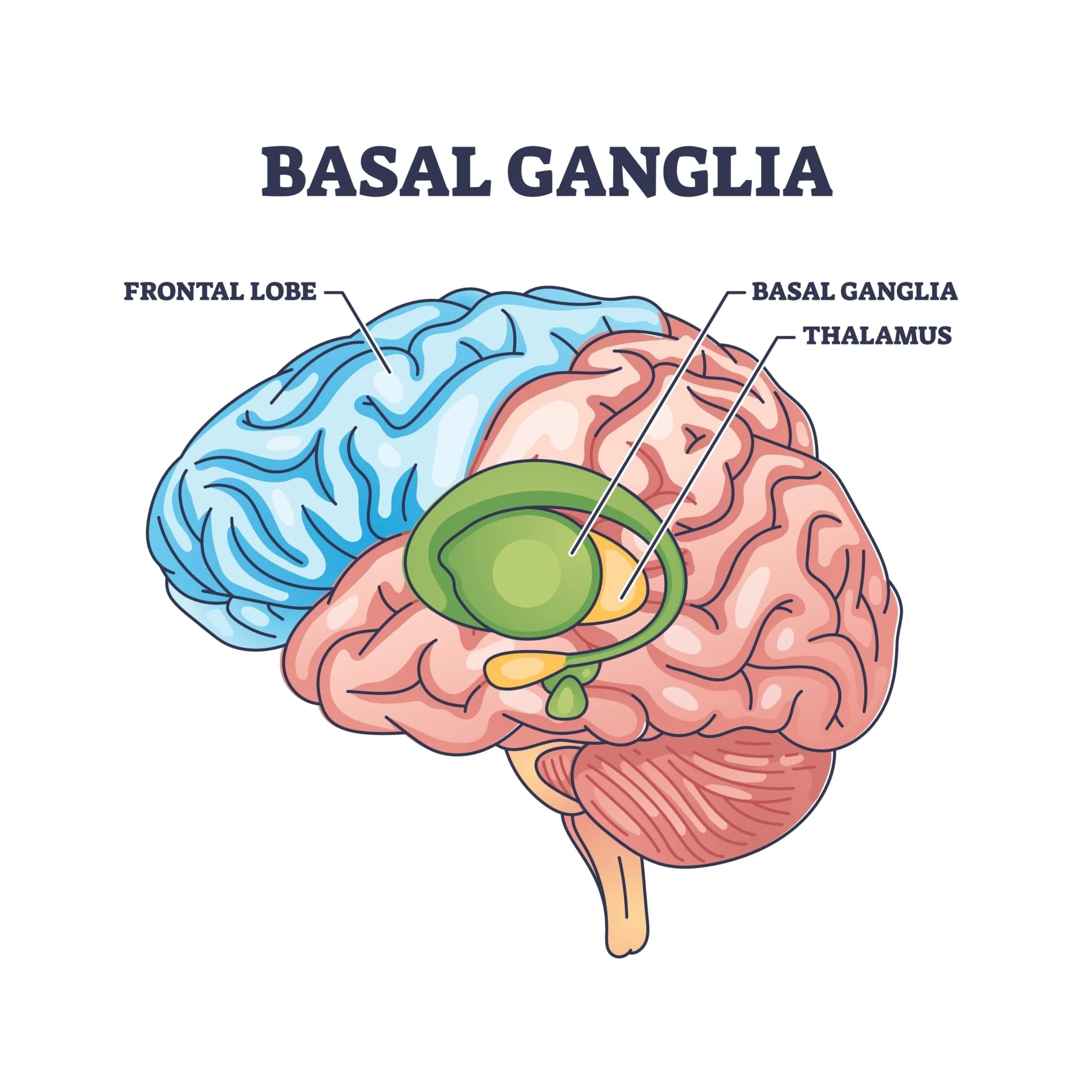
What is the function of the basal nuclei?
Regulate motor output, ensuring smooth, predictable movements and posture.
Which structures make up the basal nuclei “comma” shape?
Caudate nucleus (head, body, tail), putamen, and globus pallidus.
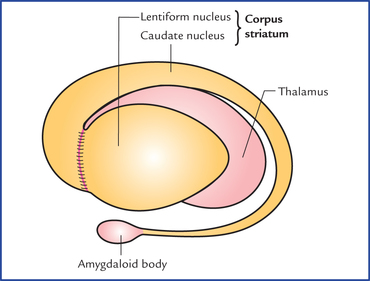
What two structures form the lentiform nucleus?
