Comprehensive Overview of the Peripheral and Autonomic Nervous System Components
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Peripheral Nervous System components
made of nerves and ganglia
attached to the spinal cord, brain, and brainstem
runs to and from targets in soma and viscera
nerves
bundles of myelinated axons and dendrites
white matter in PNS
ganglia
small switching stations of neuron cell bodies/synapses
thicker than nerves
gray matter in PNS
tracts
white matter in CNS
nuclei
grey matter inside CNS
cortex
grey matter outside layer of brain in CNS
spinal nerves
segmentally arranged in pairs
exit through intervertebral foramina
named/numbered after vertebra
how many pairs of each spinal nerve
8 cervical pairs
12 thoracic pairs
5 lumbar pairs
5 sacral pairs
1 coccygeal pair
31 pairs total
Spinal Nerve Notations
C1-C8
T1-T12
L1-L5
S1-S5
Cx1
dermatomes
zones innervated by a specific spinal nerve
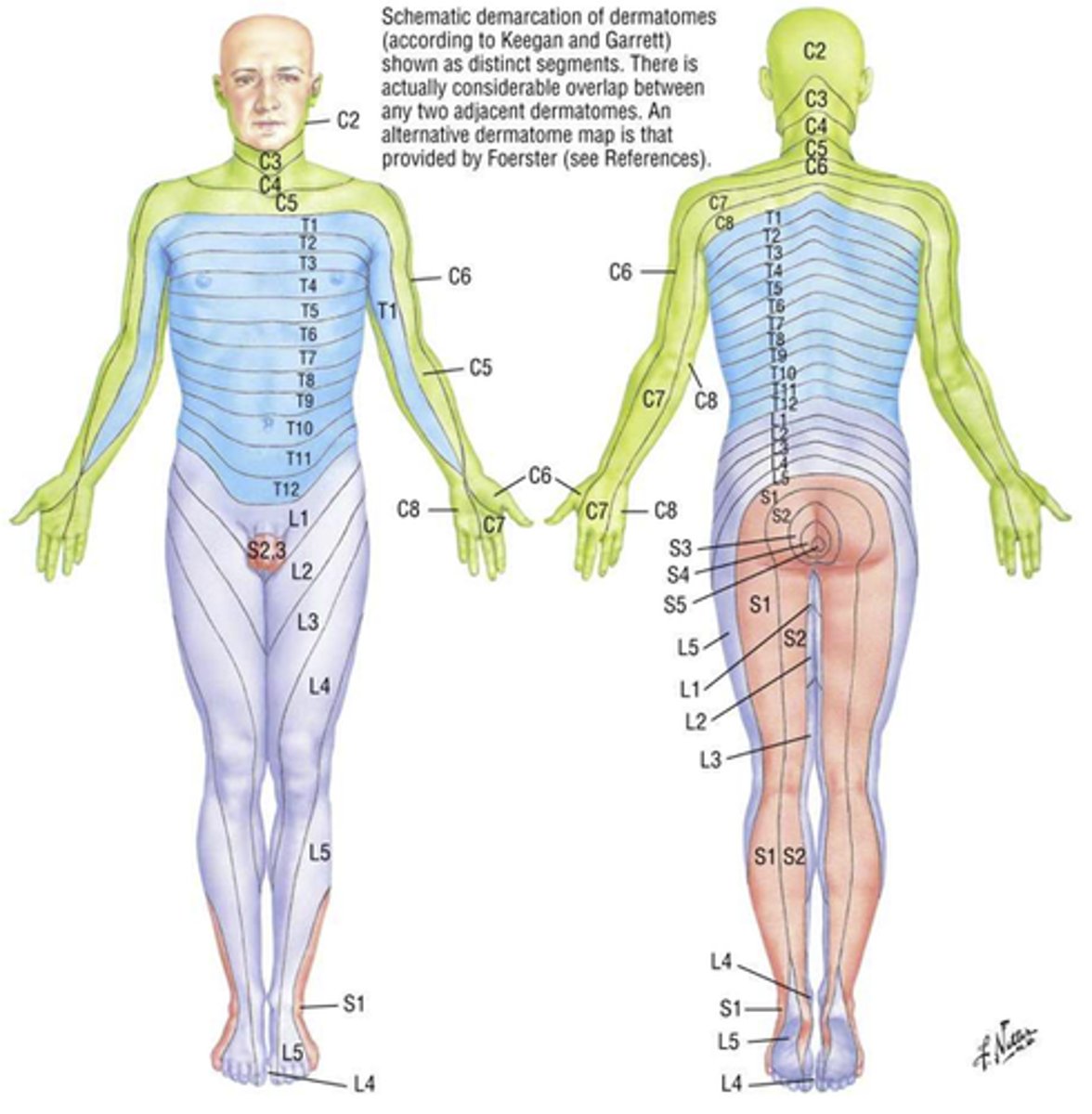
subdivisions of the NS carried by the spinal nerves
somatic motor
somatic sensory
visceral motor
visceral sensory
somatic plexi
spinal nerves join up to trade fibers
introduces redundancy into the innervation in event of trauma
plexus
network of crossing/trading fibers
somatic plexi categories
cervical plexus (C1-C4): to neck
brachial plexus (C5-T1): to UE
lumbar plexu (T12-L4): to thigh
sacral plexus (L4-Cx1): to rest of LE
intercostal nerves
nerves in T2-T11 that do not enter a plexus
lumbrosacral plexus
linked lumbar plexus and sacral plexus
reflexes
behaviors that are generated at the level of the spinal cord
types of reflexes
