4D - Gel Electrophoresis
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
what is gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory technique used by scientists to measure the size of DNA fragments. It is typically used after a sample of DNA has been cut up using restriction endonucleases or after a short sequence of DNA has been amplified using the polymerase chain reaction.
steps of gel electrophoresis
A DNA sample is loaded into wells using a micropipette. A Standard ladder is loaded into one well – this helps estimate size of unknown DNA fragments.
Gel is made of agarose jelly filled with tiny pores – immersed in buffer solution that helps carry the electrical current.
Electrical current is passed through gel using two electrodes - +ve & -ve.
Negative electrode is near the wells and positive electrode is at opposite end.
DNA is negatively charged – attracted to positive end. DNA moves from the well through the tiny pores in gel.
Smaller DNA fragments move faster through gel – they travel further. It is switched off after a few hours – DNA stops moving and settles into bands – separated based on size
4. DNA is default to see – stained with fluorescent dye e.g. ethidium bromide. Bands can be visualised using UV light – Dye can be included in the gel before or after experiment.
about the bands
Long fragments of DNA will be closer to the well while shorter fragments will move further down the gel.
example of bands
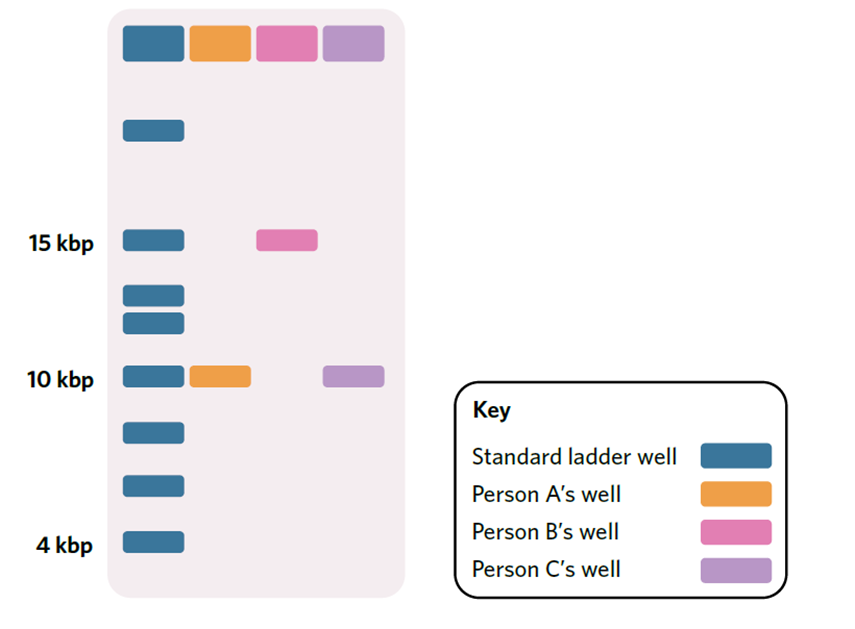
-If person A’s allele for eye colour is 10 kb long, and person B’s allele for eye colour is 15 kb long, person A’s band will move further from the well because it is shorter.
-If they shared the same allele (e.g. person A and C), the bands would end up at the same distance from the well.
what is the standard ladder
A standard ladder contains a number of different DNA fragments with a known molecular size. Molecular size indicates the length of a nucleic acid sequence and is measured in base pairs (bp) or kilobases (kb).
why are standard ladders vital
Standard ladders are vital because DNA fragments of the same size don’t always travel the same distance. Every gel type is different
Factors that affect how DNA travels through gel
•voltage – the stronger the electric force generated by the electrodes the further DNA travels.
•gel composition – gels with a greater density and agarose concentration make it more difficult for larger fragments to move through
•buffer concentration – the greater the concentration of ions the more the electric current is conducted through the gel, which causes DNA to move further down the lane.