Globus pallidus and putamen.
What are the three main components of the brainstem?
Midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
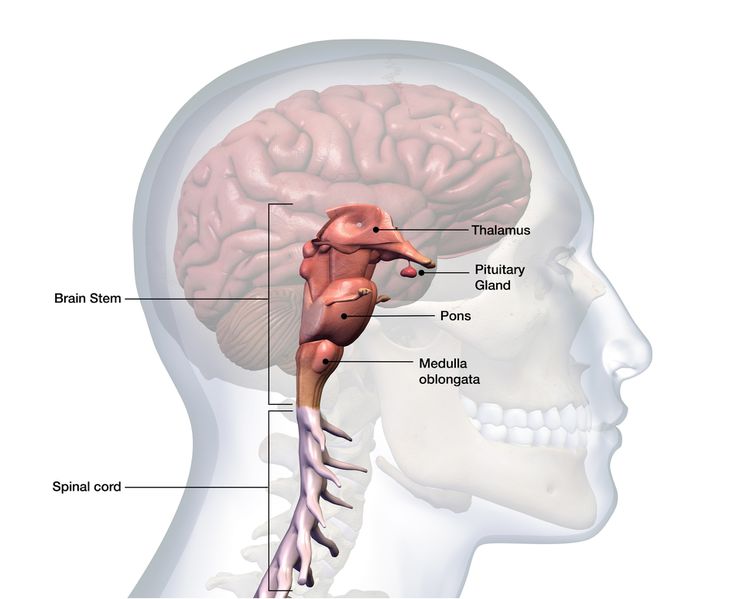
What is the function of the brainstem overall?
Connects cerebrum, cerebellum, and spinal cord; contains nuclei controlling reflexes and cranial nerve entry/exit.
What structures are found in the midbrain?
Left and right cerebral peduncles and substantia nigra (part of basal nuclei).
What is the function of the pons?
Relays info between midbrain, medulla, and cerebellum; contains cranial nerve nuclei and nuclei supporting respiratory control.
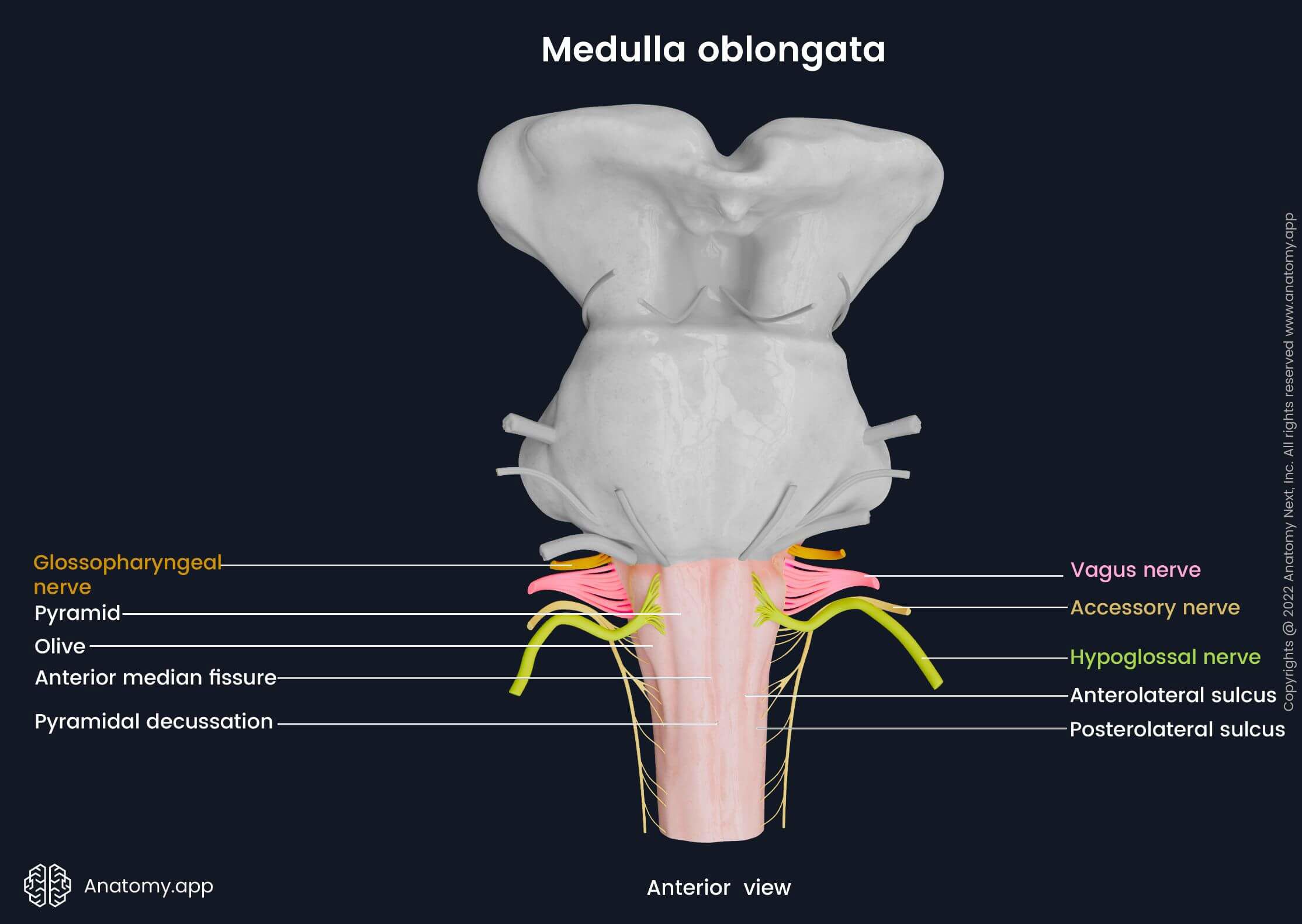
What vital centers are located in the medulla oblongata?
Cardiovascular center (heart rate, vessel tone), respiratory center (breathing rhythm), vomiting, swallowing, coughing, sneezing, hiccup centers.
What are pyramids and olives of the medulla?