somatic reflexes
visceral reflexes
sides of the reflex arc
sensory stimulus (afferent signal)
motor response (efferent signal)
CNS lies between them
sensory signal
enters the back of the spinal cord
motor signal
exits the front of the spinal cord
Interneurons
make up 99% of the neurons in the nervous system
responsible for the majority of thinking and memory
Autonomic nervous system
controls visceral organs
sensory input from organs
motor output to smooth muscles and glands
ANS structures
hypothalamus
medulla oblongata
sympathetic trunk ganglia
splanchnic nerves
primary subdivisions of the ANS
visceral sensory input
Visceral motor
sympathetic nervous system
preps body for heightened physical activity (flight, fight, fornification)
increases heart and breathing rate
suppresses digestion / peristalsis
sweat production
vasoconstriction
dilate pupils
increases sexual arousal/orgasm
parasympatheric nervous system
brings body back to resting state
decreases heart and breathing rate
stimulates digestion/peristalsis
stimulates saliva production
constricts pupil
vasodilation
penil/clitoral erection
musculocutaneous nerve
most cranial branch nerve
fairly thin
sends motor branches into the biceps and brachialis
receives sensory branches from the skin
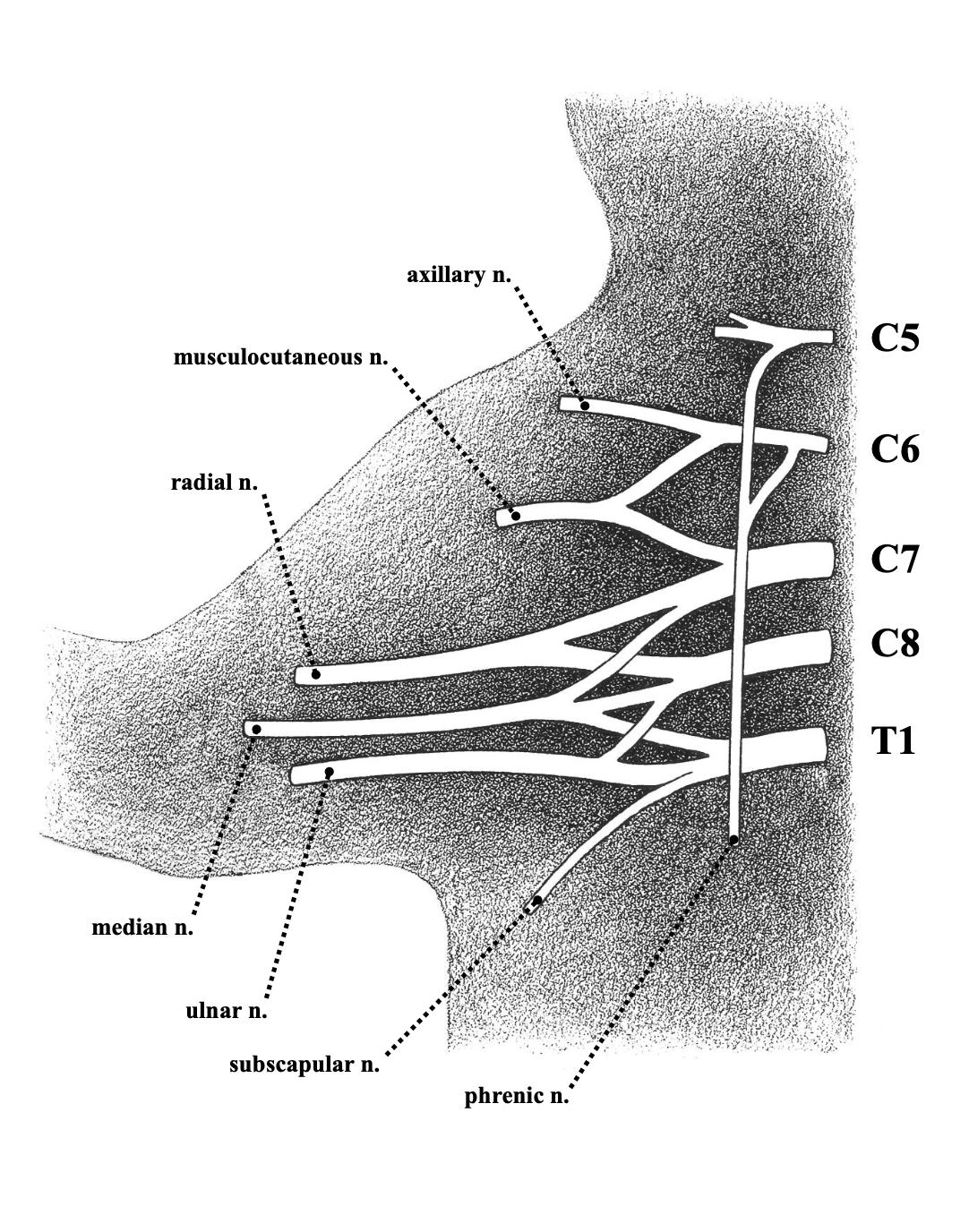
median nerve
superficial branch
thicker than musculocutaneous nerve
cross belly of teres major
motor branches to anterior muscle block of forearm
sensory branches from the skin of the radial half
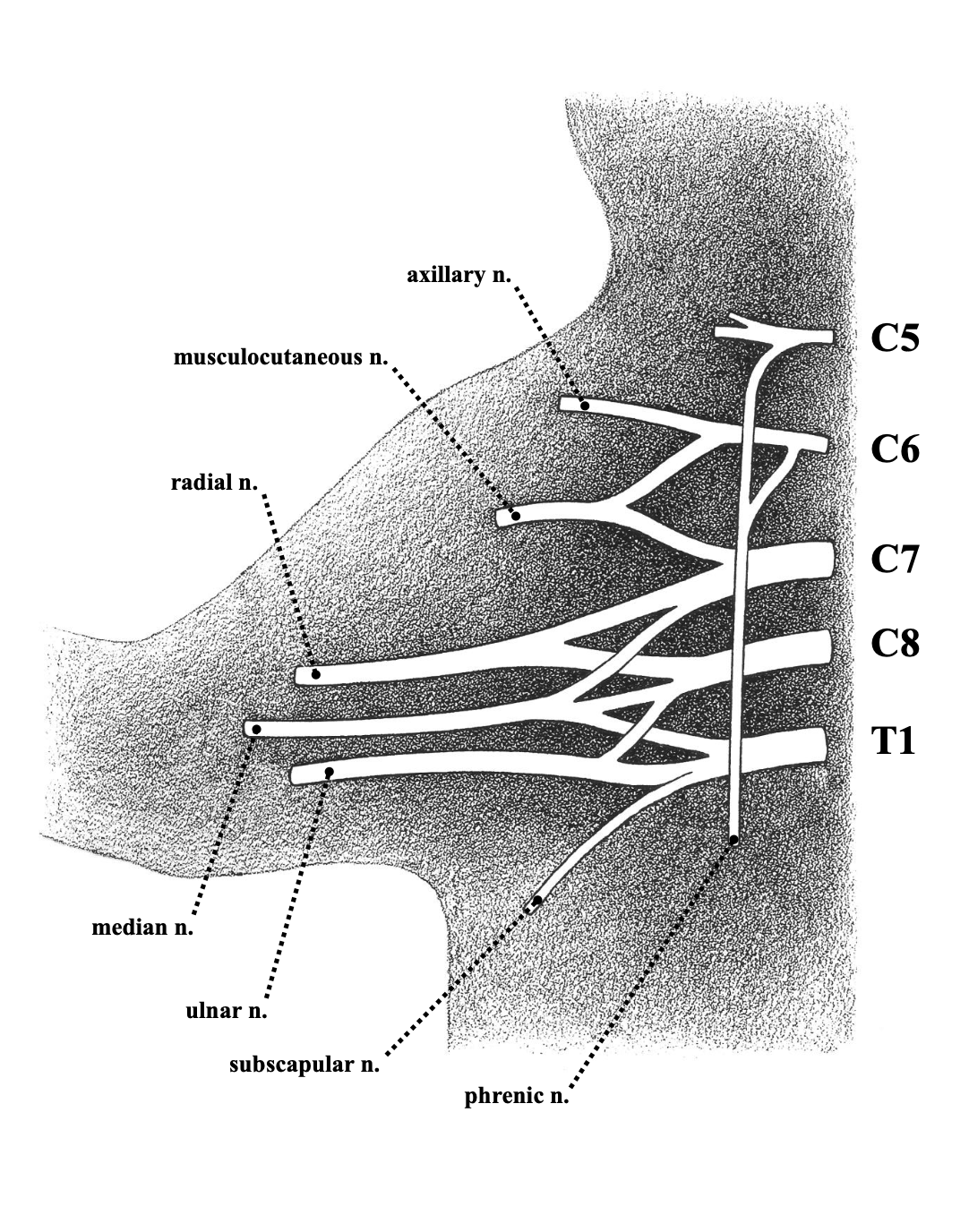
ulnar nerve
most caudal of the superficial branch
