OSU Biology 1114 - Midterm 2
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Coevolution
The joint evolution of 2+ interacting species. Pressure from each species acts as selective agent for other.
Asexual Reproduction
Formation of offspring without fusion of egg and sperm. Offspring genetically identical to parent.
Sexual Reproduction
Formation of offspring by fusion of male and female gametes. Offspring inherit traits from both parents.
Evolution will NOT occur if:
1. Mating is random
2. No natural selection
3. No mutation
4. No migration
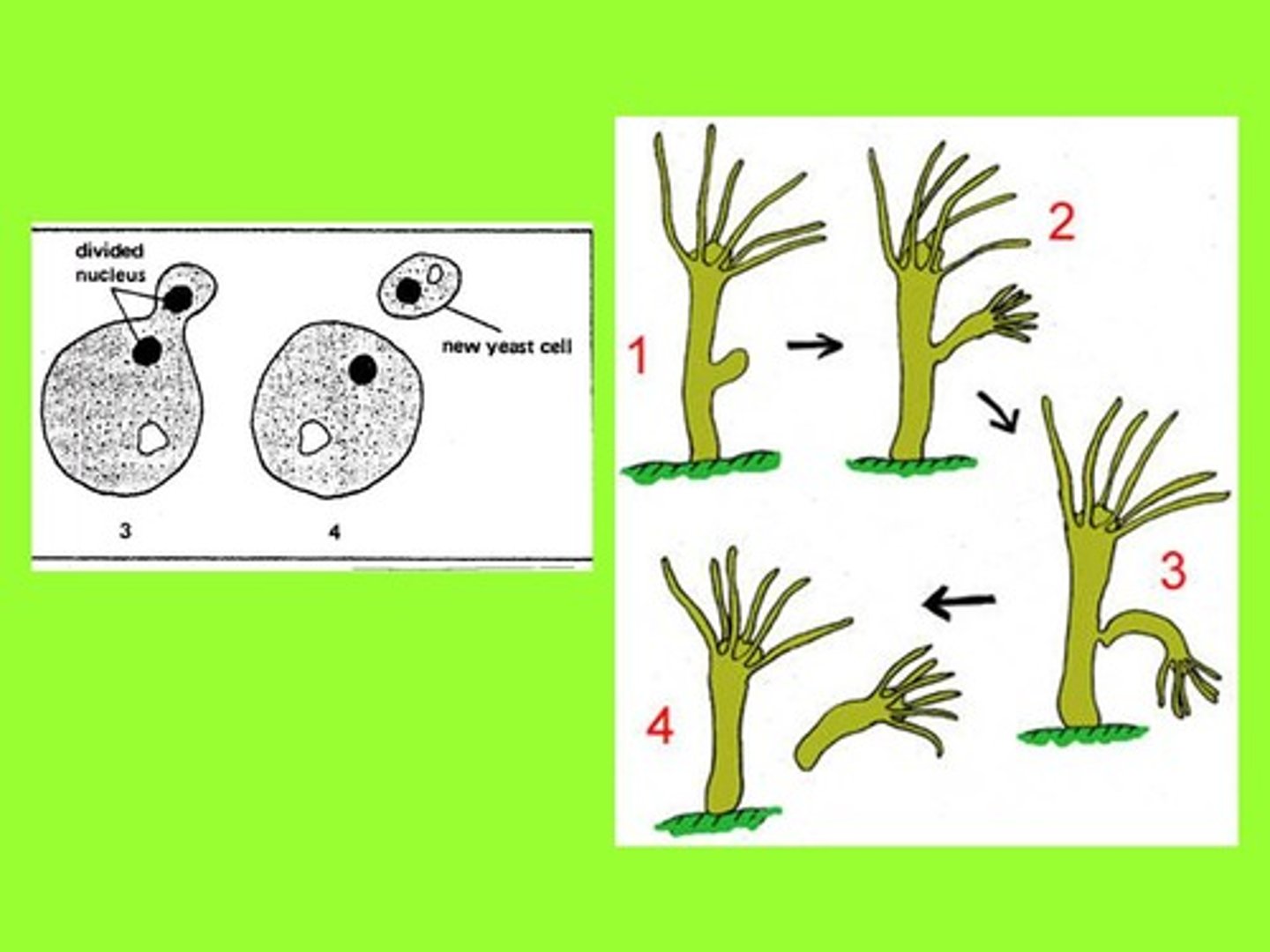
Budding
Offspring develops as outgrowth of parent
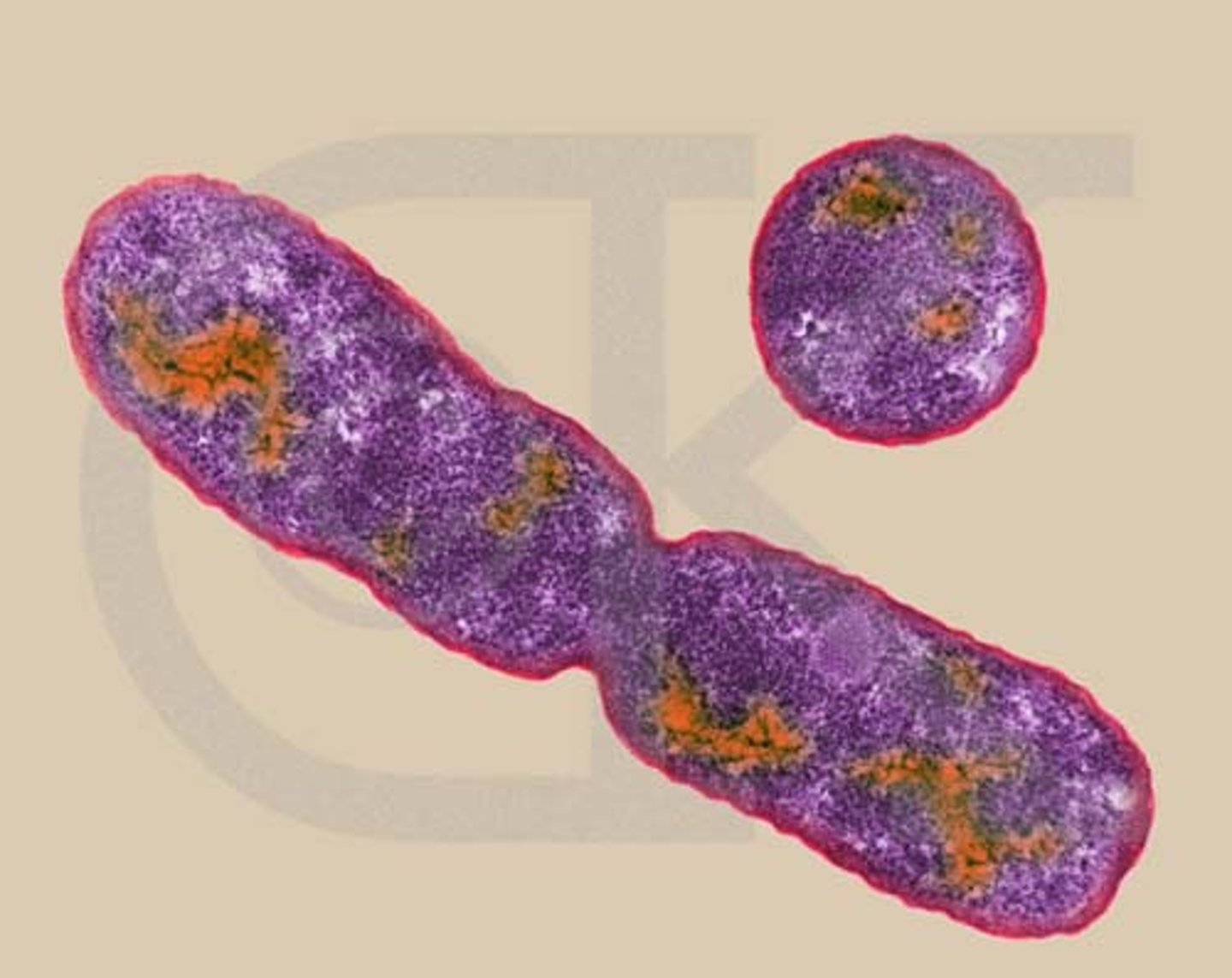
Fission
Parent splits into two organisms of about equal size.