Pyramids: corticospinal tracts with decussation (90% crossing). Olives: relay nuclei transmitting info to cerebellum.
What are the main functions of the cerebellum?
Receives proprioceptive and motor info, compares them, and makes fine adjustments to facilitate smooth movement (e.g., catching balance on ice).
What connects the cerebellum to the brainstem?
Superior, middle, and inferior cerebellar peduncles.
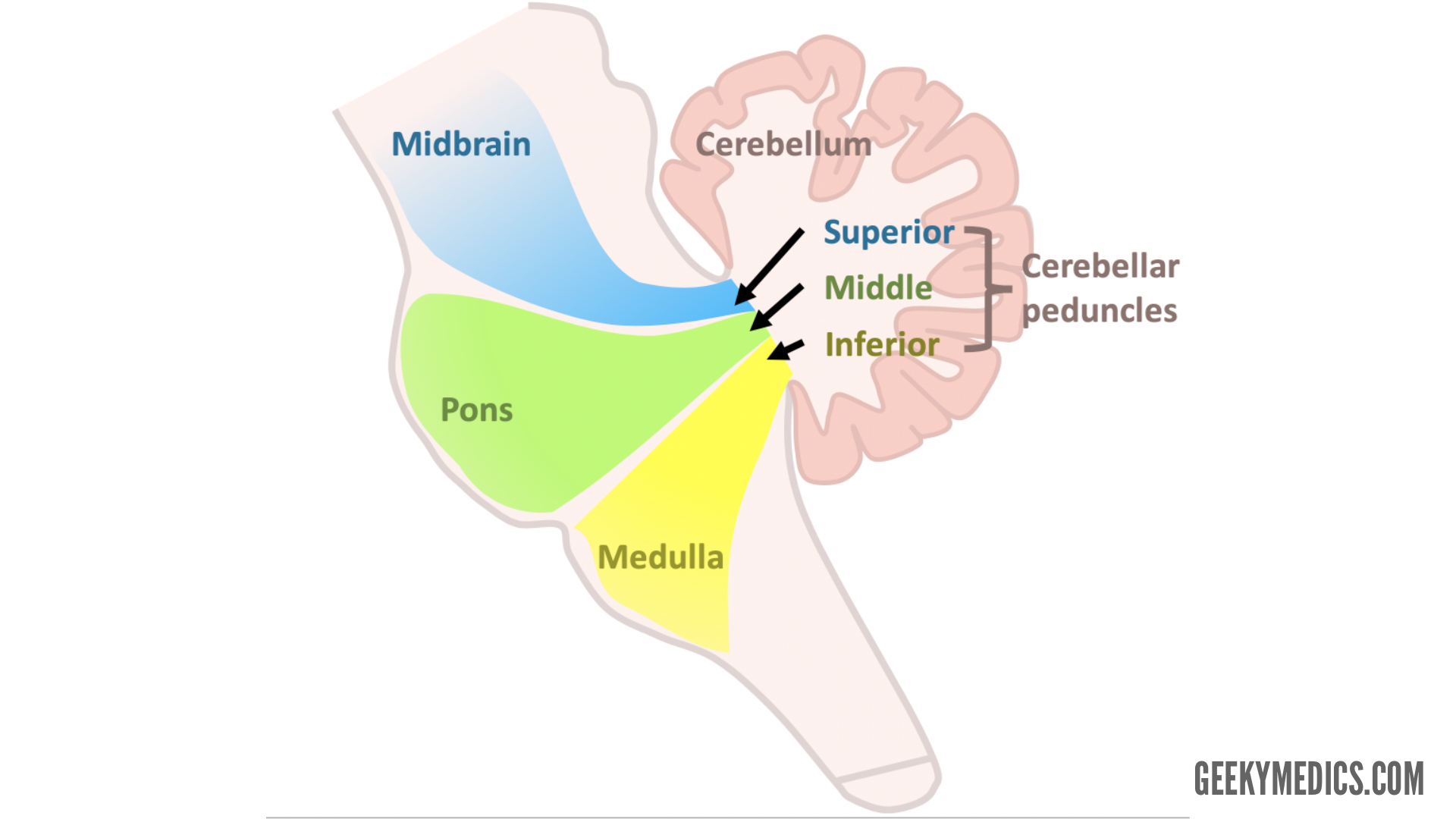
Which cerebellar peduncles are afferent vs efferent?
Superior: efferent; Middle: afferent; Inferior: both afferent and efferent.
How many spinal nerve pairs are there, and how are they distributed?
31 pairs: 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 coccygeal.
Why are there 8 cervical spinal nerves but only 7 cervical vertebrae?
The 8th cervical spinal nerve exits between C7 and T1.
What structures form the vertebral canal?