crosses teres major
responsible for funny bone sensation
sends motor branches into a few of the anterior block muscles
receives small sensory branches from the ulnar half skin
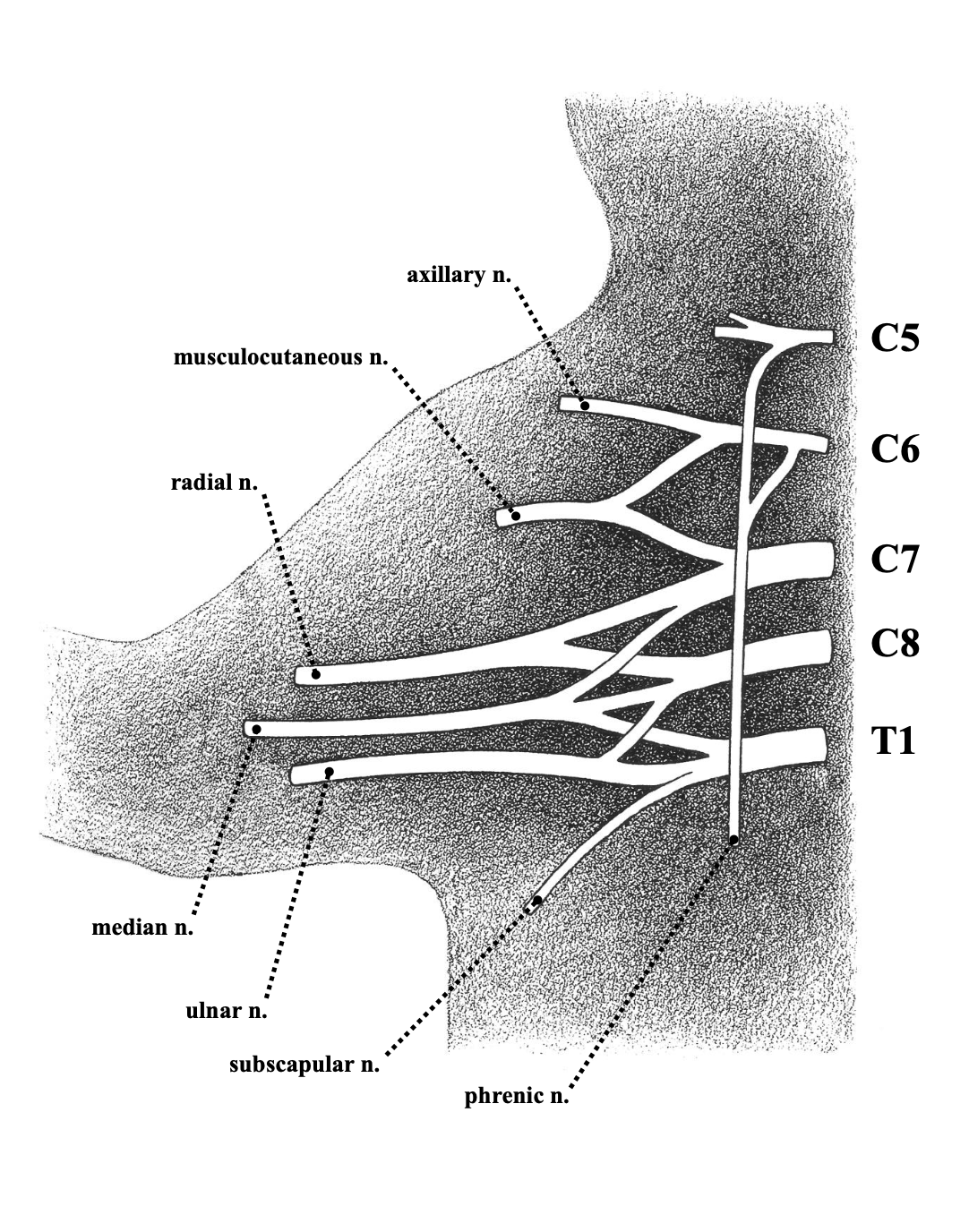
radial nerve
deep branch
crosses ventral side of teres major
thickest branch
provides motor branches to the triceps head
splits elbow into superficial branch (Brachioradialis) and deep branch (posterior muscle block)
recieves sensory branches from skin over posterior surface of brachium, forearm, and forepaw
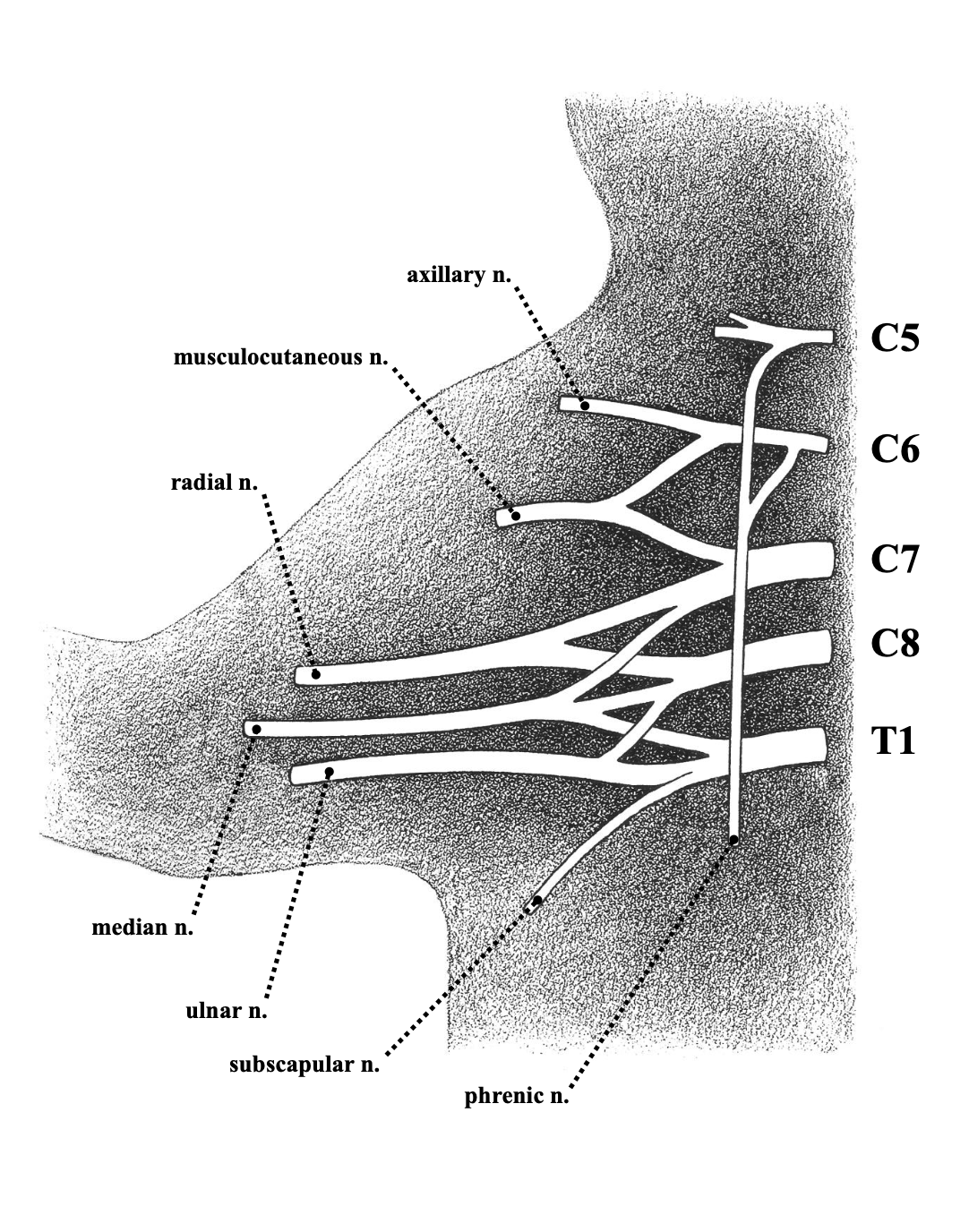
axillary nerve
second deep branch
crosses subscapularis
sends motor branches to all 3 heads of the deltoid
receives sensory branches from the skin over the shoulder
femoral nerve
runs between the sartorius and gracilis muscles
sends motor branches to the quads
small sensory branches enter from the skin over the thigh and medial side of the leg
obturator nerve
crosses proximal end of adductor magnus and longus
sends motor branch to the obturator foramen
supplies the medial muscle block of the thigh
receieves sensory branch from the skin over medial thigh
sciatic nerve
largest nerve in body
passes deep to femoris muscle
2 main branches: common fibular nerve and tibial nerve
control the posterior thigh muscles, all leg muscles, all foot muscle, most of skin areas in LE
superficial branch
runs deep to the brachioradialis
deep branch
enters into the posterior muscle block of the forearm
thoracodorsal nerve
innervates the latissimus dorsi muscle
long thoracic nerve
runs distally along surface of the serratus anterior muscle