Root Suckering
Many clonal inds. sprout from roots of single ind.

Parthenogenosis
Unfertilized eggs develop into offspring. Sex changing species - hormonal production shifts.
Frequency Dependent Selection
The fitness of a phenotype that depends on how common it is in a population. Ex: side-mouthed scale eating fish
Advantages of Sex ;)
- Variation (allows selection)
- Fewer deleterious alleles (asexual = keep being passed on, die out faster)
Mutation Meltdown
The increasing proportion of low fitness individuals with many deleterious alleles in asexual populations. Explains greater extinction rates in asexual species.
Sexual Selection
Individuals with certain inherited traits are more likely to attract mates than others. Form of Nat. Selection.
Reproductive Differences between Males and Females
Females:
- Limited # of gametes + increased time consumption
- More selective (quality)
Males:
- Excess gametes + no gestation period
- Not selective (quantity)
Operational Sex Ratio (OSR)
The ratio of males in a population ready to mate with females in pop that are ready to mate. Skewed due to reproductive differences.
Contributions to Offspring
Female:
- Often provide parental care
- Greater energetic cost (gestation, rearing)
Males:
- Often hit it and quit it
- Lower energetic cost
Differential Parental Investment (PI)
Measured as each parent's contribution to rearing offspring. Female gametes, limited = high PI. Male gametes = unlimited = low PI.
Female Reproductive Strategy
Find mate with good genes or resources so offspring have better chance of survival.
Male Reproductive Strategy
Mate with as many partners as possible, leave rearing to females.
Variable Reproductive Success
Female: Relatively Uniform
- Not limited by mating opportunities
- Gametes able to be used more often
- Limited by resources
Male Reproductive Success: Variable
- Limited by mating opportunities
- Must demonstrate desirable qualities
Average Reproductive Success
SAME FOR BOTH SEXES
Intrasexual Selection
Results from competition between members of one sex for mating opportunities (access to or resources needed). Usually male-male. (Elephant seals)
Cuckoldry
Indirect male-male competition. Males unwittingly invest parental care into unrelated offspring.
Cuckoldry - Sneaker Males
Tiny males are undetected by alphas and "free-ride" off of mating opportunities (fish wait for spawning and sneak attack with sperm).
Cuckoldry - Satellites
Too big to be sneakers, look like females so are tolerated by alphas, mate anyway.
Cuckoldry - Sperm Competition
Removing another male's sperm - barbed and curved penis.
Intersexual Selection
One sex prefers members of other sex with a certain phenotype. Usually females choosing males.
Cues for Female Choice
1. Features suggesting health/feeding capability
2. Features emphasizing distinction b/w sexes (no wasted effort on androgyny)
Sexual Dimorphism
Difference in appearance of females and males within same species.
Zahavi's Handicap Hypothesis
Individuals with well developed sexually selected characteristics have survived some sort of test. Explains extreme morphologies. Individuals that survive DESPITE the "handicap" must have a superior genotype. Honest indicator of fitness.
Correlation Coefficient (r)
Indicates direction and strength of a linear relationship b/w 2 variables. Strong is closest to 1 or -1. >0 = Positive relationship. <0 = Negative relationship.
R^2
Proportion of variation in dependant variable that is explained by variation in independent variable. Always positive, squared number + no directional value.
Altruism
An action reducing an individual's direct fitness while increasing fitness of another.
Nash Equilibrium
The strategy that is the best response given other player's response.
Prisoner's Dilemma
Confess (cooperate) or remain silent (defect), not knowing other player's decision. Selfishness is the best strategy.
Evolutionarily Stable Strategy (ESS)
The selfish strategy. A strategy that, if established, can't be invaded by something using an alt. strategy. Suggests cooperative phenotypes will be selected against.
Cooperative Breeding
Some individuals don't reproduce (lose direct fitness) and rear relatives (often siblings, indirect fitness). Non-altruistic, actually selfish.
