Air pollution
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is meant by pollution?
The contamination of the environment by harmful substances that are produced by the activities of humans
Pollution in aquatic environments + in the air and atmosphere
Aquatic environments: untreated sewage, fertilisers
Air and atmosphere: carbon dioxide, methane, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, oxides of nitrogen, CFCs
What is acid rain? What causes it?
Rain with a pH less than 5.5, caused by pollutant gases such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides dissolved in rain water.
What are main causes of acid rain?
Internal combustion engines in cars — releases nitrous oxides
Power stations burning fossil fuels — releases sulfur dioxide
How is sulfur dioxide (SO2) formed?
When fossil fuels are burned (it comes from the sulfur impurities in the fossil fuels)
How is sulfur dioxide a pollutant? + biological consequences?
It causes acid rain which damages plants, aquatic life and soil
Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides dissolve in rainwater to form a mixture of acids (sulfuric acid and nitric acid, stronger than carbonic acid).
This results in acid rain (pH of 5.2 and below).
*Normally rain has ~ pH 5.5. Slightly acidic due do carbon dioxide dissolved in it (carbonic acid). But this acid is not strong enough to cause acid rain by its own.
Causes respiratory problems in humans
What are the environmental consequences of acid rain?
Acidification of lakes causes death of fish, plants, bacteria, etc
Death of trees. Acid damages leaves and releases toxic substances from the soil, making it hard for root hairs to take up nutrients and minerals. This also slows down tree growth.
How is carbon monoxide formed? Where?
When substances containing carbon (e.g fossil fuels) are burned in a limited supply of oxygen.
In vehicle engines (car emissions).
How is CO emissions reduced?
In modern cars, catalytic converters turn carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide.
Why is carbon monoxide a dangerous pollutant?
It is a poisonous gas.
Haemoglobin binds more strongly with carbon monoxide than with oxygen so:
CO binds to haemoglobin in red blood cells, reducing oxthen transport in blood.
This prevents oxygen from reaching the cells — organs like heart or brain stop working = lead to suffocation and death in high concentrations
What is meant by the term greenhouse gas
Gases that trap heat (and contribute to global warming)
What are the greenhouse gases?
What are the greenhouse gases?
Water vapour (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrous oxides, methane (CH4) and CFCs (which are only produced by human activity).
How does human activity release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere?
Burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, etc) and petrol + diesel in vehicle engines.
Deforestation for wood clears and land for farming — forests absorb large amounts of CO2 and release large amounts of O2.
How is methane released into the atmosphere?
It is an organic gas produced when microorganisms ferment larger organic molecules to release energy. Most significant sources:
Decomposition of water buried in the ground (landfill sites) by microorganisms
Fermentation by microorganisms in rumen (stomach) of cattle and other ruminants
Fermentation by bacteria in rice fields.
How are nitrous oxides released into the atmosphere?
Released naturally by bacteria in soils and the ocean
A lot more is released from soils after fertiliser is used
Released from vehicle engines
What are CFCs? How are CFCs released into the atmosphere?
They are greenhouse gases that are man made chemicals. They are very powerful greenhouse gases.
Leaks from old fridges
Remember that the greenhouse effect is necessary for life on Earth because it maintains the surface at an adequate temp. Without it heat wood be lost to space.
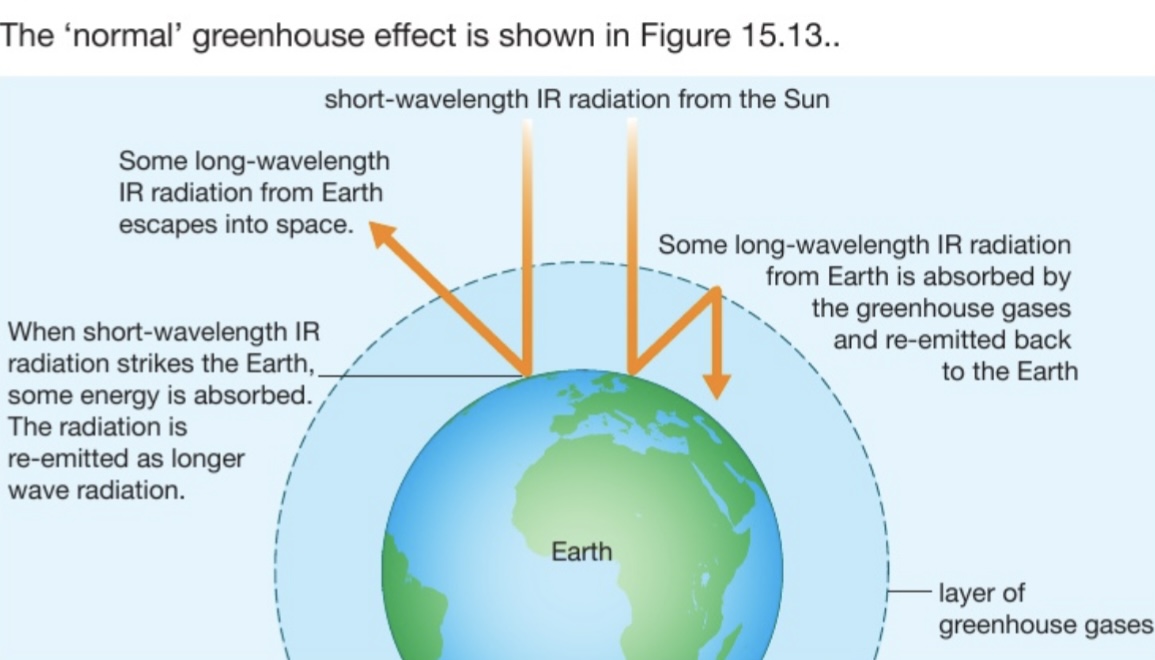
What is the greenhouse effect?
- The Sun emits short wavelength infrared radiation to the Earth.
- Heat is absorbed by Earth’s surface and re-emitted as longer wavelength IR radiation
The greenhouse gases absorb/trap and re-emit some of this long-wavelength IR in all directions (including back towards the Earth), which would otherwise escape into space. This heats up the surface of Earth
What is global warming? Why is it happening?
When the Earth's average temperature rises above normal.
This happens because of the enhanced greenhouse effect caused by the increasing levels of greenhouse gases emitted from human activities.
More greenhouse gases in atmosphere → more heat trapped → more heat re-emitted back to Earth
What are the effects of enhanced greenhouse effect? (Each bullet point = one mark on ms & bolded = mark, rest is explanation)
Global warming/temps rise (if it asks for consequences for global warming, todo lo demás menos obv ‘global warming’)
Ocean temperatures increase causing ice caps to melt and sea levels rise/flooding
Increasing temperatures causes climate change/extreme weather (e.g hurricanes, flooding, droughts)
Habitat destruction because of climate change/extreme weather events.
Decreases in biodiversity in many ecosystems as food chains are disrupted/extinction rates increase (species can’t migrate or adapt quickly enough)
More migration/ spread of pests and diseases as higher temperatures allow them to compete their life cycles quicker.