Stacking of vertebral arches.
Where do spinal nerves exit the vertebral column?
Through the intervertebral foramina.
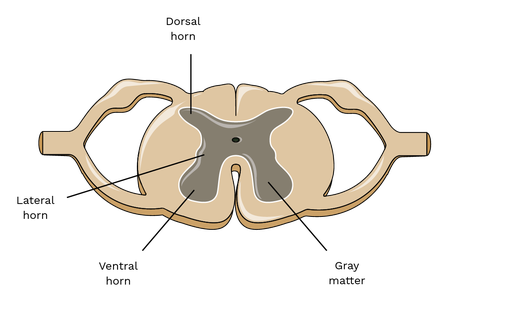
What is found in the spinal cord’s gray matter?
Neuron cell bodies of interneurons and lower motor neurons, surrounding the central canal (with CSF).
What is found in the white matter of the spinal cord?
Myelinated axon tracts carrying sensory (ascending) and motor (descending) information.
What is located in the dorsal horn?
Interneuron cell bodies that synapse with sensory neurons entering via the dorsal root.
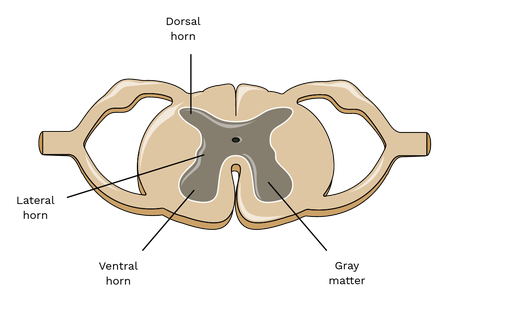
What is located in the ventral horn?
Cell bodies of somatic lower motor neurons projecting to skeletal muscle via ventral roots.
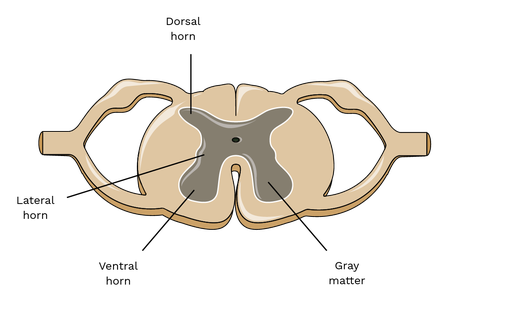
What is located in the lateral horn?
Sympathetic motor neuron cell bodies, projecting to internal organs (visceral motor innervation).