Indirect Fitness
Fitness gained by allele transmission by helping relative offspring.
Inclusive Fitness
Fitness gained through both direct and indirect methods. Inclusive fitness = direct + indirect fitness
Kin Selection
Evol. strategy in which organisms don't reproduce (lose direct fitness) to benefit a relative's reproductive success (indirect fitness). Ultimately increases total fitness of helper (selfish).
Relatedness (r)
Probability that two individuals share given allele. Used to predict if altruistic behaviors will occur. Between siblings/half-siblings (paternal or maternal), grandparents, nieces/nephews, r = .25, First cousins, r = .125.
Hamilton's Rule
Individuals should behave altruistically IF fitness gain > fitness lost from not reproducing.
Act Altruistically If:
Cost < indirect fitness gains (relatedness x benefit to relative's fitness)
Act Selfishly If:
Cost > indirect fitness gains (relatedness x benefit to relative's fitness)
Extra-pair Copulations
Females mating with males other than partner (maternity certain, paternity uncertain).
Reciprocal Altruism
Altruism b/w non-kin. Individuals interact multiple times and change individual interactions based on past behaviors. Tit for tat. Can punish selfishness by not helping in future. Ex: Vampire bats.
Genetic Drift
A RANDOM change in allele frequencies from gen to gen. Ex: volcano eruption, ant hill being stepped on. Less likely in large populations. Reduces genetic diversity - allele fixation.
Heterozygosity (H)
The probability of drawing 2 DIFFERENT alleles from the gene pool of a population. H = 1 - (p^2 + q^2)
Fragmentation
Previously large. continuous habitat broken into smaller, unconnected pores.
Founder Event
A new, smaller population of founders break off from original population. No representation lost.
Founder Effect
Occurs IF new population found has lower genetic diversity than original population.
Bottleneck Effects
Occurs when an environmental/human catastrophe decimates a large percent of population. Size may rebound, but diversity won't. Causes loss of genetic diversity.
Gene Flow
Introduction or removal of alleles from a population - changes allele frequencies.
Mutation
A permanent, RANDOM change in DNA sequence of an organism.
Genetic Polymorphism
Having multiple different alleles for a gene. Mutation increases. A function of the rate of drift and mutations.
Microevolution
Changes within a population over generation (single species).
Macroevolution
Evolutionary changes resulting in a different species (speciation).
Evolution and Species Formation
Ancestral Population --> Isolated into groups (no longer interbreed) --> Each acquires mutations INDEPENDENTLY in diff environments --> Become so differentiated that they no longer mate. Extant species can't evolve from one another, have common ancestors.
Phylogenetics
Studies evolutionary history/relatedness of groups.
Phylogeny
A hypothesis of evolutionary relationships between groups of shared characteristics, connected to a single ancestral species (outgroup - from which others diverge from).

Nodes
Common ancestors. Where species diverge from a common ancestor.
Homology
A similarity resulting from common ancestry. Ex: Mammalian forelimb.
Plesiomorphy
Character states found in the outgroup. Traits that are diverged from.
Apomorphy
Derived character states found in descendants of group. Acquired AFTER divergence.
Synapomorphy
Shared, derived character states that indicate homology (similar trait to ancestor group)
Phylogeny - Polarity
0 = ancestral state, 1 = derived state
Monophyletic Group
Clade. A common ancestor and all of its descendants. Only valid evolutionary group.
Evolutionarily Invalid Groups - Paraphyletic
A group containing a common ancestor but NOT all of its descendants. Ex: reptiles
Evolutionarily Invalid Groups - Polyphyletic
Group characterized by 1+ homoplasies (character states appear in 2 taxa but NOT evolved from same ancestor).
Homoplasy
Result of convergent evolution. Character states appear in same 2 taxa but NOT evolved from a common ancestor. Exposed to similar selection.
Convergent Evolution
Independent evolution of the same character state in multiple, separate lineages.
Parsimony
The simplest explanation. The best tree is the one with the fewest evol. steps.
Still learning (16)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!