•time – the longer the electric current is applied, the further the DNA will travel. If too much time passes, the DNA may move out of the gel.
where can gel electrophoresis be used
for genetic testing for certain conditions and DNA profiling (crimes)
Gel electrophoresis, testing for Cystic Fibrosis
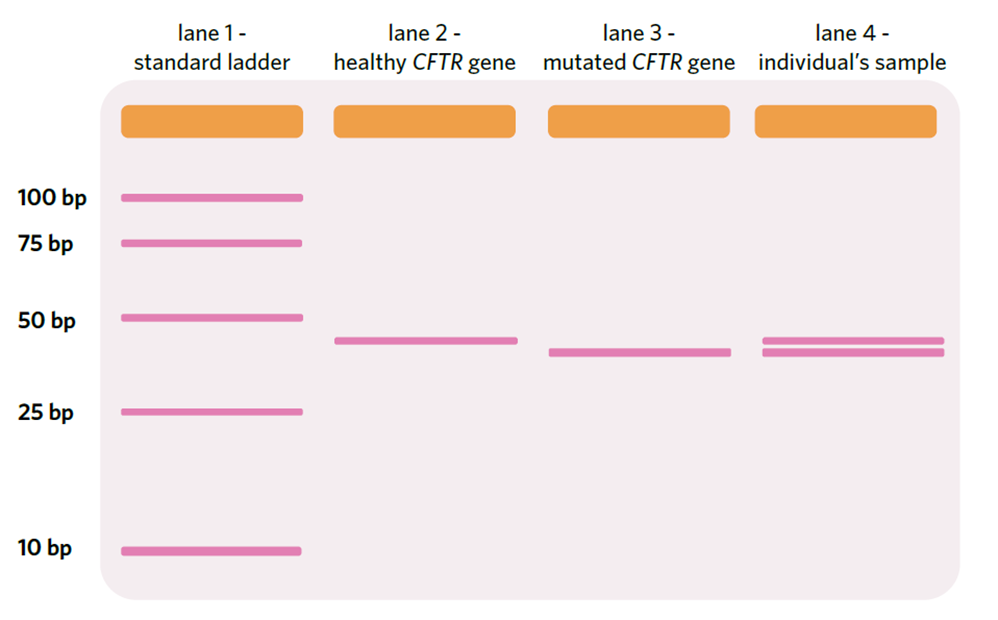
-The isolated healthy CFTR gene is approximately 40 bp.
-The individual in lane 4 is heterozygous – have DNA that lines up with a healthy and mutated gene.
-Individual doesn’t have CF as it is a recessive disorder – needs to have 2 copies of the mutated allele (homozygous positive)
STRS - DNA profiling
•Small amounts of DNA from samples obtained at crime scenes can be amplified and compared to the DNA of any suspect.
•We can analyze Short Tandem Repeats (STR’s) in DNA. If the STRs in two samples of DNA match, we can say with that the two pieces of DNA belong to the same person.
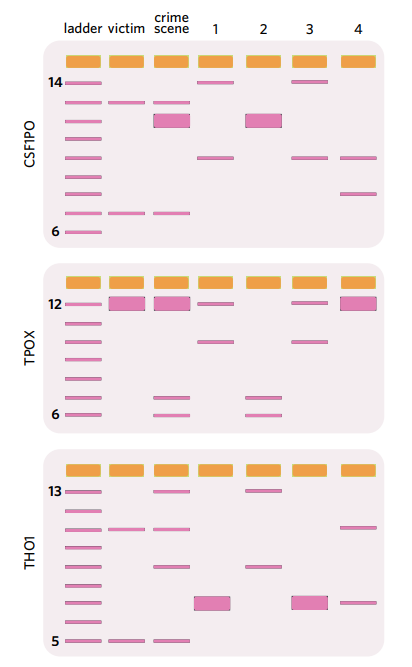
Gel electrophoresis: DNA profiling
Scientists can construct a DNA profile by using gel electrophoresis. They run a gel focusing on different STR’s – 3 different STR’s here
If the individual is heterozygous for an STR their gel will have two bands, whereas if they are homozygous their gel will only have one thick band.
transgenic
an organism or cell whose genome has been altered by the introduction of one or more foreign DNA sequences from another species by artificial means.