1.2: Exchange of Nutrients and wastes
1/10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Carbohydrates
include starch and cellulose
used as structural support
Most abundant organic molecules in nature
monosaccharides; glucose, fructose, and galactose. used for releasing energy in respiration
Disaccharides; maltose (gluc+gluc), sucrose (gluc+fructose), lactose (gluc+galactose)
Polysaccharrides; starch, glycogen, cellulose (used for strengthening plant cell walls)
Lipids
Contain C, H and O, often have hydrocarbon chains and may have phosphorus and nitrogen
each lipids is made of 3 fatty acids joined to a molecule of glycerol
Functions
Energy production; have 2x the energy content of .carbs
Energy storage; hydrophobic meaning it doesn’t add body weight in a significant amount
Insulation; a layer of fat used against temperature changes
Cell membranes
Hormones
Shock absorbet; layer of fat around eg kidneys which protects against shocks and knocks
Proteins
contain C, H O and N, and sulphur, phosphorous or other elements
more complex than carbs and lipids
made up of 20 different possible amino acids
functions vary widely depending on the different kinds of proteins
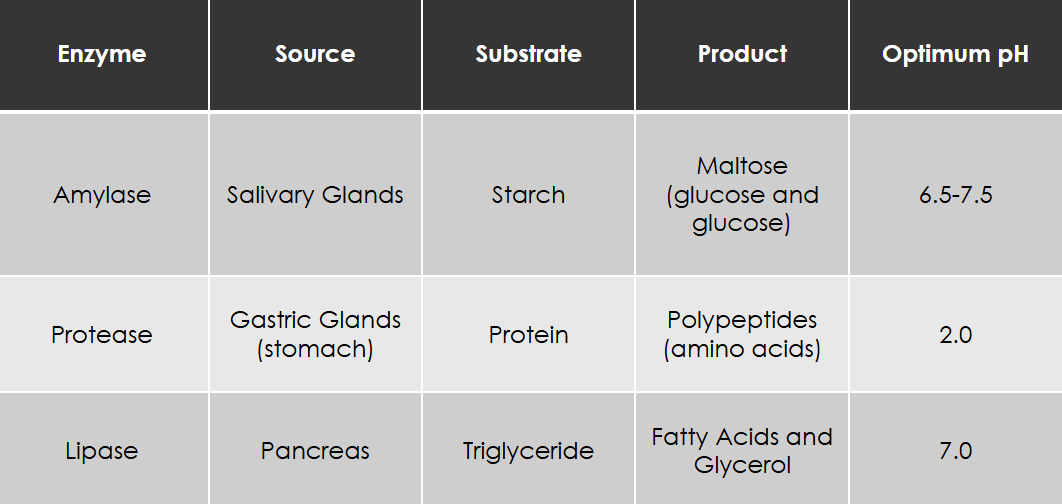
Enzymes in Digestion
Villi and Microvilli
lines intestines, which are folded
tiny finger-like projections from intestinal cells
each villus is covered with tiny microvilli
increases the surface area for the absorption of nutrients
absorption initally take splace via diffusion, but active transport also occurs.
90% of absorption occurs in the small intestine
Enzymes
a globular protein produced by a cell which acts as a biological catalyst for certain reactions.
are specific (can only do some reaction per type of enzyme)
Enzyme-substrate specificy
Shape held by different bonds (hydrogen, ionic, peptides and disulphide bridges)
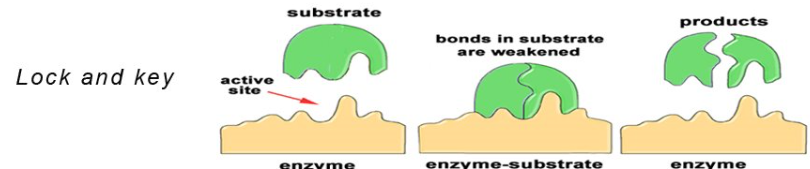
Lock and Key theory
when a specific substrate reacts with an enzyme that can be connected to perfectly
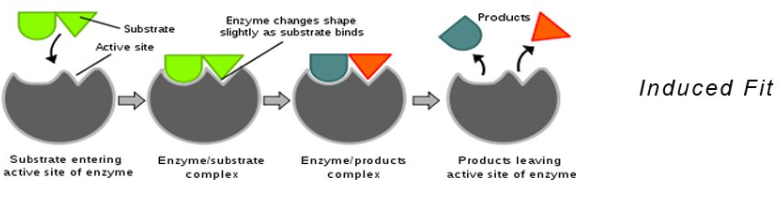
Induced fit theory
when the enzyme changes/adjust its shape to fit the substrate
Catalyst cycle
substrates enter active site
substrates held in by weak interactions
active sites can lower EA (activation energy) and speed up reaction
substrates are converted unto products
products are released
active site is able to be used again
Factors affecting Enzyme activity
Temperature; gives it more energy which speeds up reaction
Concerntration; more can increase enzyme activity to a certain level
pH; if not neutral/7 the enzymes becomes denatured
Inhabitors; competitive (competes with substrate) or non-competitive (changes shape of enzymes)
Cofactors; non-protiens molecule that supports biochemical reactions, can be produced by the body or found from food
Active Site
matches the shape and chemical properties of its enzymes
Can lower EA and speed up reaction of enzymes