APHG Ch 11 Vocab: Agriculture
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
APHG Ch 11 test 4/30/2024
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
organic agriculture
approach to farming and ranching that avoids the use of herbicides, pesticides, growth hormones and other synthetic inputs
agriculture
purposeful tending of crops and livestock in order to produce food and fiber
econmic activity
five types of economic activity that contribute to an overall economy:
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
quinary
primary
economic activity concerned with the direct extraction of natural resources from the environment; ex mining, fishing, lumbering, and especially agriculture
secondary
processing raw materials and their transformatoin into finished industrial products (manufacturing sector)
tertiary
provision of services; transportation, banking, retailing, education and routine office based jobs
quaternary
collection processing and manipulation of information and capital; finance, admin, insurance and legal services
quinary
service sector industries that require high level of specialized knowledge or skill; typically only found in core countries
plant domestication
genetic modification of plants such that its reproductive success depends on humans; made to be more useful through breeding
root crops
crop that is reproduced by cultivating the roots of or the cuttings from the plants
seed crops
crop that is reproduced through culitivating seeds of plants
First Agricltural Revolution
dating back 10000 years achieved plant and animal domestication
animal domestication
genetic modification of animals so that they are more beneficial to humans
subsistence agriculture
self-sufficient agriculture that is small scale and low technology, emphasizes food production for local consumption NOT trade
shifting cultivation
cultivatioon of crops in tropical forest clearings in which forest vegetation has been removed by cuttting and burning; usually abandoned after a few years in favor of newly cleared forestland
Second Agricultural Revolution
witness improved methods of cultivation, harvesting and storage of farm produce; occured alongside Industrial ev
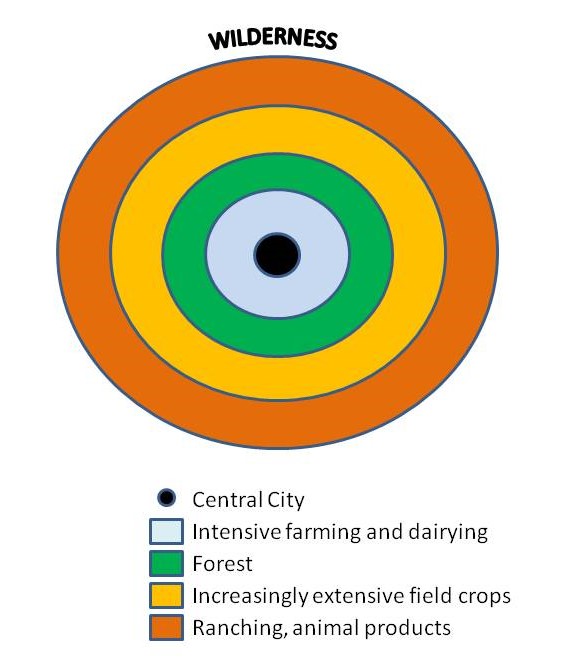
von Thunen Model
model that explains the location of agricultural activities in a commericial, profit making economy; process of spatial competition allocates various farming activities into rings around a central market city, with profit earning capability the determining force in how far a corp locates from the market
Third Agricultural Revolution
currently in progress, development of genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
biotechnology
technology designed to manipulate seed varieties to increase crop yields
Green Revolution
successful development of higher yielding fast growing varieties of rice and other cereals in certaind evloping countries, lead to increased product per unit area and a dramatic narrowing of the gap between population growth and food needs
genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
crops that carry new traits that have been inserted through advanced genetic engineering methods
rectangular survey system
also called Public Land Survey; system used by US land Office Survey to parcel land west of the Appalachin Moutains; system divides land into a series of rectangular parcels
township and range system
a rectangular land division scheme designed by Thomas Jefferson to disperse settlers evenly across farmlands of the US interior
metes and bounds system
system of land surveying east of the Appalachian Moutains; relies on descriptions of land ownership and natural features such as streams or trees; because of inprecise nature of metes and bounds abandoned the technique in favor of the rectangular survey system
long lot survey system
distinct regional approach to land surveying found in the Canadian Maritimes parts of Quebec, Louisiana and Texas whereby land is divided into narrow parcels stretching back from rivers roads or canals
primogeniture
system where the eldest son in a family or sometimes daughter inherits all the dying parent’s land
commerical agriculture
term used to describe large scale farming and ranching operations that emply vast land bases, alarge mechanized equipment, factory type labor forces and the lastest technology
monoculture
dependence on a single agricultural commodity
Koppen Climate Classification System
system for classifying world’s climates on the basis of temperature and precipitation
climate regions
areas of the world with similar climatic characteristics
plantation agriculture
production system based on a large estate owned by an individual family or corporation organized to produce cash crops; almost all plantations established in tropics
livestock ranching
raising of domesticated animals for the production of meat and other byproducts
Mediterranean agriculture
specialized farming that occurs only in areas where dry summer Mediterranean climate prevails
cash crops
crops made explicitly for mass production and trade (tobacco, corn, cotton)
luxury crops
non-subsistence crops such as tea, cacao, coffee and tobacco
agribusiness
general term for the businesses that provide the vast array of goods and services that support the agriculture industry
food desert
an area characterized by a lack of affordable, fresh and nutritious food